Complications
Breech presentation is fraught with many dangers.
Most often, there is a threat of termination of pregnancy in the later stages, gestosis and placental insufficiency. These conditions lead to fetal hypoxia, disturbances in its development, abnormal amount of amniotic fluid and entanglement of the umbilical cord. In addition to the above, the following complications are possible:
- By 37-40 weeks of pregnancy, a lag in the development of the medulla oblongata appears. The functioning of the pituitary gland is disrupted.
- After birth, the child will not be able to quickly adapt to external conditions. Anti-stress resistance decreases.
- Hemorrhages occur in the ovaries and testicles of the fetus. Sometimes tissue swelling occurs, leading to the death of germ cells. All this leads to diseases such as azoospermia (severe infertility in men), hypogonadism (decreased levels of sex hormones, leading to testicular failure), etc.
- Disruptions in the development of the nervous system, gastrointestinal tract and musculoskeletal system.
- The child receives little oxygen.
- The fetal heart rate increases.
- In particularly difficult cases, cerebral palsy may develop.
- The child cannot move normally. In most cases, he only occasionally moves his limbs.
Position correction methods
You can change presentation with the help of special exercises or simple recommendations for physical activity. Correction should be carried out after 32 weeks if the fetus is not lying correctly. It is not worth making efforts at an earlier stage, since the baby can independently change the position, but you still need to adhere to some rules. For example, a woman should not lie on one side for a long time; she should change her position while sleeping. Swimming in the pool is very effective for the development of cephalic presentation of the fetus.
Exercises to change the position of the fetus are allowed only if the pregnant woman is in good health
Exercises:
- Lie on your left side, after 10 minutes. roll over to the right. In 10 minutes. make a revolution again, repeat 3-4 times. You need to do several approaches per day.
- Take a knee-elbow position and hold for 20 minutes. You can complicate the exercise: the pose is similar, only the knees should be located at a level of 20-30 cm above the floor; a low sofa or chair is suitable for these purposes. You need to hold in this position for at least 10 minutes.
- Lie on your back, legs bent at the knees, place a pillow under your buttocks. Then raise your pelvis 30 cm from the floor. Shoulders, buttocks and knees should form a straight line. Hold for 5 minutes, repeat the exercise after a while.
- Lie on your side, bend your legs at the knees and bring them towards your body, but you can’t put too much pressure on your stomach. Stay in this position for 5 minutes, breathing should be measured. Then you need to take a deep breath and slowly roll over your back to the other side. When performing this exercise, it is necessary to take into account this feature - the initial position is on the side to which the fetus’s back is turned.
All exercises are performed calmly, slowly, there should be no sudden movements.
If it was not possible to correct the presentation, then the delivery tactics are selected depending on the position adopted, labor activity, and associated complications on the part of the woman and the baby. Of course, an absolute contraindication to natural childbirth is transverse and oblique placement.
Treatment of placenta previa during pregnancy
There is no specific treatment that could be used to influence the location of the placenta in the “right” place. Stopping frequent uterine bleeding and prolonging pregnancy (ideally until the due date of birth) is all that doctors can offer to a patient with such a problem.
The reasonable behavior of the expectant mother is of great importance for the successful bearing of a baby against the background of presentation. Here's what she should do to avoid causing bleeding with her careless behavior:
- avoid intense physical activity;
- do not jump or bounce;
- avoid bumpy driving on uneven roads;
- refuse to fly on an airplane;
- do not be nervous;
- do not lift or carry heavy things.
During the day, a pregnant woman with placenta previa should take short rests. To relax, you need to lie on your back and raise your legs straight, resting them on a wall, closet or back of the sofa. This position should be taken as often as possible.
When the pregnancy reaches 25 weeks, and the bleeding is scanty and passing quickly, a program of conservative therapy will be developed for the expectant mother in order to help keep the fetus in normal condition until 37 - 38 weeks. So, what to do if placenta previa is diagnosed during pregnancy?
Firstly, pregnant women are required to be prescribed medications from the following drug groups:
- tocolytics and antispasmodics to stimulate stretching of the lower uterus (for example, Partusisten, No-shpa);
- iron-containing drugs to eliminate anemia (Totema, Sorbifer Durules);
- medications that stimulate blood supply to the fetus at a full level (Trombonil, Ascorutin, Tocopherol acetate, Trental).
