The position of the baby in the abdomen must be assessed throughout pregnancy. If in the first 2 trimesters of pregnancy the baby does not actively change its position from week to week, then in the 3rd trimester the position of the fetus plays a special role in choosing the method of delivery.
There are some positions in which only a caesarean section is indicated. Therefore, the position of the child must be regularly monitored throughout the entire period of gestation using various methods, and not only during a control ultrasound.
General concepts of correct and incorrect position of the fetus in the abdomen during pregnancy
The position of the baby in the abdomen by week in the uterine cavity represents the direction in which the baby's face is facing. There are posterior and anterior positions of the fetus. When the baby's face is turned towards the mother's back, this is considered an anterior position. And when the face is up, that is, towards the anterior abdominal wall, one should speak of posterior presentation.
It happens:
- longitudinal;
- transverse;
- oblique
The term “presentation” refers to the location of certain parts of the baby’s body in relation to the mother’s pelvis.
It comes in the following types:
- head;
- frontal;
- facial;
- pelvic (can be leg or gluteal);
- transverse (shoulder).
The correct location is considered to be the front head. In these cases, the child's head is turned towards the entrance to the pelvis, and the face is turned posteriorly. Childbirth in this position occurs naturally along the physiological birth canal and, as a rule, proceeds safely.
Malposition of the fetus is divided into the following types:
- posterior view of cephalic presentation (face facing the anterior abdominal wall);
- pelvic (when the child’s body is turned towards the entrance to the small pelvis with the buttocks and legs);
- transverse presentation (the child lies with his shoulder to the entrance).
In addition, frontal and facial presentation occur, but medical statistics rarely mention them.
Incorrect presentation of the fetus. Types and reasons
Incorrect presentation is oblique. Its extreme form is considered transverse: the baby turns perpendicular to the birth canal. This arrangement of the fetus in the abdomen is possible with tumors of the uterus, with excessive stretching of the organ due to the too large size of the fetus or multiple births.
Breech presentation is divided into breech and leg presentation. The first is considered more favorable. It occurs due to pathologies of the fetus and a history of diseases of the mother’s reproductive system.
If fetal malposition is diagnosed
If there is any position of the child other than the head, you should consult a doctor. The decision on the method of delivery is made individually.
Transverse presentation is an absolute indication for surgery.
If pelvic birth is observed, the decision is made individually, taking into account the sex of the child (it is safer to give birth to a girl on your own than to a boy, since there is no risk of damage to the child’s genital organs), the woman’s age, the course of previous births, and the position of the baby (breech or leg presentation).
How to determine the location of the fetus
Determining the placement of the unborn child in relation to the birth canal is of exceptional importance. Therefore, monitoring of fetal movement is carried out throughout pregnancy. Diagnosis of the location of the fetus can be carried out in several ways.
These include:
- external examination by an obstetrician-gynecologist;
- auscultation of the abdomen;
- gynecological examination on a chair;
- palpation of the abdomen;
- Ultrasound examination.
According to the stomach map
The position of the baby in the abdomen week by week can be determined by the “belly map”. This diagnosis was proposed by American obstetricians.
The method is as follows:
- draw a circle (“belly”, which must be divided into 4 parts);
- mark the child’s heart on a piece of paper (in the back area);
- for several days, observe the child’s tremors (where the tremors occur more strongly, the legs are located in this place);
- you need to take a soft toy or doll and place it on your stomach, as shown on the sheet.
This way you can find out the approximate location of the child.
By aftershocks
A woman can independently assess the position of the child by his kicks. With a cephalic presentation, the shocks are felt above the navel, exactly in the place where the baby’s legs are located. With a pelvic position, the shocks are felt in the lower abdomen, and with a transverse position, they are felt on the side.
According to the shape of the belly
With the classic longitudinal position of the fetus, the abdomen has a slightly elongated oval shape. If the child is located transversely, then the stomach has an irregular shape. Parts of the fetus may be felt on one or the other side of the abdomen. When palpating, you can notice a protruding part on one side.
