by Doctor
Categories:
- Symptoms and treatment
The term “intestinal dyskinesia” is used by gastroenterologists to define a complex of intestinal disorders, the mechanism of which is caused by weakness of tone and impaired motility of the tract. Deterioration in function can be observed in different parts of the organ, but most often children are diagnosed with dyskinesia of the large intestine.
Why does dyskinesia develop?
Doctors say that the condition of the digestive organ is affected by a diet in which the child consumes little fiber. Also, the primary form of dyskinesia can develop due to intestinal infection. Secondary colitis develops in response to past and chronic diseases of the peritoneal organs (spleen, liver, pancreas). Hormonal disorders and diabetes mellitus are also among the predisposing factors.
The famous pediatrician Komarovsky calls for looking for the causes of intestinal dyskinesia in disorders of the nervous system. The pediatrician explains the neurogenic factor as the incorrect conduction of nerve impulses, which creates the preconditions for spasm or increased peristalsis. To avoid chronicity of the process, it is important to differentiate dyskinesia from other pathologies, otherwise treatment of the disease will be ineffective.
Clinical picture of dyskinesia in children
Intestinal dyskinesia, regardless of the patient’s age, occurs in two forms:
- hypomotor (atonic) pathology, characterized by constant difficulty in defecation (constipation);
- hypermotor (spastic), caused by accelerated evacuation of gastric contents into the large intestine. A sign of this form of dyskinesia is abdominal pain and diarrhea with unstructured feces.
In recent years, doctors are increasingly diagnosing functional intestinal disorders in children associated with enzymatic deficiency. Doctors find two explanations for this condition - hidden chronic pancreatitis and stagnation in the biliary system. Bile deficiency impairs the quality of processing fatty foods. A characteristic symptom of GIB is considered to be fatty stool with mucous inclusions.
Other symptoms signaling intestinal disorders include:
- bad feeling;
- decreased appetite;
- poor physical activity;
- pale skin tissue;
- painful sensations during physical activity.
A secondary inflammatory process that affects the thin or thick part of the tract is manifested by symptoms such as anemia, muscle dystrophy, and sudden weight loss. Stool analysis shows intestinal dysbiosis. Flatulence, or increased gas production, helps to suspect dyskinesia in a baby. The baby's tummy becomes hard, painful, and a loud rumbling sound is heard from it. The baby is worried, twitches its legs, and refuses to feed.
Diagnostic measures for dyskinesia
Due to its similarity with other gastrointestinal diseases, intestinal dyskinesia is diagnosed by excluding the suspected pathology. A phased examination of a child includes several activities:
- endoscopy;
- coprogram;
- irrigoscopy;
- biopsy - according to indications;
- stool occult blood test;
- exclusion of pathological neoplasms in the intestine.
Principles of disease therapy in children
Treatment of small children for intestinal dyskinesia is based on the organization of the diet and the correct distribution of hours of activity and rest. Patients are recommended to eat frequently and in small portions. In a diet that accelerates the treatment of dyskinesia, the following should prevail:
- juices;
- dried bread;
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- slimy water porridges;
- products with vegetable fiber;
- fermented milk products, especially with live lactobacilli.
When treating intestinal dyskinesia in a child under one year of age, it is important to adjust the balance of food enzymes. For this purpose, very young children are prescribed special medications to compensate for the lack of enzymes. For preschoolers and adolescents, treatment is supplemented with herbal preparations with tansy, St. John's wort, and bittersweet.
If a child suffers from severe pain, non-drug assistance can be provided by applying heat to the peritoneal area. If the procedure is unsuccessful, the patient can be given No-shpu or Drotaverine, calculating the dosage according to age and weight.
To relax the nervous system, treatment includes antidepressants or antipsychotics. Additionally, with intestinal dyskinesia, children can be prescribed autogenic training, exercise therapy, hypnosis, and acupuncture.
Folk remedies for intestinal dyskinesia
Harmless treatment of spastic and atonic colitis is carried out using folk remedies. Mint leaves, chamomile flowers, and valerian roots contribute to the restoration of normal peristalsis of the tract. The components take 1 tsp. each, pour a glass of boiling water over the phyto mixture and leave covered for 20 minutes. The napar is filtered and given to the child 3 times. 100 ml per day half an hour before meals.
Another remedy is obtained from sage and yarrow herbs, oak bark, St. John's wort flowers, and motherwort raw materials. The amount of each ingredient is 2 tbsp. l. The collection is doused with a glass of boiling water and allowed to brew for a couple of hours. Then the drug is filtered and the child is given 4 rubles. per day, measuring 100 ml of drink each time.
Our specialist comments
- Organize bowel movements in a timely manner if your baby suffers from constipation. Difficulties with the excretion of feces entail not only dyskinesia - their danger lies in general intoxication of the body, loss of appetite and decreased performance. Improper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract contributes to stagnation and rotting of food masses, which can subsequently cause the child to develop allergies.
- If dyskinesia causes a frequent urge to defecate, give your baby a decoction of chamomile and calendula flowers, thick jelly or a hard-boiled egg. Specific treatment for intestinal disorder will be prescribed by your pediatrician.
- To relieve spastic colic, use compresses. Apply a bandage soaked in vinegar solution to the intestinal area. The ratio of acidic product and water is ½ cup to 3 liters. If you have the opportunity to give your child a pine bath, be sure to take advantage of it. Treat yourself with paraffin applications.
Prevention of intestinal dyskinesia for children is to create a favorable atmosphere in the family, avoid stress, and eat high-quality foods without dyes, preservatives and flavoring additives. If you have constipation, it is important to limit your intake of rice in your diet.
Intestinal dyskinesia in a child
Intestinal dyskinesia is an intestinal disorder consisting of a violation of its motor function in the absence of any organic causes. Intestinal dyskinesia is one of the most common gastroenterological pathologies, recorded in 15–20% of the adult population, and it has been found that approximately 2/3 of patients suffering from this disorder do not seek medical help.
With intestinal dyskinesia, the prognosis for life is favorable, with regard to recovery - moderate.
The pathology can manifest itself in childhood, including at an early age, although it more often develops after 15 years of age, and women aged 30–40 years are more susceptible to it. With age, the risk of developing intestinal dyskinesia decreases.
Causes and risk factors
The main cause of intestinal dyskinesia is considered to be acute or chronic stress. Persons with a neurotic character, a tendency to somatization, increased anxiety, and emotionally unstable individuals are more susceptible to pathology.
Risk factors include:
- genetic predisposition;
- acute infectious intestinal diseases (in particular, those caused by Campylobacter and Shigella);
- endocrine disorders;
- pathologies of the central and peripheral nervous system (neoplasms and spinal cord injuries, syringomyelia, parkinsonism);
- diseases of the urogenital tract;
- poor nutrition (including eating too quickly, irregular meals, eating excessively spicy, fatty, hot foods);
- excessive mental stress;
- overweight;
- individual intolerance to certain foods;
- irrational use of medications (especially antibacterial, diuretic, psychotropic drugs);
- bad habits.
Forms of intestinal dyskinesia
Intestinal dyskinesia can be primary (occurs as an independent pathology, usually due to prolonged stress or poor nutrition) and secondary (develops against the background of another disease). The primary form of intestinal dyskinesia is more often diagnosed in children.
Depending on the consistency of stool, intestinal dyskinesia is divided into the following forms:
- with diarrhea (more than 1/4 of all acts of defecation occur with stool of liquid consistency, less than 1/4 with constipation);
- with constipation (more than 1/4 of all acts of defecation occur with dense and fragmented feces, less than 1/4 with diarrhea);
- mixed (constipation and diarrhea are observed in more than 1/4 of cases);
- unclassifiable (changes in the consistency of stool are expressed implicitly, not enough to determine the form of pathology).
Depending on the characteristics of the clinical picture, intestinal dyskinesia is distinguished with a predominance of pain, intestinal symptoms and flatulence.
It is necessary to maintain a water regime - drink 1–1.5 liters of water daily, this serves to prevent constipation, and in case of diarrhea, it prevents the development of dehydration.
Depending on the etiological factor, intestinal dyskinesia can be stressful, nutritional (associated with dietary errors) or post-infectious.
Symptoms of intestinal dyskinesia
All symptoms of intestinal dyskinesia are divided into those related directly to the intestines, to other organs of the gastrointestinal tract and non-gastroenterological manifestations. A feature of this disease is the lack of a tendency to progress.
One of the main signs of intestinal dyskinesia is abdominal pain of moderate intensity, without clear localization, occurring from time to time or regularly. It can be stabbing, cutting, dull or aching. Most often, pain is noted in the left iliac region. The pain appears some time after eating, weakens or disappears after passing gas or bowel movements, and never occurs at night.
Source: okeydoc.ru
Another symptom is flatulence, which appears a certain time after eating or in the evening. Loose stools are usually observed in the morning after breakfast and are absent at night. After defecation, there is sometimes a feeling of incomplete bowel movement. With constipation, stool resembles sheep feces; dense feces often lead to semi-liquid stool. The feces may contain an admixture of mucus, but no blood or pus is found in it.