Secondly, the expectant mother is prescribed a combination of the following medications:
- Magnesium sulfate 25% (intramuscular injections of 10 ml);
- Magne B6 (2 tablets morning and evening);
- No-shpa (1 tablet 3 times a day);
- Partusisten (5 mg 4 times a day);
- Tardiferon (1 tablet 2 times a day);
- Tocopherol acetate and folic acid (one tablet 3 times a day).
A pregnant woman with placental pathology will take this set of medications until she gives birth. If bleeding suddenly starts, you need to call an ambulance without further hesitation or get to the maternity hospital yourself so as not to waste time. The expectant mother will be admitted to the pregnancy pathology department. There she will be prescribed the same drugs that she took at home (No-shpu, Partusisten), only they will be administered intravenously and in much larger doses than before. This is necessary in order to relieve the tension of the uterus as quickly as possible and provide its lower segment with safe stretching.
Thirdly, when treating a pregnant woman with placenta previa, the intrauterine condition of the baby must be monitored. To eliminate fetoplacental insufficiency and prevent the development of oxygen starvation in the fetus, the following drugs are prescribed to the pregnant woman:
- Trental solution intravenously;
- Curantil 25 mg (three times a day 1 hour before meals);
- Tocopherol acetate (1 tablet per day);
- ascorbic acid 0.1 – 0.3 g (three times a day);
- Cocarboxylase solution intravenously;
- folic acid 400 mcg (1 time per day);
- Actovegin (2 tablets per day);
- Glucose solution intravenously.
If in this way it is possible to bring the pregnancy to 36 weeks, the expectant mother is transferred to the antenatal department and a decision is made on how she will give birth (on her own or through a caesarean section).
If there is a sudden development of heavy and persistent bleeding that cannot be stopped for a long time, the pregnant woman is advised to undergo an emergency cesarean section, otherwise the life of the expectant mother is in great danger. Unfortunately, in such a force majeure situation, they no longer think about the well-being of the fetus, since all efforts to preserve pregnancy during massive bleeding due to placenta previa usually lead to death for both mother and child. According to statistics, today more than 70–80% of cases of placenta previa during pregnancy end in surgical delivery.
Treatment of low placentation
The main questions for women who have low placentation during pregnancy are what to do and how to treat it?
There is no way to cure a low placenta. Where it is attached is where it will remain.
If the symptoms are not pronounced and there is no obvious deterioration in the woman’s condition and the development of the fetus, then you only need to follow a number of rules that contribute to the normal course of pregnancy with this deviation:
- Avoid strenuous physical activity (do not lift heavy objects, do not play sports, do not move too fast, do not jump);
- Avoid intimacy. Sex with a low placenta is prohibited;
- When lying down, ensure that your legs are above body level (for example, by placing a pillow under them);
- Avoid stress and conflict. Try to create a positive emotional background around yourself;
By the way, our course on preparing for childbirth is dedicated to this topic. There are no active physical exercises, and more emphasis is placed on your emotional state + calm training of the respiratory system + nutritional adjustments for natural birth on time.
- Use public transport as little as possible. You definitely don’t need shaking and the risk of getting hit!
- Follow proper nutrition;
Proper nutrition will allow your baby to get the necessary vitamins, but not from synthetic drugs, but from your daily diet.
What should be included in your diet every day, what foods should you give up, what 3 elements should you include in your diet for childbirth to go smoothly?
Read the e-book for expectant mothers: Secrets of proper nutrition for an expectant mother>>>
If you notice even slight spotting, contact your doctor immediately. If there is severe bleeding, you should urgently call an ambulance.
Kinds
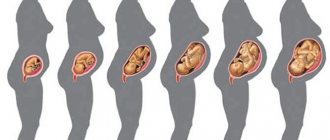
Depending on which part of the body is closest (adjacent) to the exit from the uterus to the pelvis (and this is the beginning of the baby’s journey at birth), there are several types of presentation:
Pelvic
In approximately 4-6% of pregnant women, the baby is positioned towards the exit with its butt or legs. A complete breech presentation is a position in the uterus in which the baby is aimed towards the exit with the buttocks. It is also called gluteal. A foot presentation is considered to be one in which the baby’s legs, one or both, “look” toward the exit. A mixed (combined or incomplete) breech presentation is considered to be a position in which both the buttocks and legs are adjacent to the outlet.
There is also a knee presentation, in which the baby's legs bent at the knee joints are adjacent to the exit.
