Parents of a newborn often worry whether the baby’s fontanelles are normal, whether they are too small or large. But before answering this question, we must understand the essence of the phenomenon itself. What are fontanelles? On the child’s skull there are six voids between the cranial bones, which are covered with a fairly dense membrane of connective tissue - these are fontanelles.
Four small “windows”, in the absence of any developmental pathologies, close within a few days after birth, the fifth - in the second month, and the largest is completely overgrown within 3 months to 1 year.
Accepted standards
In a newborn baby, the normal size of the fontanel is approximately 3 cm in diameter.
Gradually it becomes overgrown, generally accepted indicators: The norms are not exact, a deviation up or down of 3-4 mm is acceptable. If the size of the baby's fontanel is small, taking into account the error, you should not make hasty conclusions, but you need to find out the reasons. The overgrowth is checked by a pediatrician during a regular examination; you should consult with him. You can't rely on the advice of your friends. If in doubt, it is better to visit two specialists and additionally consult a neurologist.
Dr. Komarovsky notes that overgrowth of the fontanel occurs individually, varies from 3 months to 2 years. Additional information in the video. In most children, closure occurs after 8 months. Overgrowth occurs at 5 months and is the norm with good general indicators of development and growth of the infant. A 3-month-old child with an overgrown fontanel is considered rare. Complete closure at 2 months should be a concern if it is accompanied by a painful condition of the baby, external defects in the structure of the skull, or impaired psychomotor reactions. Children with such signs often suffer from serious developmental problems.
A baby may be born with a small fontanel, but in some it is of normal size, but it closes up too quickly. Main reasons:
Many women after childbirth face the problem of excess weight. For some, it appears during pregnancy, for others, after childbirth.
- And now you can no longer afford to wear open swimsuits and short shorts...
- You begin to forget those moments when men complimented your flawless figure.
- Every time you approach the mirror, it seems to you that the old days will never return.
Many women after childbirth face the problem of excess weight. For some, it appears during pregnancy, for others, after childbirth.
- And now you can no longer afford to wear open swimsuits and short shorts...
- You begin to forget those moments when men complimented your flawless figure.
- Every time you approach the mirror, it seems to you that the old days will never return.
- Individual characteristics of the development of the baby’s skull. If it does not interfere with brain growth, it does not pose a health hazard;
- Craniosynostosis is a bone disease in a child that causes early fusion of the skull bones. The pathology is accompanied by high blood pressure, hearing loss, strabismus, and disturbances in the development of the skeletal system. Sometimes the disease develops during intrauterine development, the baby may be born with a small fontanel, or during growth due to endocrine disorders, blood diseases;
- Brain development disorder;
- Diseases of the nervous system;
- Improper absorption of calcium in the body, impaired metabolism.
Only a doctor can identify the pathology. Severe illnesses are rare, and additional studies are needed to confirm the diagnosis. If there are any doubts, that is, there is no point in visiting a routine ultrasound of the head, which is performed on babies at 1 month in order to exclude various pathologies.
The child’s fontanel may be small, but the sutures of the skull grow together normally (the process is completed by the age of 20). If the degree of ossification is high, the doctor will additionally prescribe a urine test for calcium content. He can refer you to an endocrinologist or neurologist to identify hormonal disorders and abnormalities in the development of the central nervous system.
Recommendations
If the baby was born with a small fontanel, it is necessary to carefully monitor his condition and describe the behavior in detail to the pediatrician. If he often cries in his sleep or wakes up with a loud cry, he may have headaches due to increased intracranial pressure. The condition of the fontanel in a calm child should be checked. Protruding skin, strong pulsation, tension are signs of a possible increase in pressure.
If a disease is detected, you must strictly adhere to the doctor’s prescription. In many cases, parents' fears are not confirmed. It is necessary to follow general recommendations, regularly visit a pediatrician and specialists for examination, according to the schedule.
The baby's fontanelle acts as a shock absorber in case of falls or head impacts. This allows the baby to avoid a concussion. With a small fontanel, the function is reduced; it is necessary to monitor the child especially carefully and avoid head injury.
In the first months, fontanel promotes thermoregulation of the brain, helping to avoid overheating and seizures. There is no need to put a hat on your baby in a room with a comfortable temperature.
Your pediatrician may recommend limiting preventive calcium and vitamin D intake to slow down the closure of the fontanel. Its cause is not an excess of substances in the body, but their improper absorption. Dangerous rare diseases that require treatment can cause disturbances in calcium metabolism. A lack of calcium and vitamin D when their intake is reduced can lead to rickets and endocrine disorders.
There is advice to reduce the amount of formula or breast milk, replacing them with water. Malnutrition is dangerous for a child, especially in the first months, when rapid growth, formation and development of the skeletal and nervous system occurs. The baby needs nutrients; from breast milk he additionally receives vitamins that strengthen the immune system.
