9 monthsMother and baby
You can often hear from pregnant women that they are afraid to “feed” the baby and it is advisable that the baby’s weight before birth be less - this way, they say, it will be easier to give birth, and there will be more chances of not tearing. But is it really good if the baby weighs little at the time of birth and what are the criteria for a child’s normal weight at birth?
“If I were a queen,” said the third girl, “I would give birth to a hero for my father-tsar,” these lines of the classic are still relevant today. The first question asked by happy fathers and grandfathers after childbirth is: “What is your weight and height?” Moreover, “heroic” parameters are always perceived as an undeniable merit of the mother and a sign of the baby’s health, and the modest size of the newborn disappoints the male half of the family. Newly-made grandmothers and aunts also ask about the baby’s weight, but their reaction to the heroic data of the new family member is usually exactly the opposite: they express sympathy for the mother and clarify whether everything is fine with her and the baby’s health after such a “heroic” birth. If the newborn turns out to be miniature, the female half of the family is sincerely happy for him and for his mother and congratulates him on an easy birth!
So, among mothers - both experienced and future - there is a strong opinion that the lower the child’s weight, the better for childbirth. Let's try to figure out how true this is, whether low weight is always a sign of the baby's health and a guarantee of an easy birth, what the weight of the fetus at the time of the onset of labor depends on and whether it can be influenced, how the baby's weight affects the various stages of childbirth and what is more important in assessing the size fetal weight or other factors?
Mass factor
The weight of the fetus changes weekly and each week has its own average norms. Based on fetal weight gain, the doctor can assess the risks of pregnancy complications and identify developmental abnormalities. If the doctor suspects a violation of embryogenesis, then for confirmation and control a repeat diagnosis will be scheduled in a week or two, after which a specific diagnosis will be made and adequate measures will be taken to preserve the pregnancy, or termination will be proposed in the event that the developmental disorders of the fetus are incompatible with its life.
Of course, with such a development of events, not only weight, but also other parameters are taken into account. A deviation upward or downward indicates fetal hypoxia, exposure to external and/or internal pathogenic factors, lack of nutrients, lag or arrest of development. Therefore, by observing and monitoring the child’s weight over time, the doctor can detect the reason for underweight or overweight relative to the average normal values.
This indicator depends on the following factors:
- The functioning of the feto-placental complex, on which the child’s nutrition also depends. With premature aging of the placenta, feto-placental insufficiency develops, blood circulation in the placenta and uterus is disrupted, and the delivery of the nutrient medium for the development of the embryo is disrupted, which can result in its malnutrition.
- Poor nutrition of the expectant mother, deficiency of microelements and vitamins in the diet.
- Experiencing frequent stress during pregnancy.
- Chronic diseases of the pregnant woman, especially diabetes or obesity. Insulin affects protein metabolism; increased levels of this hormone are a factor in stimulating intrauterine growth of the child.
- Severe toxicosis.
- Maternal alcohol consumption, tobacco smoking.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Age of the pregnant woman.
- Lifestyle of the expectant mother, living conditions, including environmental conditions.
- Number of children carried.
Change by week
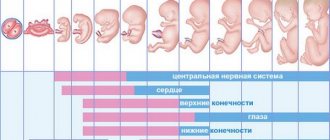
The baby in the mother's womb gains weight very quickly. At 7–8 weeks, the unborn baby weighs about 1 gram, this is not enough to track its size, but from this period the weight begins to grow rapidly. From the 15th week, after the internal organs of the fetus have formed, active development of the brain begins, while weight gain slows down slightly.
In the second trimester, the weekly increase is about 80 grams. Weight begins to rapidly increase again from 28–30 weeks. During this period, the weekly increase rate is up to 300 grams. As the baby grows, the uterus increases significantly, which before birth can reach 1200 grams (length up to 40 cm), in the early stages - up to 60 grams (length up to 8 cm). The ideal figure for a newborn is 3100–3600 grams.