Manifestations of intestinal dyskinesia can also include an unpleasant taste in the mouth and decreased appetite.
In addition, headaches, pain in the spine, increased anxiety, panic attacks, depression, phobias, irritability, a feeling of lack of oxygen, a coma in the throat, and incomplete inspiration are often observed.
One of the key points in the treatment of intestinal dyskinesia is diet.
Dyskinesia and impaired patency of the duodenum are often accompanied by cholelithiasis or peptic ulcer disease. In this case, patients experience spastic pain in the epigastric region, a feeling of fullness or pressure in the intestines, nausea, and vomiting.
Dyskinesia of the small intestine is characterized by spastic pain, rumbling and a feeling of transfusion in the abdomen, and a liquid or semi-liquid consistency of stool.
Dyskinesia of the large intestine is manifested by intestinal spasms or atony. Attacks of abdominal pain are accompanied by defecation with a large amount of mucus in the stool.
Features of the course of intestinal dyskinesia in children
Intestinal dyskinesia in children of the first years of life is manifested by an imperative urge to defecate, spasmodic pain in the abdomen or rectal area, pain often appears after physical exertion. Body weight may decrease or gain too slowly, muscular dystrophy, anemia, and dysbacteriosis may appear. Children with intestinal dyskinesia are characterized by pale skin, weakness, fatigue, and irritability. Sometimes a slight increase in body temperature is possible.
Source: progolovy.ru
Causes of ADHD in children
Mechanism of development of JVP
The gallbladder stores bile, which is secreted in the liver, and releases it into the small intestine, where it performs its function of breaking down fats that come with food.
Bile travels from the gallbladder to the small intestine through the bile duct. When the gallbladder is unable to release bile or the bile is unable to pass through the duct, it flows back into the gallbladder. Symptoms of the disorder then develop. When a person eats, the hormone cholecystokinin is released in the small intestine. It attaches to receptors distributed in the gallbladder muscle, which causes it to contract. Bile is released and passes into the intestines. In GIB, the gallbladder does not contract properly and bile is not released.
At the end of the duct there is a round muscle called the sphincter of Oddi. The hormone cholecystokinin also attaches to the sphincter receptors and gives it a signal to relax. The bile then passes into the intestines. When the function of the sphincter muscles is impaired, bile does not pass through the duct and remains in the gallbladder.
Exogenous causes
The main reason is a violation of the coordination function of the peripheral nervous system and neurohumoral control due to illiterate food intake (long intervals between meals, violation of the frequency of meals, dry snacks, abuse of carbohydrate and fatty foods) and irrational organization of the daily routine, etc.
Endogenous causes
In addition to external factors, there are internal reasons that lead to ineffective contraction of the gallbladder and relaxation of the sphincter.
- Inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis) interferes with its ability to contract.
- Sometimes, due to abnormalities in the structure of the biliary tract, bile cannot flow correctly. Such pathologies can be congenital, hereditary, or they can arise due to constant inflammation in the organ.
- Hypothyroidism (insufficient production of thyroid hormones). This condition increases the likelihood of stones forming in the bile duct. Thyroxine relaxes the sphincter, so due to a lack of this hormone, less bile enters the intestines.
- Gastrointestinal diseases. Pathologies affect the functioning of the biliary tract. Typically, children with ADHD have other associated bowel symptoms (diarrhea, constipation, food hypersensitivity).
Pregnancy and dyskinesia
Almost 70% of women carrying a child suffer from colon dyskinesia. The main problem for them is constipation. The disease adversely affects the general well-being of a woman. Dyskinesia can be the root cause of miscarriage. The uterus, increasing in size, puts painful pressure on the intestines, and intestinal spasms during illness can cause a spastic state of the uterus and the threat of miscarriage.
If there is discomfort in the abdomen, a pregnant woman should consult her doctor. He will prescribe approved medications and recommend non-drug treatment methods.
Therapy consisting of the following measures is recommended:
- treatment of gastrointestinal diseases using traditional medicine;
- adherence to a diet with the exclusion of spicy, fatty and smoked foods from the menu;
- drinking a glass of clean water on an empty stomach in the morning;
- the need for regular bowel movements at the same time;
- constant consumption of fluid in a volume of at least 1.5 liters;
- physical exercises approved by the attending physician;
- the use of a prenatal bandage to support the abdominal muscles.
The urge to have a bowel movement and urinate cannot be ignored, otherwise regular stretching of the rectal ampulla will cause premature birth.
The use of drug therapy during pregnancy is limited due to numerous contraindications for medications. Exceptions: Duphalac, Motilium, Linex, Forlax.
The main goal of therapy for pregnant women is to relieve pain, eliminate constipation, get rid of straining during bowel movements, and eliminate spasms that can cause early contractions.
Intestinal dyskinesia: manifestations, diet, tips
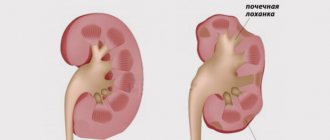
determination of the localization of pain during intestinal dyskinesia
Intestinal dyskinesia is a complex of intestinal diseases that appear against the background of impaired motor function of one of the organs of the digestive system.
An organ affected by dyskinesia cannot function normally, despite the fact that there is no organic damage. Most often, dysfunction of one organ affects the functioning of most organs of the gastrointestinal tract - the stomach, esophagus and motor function of the small intestine.
In medicine, this disease is sometimes called spastic colitis, and popularly irritable bowel syndrome.
How does intestinal dyskinesia manifest?
The symptoms of this disease cause a huge amount of inconvenience to their owners, so recognizing them is not so difficult. The most important sign of intestinal dyskinesia is pain; it can be aching, cutting and even pulling.
The duration of painful attacks is different and varies from 2-3 minutes to 3-4 hours. In addition, intestinal dyskinesia is characterized by pain of uncertain localization, which in many cases complicates the diagnosis of the disease.
By the evening, the pain syndrome usually subsides, and in the morning it resumes with the same intensity. Also, in some patients there is a relationship between food intake and increased pain.
In addition to pain, the disease manifests itself through bloating, periodic rumbling, as well as changes in the consistency and frequency of stool (diarrhea gives way to constipation and vice versa).
The manifestation of these symptoms does not depend on the food a person eats.
In the chronic form of intestinal dyskinesia, all symptoms intensify, so many people suffering from this disease stop visiting public places and minimize contact with the outside world. In particularly severe cases, the disease may be complicated by certain psychological problems:
- Depression;
- Increased anxiety;
- Hot temper;
- Decreased self-esteem;
It is noteworthy that with intestinal dyskinesia, some patients also experience pain in the back, joints, heart and some other parts of the body, but upon examination doctors are unable to detect any abnormalities in them.
allowed foods for dyskinesia
Nutrition for intestinal dyskinesia
People suffering from intestinal dyskinesia are advised to take boiled and steamed food. To stimulate intestinal motility, it is necessary to consume vegetables and fruits in moderate quantities, which enhance the evacuation function of the intestines, but do not cause irritation of the mucous membrane and fermentation of food.
The diet for hypomotor dyskinesia of the colon consists mainly of foods rich in fiber (cabbage, lettuce, tomatoes, carrots, pumpkin, beets, zucchini, and so on).
Only those foods that contain essential oils (garlic, mushrooms, onions, turnips, radishes, etc.) are excluded from the daily diet. Regular bread should be abandoned in favor of wholemeal wheat or rye bread (it is recommended to eat bread with bran).
The main emphasis is on various porridges cooked in water (buckwheat, oatmeal, pearl barley, wheat).
For hot dishes, it is best to eat soups (broth can be made from vegetables, as well as lean fish and meat). In general, with intestinal dyskinesia, you should give preference to baked and boiled vegetables.
It is allowed to eat steamed omelettes and soft-boiled eggs if the protein is well tolerated by the body (no more than two pieces per week). Up to four times a week you can eat small quantities of boiled or baked fish and meat (if you have a double boiler, you can cook meat and fish in it).
It is best to drink freshly squeezed vegetable and fruit juices. You are allowed to eat dried fruits (prunes, dates, dried apricots, figs), bananas and apples. These products contain sugar and organic acids that stimulate intestinal motility, but you should not abuse them either. It is best to follow a simple rule - eat little, but often.
It is strongly recommended to regularly consume lactic acid products (fresh natural kefir, acidophilus, yogurt). You can prepare your own drinks with bifidobacteria by purchasing the ingredients at the pharmacy.
To avoid problems with regular bowel movements, you should drink a glass of cool water on an empty stomach in the morning immediately after waking up.
You can also take bran to empty the intestines; they can be consumed both in pure form and cooked (pour boiling water).
For six weeks, take the treatment, so you need to take it three times a day, one dessert spoon at a time.
Also, quite often doctors prescribe their patients with hypomotor intestinal dyskinesia to consume animal or vegetable oil (olive, sunflower, butter or corn). As a rule, the daily dose does not exceed one tablespoon once a day.