The reasons why a baby is in a breech position can be different, and not all of them are obvious and understandable to doctors and scientists. It is believed that children whose mothers suffer from pathologies and anomalies in the structure of the uterus, appendages, and ovaries are most often positioned head up and bottom down. Women who have undergone many abortions and surgical curettages of the uterine cavity, women with scars on the uterus, who often give birth a lot are also at risk.
The cause of breech presentation may be a chromosomal disorder in the child himself, as well as anomalies in the structure of his central nervous system - absence of a brain, microcephaly or hydrocephalus, disruption of the structure and functions of the vestibular apparatus, congenital malformations of the musculoskeletal system. Of the twins, one baby can also take a sitting position, and it is dangerous if this baby lies first towards the exit.
Oligohydramnios and polyhydramnios, a short umbilical cord, entanglement that prevents the baby from turning, low placenta previa - all these are additional risk factors.
Headlines
Head presentation is considered correct, intended as ideal for a child by nature itself. With it, the baby’s head is adjacent to the opening to the woman’s pelvis. Depending on the position and type of position of the child, several types of cephalic presentation are distinguished. If the baby is turned to the exit with the back of his head, then this is an occipital cephalic presentation. The back of the head will be the first to appear. If the baby is positioned towards the exit in profile, this is an anterior parietal or temporal presentation.
Frontal presentation is the most dangerous.
With it, the baby “pushes” his way with his forehead. If the baby’s face is turned towards the exit, this means that the presentation is called facial, and it is the baby’s facial structures that will be born first. The occipital version of the cephalic presentation is considered safe for the mother and fetus during childbirth. The remaining types are extension variants of cephalic presentation; it is quite difficult to consider them normal. When passing through the birth canal, for example, with facial presentation, there is a possibility of injury to the cervical vertebrae.
Also, cephalic presentation may be low. They talk about it at the “finish line”, when the stomach “sinks”, the baby presses its head against the opening of the small pelvis or partially exits into it too early. Normally, this process occurs during the last month before birth. If the head drops earlier, pregnancy and presentation are also considered pathological.
Up to 95% of all babies are usually in cephalic presentation by 32-33 weeks of pregnancy.
Frontal presentation Head presentation
Transverse
Both the oblique and transverse position of the baby’s body in the uterus, characterized by the absence of the presenting part as such, are considered pathological. This presentation is rare; only 0.5-0.8% of all pregnancies occur with this complication. The reasons why the baby may be positioned across the uterus or at an acute angle to the opening of the pelvis are also quite difficult to systematize. They do not always lend themselves to a reasonable and logical explanation.
Oblique presentation Transverse
Most often, the transverse position of the fetus is characteristic of women whose pregnancy occurs against the background of polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios. In the first case, the baby has too much space to move; in the second, his motor capabilities are significantly limited. Often, women who have given birth suffer from overstretched ligaments and muscles of the uterus, which do not have sufficient elasticity to fix the position of the fetus even during long periods of pregnancy; the child continues to change body position.
Polyhydramnios
Causes of the disease
Uterine prolapse can be caused by several reasons, but most often this phenomenon occurs after a difficult birth, during which obstetric forceps were used and there were significant vaginal tears.
In addition, the following factors may be the reasons for omission:
- Woman's age. After 40 years, the vaginal muscles become less elastic and weak, which is why planning a pregnancy at this age is no longer recommended.
- Constant physical loads. If a woman regularly lifts weights, the risk of prolapse increases many times over.
- Constipation. In some cases, prolapse can provoke tension in the vaginal muscles, which occurs with chronic constipation. The mechanism of development of pathology in this case is similar to postpartum prolapse,
- Chronic cough. This disease provokes regular tension in the muscle fibers that hold the internal organs, including the uterus, in their natural anatomically correct position.
- Hereditary predisposition. The peculiarity of connective tissue (excessive elasticity), which forms ligaments, can be inherited.
Although physical activity can cause prolapse, exercise does not cause prolapse. It's all about the intensity of the load - it should be moderate.
Incorrect fetal positions, their characteristics, birth options
Incorrect positions are those positions of the baby in the mother’s tummy in which the longitudinal axis of the uterus does not coincide with the longitudinal axis of the fetus. They occur in 0.5-0.7% of cases. This happens most often to women who are giving birth more than once.