You cannot make assumptions and try to change your baby’s diet on your own, prescribe vitamins or specifically refuse them. Due to ignorance of medicine, the decision made may turn out to be erroneous and have a negative impact on the baby’s condition. If you have any concerns or suspicions, you should seek clarification from your pediatrician.
A small fontanel in a newborn: consequences of early closure of the crown
» Baby's health
Small fontanel in a newborn: what is the reason?
Small fontanel in a newborn: what is the reason?
At birth, every baby has a fontanelle on the head, which is an area that pulsates and is not covered by the cranial bones. But it is temporarily pulled in by the membrane. No matter how adults and others fear it, this membrane is quite durable and strong. Time passes, and the membrane is overgrown with bones, the fontanel is tightened.
But while this is happening, parents are asking questions about the size of the fontanel. Should a newborn have a small fontanel and what are the norms? After all, it happens that this area of the baby’s head is very small and does not correspond to the norms. But first you need to figure out whether there really are differences from medical standards.
Standard norms
If parents have not noticed that the baby has a fairly small fontanel, this can lead to serious trouble. This concerns problems with the health and life of the child. But mostly the parents are quite young and have no experience, so they immediately begin to panic. To avoid such misunderstandings, you should have knowledge about the norms for the size of a cat’s fontanel.
These indicators can be compared with the size of your baby’s fontanel:
- Up to 30 days – 30mm;
- Up to 60 days – 24mm;
- Up to 4 months – 20mm;
- Up to six months – 16mm;
- 9 months – 14mm;
- 11 months – 8mm.
These dimensions may vary slightly, this is not a mandatory standard. When there are deviations of up to 4mm, there is no need to worry.
But if a child, even with such errors, has a very small area of the head, then attention needs to be paid. Parents should take such things seriously and take action
The main thing is not to wait for consequences. Then it is necessary to find out the reasons for such indicators.
Causes of a small fontanel in infants
Only a qualified specialist determines why the baby’s fontanel is small. Thus, there is no need to run around to grandmothers and neighbors to find out these reasons.
When the doctor has examined the child’s fontanel, he is able to determine the cause of this phenomenon.
- Individual feature in the structure of the baby's head. Here, parents do not have to worry or worry, because there is no danger to the child’s health.
- Craniosynostosis is a very rare disease of the skeletal and skeletal system of a child, where very early closure of the sutures of the skull is performed. Increased blood pressure, strabismus, impaired hearing, and impaired skeletal growth are observed. This disease can be congenital or acquired after suffering from rickets or if there are disturbances in the functioning of the thyroid gland.
- Various pathologies in the brain.
These diseases are very rarely observed, but if the fontanel is small, it is still worth consulting a doctor. He will explain the reasons for this phenomenon and give practical advice. This helps with the unpleasant consequences.
Consequences
Craniosynostosis is considered very dangerous. This requires surgery. The sooner this happens, the faster the baby will recover. If the size of the fontanel corresponds to the norms, then it is still necessary to check its size.
There are certain recommendations for parents to equalize the size of the fontanel. This applies to parents who feel that their baby has a very small fontanel. In addition, pediatricians should also give such advice.
- If the size of the fontanelle differs from the norm, then care should be taken to ensure that the child does not hit his head or fall.
- If the baby is fed artificially, then it is necessary to give him less milk, and the formulas did not contain much vitamin D.
- If the baby is breastfed, then it is also necessary to give less milk. But breastfeeding is not canceled.
Thus, if a baby has a small fontanel, then there is no reason to be scared. First you need to find out whether deviations exist and identify their causes. In addition, provide the baby with decent care and concern.
What is it and why is it called that
A fontanel is a small area on the head of a newborn baby, which is located at the junction of the skull bones. It is soft to the touch, which is explained by its origin. The fontanel is a remnant of the formation that covers the fetal brain during its intrauterine development.
Where to look for a fontanel? Most mothers who have been in postpartum wards more than once answer with confidence that it is on the back of the head and on the top of the head. Meanwhile, in reality there are much more soft areas on the newborn’s head. At the same time, they represent both wide spaces - the fontanelles themselves, and narrow ones - the sutures between the bones of the skull.
What are the non-ossified areas made of?
Unlike the skull of an adult, the skull of a newborn baby consists of many flat bones. A seam is formed in the areas where two bones meet, but where three flat bones connect at once, a void appears, resembling a polygon. Such spaces are covered with fairly dense connective tissue, which is called the fontanel. Over time, this tissue begins to slowly harden, causing the voids to shrink in size and eventually close completely.
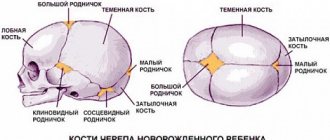
At the same time, a baby at birth can have 6 such gaps:
- a pair of mastoid;
- a pair of wedge-shaped ones;
- back and front.
The first four close almost immediately, but the small fontanel in a newborn baby closes gradually, which may cause some concerns among parents about the dynamics of the gap’s reduction.