It is not recommended to consume fatty meats, chocolate, smoked meats, coffee, canned food, tea and spicy foods. Also, if possible, it is necessary to avoid or reduce the consumption of potatoes, pasta, rice and foods that cause increased gas formation (concentrated grape or apple juice, cabbage, spinach, legumes, sorrel, and so on).
Patients with hypermotor intestinal dyskinesia are prescribed a similar diet, from which foods containing toxins are excluded. All food on this diet is prepared using vegetable fats.
As the patient’s condition improves, his daily diet is expanded, first with boiled vegetables and fruits, and then with fresh ones.
It is allowed to take bran in small quantities (with hypermotor dyskinesia, they can provoke flatulence and subsequent abdominal cramps, so not every person can use them).
Features of treatment for children
Particular attention should be paid to the health of children, because the disease can occur even in babies. Dyskinesia in children occurs with the same symptoms as in adults. The little patient just can’t talk about his problems.
The development of the syndrome is determined by a swollen tummy, frequent gas production, and unstable stool. With intestinal dyskinesia, the following are always observed:
- lack of appetite,
- pale skin,
- limited physical activity,
- frequent whims,
- profuse regurgitation.
Over time, muscle dystrophy, weight loss, dysbiosis and anemia appear. Sometimes the disease develops against the background of problems with a decrease in the production of digestive enzymes and the appearance of improper functioning of the bile ducts.
In the early stages of the disease, short-term warming of the tummy with a warm heating pad will be effective. For frequent constipation, the doctor will recommend the necessary medication. In cases of diarrhea, healing decoctions of chamomile and calendula, thick jelly based on milk or cranberries are suitable.
During treatment and remission, the sick child should be limited in physical activity. The baby needs to rest and eat properly.
Principles of diet for intestinal motility disorders
Fruits and vegetables must be sterile.
There are 2 types of intestinal dyskinesia. Treatment of each of them, as well as the diet used, requires taking into account the symptoms of the disease.
Read: Fish cutlets: pollock recipe - a well-deserved place on any table
Hypomotor dyskinesia is a decrease in peristalsis and general intestinal motility. Symptoms of hypomotor dyskinesia: rare stools, constipation, flatulence, pain and heaviness in the abdomen.
The main factor of dyskinesia is excessive sterility of products, especially fruits and vegetables, a minimum amount of fermented milk products, cereals, and wholemeal bread in the diet.
Hypermotor dyskinesia is excessive intestinal motility. The bolus of food passes through the intestines too quickly, the main substances are not absorbed through its walls, rushing to the exit. The main symptoms of hypermotor dyskinesia are attacks of spasmodic pain, frequent bowel movements, and diarrhea.
The main reason for this pathology is incompatibility of products, poisoning by microorganism toxins. Each diet has its own patterns aimed at improving the patient’s condition, however, there are general principles for the formation of a diet and new eating habits. Basic principles of the diet:
- Meals should only be fractional, the total diet should be divided into 5-6 servings, replacing the usual 3-4 meals.
- To prevent overeating, portions should be made small, the average volume of each is 200-250 ml.
- Plant fiber is very important for optimal bowel function. To obtain it, they eat vegetables, fruits, berries, and herbs. These products should be present in every meal; chopped herbs are sprinkled on every dish.
- Refractory animal fats are not included in the diet of a person with dyskinesia. You can include unrefined sunflower oil in its menu (up to 10 ml/day).
- Salted, pickled, smoked, spicy foods and dishes are not included in the diet of a patient suffering from this pathology. The preferred processing method is boiling in water or steaming, baking in the oven.
- Complex carbohydrates and refined foods are excluded from the menu for dyskinesia, and the proportion of simple carbohydrates is reduced to a minimum. These are confectionery products such as cookies, as well as tea and other dishes with added sugar (no more than 30 g in total).
The video will introduce you to the features of the diet for intestinal dyskinesia:
Diagnostic methods
Due to the fact that the symptoms of the disease are not unique, several studies are necessary to clarify the diagnosis. The main diagnostic methods include:
- Complete blood count and general urine test.
- Coprogram - a study is necessary to identify hidden blood, which is a sign of inflammation.
- Sigmoidoscopy is one of the main methods for detecting dyskinesia. If you have this disease, contractions of the intestinal walls will be observed in response to the introduction of a proctoscope.
- Irrigoscopy helps determine the area with hyper- or hypotonicity. In the first case, there will be a spasmodic part of the colon with difficult movement of feces, in the second - an expanded area with reduced tone.
- Colonoscopy allows you to take a biopsy to rule out cancer. In addition, with the hypotonic form of dyskinesia, pale and dry mucous membranes with a complete absence of peristalsis will be observed.
There are also additional studies that help make the diagnosis as accurately as possible. These include:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- scraping for enterobiasis;
- FGDS;
- plain radiography;
- sigmoidoscopy (examines the mucous membrane of the sigmoid and rectum);
- MRI.
Thanks to these studies, the doctor can not only make a correct diagnosis, but also prescribe effective treatment.
Doctor Komarovsky's opinion
Evgeny Komarovsky emphasizes that in his practice he has never encountered such a diagnosis in children from large families. Not because parents do not have time to carefully and in detail examine each of their children, but because in large families children are usually not overfed.
When a child is the only one in the family and is overly loved by everyone in the household, quite often parents make this mistake. They feed the baby not when he is really hungry and asks for food, but when mom and dad decide that the time has come and “it’s time to eat.”
Another extreme is feeding the child a volume of food that he can fit in his stomach, but is in no way able to digest.
Some mothers, but more often grandparents, “sin” by trying to make all the food for their beloved baby as soft, liquid, pureed as possible, feeding only warm and crushed food. Excessive culinary processing of foods, Dr. Komarovsky emphasizes, also often causes the disease.
Oddly enough, babies whose parents are committed to mandatory sterilization of everything the baby handles—pacifiers, bottles, pacifiers, rattles, dishes—are also at risk. Such a pathological, according to Evgeniy Komarovsky, craving for sterility does not lead to good things, since in addition to dyskinesia, it can be an indirect cause of allergic reactions.
Treatment
There is not and cannot be a single approach to the treatment of childhood biliary dyskinesia, says Evgeniy Komarovsky. Everything is strictly individual and largely depends on the reasons that led to the disruption of the outflow of bile. The doctor says that it is not the dyskinesia itself that needs to be treated, but rather the reasons that led to it.
In the treatment of all types of disease, you should adhere to a strict diet; this should be checked with your doctor. As a rule, fatty and fried foods, marinades, canned food, and sweets are completely prohibited
For hypermotor dyskinesia (excessive bile secretion), it is important to eat wheat and buckwheat porridge, greens, vegetables and bread. With this disorder, you should not eat ice cream or drink cold drinks, chicken yolks, as well as foods that contribute to gas formation - beans, peas and cabbage
Medicines require drugs that smooth smooth muscles (“No-spa”), magnesium drugs are useful. In addition, if the child does not have pain, the doctor may recommend taking medicinal mineral water in strictly defined individual dosages.
Among the accompanying procedures, such children will benefit from exercise therapy and electrophoresis with magnesium and novocaine.
Medicines prescribed include B vitamins and choleretic agents (“Cholenzim”, “Magnesia”). Children are given tubages and prescribed mineral waters.
Advice from Dr. Komarovsky
Before starting treatment, make sure that the cause of the disease is established correctly and that the diagnosis itself is not erroneous. Evgeniy Komarovsky considers ultrasound to be the most accurate way to diagnose biliary dyskinesia.
During therapy, you must strictly follow the doctor’s prescriptions and diet. Even after completing the course of treatment, there is no need to enthusiastically rush to stuff your child with everything. Proper balanced nutrition without overeating will help avoid relapses of the disease. These same principles should be considered the best prevention of the disease.
See more details below in the release of Dr. Komarovsky.
medical reviewer, psychosomatics specialist, mother of 4 children
Principles of nutrition for dyskinesia in children
The therapeutic diet for biliary dyskinesia in children involves split meals - 4-5 times a day. It is forbidden to overeat and take long gaps between meals, during which bile stagnates, provoking the proliferation of dangerous microorganisms and the development of the inflammatory process.
Smoked foods, fried foods, animal fats, duck and goose meat, lamb, fast food, processed foods, chips, crackers and other irritating ingredients are completely prohibited. You should not give children with dyskinesia fatty meat broths. It is better to cook soups in second water, in which skinless poultry, rabbit, and veal were boiled.
Every day the child should eat vegetables and fruits, cereals with low-fat milk and water. Children who eat this way for a long time and often eat small portions feel slightly hungry in the evening. It is recommended to quench it with low-calorie kefir. But you shouldn’t have a heavy dinner before bed.
Treatment of dyskinesia
Mode
The reflex effect is of great importance in the development of the disease, therefore, it is necessary to organize a rational daily routine with special care, provide the child with sufficient time to sleep - at least 7 hours, and also limit physical activity. It is necessary to protect the child from physical fatigue and stress.