By heartbeat
The heartbeat can also tell you what position the fetus is in. He is listened to every time he visits the antenatal clinic. And also every day if the woman is in the maternity hospital.
Auscultation of the fetal heartbeat is performed using an obstetric stethoscope. It is a tube that the doctor moves along the front surface of the abdominal wall. With a breech presentation, the heartbeat will be clearly heard in the navel area.
The position of the fetus can be determined by palpation (palpation) of the baby's head. Palpation is carried out slowly in the lower abdomen, gently clasping the expected area of the head with your hands.
Palpation of the abdomen is the fastest and most accessible way to determine the location of the fetus. It is carried out at every visit to the antenatal clinic.
Using ultrasound
Ultrasound is rightfully considered the most reliable method of determining the location of the child. It can also be used to identify pathological conditions associated with pregnancy. For example, polyhydramnios, umbilical cord entanglement.
To more accurately visualize the baby's position, ultrasound is best performed between 32 and 34 weeks of pregnancy. This rule is predetermined by the fact that it is by this time that the child takes his true position.
What to do next?
Gail Tully suggests that mothers who find that the baby has not yet reached the optimal position in the stomach (head down, back to the mother's belly or to the left/right side) coax him to roll over and do special exercises to relax and balance the muscles that support the uterus , pay attention to your lifestyle:
- try to squat more (resting your full foot on the floor);
- sit leaning slightly forward or with your back straight;
- When working at the computer or watching movies, do not lean back, for example, by sitting on a slightly deflated fitball (this way it is more stable).
As unusual methods: bring a switched-on flashlight to the stomach (the baby will reach for the light) or place headphones with music (the young music lover may turn over to hear better).
In addition, do pregnancy yoga, walk and dance more: this will help maintain pelvic mobility and strengthen muscles.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
.
Until 32-36 weeks of pregnancy, the fetus constantly moves in the uterus. Then its movements stop, the child prepares for birth and takes a position that will make the process of passing through the birth canal as easy as possible. Which location is optimal for rapid delivery? Why can a baby lie down incorrectly and what are the consequences?
What circumstances influence the presentation of the baby?
The reasons that influence the position of the child in the womb are most often the following:
- abnormalities of the structure of the uterus and vagina;
- multiple pregnancy (more often one of the twins is breech);
- narrow pelvis;
- light weight;
- too much weight;
- increased head volume (anatomical features, hydrocephalus);
- oligohydramnios;
- polyhydramnios;
- fetal malformations;
- hypertonicity of the uterus;
- placental abruption in the first weeks of pregnancy;
- intrauterine growth retardation in the fetus;
- chronic hypoxia;
- insufficient functionality of the placenta;
- illnesses suffered by a woman during pregnancy;
- umbilical cord entanglement;
- weak abdominal muscles in women;
- genetic abnormalities of the fetus;
- prematurity (in this case, birth occurs before the baby takes the correct position);
- improper attachment of the placenta (low attachment, placenta previa);
- various uterine pathologies (fibroids, cysts, tumors);
- repeated pregnancy (especially with a short break).
Sometimes an anomaly in the location of the fetus is registered already at the time of birth. The most common reasons for this fact are rapid labor. They happen quickly, from a few minutes to hours. And during this time the child cannot completely change his position.
Causes of incorrect position
Incorrect lying is caused by a number of reasons. The first is the excessive mobility of the child inside. As a result, excess intrauterine fluid, frail abdominal muscles, delayed development of the baby for several weeks, high tone of the uterus, abnormalities in the structure, and tumors of internal organs may occur in the mother’s body.
There are reasons that do not fall within the medical definition. The baby’s abnormal condition can occur when the baby’s mother sleeps only on one side ; even the manner of falling asleep affects the position in the womb. Having such a tendency, it is better to turn on different sides before going to bed, lie on your back, on your stomach - this is more useful for early pregnancy. Otherwise, surgery may be required. at the end of pregnancy.
Habits can change if you work on them, especially when it comes to the birth of a new person. Another reason is multiple pregnancy. If a mother is carrying twins, then competition appears inside the belly. Each fetus wants to occupy the most convenient place in a tight space, so the fetus is located in any convenient position.