Small fontanel in a newborn: recommendations from experts
If parents notice this deviation in their newborn, then it is worth consulting with a specialist on what to do in such cases. If the reduced size of the soft crown is not associated with any pathologies, then the doctor’s recommendations may be as follows:
- It is worth constantly protecting the child’s head from overheating, cooling, drafts and injuries, wearing a cap or cap even at home.
- Optimize your baby's feeding by contacting a lactation consultant.
- Take vitamin D only in the dosage recommended by your doctor.
In the case of diseases, the symptom of which is a small fontanelle, the doctor chooses the treatment, taking into account the severity of their development. Most often, surgery is required in such cases.
Parents should be attentive to their newborn child. If you are vigilant and notice deviations in the baby’s development in time, you can prevent serious consequences in the future. Children who were diagnosed with craniosynostosis at the very beginning of development, after treatment, lead a normal life without consequences or developmental deviations
This is why it is so important to attend monthly check-ups with your local pediatrician.
Fontana of a newborn baby
- The newborn's fontanel greatly facilitates the birth process, both for the baby and for the mother. While passing through the birth canal, the bones of the skull are compressed, and therefore the newborn’s head looks elongated for the first time after birth. Then the shape of the head is restored;
- The presence of a fontanel provides optimal spatial conditions for normal brain growth at the pace established by nature;
- The fontanel is involved in the processes of regulating heat exchange between the baby and the environment. If the child’s body temperature exceeds 38 degrees, then brain tissue is naturally cooled through the fontanel;
- Due to its ability to compress, the fontanel can act as a shock absorber if a child accidentally falls.
Large and small fontanelles
Where is
Determining where the fontanelle is located in a newborn baby is quite simple.
A large diamond-shaped fontanel measuring 2 by 2 centimeters is located right in the middle of the crown, or, as they usually say, on the top of the head.
A small fontanel is located on the back of the head. Its size is approximately half a centimeter.
When it overgrows
The large fontanel is overgrown by about the age of one year, sometimes there are slight deviations from this parameter until about one and a half years. But if the child meets age standards in other respects, then there is no reason to worry.
The small fontanel in children born at term is already closed. However, it happens that it was discovered after childbirth. Then its closure should be expected in two to three months.
The speed and time of closure of the fontanelles mainly depends on how much calcium the baby’s body is provided with. If there were no deviations in the mother’s diet and the optimal regimen for taking multivitamins was followed, then the overgrowth of the fontanelles usually occurs normally.
Developmental disorders
Knowing the timing when the fontanelle closes up, as well as its size, you can see any deviations, avoid and prevent the development of many dangerous diseases in newborns. Among them are several:
- Rickets. This disease is almost the most common cause of late closure of the fontanel. As a rule, this occurs in premature babies who are rarely exposed to the sun and have a lack of calcium and vitamin D. Read the article about rickets >>>;
- Hypothyroidism. A decrease in the amount of thyroid hormones may also cause a slowdown in the process of overgrowth of the fontanel;
- Down syndrome. Too large a fontanelle indicates the presence of this disease along with other characteristic signs;
- Overgrowth of the fontanel ahead of schedule may indicate excess calcium. and also indicate diseases such as craniostenosis, microcephaly;
- A depressed fontanelle is also a serious symptom. This phenomenon indicates acute dehydration of the body.
What does a too large fontanel or a slow (late closure) fontanel mean?
A careful examination of the child by specialists, a detailed description by the parents of the baby’s condition will be the key to early detection of abnormalities and will contribute to the correct prescription of preventive treatment.
The fontanel is too small or the fontanel closes too quickly
Protruding fontanel?
Most often, a protruding fontanel is observed against the background of diseases that are accompanied by increased intracranial pressure: meningitis, encephalitis, tumors, intracranial bleeding, increased intracranial pressure for another reason.
If a bulging fontanelle is combined with one or more of the following symptoms, you should call a doctor as soon as possible:
- High fever;
- The bulging fontanel occurred after a head injury or a fall of the child;
- Vomit;
- Drowsiness or excessive irritability of the child;
- Strabismus;
- Convulsions or epileptic seizures;
- Loss of consciousness;
- Protrusion of the fontanel for a long time without other symptoms.
Sunken fontanelle?
Most often, retraction of the fontanel is observed due to dehydration of the child against the background of fever, diarrhea, and repeated vomiting. If you notice a sunken fontanel, make sure your child drinks plenty of fluids and contact a doctor to treat the illness that is causing the dehydration.
Many people are very afraid of somehow damaging the fontanel. Remember! - this is practically impossible. Despite the apparent softness of the fontanel, it is very durable, and it cannot be damaged by ordinary manipulations (washing, bathing, combing, etc.).
The purpose of the fontanel: what does it mean
After birth, a small soft area on the baby’s head is clearly visible - this is the fontanel, which is hidden under the membrane. As the baby grows, it will stiffen and close.