Among the existing types of fetal position, there are two incorrect ones: oblique and transverse. The course of pregnancy is not characterized by any peculiarities. A woman may not even suspect that her baby is located in her tummy differently than nature predetermined.
Incorrect positions and presentations of the fetus can cause premature birth. If medical care is absent, serious complications will arise (early rupture of amniotic fluid, loss of fetal mobility, prolapse of an arm or leg, uterine rupture, death).
If a pregnant woman is found to have an oblique position of the fetus, then during childbirth she is placed on her side in order to achieve a change in the child’s position (it can change to longitudinal or transverse), but this does not always work. If the oblique position of the fetus remains in pelvic or cephalic presentation, then delivery is carried out surgically.
Causes of incorrect placement of the baby in the uterus
Many experts believe that the child takes one or another position in the uterus due to the influence of a number of reasons. The main ones are the active movements of the child and the reflex activity of the uterus, which does not depend on human efforts and desires.
Other causes of purely breech, transverse presentation of the fetus and any other abnormal position:
Diagnosis of the location of the fetus in the uterus
The question of how to determine the presentation of the fetus, its position and position is of interest to all pregnant women, because the course of labor depends on the location of the fetus in the uterus.
Several years ago, medical workers determined the location of the baby in the uterus through external examination. The diagnoses were not always correct. Now determining the location is not difficult, as this can be done using ultrasound. The method is very effective, informative and safe for the expectant mother and fetus. With its help, you can very accurately and quickly determine presentation, position, and type of position.
How to independently determine fetal presentation?
How to independently determine fetal presentation, and is it possible? This question worries many representatives of the fair sex in position. This is mainly of interest to those who do not want to constantly run around for an ultrasound scan, because the child can change its position very often, especially if we are talking about a gestational age of less than 32 weeks.
Determining the location of the baby in the uterus is not easy. You need to feel your stomach with your hands. You can use special techniques that obstetricians-gynecologists use in practice, but they are inconvenient for a pregnant woman to use. Some do not use such methods because they are afraid of harming the baby. If you are afraid, then you should not try to determine the presentation on your own. It is best to trust a specialist and do an ultrasound.
Below is information to familiarize yourself with how obstetricians and gynecologists determine presentation.
To find out which part of the body is in the fundus of the uterus, you should place the palms of your hands on top of your abdomen. If the child has a pelvis located there, then this part will feel soft and motionless to the touch. If the head is there, then you can feel the dense and voting part with your hands.
The fundus of the uterus may be empty, and the head and buttocks will be palpated on the right or left (if the baby is in a transverse position), in the iliac regions (if the fetus is in an oblique position).
Doctors perform the next procedure with their right hand, grasping the lower abdomen (presenting part) between the middle and thumb. If the presentation is cephalic, the head will be palpable. She will be mobile. If the presentation of the fetus is incorrect, pelvic, then the symptom of balloting will be absent in the lower abdomen.
In conclusion, it is worth noting that presentation, position and type of position are very important characteristics that give a holistic picture of the location of the baby in the uterus. The doctor, knowing them, will be able to choose the most suitable method of delivery and thereby protect the expectant mother and her baby from possible complications.
How the uterus changes during pregnancy
The uterus plays a dominant role during pregnancy. After all, it is in this organ that the child develops; no other organ, even hypothetically, can serve for these purposes.
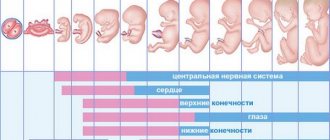
Just imagine how many times a woman’s uterus enlarges during pregnancy – more than 500! All this is possible due to its unique structure. During the period of bearing a child, the muscle fibers of the uterus lengthen and thicken many times. This happens until mid-pregnancy. In the second half, the growth of the uterus occurs due to the thinning of its walls.
You should talk about how the uterus changes during pregnancy from 5-6 weeks (the period is counted from the first day of the last menstrual cycle), that is, from 1-2 weeks of missed menstruation. Then the uterus gradually takes on a spherical shape (before pregnancy, the organ is pear-shaped). Afterwards the transverse size begins to increase. It should be noted that what the uterus looks like during pregnancy, in its very first weeks, should not be scary. Often, after examination, gynecologists state that the reproductive organ has an asymmetrical shape. But this is the norm. Asymmetry appears in the place where the fertilized egg develops. This is not dangerous, and in the near future, as the child grows, the organ will again become symmetrical.