Dietary recommendations
The principle of fractional meals of 5–6 meals a day is shown (table No. 5 according to M.I. Pevzner). Recommend low-fat poultry, fish, meat, cottage cheese and other dairy products; the protein quota should be 20% higher than it should be. Limit foods containing fats by 10–20% with the exception of products with animal fats. Products at cold temperatures are not recommended for consumption, as this can lead to sphincter spasm.
| JVP form | Recommended | Limited | Excluded |
| Hypokinetic | Products that stimulate the secretion of bile: vegetables, fruits, vegetable oil, eggs. | Foods containing fats are cold and cause sphincter spasms. | Fried, pickled, smoked foods, mushrooms, cocoa, coffee, rich broths, carbonated drinks. |
| Hyperkinetic | Low-fat types, poultry, fish, meat, cottage cheese, etc. Increase the protein quota by 10 - 20% of the required amount. | Products that stimulate bile secretion: fatty poultry, fish, meat, vegetable oil, eggs. |
Basic Pharmaceuticals
For the hypermotor type, neurotropic medications with a sedative effect (valerian, bromine, Persen, Adaptol) are recommended.
Antispasmodic drugs for pain relief are used depending on the age of the patient: Papaverine - from six months, Drotaverine - from 6 years, Mebeverine - from 12 years, Pinaveria bromide - from 18 years. Choleretic drugs (choleretics), which have a cholespasmalytic effect, are prescribed 2 weeks a month for six months: Odeston, Olimetin, Flamin, Hofitol, etc.
For hypomotor dysplasia, neurotropic medications with a stimulating effect are prescribed: aloe extract, ginseng tincture, Pantocrine. Cholekinetics (stimulating bile duct motility) are indicated: magnesium sulfate, Xylitol, Sorbitol, Chofitol, Ursosan, Odeston, Galstena, etc.
Enzymes are prescribed when relative pancreatic insufficiency is detected.
If there is sphincter spasm, choleretic drugs are strictly contraindicated; therapy includes Drotaverine, Papaverine - drugs that reduce the tone of the gallbladder. For sphincter of Oddi dysfunction - Domperidone (gastrointestinal motility stimulant).
Diet for intestinal dyskinesia
Dyskinesia is a disease of the gastrointestinal tract, provoked by a complex of disorders of the motor functions of the colon. With this disease, the patient experiences severe organic disturbances. This is due to the fact that the organs are not able to perform their functions fully.
Statistics show that intestinal dyskinesia affects two thirds of the entire world population. And this, you see, is not little. What are the main measures if signs of such a disease occur? Of course, a proper, balanced and regularly maintained diet.
It is a healthy diet that can establish normal intestinal functioning and restore stool.
What should you not eat if you have dyskinesia?
If you have dyskinesia, it is undesirable to eat quickly. Forget about any fast food, hot dogs, chips, shawarma, salted or fried peanuts, crackers. Such products not only negatively affect the digestive process, but also worsen the general condition of the patient’s body.
Avoid all kinds of sweet, flour, bakery and confectionery products. Ice cream, fresh pastries, muffins, cakes, a variety of creams, pies, cookies and cakes - all this must be completely excluded from your diet.
The patient's health is also extremely negatively affected by animal fats, lard, butter (in large quantities), canned and smoked foods, legumes, onions, radishes, mushrooms, and garlic. Patients suffering from dyskinesia should exclude seasonings and spices, millet cereals and alcohol from the menu.
Sugary carbonated drinks and coffee will also be superfluous.
What can you eat if you have dyskinesia?
Boiled fish Vegetable broths Lean boiled meat
For dyskinesia, it is recommended to eat lean meats and fish. Before direct consumption, experts recommend boiling them. Hot meals can bring tangible benefits to the body.
Broths boiled from “tender” fillet, vegetable and rice soups, low-fat types of dairy and fruit dishes - all this will have a positive effect on the health of a patient suffering from dyskinesia.
It is also advisable to consume fermented milk products, boiled or steamed vegetables, bran, eggs, vegetable oils, and honey. A separate discussion - fruits. The more of them there are, the sooner the patient will “get back on his feet.”
It is recommended to eat fruits and berries in any form and in any quantity. You can wash down your food with sweet, weak tea, juice, milk, rosehip decoction or clean water.
For people who regularly suffer from dyskinesia, the following daily menu is recommended:
- First breakfast. Includes a small portion of vinaigrette dressed with olive oil, as well as cottage cheese and milk.
- Lunch. Consists exclusively of fruit juice. You can bet on orange, lemon, apple, grapefruit or carrot juice.
- Dinner.
Includes vegetable, meat or rice soup, a piece of boiled or baked lean meat, stewed beets and compote or rose hip decoction. - Afternoon snack. Before dinner, drink another glass of fresh, cool juice.
- Dinner. Consists of boiled fish, potatoes or rice, and a glass of sweet tea.
- Before going to bed, it is preferable to drink a glass of kefir or milk.
The weekly menu for dyskinesia includes:
| Day | Menu |
| Monday | breakfast: vegetable salad, any crumbly porridge, kefir or milk |
| lunch: vegetable soup, fruit, glass of sweet tea | |
| dinner: baked fish or boiled meat, boiled potatoes, kefir | |
| Tuesday | breakfast: boiled beets with lemon juice, pudding |
| lunch: rice soup, grated carrots with apples | |
| dinner: buckwheat, chicken fillet, glass of plain water | |
| Wednesday | breakfast: meat or vegetable salad, glass of juice |
| lunch: low-fat borscht, stewed beets, rosehip broth | |
| dinner: steamed egg white omelet, fruit, sweet tea | |
| Thursday | breakfast: dried apricots, apple, kefir |
| lunch: carrot soup, tomato and cucumber salad, compote | |
| dinner: stewed cabbage, baked fish, pancakes with meat | |
| Friday | breakfast: cottage cheese with sour cream, boiled fish, tea |
| lunch: chicken broth, boiled potatoes, squash caviar, water | |
| dinner: fruit salad, prunes or raisins, a glass of fresh juice | |
| Saturday | breakfast: meat in white sauce, buckwheat porridge |
| lunch: light rice soup, fruit or fresh vegetables, juice | |
| dinner: squash caviar, greens, glass of compote | |
| Sunday | breakfast: meat salad, boiled beets, milk |
| lunch: green cabbage soup, fresh cabbage, fruit | |
| dinner: boiled potatoes, whole beef, carrots, tea. |
How to make vegetable broth.
Source: https://okishechnike.com/diskineziya-kishechnika/dieta-pri-diskinezii-kishechnika.html
Diagnostic methods
The vagueness of pain and the commonality of symptoms of dyskinesia with signs of other diseases makes the diagnostic process difficult.
Mandatory diagnostic measures include the following tests and examinations:
- Urine and blood tests to confirm the absence of certain diseases.
- Coprogram - examination of the patient's stool to detect hidden blood and dysbacteriosis.
- Sigmoidoscopy, which allows you to prove the presence of dyskinesia in parts of the large intestine. If this disease is present, then the rectoscope is difficult to insert, and convulsive contractions of the organ membrane are detected.
- Irrigoscopy will help identify a spasmodic area with incomplete bowel emptying - in the hypermotor form of the disease; decreased tone with cavity expansion of the organ - with hypomotor dyskinesia.
- Colonoscopy for hypertensive dyskinesia will identify spasmodic areas of the intestine and healthy-looking mucous membrane. In the hypotonic form, a dull and dry intestinal mucosa with a lack of peristalsis will be detected. Colonoscopy allows a biopsy to be performed to rule out cancer.
Additional diagnostic methods (if equipment is available) are:
- Ultrasound of the peritoneal organs,
- plain radiography,
- EFGDS,
- scraping for enterobiasis,
- sigmoidoscopy,
- MRI.
Only based on the results of the studies, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes the necessary treatment. In order for the treatment to give results and have the necessary effectiveness, it is necessary to follow a diet, carry out complex therapy with the help of medications prescribed by a doctor, and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Symptoms
Symptoms of pathology manifest themselves differently, depending on its form. In total, there are two types of the disease: hypertensive and hypotonic JVP.
Pain in the right hypochondrium is one of the most common symptoms of ADHD.
Hypertensive dyskinesia is accompanied by hypertonicity of the gallbladder and its ducts. Symptoms of this form of pathology appear:
- periodic paroxysmal pain in the right hypochondrium and navel area, which can sometimes radiate to the shoulder or shoulder blade;
- short-term dyspeptic disorders: nausea, bloating, changes in stool;
- attacks of VSD: loss of strength, mood swings, tearfulness, irascibility, cephalgia, tachycardia.
Palpation examination of the gallbladder area reveals its pain, the size of the liver is within normal limits.
In children with the hypotonic form of the disease, hypotonicity and suppression of the contractile function of the affected organ are observed. Symptoms of this type of pathology appear:
- persistent, aching and bursting pain in the area of the right hypochondrium or navel;
- dryness and a feeling of bitterness in the mouth;
- aversion to fatty and “heavy” foods;
- belching;
- nausea;
- vomiting (sometimes);
- bowel disorders - constipation or diarrhea.