You can find out the weight of the fetus by week of pregnancy from the table:
| Weeks of pregnancy | Approximate length of the child, centimeters | Approximate fruit weight, grams |
| 7 | 3 | |
| 8 | 5 | |
| 9 | 7 | |
| 10 | 9 | |
| 11 | 4,1 | 11 |
| 12 | 5,4 | 19 |
| 13 | 7,4 | 31 |
| 14 | 8,7 | 52 |
| 15 | 10,1 | 77 |
| 16 | 11,5 | 118 |
| 17 | 13 | 160 |
| 18 | 14,2 | 217 |
| 19 | 15,3 | 270 |
| 20 | 25,8 | 345 |
| 21 | 26,7 | 410 |
| 22 | 27,8 | 506 |
| 23 | 28,9 | 607 |
| 24 | 30 | 733 |
| 25 | 34,6 | 844 |
| 26 | 35,6 | 969 |
| 27 | 36,6 | 1135 |
| 28 | 37,6 | 1319 |
| 29 | 38,6 | 1482 |
| 30 | 39,9 | 1636 |
| 31 | 41,1 | 1779 |
| 32 | 42,4 | 1930 |
| 33 | 43,8 | 2088 |
| 34 | 45 | 2248 |
| 35 | 46,2 | 2414 |
| 36 | 47,4 | 2612 |
| 37 | 48,6 | 2820 |
| 38 | 49,8 | 2992 |
| 39 | 50,7 | 3170 |
| 40 | 51,2 | 3373 |
The weight of the child by week of pregnancy in this table is average and approximate, since many factors influence changes in fetal weight, and certain criteria must be taken into account when making calculations. In the early stages, the range of values is the same for almost all embryos; a noticeable difference occurs at later gestational stages.
Accepted standards
It takes a woman 40 weeks to carry a healthy baby. During this time, the size of the fetus changes, in particular, the weight, which should be paid special attention to.
Depending on the week of pregnancy and the sex of the baby, weight may vary as follows:
- 1 Week. In medical practice, it is customary to start counting the 1st week from the menstrual cycle preceding conception. Therefore, it is impossible to talk about the weight of the fetus at this stage.
- Week 2. At this time, the period of ovulation begins and conception occurs. The weight of the fetus corresponds to the size of the fertilized egg.
- 3-7 weeks. This is the period during which the embryo is formed. Its weight is less than 1 g.
- Week 8. Accelerated growth of the embryo occurs. Its weight can be about 3 g.
- Week 9. The embryo continues to form important structures. It can weigh about 5 g.
- Week 10 At this time, by medical standards, the embryo begins to be considered a fetus. It weighs approximately 7 g.
- Week 11 The time when the fetus is clearly visible on ultrasound. It weighs up to 10 g.
- Week 12. The end of the 1st trimester and the end of the formation of internal organs. The weight of the fetus is between 10-15 g.
- Week 13. The weight of the fetus crosses the 20 g mark.
- Week 14 The baby continues to grow rapidly. By the end of the week, he can already weigh 30 g.
- Week 15. Externally, the fetus looks almost like a newborn. Weighs up to 50 g.
- Week 16 The weight increases almost 2 times and is 100 g.
- Week 17 The child continues to gain weight, which can already be up to 150 g.
- Week 18. The formation of important brain structures continues. The fruit weighs almost 200 g.
- Week 19. The baby's movements in the stomach become noticeable, and the weight crosses the 230 g mark.
- Week 20 After half the period, the fetus weighs 300 g.
- 21 weeks. The weight of the fruit reaches 360 g.
- Week 22. At this stage, the child’s weight reaches almost 450 g.
- Week 23. At this time, the weight of the fetus is influenced by gender. A boy, on average, weighs 600 g, and a girl weighs about 550.
- Week 24. End of 2nd trimester. The weight of a male child is approximately 670 g, and that of a female child is 650 g.
- Week 25. The boy already weighs almost 800 g, the girl - 750.
- Week 26. By this point, the boy’s weight can already cross the 1 kg mark, while the girl weighs about 900 g.
- Week 27. The average weight of a boy at this time is 1100 g. The weight of a girl crosses the line of 1 kg.
- Week 28 Starting from this period, the fetus will gain 100-200 g. The weight of a boy is 1200-1300 g, a girl is 1100-1200 g.
- Week 29 The boy already weighs about 1400 g, the girl – 1300 g.
- Week 30 Weight increases to 1500-1700 g for a boy, to 1400-1600 g for a girl.
- 31 weeks. At this stage, a male fetus tends to weigh 1600-1700 g, and a female fetus – 1500-1600 g.
- Week 32 The average weight of a boy reaches 1800 g, girls - 1700 g.
- Week 33 Rapid weight gain continues, boys up to 2 kg, girls up to 1 kg 900 g.
- Week 34 In most cases, the weight of children of both sexes reaches 2 kg. A boy's weight is approximately 2100-2300 g, a girl's weight is 1900-2100 g.