Important: neglecting the mandatory conditions for the birth of children with incorrect intrauterine placement can cause surgical intervention by doctors, which is always difficult for the body of a young mother, because childbirth itself is a huge stress and colossal strain on the mother in labor.
What should be the location of the fetus in the uterus by week?
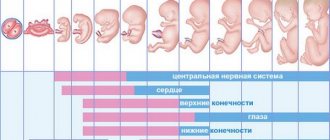
The position of the baby in the stomach by week depends on the trimester. In the first weeks of pregnancy, the child is just a developing embryo. Therefore, its position in the uterine cavity may be unstable.
In the second trimester, the baby’s weight is still quite small, so it is advisable to evaluate its position only starting from the end of the 2nd trimester. At the beginning of the third trimester, the child should already take his true position before childbirth; if this does not happen, the question of choosing a method of delivery is decided.
1st trimester: 1-12 weeks
In the first trimester of pregnancy, the fertilized egg attaches to the uterine cavity. The fetus is just beginning to form, so its future location cannot yet be assessed with high probability. The fertilized egg also has its own localization.
It can be attached:
- along the back wall of the uterus;
- along the anterior wall of the uterus;
- along the lateral walls of the uterus.
In the place where implantation occurred, the baby will develop and the placenta will form.
If the fetus is attached too low, close to the cervix, it may cause some concern to the doctor, since this position can lead to the threat of spontaneous abortion. Although, in many cases this does not happen, since the woman, together with the obstetrician-gynecologist, carries out comprehensive preventive measures to prevent this condition.
2nd trimester: 13-27 weeks
During the second trimester of pregnancy, the pelvic position of the fetus is often recorded until the beginning of the third trimester. But later it changes to the head one. During this period, the position of the child in the uterine cavity is constantly changing due to its high activity. This activity gradually decreases towards the end of the 2nd trimester.
Position of the baby in the stomach by week of pregnancy: 2nd trimester
Active change in position depends on the presence of a large volume of amniotic fluid, which has a significantly higher mass compared to the weight of the fetus. While in the 3rd trimester the weight of the fetus is almost comparable to the weight of a newborn baby, it continues to grow. Because of this, his activity decreases, and he takes a position in which he will remain until childbirth.
3rd trimester: 28-40 weeks
In the 3rd trimester, the final position of the fetus is formed, in which it will remain until birth. But it should be remembered that the baby reaches its final position by 33–34 weeks of pregnancy.
The most favorable position before childbirth is considered to be the head position. In this case, the child wedges his head to the entrance to the pelvis. This position is the most physiological, and is considered the main indicator for delivery through the natural birth canal.
Fetal presentation
The position of the fetus relative to the cervix, called presentation, also matters. It can be cephalic (the baby's head is below), and pelvic (close to the mother's cervix - the baby's buttocks). Head presentation with a longitudinal position is the key to an easy and natural birth, experts say.
Considering the location of the fetus in the uterus by week, it can be noted that it is active from 7 to 24 weeks. By week 36, the baby in the uterus becomes almost motionless. The expectant mother cannot independently predict the final position and presentation of the fetus. Only a doctor can draw a conclusion by conducting regular examinations and using ultrasound results.
How can the fetus be positioned before birth?
The position of the baby in the abdomen in the weeks before birth is often longitudinal. Its head is located at the entrance to the pelvis, facing posteriorly. This is the most physiological position of the baby before birth. In addition, the second most common position is the pelvic one. More rare positions are oblique and transverse.
Longitudinal position
This option involves the longitudinal position of the child relative to the uterine cavity longitudinally. In this case, delivery also occurs naturally.
Transverse position of the fetus
This positioning of the fetus occurs when the baby lies perpendicular to the axis of the uterus. That is, the presenting part of the fetus is located on the side, just above the level of the ilium.
Thus, the presenting part of the fetus forms a right angle to the uterine cavity.
Oblique position of the fetus
Oblique position is a condition when the presenting part of the fetus is located below the level of the ilium. This relationship of the fetus to the axis of the uterus forms an acute angle.