A sick child suffers from vegetative syndrome. When palpating the abdomen, enlargement and atony of the diseased organ can be observed.
Another form of the disease is mixed. It is characterized by combinations of manifestations of hypertensive or hypotonic types of dyskinesia.
Intestinal dyskinesia in children: symptoms and treatment, causes of gastrointestinal pathology
Diseases of the digestive system are common in childhood. As a rule, the cause of their appearance is poor nutrition and emotional stress. School-age children may develop intestinal dyskinesia. Often the pathology also affects children. Parents should know the first symptoms of the disease and treatment methods in order to provide the necessary assistance in a timely manner.
Concept and causes of intestinal dyskinesia in children
Dyskinesia is an intestinal pathology in which the tone of the walls of the gastrointestinal tract organs decreases and their motor function is impaired. In this case, the disease affects only the digestive system, without affecting the functioning of other systems of the child’s body.
Most often, the disease appears due to non-compliance with nutritional rules, in particular, when there is a lack of fiber in the diet. In the presence of pathologies of other abdominal organs, the risk of developing dyskinesia increases. Other causes of the disease:
- abuse of fatty, salty, smoked foods and carbonated drinks;
- overeating and long gaps between meals;
- constant emotional stress that negatively affects the nervous system;
- lack of normal sleep;
- gastrointestinal tract infections;
- genetic predisposition;
- gynecological problems;
- dysbacteriosis, a lack of beneficial bacteria leads to decreased peristalsis;
- insufficient amounts of pancreatic and gallbladder enzymes;
- pathological production of hormones;
- diseases of the central nervous system;
- individual intolerance to certain foods;
- long-term use of hormonal and antibacterial drugs;
- poor motor activity of the child;
- insufficient fluid intake.
Types and symptoms of pathology
The appearance of dyskinesia is explained by the influence of various factors:
- primary – affects only the digestive organs;
- secondary – appears in the presence of other pathologies.
Types of secondary dyskinesia:
- medicinal – occurs due to illiterate treatment of dysbacteriosis (diarrhea, constipation);
- allergic – the body reacts to irritants, disrupting intestinal motility;
- other types associated with disorders of the stomach and gallbladder.
Classification according to the nature of the flow:
- Hypermotor (spastic). Characterized by the appearance of diarrhea due to increased tone of the digestive system. Active contraction of the walls leads to diarrhea.
- Hypomotor (atonic). In this case, intestinal tone decreases significantly and peristalsis slows down. This provokes constipation and intestinal obstruction. Abdominal pain appears.
Other symptoms of dyskinesia:
- weight loss;
- pale skin color;
- increased gas formation;
- lack of hemoglobin in the blood;
- decreased or lack of appetite;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- nausea, belching;
- weakness;
- Children under one year of age develop moodiness.
Diagnosis and treatment
Basic diagnostic methods:
- stool analysis for the presence of worms and digestive problems;
- biochemical blood test;
- colonoscopy;
- Ultrasound of internal organs;
- radiography.
Treatment is selected individually, taking into account the type, severity of the pathology and the age of the child. For spastic dyskinesia the following are prescribed:
- antispasmodics - to normalize the movement of feces in the intestines (Drotaverine, No-shpa);
- antiemetics – act on the brain, slowing down the functioning of the vomiting centers (Cerucal);
- enemas – have an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect (Buscopan);
- enveloping agents – Almagel, Maalox.
To treat the atonic form, use:
- laxatives - to liquefy hard stool (Duphalac, Regulax);
- enzymes - to facilitate the process of digesting food (Mezim, Festal);
- preparations to improve the process of mixing food with enzymes - Motilium.
Nutrition for intestinal dyskinesia in a child
It is better to eat smaller meals, 4-5 times a day, excluding overeating. Fatty, smoked, salty and sweet foods, carbonated drinks and other foods that cause bloating and rot in the intestines should be removed from children's diets. It is allowed to eat steamed or boiled food. You need to follow a drinking regime - drink at least 1.5 liters of liquid per day.
Symptoms of intestinal dyskinesia in children, causes of development, treatment methods
Intestinal diseases are quite common in children. Young children are especially susceptible to this pathology. At the same time, intestinal dyskinesia occupies a special place among the complex of intestinal disorders.
Gastroenterologists use this term to designate disorders caused by impaired motility of the intestinal tract and weakness of its tone.
In young children, in most cases, dyskinesia of the large intestine is diagnosed, although the duodenum and other parts of the digestive tract may be affected by pathological effects. Both adults and children suffer from intestinal dysfunction
Reasons for development
All pathologies of the digestive system in childhood develop mainly due to poor nutrition. Insufficient fiber content in food negatively affects intestinal motility.
But there are a number of factors that can trigger the pathological process:
- intestinal infections,
- chronic diseases of the abdominal organs,
- hormonal disorders,
- diabetes.
Another cause of dyskinesia in children, which doctors do not exclude, is nervous disorders. It is very important to recognize the disease in time and prevent it from becoming chronic.
Symptoms and manifestations
Often in children, dyskinesia is asymptomatic against the background of a normally functioning intestine. The absence or dullness of symptoms may lead to an incorrect diagnosis. Therefore, it is worth knowing about the peculiarities of the course of this pathology in children.
Intestinal dyskinesia in a child is divided into two types:
- Atonic – when intestinal motility is reduced, as evidenced by constant constipation.
- The spastic form, on the contrary, is characterized by a tendency to diarrhea, the presence of undigested food residues in the stool, and abdominal pain.
- weakness and lethargy,
- lack of appetite,
- refusal to play, decreased activity,
- pale skin,
- low-grade fever (up to 37.5), but sometimes it rises to higher numbers.
The following symptoms signal an intestinal disorder in a baby:
Lack of appetite may indicate bowel dysfunction
Increasingly, pediatricians are having to diagnose disorders associated with enzymatic dysfunction in young children. This is explained by two factors:
- dysfunction of the biliary tract,
- chronic pancreatitis in a latent form.
For high-quality food processing, a sufficient amount of bile is required. If it is not enough, mucus inclusions will be present in the stool.
Intestinal dyskinesia is especially pronounced in infants. Small children experience bloating and intense gas formation. During this period, the baby becomes restless, writhes his legs, is capricious, sleeps poorly and refuses to eat.
Diagnosis of intestinal problems
All diagnostic measures for intestinal dyskinesia in children are aimed at excluding other pathologies.
A step-by-step examination is carried out, including the following diagnostic methods:
- endoscopic examination of the intestine,
- coprogram - a laboratory analysis of stool that allows you to assess how the stomach and other digestive organs function,
- checking stool for occult blood,
- if necessary, the patient is referred for irrigoscopy - one of the types of x-ray examination of the large intestine using a contrast agent,
- in rare cases, a biopsy is performed to exclude oncological pathology.
Endoscopic examination of the intestine is a necessary measure in making an accurate diagnosis
The entire range of measures when diagnosing intestinal disorders in newborns and children of the first year of life comes down to identifying dysbiosis and disturbances in the production of enzymes.
What is therapy?
If symptoms characteristic of this pathology indicate dyskinesia in an infant , then the doctor begins treatment by eliminating the main causes.
First of all, the balance of food enzymes is corrected. For this purpose, the child is prescribed special medications that can compensate for enzyme deficiency.
Drug treatment is aimed at relieving pain and other symptoms that negatively affect the general condition of the child.
When treating older children, the therapeutic complex is based on creating an adequate nutritional regimen for a particular child.
In this case, a dietary diet implies adherence to a strict meal schedule. Often the treatment complex is supplemented by physiotherapeutic procedures and therapeutic exercises.
When developing a treatment program, doctors attach great importance to organizing the child’s active leisure time and sleep patterns.
Nutrition for intestinal dysfunction
The basis of therapy for any intestinal problems in children is a balanced diet. It is useless to try to treat dyskinesia with medications alone, because without following a special nutrition program it is impossible to achieve a positive result. When forming a diet for a sick child, factors such as the quality of food and cooking methods must be taken into account.
It is important to follow the following recommendations:
Priority is given to products that contain live lactobacilli: sour cream, low-fat cottage cheese, kefir.
Eating small portions to your child will help the food be better absorbed in the intestines and prevent overeating.
In addition to drug treatment for intestinal problems, you need to focus on proper nutrition
Drug treatment
After the diagnosis, the doctor decides to prescribe drug therapy. Usually, children with dyskinesia are given enzymatic agents, vitamins, sedatives and choleretic drugs.
If a child complains that his stomach hurts a lot , parents can give him some of the antispasmodics (No-shpa, Papaverine) in a dosage appropriate for his age.
It is not recommended to give other medications to children on their own.
Gymnastics
A special set of exercises helps improve intestinal motility of a sick child. For atonic type dyskinesia, therapeutic exercises are aimed at strengthening the abdominal muscles.
The complex includes walking and breathing warm-up - the emphasis is on mastering diaphragmatic breathing techniques.