- Week 35 A boy weighs approximately 2500 g, and a girl weighs 2200.
- Week 36. There is a noticeable difference in weight indicators among boys. Their standard indicators range from 2500 to 3000 g. Fluctuations in weight in girls are much less - 2200-2500.
- Week 37. The average weight for boys at this stage is 3 kg. But in some cases, their weight reaches 3 kg 500 g. Girls by the end of 37 weeks weigh 2300-3500 g.
- 38 week. The average weight of a male fetus increases by 300 g and reaches 3300. A girl, on average, can weigh 3100 g.
- Week 39. The fetus no longer gains weight as rapidly. A boy weighs about 3400 g, a girl - 3200.
- Week 40. By the end of pregnancy, a boy's weight is approximately 3000-4300 g, and a girl's weight is 2800-4200.
Normally, boys weigh 100-200 g more than girls.
Calculation based on other indicators
To determine the weight of the fetus by week of pregnancy, the most accurate diagnostic method for this case is used - ultrasound sonography. A scheduled examination is carried out three times in each trimester and unscheduled when necessary. Ultrasound allows you to perform fetometry, monitor the progress of gestation, identify the risks of possible complications, make many other measurements, determine vital criteria, and assess the health of the mother.
There are other methods for calculating fetal weight that are less reliable than ultrasound, but they are still used. So, the height of the fundus of the uterus and the circumference of the abdomen are measured in centimeters, these values are multiplied, and the weight of the child is obtained. The error of the method is up to 200 grams since it is impossible to take into account the amount of amniotic fluid, the constitution of the mother, presentation, and genetic characteristics. This technique can only be used after 32 weeks of gestation.
The website has a convenient service for calculating the baby's weight by week of pregnancy. Several values are entered into special columns and automatic calculation shows the required parameter. The entire operation takes a minimum of time. But using this online form you can only control the required values; the main calculations are made by the doctor during examination and ultrasound examination.
If a woman does not have any special health problems during pregnancy and there are no complications, then the baby’s weight will be normal both during intrauterine development and at birth. If some values do not coincide with the data in the table, then you do not need to draw conclusions yourself; remember that everything is individual and only a specialist can make the final verdict.
Is it possible to increase fetal weight during pregnancy?
If the fetal weight is less than normal, then the first thing the doctor will advise is nutritional correction. A pregnant woman should reconsider her diet; there must be a normal balance of vitamins, trace elements, and minerals. You need to stick to the diet if it is prescribed by your doctor. Many women suffer from swelling and high blood pressure when carrying a child. In this case, it is recommended to reduce the consumption of salt, marinades, sauces, smoked foods, and fatty foods.
The correspondence of a woman’s weight to her gestational age can be calculated using a pregnant woman’s weight norm calculator.
The expectant mother should not drink alcoholic beverages that negatively affect embryogenesis. It is necessary to completely eliminate smoking, which can lead to oxygen starvation of the fetus, which leads to a decrease in its weight. There are nutritional mixtures that are recommended for women during the gestational period. This will help maintain the child’s weight at the proper level in accordance with the deadlines. The main thing that the doctor must find out is the reason for the insufficient increase, to stimulate which the pregnant woman can be hospitalized in a hospital to carry out compensatory therapy.
What determines the body weight of the unborn baby?
"How much does he weigh?" - a question that every mother asks the midwife. A baby's weight at birth is of great importance for his future health. That is why this parameter must be kept under control throughout the pregnancy.
Normally, a full-term newborn should weigh 3200–3500 grams with a body length of 50–51 centimeters. Experts note that deviations from these generally accepted indicators, as a rule, indicate certain problems with the baby’s health: excessive weight may hide some endocrine disorders, for example, diabetes, and underweight may indicate weak immunity. However, hereditary predisposition also plays a significant role here. If large babies have always been born in your family, then you also have a great chance of giving birth to a “hero.” In some families, on the contrary, all children from generation to generation are born with low body weight and do not have any deviations in further development. It has been noticed that most often children with low body weight are born to thin parents of short stature.
How to measure the weight of an unborn baby A gynecologist determines the circumference of the abdomen and the height of the uterine fundus using a measuring tape. These parameters are key to determining the approximate weight of the fetus. Obstetric formulas are used to calculate weight. The simplest: the abdominal circumference (in cm) is multiplied by the height of the uterine fundus (in cm). This formula is very approximate, as it does not take into account the thickness of the subcutaneous fat of the expectant mother. It should be noted that a large belly during pregnancy does not mean that the baby will necessarily be born large. The abdomen may be voluminous due to polyhydramnios or excess weight of the woman.