Oblique position is an absolute indication for operative delivery.
Breech presentation
Breech presentation is also called breech presentation. With it, the child lies with his buttocks towards the outlet of the small pelvis.
This type of presentation is divided into several types:
- complete;
- partial;
- single.
This presentation is pathological, since the child’s buttocks are smaller than his head. While the cervix dilates precisely to the diameter of the presenting part. The main complication with this option is incomplete dilatation of the cervix. Therefore, there is a risk of the baby’s head getting stuck in the birth canal.
Previously, it was believed that all types of breech presentations were fatal for women and children. But at the moment, cesarean section is used for effective delivery. And also in some cases, using a special technique, delivery is carried out through the natural birth canal.
Correct and incorrect placement
A child who is in a head-down position, with the back of his head turned toward the stomach, has a normal position in the uterus.
With this phenomenon, there is no doubt that the birth will be successful. Since the upper part of the head exerts uniform pressure on the cervix, labor becomes easier.
But there are other types of baby positions, which are divided into correct and incorrect options:
- Longitudinal position of the child. It is characterized by cephalic presentation of the fetus and is positioned as correct.
If, with this arrangement, the ultrasound report indicates that the presentation is breech, then various pathologies may occur during childbirth.
This type is considered rare and is observed in only 5% of expectant mothers. If a woman gives birth on her own, childbirth is accompanied by difficulties, so a caesarean section is most often prescribed. Oblique location. The difference is that the axis of the uterus and the spine intersect at an acute angle. The baby's head and pelvis are located on both sides of the mother's abdomen - this is considered a deviation from the norm.
The phenomenon is observed in less than 1% of women, often having second births. The reasons for the oblique position of the fetus are high levels of water, a large child, and obstacles on the way out of the womb.
In multiparous mothers, this is due to a weakening of the anterior abdominal wall. The safest solution is a caesarean section.
- Transverse position. In this case, the fetus crosses the uterus transversely. It is considered incorrect and occurs due to congenital pathologies in the development of the uterus, a narrowed pelvis, and incorrect localization of the placenta. With this phenomenon, premature birth often occurs.
It is worth understanding that in the early stages of pregnancy the baby is fully mobile, and after 33 weeks he stops actively behaving and is preparing to leave.
The normal position of the fetus is longitudinal with a cephalic presentation; in other cases, it is worth carefully monitoring the pregnancy.
If incorrect presentation has been diagnosed, there is no need to panic; it is best to consult with a qualified obstetrician.
Useful video
Why are some children in the back position?
The position of the baby in the abdomen in the posterior position by week may be associated with the individual characteristics of the child and the degree of his full term. Maternal factors, oligohydramnios or, conversely, polyhydramnios, and chronic diseases of the reproductive organs also play an important role.
In addition, a long delay in the posterior position can be caused by the low weight of the fetus. In children with a weight that does not correspond to the gestational age, a similar situation is often diagnosed.
How to rotate the fruit yourself
Before proceeding with any actions, it is necessary to undergo an ultrasound and determine the correct position of the child. If the baby is in the wrong position, then certain measures are taken to catch it before birth.
Physical exercises should begin after 32 weeks, when the fetus has already taken a comfortable position and does not seem to be going to change it. The set of classes is quite simple and effective, but it must be agreed upon with a gynecologist-obstetrician.
You need to monitor the behavior of the fetus every day, but to do this you need to know how to determine the location of the baby in the stomach. If everything is done correctly, then every day the woman will observe unhurried and unhurried revolutions. The effectiveness of such activities is 75%, so you should definitely try to change the situation for the better.
The lifestyle of the expectant mother also helps resolve the issue. Experts recommend sitting only on hard chairs, swimming, walking and eating healthy foods. All these moments work perfectly together, helping the baby to position himself correctly and be born naturally.
Modern research methods make it possible to accurately and reliably determine fetal presentation at any time. But for some reason, the expectant mother in labor does not always resort to them. In this article we will tell you how to independently, without the help of complex equipment, determine the position of the baby in the stomach, what methods exist for this, and whether this can always be done.