Imitation of cycling and exercises to change body position help well with intestinal atony.
In spastic forms of the disease, the emphasis of the therapeutic gymnastics complex is on relieving spasms. Therefore, all exercises are performed at a slow pace with limited range of motion. A specialist from the exercise therapy department should draw up a training program and select exercises that are appropriate for the age of the sick child.
Traditional methods of treatment
Medicinal herbs are widely used to treat dyskinesia in children. The natural medicine is completely harmless to the child’s body and quickly normalizes intestinal activity. From herbs you can prepare decoctions, infusions, and medicinal teas.
The list of useful herbs includes:
- chamomile,
- senna,
- mint leaves,
- oak bark,
- valerian root,
- buckthorn bark and other natural ingredients.
Any traditional recipe must be agreed with your doctor.
The specialist will advise which composition is most suitable for the sick child.
It is worth remembering that different ingredients are used for spastic and atonic forms. The dosage and regimen for taking medicinal formulations should also be determined by a medical professional.
But if the main symptom of dyskinesia suddenly manifests itself at home - spastic colic, parents can do the following:
Chamomile, familiar to everyone, can relieve a child of intestinal problems.
The main thing is to know how to prepare the decoction
Conclusion
It is easier to prevent any intestinal problems than to treat them. Therefore, competent prevention plays a key role in this matter.
It is recommended that the child create favorable conditions at home for rest and activities; he must carefully monitor his diet, avoid “dry snacks” and exclude harmful additives from the diet. You need to be especially careful when choosing a menu for kids.
If the slightest intestinal disorder occurs, parents should immediately contact a medical facility.
Loading…
Source: https://MedBoli.ru/gemorroj/drugie-zabolevaniya/simptomy-diskinezii-kishechnika-u-detej-prichiny-razvitiya-metody-lecheniya
Diet
Dietary nutrition for dyskinesia has a beneficial effect and helps restore health. Diet is the basis of treatment! If you follow all the necessary principles of a healthy and rational diet, the symptoms of dyskinesia will pass and the disease will recede.
All dishes must be well boiled or steamed. The products are not chopped the day before cooking, but cooked whole, cutting before serving.
It is worth excluding foods that cause fermentation in the intestines. To improve gastrointestinal motility, the diet should include fruits and vegetables without prior heat treatment: white cabbage, pears, apples, apricots.
Table: nutrition rules depending on the type of problem
| Hypomotor form | Hypermotor form |
The menu should contain foods rich in fiber:
| The diet should not contain baked goods or starch-containing products. |
| The diet should include lean meats and fish. The presence of soups, cereals without oil, and black bread is required. | You should completely avoid “harmful foods”: smoked meats, spicy, fatty, fried, salty foods. You should not drink black tea and coffee. |
| Freshly squeezed juices from fruits, berries and vegetables are recommended. | The best nutritional choice would be a slag-free diet based on vegetable oils. High fiber foods should be excluded from the diet. Vegetables and fruits will have to be boiled or steamed. |
| Apples and bananas are necessary due to their high content of organic acids, which stimulate intestinal functions. | It is required to limit the menu, reducing the consumption of potatoes, legumes and mushrooms to a minimum. |
| It is beneficial to eat fermented milk products. | |
| You will have to give up the use of herbs and spices, like sweets and chocolate. | |
| To improve bowel movements, nutritionists recommend eating unheated foods. For breakfast, you can eat wheat bran, poured with boiling water and left for 15 minutes. Their use will help restore bowel movements. | |
| Drinking should not be limited to one and a half liters per day. It is recommended to drink mineral and pure water without gas, rosehip decoction, green tea, compotes and non-acidic juices, preferably without sugar. In accordance with the patient’s condition, the doctor prescribes water with high (Essentuki, Batalinskaya, Borjomi, Nabenglavi, Kvasova Polyana) or low (Smirnovskaya, Darida, Slavyanovskaya, Slavyanochka, Naroch, Jermuk) mineralization. |
About the disease
Gastric dyskinesia is a disease that leads to functional disorders of its motility, often accompanied by a pronounced pain syndrome and a complex of dyspeptic disorders against the background of the complete absence of any organic changes.
Depending on the type of gastric motility disorder, dyskinesia occurs:
- hypertensive (characterized by increased contractile activity);
- hypotonic (accompanied by decreased motor function);
- atonic.
According to another classification, which considers the pathology from the point of view of the predominant clinical symptoms, gastric dyskinesia is usually classified as one of three types:
- painful;
- dyspeptic;
- mixed
Depending on the etiology of origin, gastric dyskinesia is divided into:
- exogenous, caused by the influence of external factors;
- endogenous, developing as a result of diseases of other internal organs and systems.
Intestinal dyskinesia
Intestinal dyskinesia or “irritable bowel syndrome” is a disease in which the motor function of the intestines (mainly the colon) is impaired.
It can occur as an independent disease, or it can be a consequence of other disorders (for example, peptic ulcer, cholelithiasis, cholecystitis and others)
It is important to know that with intestinal dyskinesia, the functions of other organs of the gastrointestinal tract (digestion, stomach, etc.) are also impaired. Therefore, it is necessary to immediately establish the cause of the disorder and begin treatment.
Causes of intestinal dyskinesia
Intestinal dyskinesia can be primary (an independent disease) and secondary (that is, as a symptom of other diseases).
Diseases of the secondary form of intestinal dyskinesia include:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (peptic ulcer, chronic gastritis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, liver disease);
- diseases of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus, diseases associated with dysfunction of the pituitary gland - pituitary disorders, myxedema, hyperparathyroidism, obesity);
- gynecological diseases (diseases that cause impaired motility of the large intestine).
The cause of secondary intestinal dyskinesia can also be the abuse of certain medications (anaesthetics, antibiotics, psychotropic drugs, diuretics and others).
Primary intestinal dyskinesia occurs due to stress, disruption of the usual diet, or frequent consumption of food that contains little dietary fiber.
Symptoms of intestinal dyskinesia
Symptoms of intestinal dyskinesia are very diverse. The most common include:
1. Pain in the abdomen
Mainly around the navel and lower abdomen. Moreover, a distinctive feature of such manifestations with intestinal dyskinesia is the absence of pain at night.
2. Flatulence
The disease is often accompanied by severe rumbling and pain in the abdomen (worsens in the evenings or before defecation)
3. Nausea, heaviness in the abdomen, belching (symptoms of ulcerative dyskinesia)
4. Abnormal stool
Mainly constipation. Sometimes short-term diarrhea may occur.
5. Neurotic disorders (increased anxiety, nervousness or, conversely, depression), deterioration in mood and performance
It is extremely difficult to identify intestinal dyskinesia in a patient, so the diagnosis is often made by excluding other diseases.
Please note that if you ignore these symptoms and do not start treatment on time, your condition will worsen. This can lead to various types of inflammation.
Treatment of intestinal dyskinesia
Intestinal dyskinesia can be cured if you follow proper nutrition and lead a healthy lifestyle: you need to protect yourself from stress, normalize your food intake, play sports and maintain a healthy state of the body.
In our sanatorium you can cure your disease and start a healthy life. We help patients cope with both primary and secondary intestinal dyskinesia and fully restore their health.
Our nutritionist will develop a special diet for you that will restore normal functioning of the digestive tract. And a delicious menu will help you fall in love with “proper cuisine.” Special natural herbal biological preparations will help eliminate disturbances in the functioning of the colon.
Please note that treating intestinal dyskinesia with conventional medications can only worsen your condition.
Our wellness programs also include procedures for cleansing the intercellular space of toxins, toxins and microbes, visceral massage (massage of internal organs), physical therapy, herbal medicine, Finnish sauna and much more.
We help our guests fully restore their health, improve their performance, get rid of stress, relax and restore vitality.
After a holiday in our sanatorium, you will get rid of intestinal dyskinesia, the normal functioning of all organs of the body will be restored, and you will improve your appearance.
You will enjoy sound, healthy sleep and excellent performance.
Our goal is your health! Together we will cope with intestinal diseases and return you to a healthy life!
Go to the “Detox – Classic” program (7 days)
Intestinal dyskinesia: symptoms and signs of intestinal disorder in children
The term “intestinal dyskinesia” is used by gastroenterologists to define a complex of intestinal disorders, the mechanism of which is caused by weakness of tone and impaired motility of the tract. Deterioration in function can be observed in different parts of the organ, but most often children are diagnosed with dyskinesia of the large intestine.
Why does dyskinesia develop?
Doctors say that the condition of the digestive organ is affected by a diet in which the child consumes little fiber. Also, the primary form of dyskinesia can develop due to intestinal infection.
Secondary colitis develops in response to past and chronic diseases of the peritoneal organs (spleen, liver, pancreas). Hormonal disorders and diabetes mellitus are also among the predisposing factors.
