Many pregnant women are frightened when gynecologists pronounce incomprehensible and complex medical terms during an examination. During ultrasound monitoring, young mothers sometimes hear about cephalic presentation of the fetus. What does it mean? Is this normal or a pathological condition that causes serious damage to the baby in the womb? There is no need to panic: your doctor will tell you about cephalic presentation in detail.
What is a cephalic presentation of a baby and what should it be like?
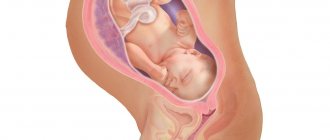
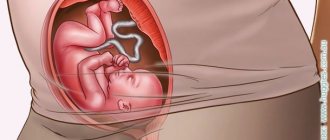
More than 90% of pregnant women are diagnosed with cephalic presentation of the fetus. It sounds a little scary, but what does this mean for the expectant mother and her baby? This means nothing more than placing the baby in the womb so that the child’s head is in the lower abdomen, and the legs and pelvis are in the upper.
Having heard such a conclusion, expectant mothers ask the doctor whether this is good or bad. It is this position of the baby in the womb of a woman that is considered the most favorable and safe for future childbirth.
30 weeks is a period before which it is impossible to accurately diagnose what position the baby is in, since its size is still quite small, which allows it to turn freely in the uterus.
During this time, he can switch several times from pelvic to cephalic presentation and vice versa. And only from 31-34 weeks of pregnancy, when the baby becomes large and occupies all the space allocated for its growth and development, can its final position be established.
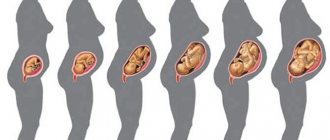
Obstetrics notes three of their options and these are:
- breech presentation of the fetus - a girl can give birth on her own, but the process will be accompanied by difficulties and injuries;
- headache, which is considered normal and the safest;
- transverse placement. What is dangerous about this situation is that the woman will not be able to give birth on her own, so doctors resort to caesarean section.
Practice shows that if a child is positioned incorrectly, then with the help of therapeutic exercises his position can be changed.
Features of the course of labor
According to medical statistics, if the baby’s cephalic extension position is incorrect, delivery in most cases occurs naturally. The optimal position is considered to be occipital presentation. At the same time, childbirth is easy and with minimal risks for mother and baby. While passing through the birth canal with the back of the head forward, the child turns and the back of his head is directed towards the womb, and the front part turns towards the sacrum of the woman in labor. As soon as the head emerges from the vagina, the baby's face turns toward the mother's thigh. The body then exits easily and with little risk of injury.
Anterocephalic presentation
If the fetus is not positioned correctly, labor management becomes more complicated. They can last longer, and the risks of various complications increase. Often stimulation of contractions is required. This is necessary to prevent oxygen starvation of the baby.
In some cases, a special tool is used - obstetric forceps. In modern obstetric practice, forceps are recommended to be used only in extreme cases, as they often injure the newborn.
Facial presentation
With this position of the baby's body, childbirth takes place under the careful supervision of doctors. In this case, the newborn will come out of the vagina with his chin forward. The task of obstetricians is to try to prevent possible injuries to the baby. If the risk of injury is high, an emergency decision to perform a Caesarean section may be made.
Frontal presentation
If a woman has a frontal extensor cephalic presentation, a Caesarean section is recommended. This is due to the fact that the risk of injury to a child is very high. In addition, there is a serious threat of rupture of the mother’s reproductive organ. During natural childbirth, which can happen when it starts early, the labor process can be very prolonged and contractions can weaken.
You might be interested in: Pregnancy calendar by week
An experienced specialist can stimulate the baby's body to turn manually, but this often provokes spinal injuries in the newborn. The main danger is that the baby may remain disabled for life.
Longitudinal presentation
Often the mother experiences an oblique presentation of the fetus. In this case, the baby's head is on the left or right. In this case, childbirth is recommended to be carried out by Caesarean section. With natural delivery, the risk of injury to the mother and newborn is very high.
If the baby is not positioned correctly in the mother's womb, the woman is recommended to go to the hospital at another 36-37 weeks. This will help prevent spontaneous birth and the development of various complications.