How to help your child take a forward position?
In order to help your child change his position, you need to adhere to the following rules:
- normalize the daily routine;
- include gymnastics (turns from side to side);
- use antispasmodic drugs (to reduce uterine tone).
If this does not help change the position of the child, the pregnant woman is hospitalized in the obstetric hospital in the pregnancy pathology department.
The following methods are used to change the position of the fetus:
- External rotation of the fetus.
- Rotation of the fetus using Leopold-Levitsky techniques.
- Turning the fetus onto its leg. This procedure is performed for urgent reasons, at a time when the woman is already in labor and only after the cervix is fully dilated.
Currently, if the fetus is abnormally positioned, a caesarean section is performed. However, in some cases, provided that the condition of the mother and child allows, childbirth is carried out naturally.
Exercises for cephalic presentation
There are several effective techniques to change the position of the fetus:
| Therapeutic gymnastics technique | How to do it |
| Gymnastics according to Bryukhina | This technique is recommended from 32 weeks of pregnancy until 38 weeks. You need to do the exercises 2 times every day. It is optimal to maintain an interval after eating of 1.5 - 2 hours. · Light warm-up. · Position with emphasis on your elbows (you need to take 1 deep breath and then exhale smoothly). · Same position, you need to touch your chin to your elbows (repeat 5 times). · Raise your right leg up, without bending, and gently lower it onto your toes (repeat 5 times). · Starting position on all fours, head down, back “round”. Smoothly begin to arch your lower back, then return to the starting position. In this case, you need to take a deep breath and exhale smoothly. The final part of the exercises can be considered strengthening the pelvic floor muscles. To do this, you need to pull in the muscles of the vagina and anus, count to 10. And then smoothly relax them. Repeat 4 times. |
| Dikan's technique | Exercises using the Dikan method consist of turning a woman from side to side into a lying position. To do this, the woman alternately lies on her right side, then on her left. After which she is recommended to sleep on her side, which corresponds to the position of the fetus. |
Why can’t you independently determine the position of the baby in the womb?
If the mother has polyhydramnios, and also if the woman is overweight and has a large layer of fat, it is difficult to independently determine the position of the fetus. Difficulties also arise if the placenta is attached to the anterior wall or the tone of the uterus is increased and the muscles of the abdominal wall are very tense.
It is also necessary to understand that the closer to childbirth, the greater the opportunity to correctly determine the position of the baby. In the early stages, this is difficult for any woman to do, and there is no direct need for it.
And if you have tried all the methods and still have doubts about the correct position of the fetus, do not delay in visiting a gynecologist. After all, modern medicine has all the means to help you. Just be sure that it is within your power to make labor easier and ensure a less painful birth of your baby.
Especially for
— Elena Kichak
The expectant mother is interested in everything related to her baby: his development week by week, how he looks, moves and grows. As the period increases, she begins to feel his movements: the tiny man moves freely in the uterine cavity. But towards the end of pregnancy, when the baby is already getting big, he occupies a certain position in the mother’s belly, in which he is most often born. However, it may not always be correct, and the course of labor largely depends on this. It is not surprising that a pregnant woman worries and strives to find out how to determine the position of the fetus in the womb and whether it is possible to do this herself.
What happens if the baby is not positioned correctly in the womb before birth?
The main complications of fetal malposition can be considered:
- premature birth;
- rapid labor;
- premature rupture of amniotic fluid;
- loss of fetal parts;
- addition of infectious complications;
- fetal hypoxia;
- fetal asphyxia;
- bleeding;
- umbilical cord prolapse;
- sepsis;
- uterine rupture;
- fetal death.
Incorrect positioning of the fetus can cause dangerous complications. Therefore, it is necessary to properly manage the pregnancy and monitor the position of the baby in the stomach during the weeks of pregnancy. To do this you need to use
Ultrasound according to the timing of pregnancy, and pay special attention to the position of the child after 34 weeks of pregnancy. If the rules and diagnostic measures are followed, the frequency of complications is significantly reduced.