The famous pediatrician Komarovsky calls for looking for the causes of intestinal dyskinesia in disorders of the nervous system. The pediatrician explains the neurogenic factor as the incorrect conduction of nerve impulses, which creates the preconditions for spasm or increased peristalsis. To avoid chronicity of the process, it is important to differentiate dyskinesia from other pathologies, otherwise treatment of the disease will be ineffective.
Clinical picture of dyskinesia in children
Intestinal dyskinesia, regardless of the patient’s age, occurs in two forms:
- hypomotor (atonic) pathology, characterized by constant difficulty in defecation (constipation);
- hypermotor (spastic), caused by accelerated evacuation of gastric contents into the large intestine. A sign of this form of dyskinesia is abdominal pain and diarrhea with unstructured feces.
In recent years, doctors are increasingly diagnosing functional intestinal disorders in children associated with enzymatic deficiency.
Doctors find two explanations for this condition - hidden chronic pancreatitis and stagnation in the biliary system. Bile deficiency impairs the quality of processing fatty foods.
A characteristic symptom of GIB is considered to be fatty stool with mucous inclusions.
Other symptoms signaling intestinal disorders include:
- bad feeling;
- decreased appetite;
- poor physical activity;
- pale skin tissue;
- painful sensations during physical activity.
A secondary inflammatory process that affects the thin or thick part of the tract is manifested by symptoms such as anemia, muscle dystrophy, and sudden weight loss. Stool analysis shows intestinal dysbiosis.
Flatulence, or increased gas production, helps to suspect dyskinesia in a baby. The baby's tummy becomes hard, painful, and a loud rumbling sound is heard from it.
The baby is worried, twitches its legs, and refuses to feed.
Diagnostic measures for dyskinesia
Due to its similarity with other gastrointestinal diseases, intestinal dyskinesia is diagnosed by excluding the suspected pathology. A phased examination of a child includes several activities:
- endoscopy;
- coprogram;
- irrigoscopy;
- biopsy - according to indications;
- stool occult blood test;
- exclusion of pathological neoplasms in the intestine.
Principles of disease therapy in children
Treatment of small children for intestinal dyskinesia is based on the organization of the diet and the correct distribution of hours of activity and rest. Patients are recommended to eat frequently and in small portions. In a diet that accelerates the treatment of dyskinesia, the following should prevail:
- juices;
- dried bread;
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- slimy water porridges;
- products with vegetable fiber;
- fermented milk products, especially with live lactobacilli.
When treating intestinal dyskinesia in a child under one year of age, it is important to adjust the balance of food enzymes. For this purpose, very young children are prescribed special medications to compensate for the lack of enzymes. For preschoolers and adolescents, treatment is supplemented with herbal preparations with tansy, St. John's wort, and bittersweet.
If a child suffers from severe pain, non-drug assistance can be provided by applying heat to the peritoneal area. If the procedure is unsuccessful, the patient can be given No-shpu or Drotaverine, calculating the dosage according to age and weight.
To relax the nervous system, treatment includes antidepressants or antipsychotics. Additionally, with intestinal dyskinesia, children can be prescribed autogenic training, exercise therapy, hypnosis, and acupuncture.
Folk remedies for intestinal dyskinesia
Harmless treatment of spastic and atonic colitis is carried out using folk remedies. Mint leaves, chamomile flowers, and valerian roots contribute to the restoration of normal peristalsis of the tract. The components take 1 tsp. each, pour a glass of boiling water over the phyto mixture and leave covered for 20 minutes. The napar is filtered and given to the child 3 times. 100 ml per day half an hour before meals.
Another remedy is obtained from sage and yarrow herbs, oak bark, St. John's wort flowers, and motherwort raw materials. The amount of each ingredient is 2 tbsp. l. The collection is doused with a glass of boiling water and allowed to brew for a couple of hours. Then the drug is filtered and the child is given 4 rubles. per day, measuring 100 ml of drink each time.
Our specialist comments
- Organize bowel movements in a timely manner if your baby suffers from constipation.
Difficulties with the excretion of feces entail not only dyskinesia - their danger lies in general intoxication of the body, loss of appetite and decreased performance. Improper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract contributes to stagnation and rotting of food masses, which can subsequently cause the child to develop allergies. - If dyskinesia causes a frequent urge to defecate, give your baby a decoction of chamomile and calendula flowers, thick jelly or a hard-boiled egg.
Specific treatment for intestinal disorder will be prescribed by your pediatrician. - To relieve spastic colic, use compresses.
Apply a bandage soaked in vinegar solution to the intestinal area. The ratio of acidic product and water is ½ cup to 3 liters. If you have the opportunity to give your child a pine bath, be sure to take advantage of it. Treat yourself with paraffin applications.
Prevention of intestinal dyskinesia for children is to create a favorable atmosphere in the family, avoid stress, and eat high-quality foods without dyes, preservatives and flavoring additives. If you have constipation, it is important to limit your intake of rice in your diet.
Intestinal dyskinesia in a child
Source: https://LechenieDetok.ru/gastroenterolog/diskineziya-kishechnika-u-detej.html
Prevention of dyskinesia
In order to prevent the development of this disease, you should adhere to the following important recommendations:
- Lead an active lifestyle and be sure to play sports. It could be running, yoga, fitness, cycling or anything else. The main thing is that this sport makes you leave the house and spend time usefully. In addition, such training must be regular, otherwise there will be no expected benefit from it.
- Watch your diet. To do this, you should keep a so-called food diary. You need to write down everything you consume during the day. Thus, these records will help you control your diet and improve it.
It is also recommended to eat properly not only at home, but also when visiting, at work, etc. Let a healthy menu not only be “on holidays or when your stomach hurts,” but become a truly important rule.
- Give up bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol), as they not only have no benefit, but also cause great harm to the body.
- Avoid stress and nervous tension. To do this, you need to be more sociable, have a positive outlook on the world and be able to relax mentally. An interesting hobby, new hobbies and love will help you with this best.
It is also necessary to promptly treat those diseases that can provoke the development of hypomotor dyskinesia.
Site doctor: Anton Palaznikov
Gastroenterologist, therapist
Work experience more than 7 years.
Professional skills: diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and biliary system.
Treatment of dyskinesia
As a rule, ADHD in children can be easily eliminated by correcting the diet and switching to a diet. Teenagers are advised to reconsider their lifestyle, play sports and give up junk food. Medicines are prescribed to reduce pain; antispasmodics cope with this task.
If concomitant diseases are identified, they must be treated. Antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs according to indications, and choleretic drugs for hypotension of the biliary tract are prescribed by a gastroenterologist. In case of hypertensive diarrhea, it is recommended to take sedatives so as not to provoke an exacerbation.
The treatment complex necessarily includes physiotherapeutic procedures:
- medicinal electrophoresis on the area of the right hypochondrium with antispasmodic drugs, magnesium sulfate;
- applications with paraffin;
- treatment with galvanic current;
- endometrium - a method of warming up with high-frequency electric current;
- Diadynamic therapy is a method of impulse therapy;
- inductothermy is a therapeutic effect of an alternating magnetic field.
The course of physiotherapy is complemented by reflexology and massage of the collar area.
Diet
The key to eliminating functional disorders is proper nutrition. It should be based on low-fat foods, plant foods rich in vitamins and minerals. A child with biliary dyskinesia can eat:
- first courses with vegetable broth;
- porridge with low-fat milk;
- mashed potatoes, boiled pasta;
- fresh and baked vegetables and fruits;
- milk and fermented milk products;
- bagels, crackers, buns, dry sponge cake, but without cream;
- fruit jellies, marmalade, marshmallows, chocolate in limited quantities;
- Drinks include compotes, jelly, decoction of chamomile, rosehip, weak tea with honey.
Parents are advised to limit eggs and confectionery in their child’s diet. The absolute ban applies to sweet carbonated water, fast food, chips, crackers, fatty meat, smoked meats, pickles, and canned food.
Folk recipes
Herbal medicine for gallbladder dyskinesia is used only as prescribed by a pediatrician. Natural components used in folk medicine can bring not only benefits, but also harm to the body
Children are more likely to have allergies than adults, so you need to be careful when using herbs.
The simplest folk remedies are rosehip decoction and chamomile tea. For many decades they have provided benefits and assistance in the treatment of the biliary system. To prepare the remedy, just brew rose hips or chamomile flowers with boiling water and leave for a little while.
Medicinal tea for dyskinesia can be prepared with the addition of corn silk. To do this, you will need dry raw materials; you can buy them at the pharmacy. Stigmas are combined with black currant leaves, thyme, and mint. The tea is brewed for 20 minutes, after which the child is given to drink: half a glass in the morning, the other part in the evening. If you simmer corn silk over low heat for an hour, you will get a decoction. They treat the child for 14 days.
Tyubazhi
Blind probing is done for children only as prescribed by a doctor. The gastroenterologist selects a remedy that will be used to cleanse the bile ducts. Preference is given to herbal infusions or mineral water. They provide gentle cleaning without aggressive effects.
Tubage is carried out in a hospital setting or at home. The child drinks the prepared solution on an empty stomach, after which he is placed on his right side, placing a warm heating pad under the right hypochondrium. 2 hours after the warming procedures, active cleansing begins naturally.