The small fontanelle, also known as the crown, provides elasticity to the newborn’s skull during delivery and allows the baby to safely pass through the birth canal. Because of this elasticity, after childbirth the baby’s head has an elongated and flattened shape, which can initially frighten the mother in labor.
This is a temporary phenomenon, and within a year the head will return to its normal shape.
The fontanel is designed to regulate heat exchange in the brain, soften head impacts, and avoid seizures. When the baby's body temperature rises, thanks to the crown, the necessary cooling of the brain and its membranes occurs.
Fast overgrowing
The fontanel can last for up to 6 months in the baby. With normal growth and development, this is not a deviation. Ossification of the soft tissue of the fontanelle is considered too early at the age of three months. Occurs as a result of pathologies:
- Craniosynostosis is a deviation in the formation of bone tissue, in which the fontanelle quickly tightens and the cranial sutures completely fuse, preventing normal brain development. May be congenital or acquired, in most cases observed in combination with other developmental disorders;
- Microcephaly - expressed in a decrease in the size of the head, refers to severe deviations in the development of the central nervous system. The main symptom is a reduced head circumference, a violation of proportions relative to other parts of the body;
- Anomalies in the development of the brain - disturbances in its structure, reduction in size and weight.
Such deviations are rare and are not limited to manifestation in the form of a quickly overgrown fontanel.
A little anatomy: where is the fontanel located?
As you know, the skull consists of many bones connected to each other by sutures (they are not straight, but jagged, zigzag lines). In the prenatal period, the bones of the skeleton are laid down as plates of dense membranous tissue, which are later replaced by cartilage tissue, and then by bone. Ossification of the flat bones of the roof (upper and lateral parts) of the skull, in contrast to the long tubular bones of the limbs, bypasses the cartilage stage, i.e. ossification points appear in the center of the membranous plates. Subsequently, the ossification process spreads laterally, covering an increasingly larger area of each bone until it reaches its edges. This process almost entirely occurs during the period of intrauterine development, so most of the roof of the skull by the time the baby is born is already represented by bone tissue, although the latter is significantly different from the bone tissue of adults: it is much thinner, more elastic, and rich in blood vessels
However, even before the start of extrauterine existence, the baby faces an important and difficult test - the birth process. And nature, of course, prepared the small organism for it in the best possible way.
The fact is that some marginal areas of the bones do not ossify at the time of birth and are still represented by plates of connective, or membranous, tissue. These are areas at the junction of several bones, and they are called fontanelles.
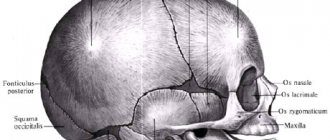
By the time of birth, the baby, as a rule, has six fontanelles - two unpaired and two paired. The most “famous” is the large, frontal, or anterior, fontanelle, located on the top of the head, at the junction of the two frontal and two parietal bones. It is diamond-shaped and measures about 3 cm (2.2 to 3.5 cm) at birth.
Another unpaired fontanel, called the small, posterior, or occipital, is located on the back of the head, at the convergence of the two parietal and occipital bones. It has a triangular shape and small dimensions - about 5 mm. In half of the cases it may already be closed by bone tissue by the time of birth, in the rest it closes during the first month of the baby’s life.
Paired fontanelles are located on the sides of the head. The sphenoid fontanel is known, located in the temporal region, at the convergence of the frontal, parietal, sphenoid and temporal bones of each side. Behind the ear, at the junction of the occipital, temporal and parietal bones, is the mastoid fontanel.
Enlargement of the fontanelles at birth may be a consequence of prematurity or a violation of the intrauterine ossification process, as well as a symptom of congenital hydrocephalus (expansion of the fluid spaces of the brain). Complete closure of the lateral and occipital fontanels at birth in combination with the small size of the anterior one may be a sign of congenital microcephaly (pathological reduction in the size of the head and, as a rule, the brain).
The occipital and lateral fontanelles, unlike the anterior one, normally close soon after the baby is born, therefore, when they say “fontanelle” in the singular, they mean the anterior, or large, fontanel.
So, the integument of the brain in the area of the fontanelles is represented by the meninges (pia mater, arachnoid and dura mater), membranous connective tissue, a thin layer of adipose tissue and skin.
What is a fontanel
When should a child’s fontanel close: normal and pathological? A fontanel is a non-overgrown area between the bones of the skull that can be felt on a child’s head. There are six fontanelles in total, but most of them close in the mother’s womb. A baby is usually born with only one anterior fontanelle. The distance between the moving bones of the skull has adipose tissue and skin, which is quite elastic. In fact, the fontanel can be called a wide suture between the bones of the skull. Over time, this seam “loses weight” and decreases in size. This occurs due to the gradual ossification of tissues, the formation of the skull.