Olga Sekirina, gynecologist-endocrinologist, doctor of the highest category, candidate of medical sciences: “The baby’s weight is genetically determined. The weight of the fetus decreases when the conditions of intrauterine existence worsen - with a lack of oxygen and nutrients, malnutrition occurs. The baby is born on time, but his weight is below normal. Under normal conditions, a child inherits weight from his parents. If mom and dad are overweight, a tendency to which they have inherited, this will affect the formation of the fetus. Birth weight is especially closely inherited. If the future father was born weighing 4600 g, then the child will have a similar weight, regardless of gender. Children of such parents are born with a gigantic weight of 5–6 kg, through cesarean section. To normalize the weight of the fetus, pregnancy without complications, vitamin therapy, a healthy diet, and most importantly, weight gain during pregnancy should not exceed 7–9 kg. An increase of 15–20 kg reduces the oxygen supply to the fetus. The body requires oxygen in the same way as the fetal tissue, but the baby's share decreases due to the increase in the body of the expectant mother. This is exactly how malnutrition (malnutrition) and hypoxia (oxygen starvation) of the fetus occur.”
Low-weight baby Low- weight babies include babies whose birth weight is less than 2500 g. If we are not talking about a constitutionally low-weight fetus, when the small weight of a healthy baby is inherited from the parents, then a small fetus may indicate a pathology - intrauterine growth retardation syndrome (hypotrophy). Hypotrophy can be symmetrical or asymmetrical. With symmetrical, all organs are reduced evenly; with asymmetrical, the brain and skeleton develop normally, but the internal organs suffer. The first signs of malnutrition may appear at 24–26 weeks, and a symmetrical shape is noted. The onset of the syndrome after 32 weeks is characteristic of the asymmetric form, usually accompanied by fetal hypoxia.
Reasons for the development of malnutrition ✓ Smoking and drinking alcohol cause severe vasoconstriction and reduce uteroplacental blood flow. ✓ Chronic infections: tonsillitis, bronchitis, pyelonephritis, cardiovascular diseases, anemia, respiratory diseases. All diseases in which the expectant mother’s body suffers from intoxication and oxygen deficiency most often cause asymmetric malnutrition, especially in the last trimester of pregnancy. ✓ Age of the expectant mother. Less than 15 years old - the body of a girl who is too young is not yet ready for the stress of pregnancy. Over 35 years old - a woman often comes to this age already with a “baggage” of chronic diseases. ✓ Multiple pregnancy, when nutrients have to be divided between two (three) babies. All these factors interfere with the normal functioning of the placenta, which provides the baby with everything necessary. As a result, the transport of nutrients is disrupted, and subsequently the gas exchange of the fetus, which leads to a delay in its growth and the development of intrauterine hypoxia.
What threatens Low birth weight babies tolerate childbirth worse, they more often develop hypoxia and asphyxia, and neurological disorders. Children who suffer from oxygen deprivation often develop lung diseases. This is explained by the immaturity of the lung tissue - the bubbles in the lungs do not expand completely, which contributes to the penetration of infections into the respiratory alveoli. Such newborns have difficulty adapting, suffer from hyperexcitability, increased or decreased tone, do not gain weight well, and may lag behind in psychomotor development. The consequences of the condition can affect even at an older age. Recent studies have shown an association between low birth weight and the risk of developing cardiovascular disease, obesity, non-insulin-dependent diabetes and elevated blood lipids. These diseases are associated with congenital pathology of the endocrine system in low birth weight babies.
Treatment and childbirth Vasodilators are prescribed to improve blood supply, drugs that relax the muscles of the uterus - its contractions impair blood flow. Medicines are also used against fetal hypoxia, since it usually accompanies malnutrition. The timing and method of delivery depend on the condition of the baby. If therapy is going well, there is no point in rushing things. It’s another matter if, despite all efforts, the baby does not gain weight, then they resort to early birth. The operation is performed if the baby is too weak to be born naturally.