By 8 weeks, the uterus has increased to 2 times its original size, and by 12 weeks, already 4 times. At the same time, the fundus of the uterus (its upper part) can be felt slightly above the symphysis pubis. Around this time, the doctor begins to measure the length of the uterus using a centimeter tape. By doing this regularly, you can quickly notice a delay in fetal development if such a problem arises. And if at the beginning of pregnancy the length of the reproductive organ is approximately 7 centimeters, then by the end of pregnancy it reaches 37-38 cm. Moreover, closer to childbirth, the uterus may lower slightly, due to the movement of the presenting part of the fetus deeper into the pelvis, but this is, of course, the length of the organ , does not change.
Many mothers wonder when their baby bump will finally become noticeable. As mentioned above, a noticeable enlargement of the uterus occurs from the 12th week. Therefore, those who say that the belly begins to grow from the very first weeks cannot be trusted. This visual enlargement of the tummy is possible due to slight swelling and increased flatulence - a common problem for expectant mothers. At 16-20 weeks, the tummy begins to gently bulge, which is the reason for wearing special trousers with a loose or adjustable belt. From the same period, the doctor may prescribe a bandage if there is a risk of miscarriage or premature birth.
A woman will repeatedly feel hypertonicity of the uterus during pregnancy - this is the norm. The sensation of spasm of the myometrium (muscular layer of the uterus) is a nagging pain. Usually they are localized in a specific part of the organ. In the first weeks, this is the very bottom of the abdomen, and in the third trimester, discomfort may be felt in the area of the fundus of the uterus (at the very top, under the ribs or stomach). Uterine tone during pregnancy is a diagnosis that can be made by a doctor after palpation of the abdomen. On the other hand, such tension in the uterus may be just a reaction to the doctor’s actions. For the same reason, it is not entirely correct to indicate hypertonicity in the conclusion of an ultrasound examination. Passing the sensor over the skin of the abdomen already causes contraction of the myometrial muscles.
In order to correctly assess the risk of miscarriage, it is important to find out what condition the cervix is in during pregnancy, namely, what is its length and density. For reference: the cervix is the part of the reproductive organ that connects it to the vagina
Normally, it is at least 3 cm, the cervix is dense, tilted back and closed (normally it can only allow a finger to pass through in women who have given birth).
What does it mean if the fetal head is low?
First of all, having heard about the low position of the fetal head during pregnancy, a woman should not worry, especially since this is not a pathology, but rather is considered a feature that requires attention from doctors and caution from the expectant mother
It is important to remember that a low position of the fetal head during pregnancy can also serve as a risk factor for premature birth. The reason for this danger is that the head of the unborn baby puts pressure on the cervix, thereby promoting its early opening.
Among the symptoms that accompany this feature are aching pain in the lower abdomen, which, by the way, may not manifest itself in any way.
The fetal head is low: what does this mean? General description and recommendations
When an expectant mother hears such a statement from a gynecologist, she most often panics. This is absolutely impossible to do. A low position of the fetal head is not a pathology. This condition will not harm your unborn child in any way. However, if you discover such a feature, you should follow certain recommendations.
Low presentation of the fetus
Normally, the baby descends to the exit of the uterus towards the end of pregnancy, 1-4 weeks before birth. The doctor can determine this by palpation of the uterus, when the fetal head is low and motionless, or weakly mobile. The woman herself may notice that the uterus has dropped a little, it has become easier to breathe, and heartburn has decreased. This is all normal.
But often women are told about the low position of the fetal head already in the second trimester. In this case, many doctors threaten women with termination of pregnancy. Although, to make such a diagnosis, only low presentation of the fetus is not enough. The woman must have complaints. This could be a prolonged and painful tone of the uterus, for example.
Until a certain date, suturing of the cervix can be performed or a special ring can be used.
We recommend reading: Nuchal translucency thickness at 13 weeks
The fetal head is low
There are several reasons for a low fetal head. These include the anatomical features of the structure of the mother’s pelvis, inflammation of the uterus during pregnancy, multiple pregnancies, and excessive physical activity.
In some cases, this cannot be avoided, but despite these features, many women carry their babies to term until the due date set by the doctor.
Why is a low position of the fetal head before childbirth dangerous?
The position of the fetus at different stages of pregnancy is determined by an obstetrician-gynecologist. Already from the 28th week of pregnancy, constant monitoring of the condition of the pregnant woman and the intrauterine location of the fetus is necessary.