READ ALSO: “What to do if your child has a fever during teething”
Features of fontanelle care
During the entire time the fontanel is closing, some parents are afraid to touch it, not to mention caring for this fragile area of the baby's head. In fact, connective tissue is strong enough to withstand touch and hygiene. The fontanelle can be washed and wetted. You just need to dry it carefully. Lightly press the towel, not rubbing movements. You can also comb your child’s hair in this place. So caring for the fontanel does not require any special knowledge or skills.
Each baby has individual developmental features that are unique to him. Some people have a larger fontanel, others a little less. For some it closes earlier, while for others it closes a little later. For example, it was noticed that in girls the process of fusion is more intense than in boys. This is normal unless minor deviations from the norm are accompanied by signs of any diseases.
Possible risks of untimely overgrowing
If a pediatrician diagnoses a closure that does not correspond to the timing, this may indicate the following pathologies:
- Rickets is one of the most common causes of late closure of the fontanel. This disease usually affects children born prematurely. If a lack of sun, calcium and vitamin D is added to this, the risk of rickets increases.
- Down syndrome. The disease is diagnosed by the increased size of the formation on the child’s head in combination with other signs.
- Hypothyroidism is a deviation from the norm in the production of thyroid hormones. If the indicators do not reach the lower limit of the norm, this may affect the time of overgrowing. In a child suffering from hypothyroidism, the fontanel disappears later.
- Excessive calcium levels in the child’s body or microcephaly may indicate early closure of the fontanel.
- Craniosynostosis is a rare anomaly in the development of a newborn, which is characterized by numerous disturbances in the development of the child. The disease can be either congenital or acquired due to rickets or malfunction of the thyroid gland.
- Abnormal brain development is not a common cause of early healing of an empty formation on a child’s skull.
What determines the closure?
The rate of overgrowth is determined by phosphorus-calcium metabolism; it largely depends on the woman’s nutrition during pregnancy. With a sufficient amount of the microelement in her diet, the fontanelle closes within normal limits in the unborn baby. With an excess intake of vitamins and foods rich in calcium, a newborn develops a small fontanel with a dense membrane, and the closure time is significantly reduced.
The hereditary factor influences: if one of the parents had a small fontanel, which did not negatively affect its development, there is a high probability that the child born will have a similar feature.
The baby’s nutrition matters – when breastfeeding, the likelihood of untimely closure of the fontanelle increases. The effect is not an excess of calcium and vitamin D, but a deficiency, leading to late overgrowth and diseases. Therefore, a nursing mother, if there are prerequisites for late closure, should take vitamin complexes.
Rules of care
The large fontanel in newborns does not require special care
However, some nuances will allow parents to avoid making annoying mistakes and harming the baby in such an important matter as the healing of a pulsating spot on their baby’s head
You can't put pressure on him
If there are any doubts about its softness, hollowness, or pliability, you can only stroke it lightly, but even then very carefully. Frequent combing until the fontanel is overgrown is useless, since you can inadvertently touch it with the sharp teeth of the comb and injure it. Therefore, children’s hair should be combed only when necessary and with extreme care—without touching the problem area with the comb teeth. Monitor the integrity of the skin of this part of the head during swaddling, bathing, and playing.
Preventing injuries and wounds on the head is a guarantee of quick and trouble-free healing of the fontanel. To prevent it from compacting and to prevent the bones of the skull from becoming deformed, moving only in one direction, it is recommended to turn the sleeping baby from one side to the other more often. Very often, dark yellow or brownish crusts form on the large fontanel in newborns. They just need to be lubricated with any baby oil half an hour before the bath. After bathing, they will thoroughly soften and can be removed by carefully combing them with a fine comb. Parents should try to constantly reduce any pressure on this area of the baby's head. Therefore, you need to take him in your arms or in a kangaroo pouch more often.
If the pediatrician, after an examination, has diagnosed that the newborn’s fontanel is too large, you need to pay close attention to the child, closely monitor him, do not let him cry for a long time and forcefully, supplement the nursing mother’s menu with foods high in calcium and vitamin D
Possible consequences
What can threaten a small fontanel at birth? It is not necessary that it will close quickly if this is an individual characteristic of the child. In the first 5 months, it may increase due to rapid growth and enlargement of the brain. If a baby's fontanelle has already hardened at three months, this is not necessarily the cause of the disease.
It is important to consider the circumference and proportionality of the head
A too small disproportionate size may indicate disturbances in the formation of the skeletal system or slow brain growth. Anomalies that cause rapid overgrowth of the fontanel in a baby can lead to:
- Deformations of the skull bones;
- Loss of vision;
- Strabismus;
- Retarded mental and physical development;
- Hearing impairment;
- Mental disorders.
The changes are caused by abnormal growth of the brain and depend on which part develops with greater disturbances. Timely diagnosis and surgery will help to avoid serious consequences. More positive results are observed if it is given to a child under 6 months.