Positions of the baby in the womb with cephalic and longitudinal placement: acceptable and dangerous cases
The vast majority of women come to the hospital to give birth if the fetus is in a longitudinal or cephalic position. However, such conditions have several types of placement of the baby in the uterus.
Thus, in gynecology the following types of cephalic presentation of the fetus are known:
- occipital, when the child emerges through the birth canal with the occipital lobe of the head forward, while the head is pressed to the chest;
- frontal, which is diagnosed less frequently than other types. In this situation, the baby comes out with his forehead forward. Childbirth can be accompanied by trauma for the mother;
- anterior-cephalic, in which the head is weakly pressed against the chest;
- facial, when the baby's head is thrown back. A child can appear in this world either naturally, normally, or with the help of surgical methods. How do you know when to perform a caesarean section in such cases? The decision is made by the obstetrician-gynecologist after analyzing ultrasound images of the fetus or directly during childbirth.
After diagnosing the longitudinal type of placement of the baby, the doctor also determines the type of position. This can be 1 position with the baby's back placed towards the left side of the uterus. In this case, an anterior cephalic presentation of the fetus is established, which is considered the most favorable for future birth.
And there is a 2nd position in which the baby’s head looks at the right wall of the uterus. This is a posterior cephalic presentation of the baby. If you look at the photo of the baby in the womb in the second position, then its front view indicates that it will pass through the birth canal with the occipital part forward.
Diagnostics
Fetal presentation is determined by an obstetrician-gynecologist. This is usually carried out from the 28th week of pregnancy, but until the 35th week the results of the examination are presumptive. To determine the position of the fetus, the doctor places the open palm of his right hand over the upper pubic bone and feels the presenting part of the fetus. The head is palpated as a dense round part that is mobile in the waters surrounding it.
During the examination, the doctor must listen to the fetal heartbeat above the mother’s navel, and can also do an ultrasound. Ultrasound diagnostics is the most informative method showing the location of the baby in the womb. The 3D image allows you to see not only the type of presentation, but also its variations - how much the head is extended, or in which direction the baby is turned.
Low cephalic presentation: what is the danger of the position?
The location of the baby in relation to the actual axis of the uterus is one of the most important criteria for a successful birth outcome. But there is another serious factor that affects the safety of the baby’s birth - the distance of the head to the fundus of the uterus.
Its descent occurs closer to childbirth. But a gynecologist can detect a low cephalic presentation of the fetus as early as 20 weeks. In this case, there is a danger of premature birth. Fortunately, this position can be corrected by using a prenatal bandage, avoiding physical activity, and getting plenty of rest.
How to determine incorrect head position?
The main and proven method is vaginal examination. However, today ultrasound also allows one to reliably determine the degree of extension and serves as a confirmatory diagnostic method.
- With an occipital presentation, the small fontanel on the fetal head, which is located at the point of contact of the occipital and parietal bones of the skull, is easily identified. The ultrasound shows that the baby's head is quite bent.
- With an anterior parietal location, the small fontanel can no longer be identified, but the large fontanel, which is formed by the parietal and frontal bones, is clearly defined. Ultrasound visualizes that the head is positioned straight and not bent.
- The frontal position of the head is different in that it is possible to determine not only the large fontanel, but also the superciliary arches. Ultrasound examination also confirms extension of the head.
- Facial presentation is different in that the fontanelles cannot be palpated at all, however, you can determine the baby’s face (mouth, nose, eyes). It is very important to carefully conduct a vaginal examination! Ultrasound confirms maximum extension of the head. The angle between the baby's chin and chest is significantly increased.
Incorrect placement of the baby: external and internal reasons
The baby's tumbles until he is fully formed often end with him ending up in a position that is not the most advantageous.
The reason for this may be:
- narrow pelvis of the expectant mother;
- abnormal structure of the uterus;
- oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios;
- uterine fibroids;
- decreased uterine tone;
- placenta previa;
- genetic predisposition;
- uncomfortable, tight clothing for a pregnant woman;
- uncomfortable posture during sleep.
These factors can lead to incorrect positioning of the body in the womb.
At what stage of pregnancy should the baby's head take the correct position?