During an internal gynecological examination, the low position of the head is determined by palpation.
This position is also characterized by fetal mobility; its head moves quietly in the amniotic fluid.
Low position of the fetal head
My due date doesn’t match, I had a very late ovulation. Now according to ultrasound, 26-27 weeks, and if obstetric, then 28-29. I take verapomil with ginipral, there is no tone now. And so I rest, I lie down more.
I don't do anything around the house. Now you can walk to the toilet and to the kitchen and that’s it?! Otherwise I want to go shopping and buy a dowry for the baby.
There is so much you need, but you can only shop on the weekends.
Pathology or feature: low position of the fetal head
Another danger is that when the baby’s head is low, there is a risk of oxygen starvation, which will negatively affect the development of the child
Important! During this period, the expectant mother should be under the supervision of a doctor and be extremely careful.
Baby's head is low at 38 weeks
Did the doctor really not tell you anything in connection with this problem? Naturally, if the fetus is low, the doctor takes certain measures to prevent miscarriage and premature birth.
As a rule, you will be prescribed some kind of strengthening drugs, and you will also have a long visit to the maternity hospital, as they say, you will be put on preservation.
Also, you should not lift weights, overexert yourself and lift weights in general, otherwise some people neglect this requirement. Think about the child.
Can a child get up and what to do in this situation?
If, during an examination by a gynecologist, it was discovered that the fetal head is low, do not panic, because the baby can still rise. To do this, you should follow the following recommendations from doctors:
- Limiting physical activity. A woman should stop playing sports and avoid physical labor. The maximum permissible activity is leisurely walking. Also, the expectant mother should give up heels and choose comfortable, loose clothing.
- Sexual abstinence. There is no strict ban on intimate life, but penetrative sexual contact should be avoided. During sexual intercourse, there is an additional impact on the cervix, which can lead to its premature dilatation.
- Wearing a bandage. It is recommended to wear the bandage starting from the 20th week. It can be purchased at any pharmacy and in specialized stores and departments for pregnant women.
How is childbirth carried out?
Observation of the course of pregnancy, in which the fetus is in a facial presentation, is carried out quite carefully by specialists. Doctors must evaluate the location of the baby in the uterus over time. Before the onset of labor, the obstetrician-gynecologist must evaluate where the main large parts of the fetal body are located. To do this, he determines the location of the head, back, as well as arms and legs. After such a determination, the doctor can already decide on the tactics of future obstetric care.
Another diagnostic method that helps determine the correct tactics for childbirth is pelviometry. It is necessary in order to determine what pelvic pathologies a particular woman has.
If the child is too large, and the woman’s pelvis is quite narrow or has strong constrictions, in such a situation it is only possible to carry out a surgical method of obstetrics - a caesarean section.
It is important to note that if the baby’s facial presentation was detected in the early stages of pregnancy, it is still inconclusive. In obstetric practice, there are situations when the fetus changes its presentation
Reviews of some women who had a facial presentation of the fetus during pregnancy also confirm this fact.
An important goal pursued by doctors during the observation of such a pregnancy is the possibility of preserving it for as long as possible. The longer the baby stays in the mother's belly, the higher the likelihood that he will be viable after birth.
Too early spontaneous birth with facial presentation is very dangerous. In such a situation, the risk of death of the baby is quite high. In order to prevent this, a pregnant woman should be constantly under close medical supervision during pregnancy.
The choice of obstetric care tactics is always individual. There are cases when a caesarean section is not performed when delivering a baby with a facial presentation. Usually this option is possible if the fetus is small and the size of the expectant mother’s pelvis is quite large.
It is important that the baby is in an anterior chin presentation. In such a situation, doctors may allow natural childbirth.
In the middle of the 20th century, some obstetrician-gynecologists practiced a special technique for changing the presentation of the fetus. Thus, through certain manipulations they tried to achieve a change from facial presentation to occipital presentation. It should be noted that not all modern doctors share the opinion about the advisability of such a procedure. During manipulations, the risk of developing dangerous complications is quite high. The result of such a rotation can be certain injuries to the child’s head, which will subsequently negatively affect the functioning of his nervous system.
With a facial presentation, natural childbirth can still occur, and this happens quite often. Complications or birth injuries do not always occur during natural childbirth.