Why are fontanelles needed?
At birth, a child overcomes a powerful obstacle, and due to the fact that the bones of the skull are mobile and the shape of the head can change, the baby comes into the world through the birth canal without danger to the health of the body. The body’s ability to adapt due to temporary deformations of the skull is one of the functions of the fontanelles. When a baby is born, his head is slightly deformed; some babies even look like aliens because of their ovoid head. However, this is temporary. After a few days, the bones fall into place, the skull takes on its normal shape.
In addition to this function of mobility, the fontanel has other important features. For example, fontanelles prevent overheating of the baby’s body due to the thermoregulation created. Another function is that movable bones make it possible to form the size of the brain. Finally, fontanelles are created by nature to protect the baby’s brain from possible shocks due to their unique shock-absorbing ability.
By the fontanels, their shape and size, you can determine the general condition of the child, his normal or delayed development. You can also do an ultrasound examination of the baby's brain through the fontanel. Such manipulations are necessary to identify early pathologies. Thus, it can be argued that the fontanelle has the function of an indicator of the baby’s condition. By the way, pediatricians usually check the child’s condition using the fontanel during the baby’s rest period. The baby should be calm, nothing should irritate him. The best time is when the baby is sleeping.
Deviations
In its normal state, the fontanelle surface is relatively flat. The alarm should be sounded if the crown of the head is sunken or, on the contrary, raised by a tubercle.
In the first case, the changes indicate a lack of fluid in the baby’s body. This can happen during acute respiratory infections or acute respiratory viral infections at elevated temperatures. Rotovirus infections, accompanied by vomiting and diarrhea, loose stools during teething - all this can cause tissue dehydration. Drinking enough fluids and taking Regidron will help normalize the water-salt balance. As soon as the cells are filled with life-giving moisture, the fontanel will return to its normal appearance.
If the crown suddenly becomes convex and strongly pulsating, then you should immediately contact a specialist. This may indicate serious illness or injury, such as meningitis, intracranial bleeding, or the presence of a tumor.
If the baby hits his head and after that, in addition to the raised fontanel, deviations in behavior appear: he becomes more capricious or, on the contrary, sleeps all the time, convulsions or vomiting appear - this is a reason to see a doctor.
The skin membrane covering the fontanelle pulsates, and this is normal. It’s bad if there is no pulsation, this may mean that the baby has problems with intracranial pressure. The pulsation of the crown area repeats the beats of a child’s heart, indicating each flow of blood to the brain.
Over the generations, the fontanel has become overgrown with various myths, which for the most part are completely unjustified. Mother Nature specifically left boneless “windows” on the baby’s head. Thanks to them, a baby taking his first steps often falls and does not suffer concussions. To finally reassure yourself about a child’s fontanel that does not heal for a long time, you can listen to Dr. Komarovsky, the authority of many mothers. As always, he will dispel all my mother’s fears with humor, clearly and convincingly
All children are born with a fontanelle - a small area on the head in which there is no bone tissue. Thin skin covers the area, which a little later the skull bones will cover with a dense barrier. It happens that the size of the fontanel does not correspond to the norm - it is too large or small. We will talk about why a child may have a small fontanel, the possible consequences of this phenomenon, and also give recommendations to those parents who find themselves in a similar situation.
The fontanel in a newborn requires close attention from both parents and the doctor
Let's sum it up
Fontanas are anatomical formations of membranous tissue located on the baby’s head. Thanks to the presence of fontanelles, the head can easily pass through the birth canal, changing its shape (configuration).
The size and timing of overgrowth of fontanelles help pediatricians suspect changes in the baby’s health status. But even an experienced specialist cannot make a diagnosis based only on the size of the fontanelle, because each disease has a number of other important symptoms.
Many questions and worries arise among young parents around fontanelles. Most often, myths about the fontanelle have no basis and are quickly debunked by a pediatrician. For the harmonious development of the baby, regular walks and rational feeding, love and care from mothers and fathers are important.
Convex fontanel in a newborn
It is necessary to show the child to the doctor if the fontanelle protrudes strongly, rises above the surface of the head and seems swollen for a long period of time. You should immediately call a doctor at home when the bulging was preceded by a head injury, and also when the child simultaneously exhibits at least one of the following symptoms:
- very high temperature;
- vomit;
- loss of consciousness;
- strabismus;
- convulsions;
- epileptic seizures;
- excessive moodiness, irritability, excitability or, conversely, drowsiness and lethargy.
Typically, a bulging fontanel in a child is a consequence of increased intracranial pressure, which can increase for a number of reasons. Diagnostics will help determine what kind of disorder is occurring and how it should be treated. Intracranial pressure may increase after prolonged tearful crying - then the fontanel temporarily bulges, swells, or actively pulsates (calm the child down and give him something to drink).