Drug therapy
In children, treatment of biliary dyskinesia is exclusively symptomatic:
- antispasmodics to reduce the severity of a painful attack;
- sedatives to reduce reactions to stimuli;
- means for gentle removal of bile;
- probiotics to normalize intestinal function.
Doctors prescribe a complex of multivitamins to improve immunity.
Diet for intestinal dyskinesia menu
Intestinal dyskinesia is a pathology caused by a decrease in intestinal tone and motor function.
The main category of patients is women and children; intestinal dyskinesia is much less common in men. In women, gynecological diseases are added to the provoking factors common to all. Problems of the pelvic organs cause disturbances in the motility of the digestive organs. Children suffer from this disease due to their excitability or hypovitaminosis, which has a detrimental effect on the growing body.
Diet is an important part of treatment
If you have dyskinesia, you should not eat fatty foods.
Most often, this disease is provoked by dietary disorders and bad eating habits.
In children, such habits are formed by parents, so most of the responsibility for the appearance of dyskinesia in a child falls on them.
Excess weight is another cause of intestinal pathology. Following a diet will help restore the optimal weight of a sick person.
In addition to overeating, dyskinesia is caused by dietary disorders - an excess of refined foods and animal fats. To achieve sustainable remission, you will have to stick to the diet for a long time. Basic Rules:
- Do not eat fatty foods;
- Adhere to gentle methods of food processing - stewing, steaming;
- Keep your food intake even - at least 5-6 times a day.
- Avoid overeating, eat small portions.
In case of exacerbation of dyskinesia, adhere to the following nutritional principles for 2 weeks:
- You need to eat pureed food, or twisted through a meat grinder, evenly chopped.
- Fruits are baked in the oven or rubbed through a sieve;
- Fresh fruits should not be consumed during an exacerbation; even bananas are steamed and wiped afterwards;
- Fruit and berry juices are diluted by half or a third with water; vegetable juices are not consumed at all.
Principles of diet for intestinal motility disorders
Fruits and vegetables must be sterile.
There are 2 types of intestinal dyskinesia. Treatment of each of them, as well as the diet used, requires taking into account the symptoms of the disease.
Hypomotor dyskinesia is a decrease in peristalsis and general intestinal motility. Symptoms of hypomotor dyskinesia: rare stools, constipation, flatulence, pain and heaviness in the abdomen.
The main factor of dyskinesia is excessive sterility of products, especially fruits and vegetables, a minimum amount of fermented milk products, cereals, and wholemeal bread in the diet.
Hypermotor dyskinesia is excessive intestinal motility. The bolus of food passes through the intestines too quickly, the main substances are not absorbed through its walls, rushing to the exit. The main symptoms of hypermotor dyskinesia are attacks of spasmodic pain, frequent bowel movements, and diarrhea.
The main reason for this pathology is incompatibility of products, poisoning by microorganism toxins. Each diet has its own patterns aimed at improving the patient’s condition, however, there are general principles for the formation of a diet and new eating habits. Basic principles of the diet:
- Meals should only be fractional, the total diet should be divided into 5-6 servings, replacing the usual 3-4 meals.
- To prevent overeating, portions should be made small, the average volume of each is 200-250 ml.
- Plant fiber is very important for optimal bowel function. To obtain it, they eat vegetables, fruits, berries, and herbs. These products should be present in every meal; chopped herbs are sprinkled on every dish.
- Refractory animal fats are not included in the diet of a person with dyskinesia. You can include unrefined sunflower oil in its menu (up to 10 ml/day).
- Salted, pickled, smoked, spicy foods and dishes are not included in the diet of a patient suffering from this pathology. The preferred processing method is boiling in water or steaming, baking in the oven.
- Complex carbohydrates and refined foods are excluded from the menu for dyskinesia, and the proportion of simple carbohydrates is reduced to a minimum. These are confectionery products such as cookies, as well as tea and other dishes with added sugar (no more than 30 g in total).
The video will introduce you to the features of the diet for intestinal dyskinesia:
Features of nutrition for hypomotor dyskinesia
Dried fruits stimulate intestinal function.
Since the main goal of this type of diet is to stimulate motility and speed up bowel movements, it is important to include certain dishes in the menu.
Despite the restrictions, such a diet must take into account all the needs of the body. Foods and dishes that stimulate bowel function:
- fresh, baked, stewed, steamed
- vegetables, greens;
- fresh fruits, berries, apples are especially useful;
- dried fruits;
- hard-boiled eggs (no more than 2 pieces per day);
- wholemeal bread;
- dairy products;
- first courses, mainly cooked in vegetable broth (borscht, pickles, cereal-based soups);
- well-boiled porridge cooked in water;
- lean varieties of veal, beef, rabbit, chicken,
- turkey, offal, sea and river fish;
- natural butter, vegetable oils;
- sweets in minimal quantities (honey, jelly, jam, ice cream);
It is very useful to add bran from various cereal crops (wheat, buckwheat, rye) to the first and second courses in courses of 6 weeks. They are poured with boiling water in advance or mixed with soups and side dishes. Bran helps to establish regular bowel movements. For the same purposes, it is recommended to eat cold food.
Spices are added to dishes in moderation. Recommended drinks are kvass, weak black and green tea. It is undesirable to consume foods that stimulate fermentation and rotting of food, or foods that remain in the digestive tract for a long time. Prohibited products:
- fatty varieties of meat and fish products, canned food from them;
- rice products, semolina, rolled oatmeal, pasta;
- pastries, white bread, cookies;
- confectionery with chocolate, coffee, cocoa;
- astringent fruits (blueberries, quince);
- cabbage and legumes;
- juices from apples and grapes;
- alcohol of any strength.
Features of nutrition for hypermotor dyskinesia
Kissel slows down the progress of the food bolus.
With increased intestinal motility, the main goal of the diet is to provide the body with mineral salts, vitamins, proteins, fats and carbohydrates that are missing due to too rapid bowel movements and frequent diarrhea.
For these purposes, it is recommended to give up vegetables in the first stages of the diet, since a large amount of fiber stimulates motor skills and causes painful spasms.
They begin to be introduced into the diet after a persistent improvement in health, preferably in boiled form, as well as in the form of juices (from a quarter to half a glass 2-3 times a day). Foods and dishes to slow down intestinal motility:
- Mucous soups, pureed porridges, jelly are the best astringents for slowing down the movement of the food bolus without irritating the intestinal mucosa.
- Compotes and baked desserts from pears, bird cherry, quince, blueberry, dogwood. The tannins contained in these berries and fruits bind and firm the stool. In their raw form, these products have the opposite effect, stimulating peristalsis.
- Strong green tea.
- Side dishes and dishes made from rice and semolina.
To slow down peristalsis, it is advisable to eat food warm. A slag-free diet with minimal fiber content and a high concentration of vegetable fats will help treat hypermotor dyskinesia. Prohibited foods for increased peristalsis:
- Fatty meats (pork, lamb, beef, goose, duck);
- Fatty fish (mackerel, salmon, sturgeon);
- Baking, white bread;
- Foods high in starch;
- Products that cause gas formation and irritate the mucous membrane (white cabbage, radish, peas, radishes, onions, garlic);
- Carbonated drinks, alcohol in any form;
- Fried, smoked, canned, pickled foods.
- Hot seasonings, spices (mustard, horseradish, pepper, adjika).
Sample menu
The morning should start with cottage cheese.
Taking into account the above recommendations, it is not difficult to create a menu for intestinal dyskinesia.
- Morning - porridge with water, salad of boiled vegetables or cottage cheese with sour cream, or buckwheat porridge with dried fruits. Drinks – tea with dried bread, fermented baked milk.
- Second breakfast - fresh fruit or compote, jelly.
- Lunch - vegetable soup with cereals or vegetarian noodle soup, for the second - vinaigrette with vegetable oil or stewed fish with vegetables, for the third - dried fruit compote, jelly.
- Afternoon snack – fresh fruit, compote with dry cookies, biscuits, crackers.
- Dinner – buckwheat or millet porridge, steamed omelette, tea with bread.
- Snack before bed - kefir with soaked dried apricots or prunes.
Source: https://shokomania.ru/dieta-pri-diskinezii-kishechnika-menju/
Classification
There are several types of dyskinesia based on intestinal motor function:
- the spastic (hypermotor, or hypertensive) type is characterized by intestinal tone above normal and its constant contractions, which is accompanied by diarrhea, as well as unpleasant colic in the abdomen;
- the atonic (hypomotor, or hypotonic) appearance is caused by sluggish peristalsis and a sharp weakness of tone, manifested by constipation, bloating, and, in extreme cases, symptoms of acute intestinal obstruction;
- mixed form, which combines symptoms of both types.
There is another classification of dyskinesias according to the time of occurrence, where they distinguish:
- primary type - dyskinesia appeared independently and was not caused by background concomitant pathologies;
- secondary type, when dyskinesia is a symptom of gastrointestinal disease.