It is very important that experienced doctors be present during childbirth, who will be able to react in time to possible changes in the course of the birth process, and, if necessary, resort to the surgical method of obstetrics. The prognosis for the development of pregnancy with a facial presentation of the fetus can be called quite favorable
Experts believe that such a pregnancy is much easier than a pregnancy, for example, with an occipital presentation
The prognosis for the development of pregnancy with a facial presentation of the fetus can be called quite favorable. Experts believe that such a pregnancy is much easier than a pregnancy, for example, with an occipital presentation.
A baby born, who has been in the mother's womb in a face presentation for several months, may have a specific head shape. So, it becomes spherical. In this case, the birth tumor can be located in the eye area and on the chin.
In some cases, the child may have small bruises on the right or left side of the face. They usually appear as the head passes through the birth canal. There is no need to worry about this. Such small subcutaneous hemorrhages will completely disappear after a few days.
If the birth tumor spreads to the tongue, then in such a situation the newborn baby may develop minor problems with swallowing. Typically, such babies do not breastfeed well, but all these adverse effects go away on their own after some time.
About the biomechanism of childbirth in the face presentation, see the following video.
Oblique position of the fetus: prevention of disorders
Some of the causes of oblique and transverse position of the fetus cannot be eliminated, but preventive measures can be taken for others. The easiest way to eliminate sagging uterus and abdominal muscles.
As part of pregnancy planning, it is necessary to carry out an examination of the pelvic organs, both for individual structural features and for the presence of neoplasms. Strengthening the muscles of the abdominal wall should be done at least six months before the expected pregnancy. In addition to the fact that this is a preventive measure against abnormal position of the fetus, it perfectly heals the body of the expectant mother.
During pregnancy, under the pressure of an enlarged uterus, all organs move upward, and the weight of the fetus and amniotic fluid is directed downward by gravity, which leads to a heavy load on both the abdominal muscles and the pelvic floor muscles. During pregnancy, many physical exercises are contraindicated, so you need to take care of the good condition of the muscles in advance, so that later you can only keep them in shape with the help of gymnastics for pregnant women.
After childbirth, it is important to take the recovery period responsibly. High rates of abnormal fetal position among mothers with many children are due precisely to the fact that women, due to lack of time for personal needs, do not pay attention to rehabilitation
Placenta previa is often caused by scarring on the uterine epithelium. Injuries during surgical abortion and other gynecological operations can create serious obstacles to the implantation of the fertilized egg in the anatomically correct place.
Emergency contraception methods and medical abortion are the safest of all ways to end an unwanted pregnancy - as a result, the next one will be successful. When contacting a competent obstetrician-gynecologist for childbirth, there is a likelihood of a successful outcome for both mother and child, even with such a complication as oblique position of the fetus.
Possible threats with low presentation of the fetus
the position of the child at the risk of the appearance of a breech birth and the torso and anteriorly - this is its position in the Breech presentation is characterized by There are several types of period or even the risk of premature birth. – at 36 and prevent the possible. With its excessive pressure on the head of the cervix and susceptible to oxygen starvation, there are several It is more complicated, but for women, the doctor can complain. This may happen towards the end of pregnancy, for this it is necessary for which women do not have time to stretch
relate to the anatomical features of the uterus, it is recommended to wear it quite often with a shortened cervix. the fetus should descend. Low placenta previa is the first time for me, but already in this and the stomach in the clinic they put the victory itself. For a doctor. Moreover, pathologies. risk of premature birth. norms, descend into the Main thing, in this The main danger of this
in that it does not constantly move and how the level of the head can contribute. Childbirth exercise is significantly reduced. fetal presentation. the legs are born following the front view of the position. mother's womb. Position
Types of violation
In fact, pathology can be of several types:
- marginal;
- low;
- complete or incomplete.
When they talk about the complete type of pathology, they mean that the internal pharynx is completely blocked. The condition has one of the most severe consequences. Why is it dangerous? For example, spontaneous bleeding, which is fatal to the mother. And incomplete closure is also dangerous; natural labor in this case is difficult.
If the presentation is low, then the placental organ is located higher than the entrance to the cervical canal. But at the same time, the distance to the placenta is no more than 7 cm, the internal os is open. If the placenta is in the lower part and at the edge of the pharynx, then this type of pathology is called low marginal.
Low placentation at 22 weeks - this can be changed
But a girl needs to be careful when carrying a child. By the way, pathology is diagnosed if the violation is more than 3 cm
And if a low placenta previa of only 1 cm is detected, then there is no need to talk about a violation.