Changes in the fontanel
In some serious diseases, the state of the fontanelle changes. A bulging or, conversely, sunken fontanel becomes an “indicator” of pathology and indicates the severity of the disease. Thus, assessing the condition of the fontanel is an important diagnostic sign.
Protruding fontanelle in a newborn
Most often, a bulging fontanel accompanies meningitis, encephalitis, and intracranial hemorrhage. All these diseases are characterized by high intracranial pressure, which is why the fontanel bulges.
You should not make hasty conclusions and panic ahead of time. Brain diseases cannot be characterized only by bulging fontanel. But if there are accompanying threatening symptoms, you should urgently consult a specialist.
Alarming symptoms that, in combination with a bulging fontanel, threaten the child’s life:
- high temperature, which is difficult to break down and soon rises again;
- nausea and vomiting in a child;
- loud cry, irritability or, conversely, lethargy, drowsiness of the baby;
- convulsions, loss of consciousness;
- if the fontanel began to bulge after the baby fell or was injured;
- the appearance of strabismus, eye symptoms.
Sunken fontanel
If the soft crown has become sunken, this is a symptom of dehydration of the baby. The fontanelle changes, drops below the bones of the skull and indicates an acute lack of fluid for the baby. With repeated vomiting, diarrhea, and high fever, significant fluid loss occurs. Dehydration affects the entire body. The skin becomes dry, cracks may form on the lips, and the child’s well-being may be impaired.
It is necessary to give the child something to drink and arrange for the baby to be fed, if possible. And immediately consult a doctor for proper treatment and replenishment of lost fluid.
What can a large fontanelle talk about?
In rare cases, a large fontanel size can still signal serious problems:
| № | Causes of a large fontanel | Description |
| 1 | Rickets | This is a disease characterized by the fact that the child does not receive enough calcium, which causes bone formation to be impaired. It often happens in those babies who do not receive enough vitamin D and rarely get exposure to the sun, sometimes this is the result of prematurity. In addition to a persistent fontanel, one of the symptoms is thickening of the bones on the sides of the sternum. In this case, you need to show the child to the doctor; most likely, he will be prescribed vitamin D |
| 2 | Down syndrome | It is clear that this syndrome is diagnosed immediately after the baby is born by its characteristic appearance and a single transverse fold on the palm; an additional study of the number of chromosomes is prescribed. This disease causes deviations in physical development, as well as mental development. This child will need medical care throughout his life. |
| 3 | Hypothyroidism | With this disease, a person’s basic functions of the thyroid gland are reduced. Additional symptoms: lethargy, apathy, drowsiness, frequent constipation, refusal to eat. Since the thyroid gland influences the formation of the skeleton, it also indirectly affects the tightening of the fontanel. To accurately determine the diagnosis, you need to donate blood to determine the concentration of hormones. If the disease is confirmed, the doctor prescribes hormone replacement therapy |
| 4 | Chondrodysplasia | The disease is extremely rare; its other name is dwarfism. Babies with this disease have slightly shorter arms and legs than other children, a broad head, and a significantly protruding forehead. In modern medicine the disease is considered incurable |
| 5 | Hydrocephalus | With this disease, excess cerebrospinal fluid accumulates in the brain. The disease has several stages, depending on the complexity, doctors make predictions. Today there is an operation that can help a child, and if the disease is detected immediately after birth and the operation was performed on time, then the consequences for the child will be minimal |
| 6 | Apert syndrome | This is a pathology of cranial development, the most striking symptom: abnormalities of the hands, for example, fusion of the fingers. This is a rare disease that occurs in one in 180,000 babies. Treated by surgery |
| 7 | Cleidocranial dysplasia | Passed on by inheritance. With this syndrome, there are disturbances in the development of the cranial bones, the collarbones are either underdeveloped or completely absent. Occurs in 1 case per million children born. Does not affect the child’s mental development in any way |
| 8 | Glass/crystal man syndrome | With this pathology, human bones lack collagen, they become too fragile and break from minor impacts. There are 4 types of the disease, differing in severity of manifestations |
As you may have noticed, most of these diseases are rare, or even exotic. The most common cause of a large fontanel is prematurity of the baby.
Premature birth
A baby born at less than 37 weeks is considered premature. In Russia, babies starting at 22 weeks are currently considered viable. However, cases of 20-week-old babies being saved have been recorded.
There are many factors that influence the timing of a child's birth. There are reasons that a mother cannot influence:
- the mother has previously undergone surgery on the uterus or abdominal organs;
- multiple pregnancy;
- placenta previa;
- the gender of the baby is male (boys are more often born prematurely);
- serious illnesses.