Large baby A child is considered large if at the time of birth he weighs 4000 grams or more. According to recent studies, the incidence of large fetus births is quite high and varies between 8–8.5%. Babies weighing more than 5000 g are rare - 1 in 3000–5000 births. Reasons ✓ Post-term pregnancy. Despite the missed due date, the baby continues to grow, which inevitably leads to him gaining excess weight. ✓ Diabetes mellitus. Causes an increase in glucose levels in the baby, which stimulates excessive secretion of insulin - growth hormone - in his body. In this case, special pregnancy management is required. Most likely, you will have to go to the maternity hospital no later than the 32nd week so that doctors can keep the sugar levels in the blood and urine of the expectant mother under control. Very large babies are also often born to mothers with hypothyroidism, in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones. Such children, as a rule, suffer from metabolic disorders. ✓ An incorrectly prepared diet for the expectant mother is one of the most common reasons for the birth of an oversized baby.
What threatens Large newborns are more likely to have birth injuries, for example, a fractured collarbone or cephalohematoma (an accumulation of blood under the periosteum of the skull). They often suffer from metabolic disorders. If the baby suffered intrauterine hypoxia or asphyxia during childbirth, then disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system may be observed. Such babies must undergo neurosonography, and they are regularly observed by a neurologist. Fat people, as a rule, are big lazy people and do not like to move, so they have delays in motor development.
We give birth to a “hero” Such births, as a rule, take longer, since the passage of the baby’s large head through the birth canal takes more time. Difficulties may arise if the baby lingers in the mother's womb - his skull bones are denser and adapt less well to the birth canal. Due to overstretching of the uterus, labor may be weak. Be prepared to have an episiotomy. This will protect against rupture of the birth canal and injury to the rectum. The question of a caesarean section may arise: ● with an oblique or transverse position of the fetus and breech presentation; ● if there has already been an operation; ● with a clinically narrow pelvis; ● during complicated pregnancy; ● if the baby suffers during a post-term pregnancy.
Let's eat right! The weight of the baby largely depends on your diet. Can't give up cakes, fatty meats and fried potatoes? In 9 months you will get a well-fed cherub with thick cheeks. Following fad diets even during pregnancy is the other extreme. This can lead not only to the birth of a low birth weight baby, but also to miscarriage. Except in special cases, the expectant mother does not need a special diet. The main thing is that the diet is balanced and varied. At the same time, do not forget to monitor your weight gain, especially in the 2nd half of pregnancy. You should not gain more than 300–350 g per week. The total number of kilograms gained depends on your constitution. With a normal build - 10-12 kg, thin - up to 14 kg, overweight - no more than 7-9 kg.
First trimester Calorie needs are no different from the usual norm before conception. At the same time, remember that the baby’s organs are now being formed. Provide him with all the necessary elements. Folic acid. Deficiency leads to low baby weight and nervous system defects. Introduce liver, lentils, spinach, and wholemeal products into your diet. It is recommended to take folic acid in the form of a supplement. Vitamin B12. The deficiency leads to impaired lipid metabolism in the fetus, and subsequently to obesity. Sources of vitamin B12 are meat, liver, yolk, milk. Zinc. Deficiency can cause low weight and weak immunity. Do not give up beef, pork, dairy and seafood, and cereals.
II trimester The baby is rapidly gaining weight, which means the need for nutrients increases - by 200–400 kcal/day. The increase should come from protein, the main building material. It is also necessary to increase the intake of essential vitamins during this period. Calcium. Reduces the risk of having a low birth weight baby. Include fermented milk products, green vegetables, legumes, nuts, and figs in your diet. For complete absorption of calcium, phosphorus and magnesium are also needed. Milk, chicken, and fish are rich in phosphorus. Magnesium - nuts, soy, vegetables. Iron. Deficiency can lead to anemia, which can lead to premature birth and decreased birth weight of the newborn. Iron is best absorbed from meat. Also include fish and eggs in your diet.
Third trimester Your diet has the greatest impact on your baby's weight. Monitor the presence of proteins, fats and carbohydrates in your diet. Squirrels. Their presence in sufficient quantities is especially important - the baby is gaining weight more actively than ever. Sources of complete protein are meat, fish, milk, low-fat cottage cheese, low-fat cheeses. Fats. Even a temporary fat deficiency leads to a decrease in fetal body weight. Therefore, 25–30 g of vegetable oil per day is now the norm for you. Carbohydrates. Their deficiency leads to a decrease in blood glucose levels. Then proteins will be used as fuel, which will negatively affect the development of the baby. The best carbohydrates are wholemeal bread, unrefined cereals, fresh vegetables and fruits.
Related posts:
ideal mother,
how should she wear a bandage?
Dmitry Dibrov