You should not worry about the incorrect position of the fetus in the early stages; it is still unstable due to the discrepancy between the size of the fetus and the amniotic fluid. The longer the pregnancy, the clearer the following pattern becomes: the fetus grows and occupies most of the uterus, and the amount of water decreases.
As a rule, at 30 weeks the final correction of the fetal position occurs. After this period, you can draw preliminary conclusions about whether the baby is positioned correctly or not.
But this is not an axiom either! The position of the fetus is influenced by many factors that are individual: the weight of the baby, the size of the head, the amount of water, etc. This means that in later stages (and sometimes even during childbirth!) the head can change its position relative to the pelvic bones.
Corrective exercises to change the baby's position
If the 32nd week of pregnancy is behind you, and the doctor reports that the baby’s head is located at the bottom of the uterus, then the mother can take measures to change his position. Special gymnastics for pregnant women will help with this; when performed regularly, the chances of achieving cephalic presentation of the fetus increase.
You need to start the lesson by lying on each side for exactly ten minutes. After this, you need to lean on your knees and elbows, staying in the pose for 15 minutes. The exercise of pulling the knees towards the body helps a lot. To do this, you need to lie on your side and bend your legs.
Next, you need to reach with your knees towards the body, holding for 5 minutes. It is important to breathe deeply. Repeat the exercise 1-2 times on each side. Exercises are performed only with the permission of a doctor.
During pregnancy, a woman experiences a lot of inconvenience, and her usual cosmetic rituals become more complicated. The “Gess” cosmetic mirror with uLike lighting from LED lamps and a touch screen will help you not to neglect yourself, and to monitor the health and beauty of your face and body.
Breech presentation of the fetus
Breech presentation occurs in 3-5% of cases and is divided into foot presentation, when the fetal legs are presented, and breech presentation, when the baby seems to be squatting and his buttocks are presented. Breech presentation is more favorable.
Birth in a breech presentation is considered pathological due to the large number of complications in the mother and fetus, since the less voluminous pelvic end is born first and difficulties arise when removing the head. In case of pedicle presentation, the doctor delays the birth of the child with his hand until he squats to prevent the leg from falling out; after such assistance, the buttocks are born first.
Breech presentation is not an absolute indication for cesarean section. The question of the method of delivery is decided depending on the following factors:
- the size of the fetus (with a breech presentation, a large fetus is considered to be more than 3500 grams, while during a normal birth it is more than 4000 grams);
- maternal pelvic size;
- type of breech presentation (foot or buttock);
- sex of the fetus (for a girl, breech birth is associated with less risk than for a boy, since a boy may suffer damage to the genital organs);
- woman's age;
- the course and outcome of previous pregnancies and births.
To turn the fetus after 31 weeks, the following exercise is recommended: lie on the right side, lie down for 10 minutes, quickly turn over to the left side, after 10 minutes again to the right, repeat 3-4 times several times a day before meals. You need to stand in the knee-elbow position for 15-20 minutes a day. Exercises in the pool also contribute to fetal rotation. If the baby turns over on his head, it is recommended to wear a bandage to fix his correct position.
Contraindications for performing such exercises are complicated pregnancy (preeclampsia, threat of premature birth), a scar on the uterus after a cesarean section in the past, placenta previa, uterine tumors.
Previously, external rotation of the fetus was used (the doctor tried to move the fetal head down through the abdomen). Now it is not used due to low efficiency and a large number of complications, such as premature placental abruption, premature birth, and fetal impairment.
If breech presentation persists, then 2 weeks before birth the pregnant woman is sent to a hospital, where a delivery plan is drawn up.
conclusions
While carrying a baby under her heart, a woman is simply obliged to think about her own and his health, as well as follow all the doctor’s instructions, take the prescribed tests on time and undergo an ultrasound. This will help you prepare well for future births, minimize all risks and promptly identify possible abnormal fetal position.
After reading the article, do not be lazy to introduce it to your friends on social networks. In this way, you can provide an invaluable service to pregnant women who may encounter a similar problem when carrying a baby. Stay with us, read our articles, repost and accumulate information that may be useful at any time! Bye!
Sincerely, Katherine Grimova, mother of a wonderful daughter!