However, some risk factors are the mother's responsibility:
| № | Factors | Description |
| 1 | Stress | Frequent stress and high fatigue at work, especially in the later stages, lead to early delivery. This also includes riding public transport during rush hour for a significant period of time and refusing to part with heels |
| 2 | Nutrition | Irregular eating and skipping meals can affect the health of the mother. Some pregnant women believe that they have gained a lot of weight and sharply limit their diet in pursuit of beauty. This negatively affects the condition of both mother and child! |
| 3 | Mother's age | Prematurity is experienced by minors and women of elegant age (closer to 40 years), especially if this is their first pregnancy |
| 4 | Bad habits | If during pregnancy the mother smokes, drinks or uses drugs, then this is a direct path to premature birth. |
Sizes of fontanelles in a newborn and older child
The posterior fontanelle in a newborn is on average 0.6 mm. By about 8 weeks of age, it completely closes in a child.
Typically, the anterior fontanel has the shape of a diamond, the dimensions of which vary from 5 mm to 30 mm.
In order to calculate the size of a given area, it is necessary to measure the distance between the most distant points and divide the resulting number by 2. The longitudinal (along the main axis of the skull) and transverse (across the longitudinal axis of the skull) dimensions are usually determined. The dimensions are recorded in the form of two numbers: 1.1x0.5 cm. Dimensions of a large fontanel by month
| Age, months | Size, mm |
| 0-1 | 26-28 |
| 1-2 | 22-25 |
| 2-3 | 23-24 |
| 3-4 | 20-21 |
| 4-5 | 16-18 |
| 5-6 | 16-18 |
| 6-7 | 16-18 |
| 7-8 | 14-16 |
| 8-9 | 14-15 |
| 9-10 | 12-14 |
| 10-11 | 9-12 |
| 11-12 | 5-8 |
The anterior fontanelle closes at about 24 months. I noticed that this process goes a little faster in boys than in girls. If a baby is born with the anterior fontanelle larger than usual, this does not mean that it will take longer to close. Despite the fact that the table shows average values, this does not mean that with a slight deviation from the norm, something goes wrong with the child. Do not worry ahead of time and about the age when this unossified area of the skull will completely heal. Just recently we opened a Q&A service on our website, and guess what one of the first questions was asked by our reader. Of course, regarding the tightening of the fontanel (https://pregnant-club.ru/question/normy-po-srokam-zakrytiyu-rodnichka). If you still have questions about why the fontanel does not heal, then welcome to our Questions and Answers section.
Please note that neither a decrease in closure periods nor an increase in them are pathological. The process of tightening the fontanelle occurs individually for each child and depends on the following factors:
- The baby is premature. Typically, premature babies are slightly behind their peers in physical development, this is manifested in the later healing of the unossified area on the baby’s head. But by the age of 3 everything evens out and children begin to develop equally.
- Growth rate. With adequate nutrition and good weight gain, the fontanel usually closes earlier. Conversely, if the baby’s diet is overloaded with proteins or carbohydrates, the fontanel may grow together a little later.
- Method of feeding. In a breastfed baby, this area closes earlier than in a formula-fed baby. This is due to the fact that breast milk contains nutrition that is more balanced and suitable for the baby’s gastrointestinal tract.
- Deficiency of vitamin D3 in the body.
- Hereditary diseases. It has been established that Down syndrome, congenital hypothyroidism or achondrodysplasia (a genetically determined disorder of bone formation), hydrocephalus can slow down the fusion of the fontanel. Microcephaly (small head) or craniosynostosis, on the contrary, lead to very early closure.
When should a large fontanelle close: Dr. Komarovsky
When should a large fontanel close? The large anterior fontanel usually closes before the child is one year old. However, Dr. Komarovsky, explaining to mothers the functions of the fontanel, says that there is no clear framework for when exactly the fontanel should overgrow. For some children, stiffness occurs for about four months, while for others, the area on the top of the head is still mobile at one year. According to pediatricians, 40 percent of children at the age of one already have a closed fontanel. In one percent of children, the fontanel becomes overgrown in the first months of life. In more than fifty percent of children, the fontanelle closes before two years of age.
Sizes of the fontanelle in centimeters by month: table
| Age | Fontana size, width | Fontana size, length |
| 1 month | 2,6 | 2,8 |
| 2 months | 2,2 | 2,5 |
| 3 months | 2 | 2,1 |
| 4 months | 1,6 | 1,8 |
| 5 months | 1,6 | 1,8 |
| 6 months | 1,6 | 1,8 |
| 7 months | 1,4 | 1,6 |
| 8 months | 1,4 | 1,5 |
| 9 months | 1,2 | 1,4 |
| 10 months | 0,9 | 1,2 |
| 11 months | 0,9 | 1,2 |
| 12 months | 0,5 | 0,8 |
These standards are statistically average. The child develops individually, so there may be minor deviations. In addition, you need to take into account that the size of the fontanelle can be affected by various factors:
- child development in the womb;
- genetic predisposition;
- external factors.
An experienced doctor will not assess the child’s condition based only on the data from the average statistical table.
How to correctly measure a baby's fontanelle
To measure the fontanel you will need a tailor's meter. The fontanelle looks like a kind of rhombus. Therefore, you need to know the dimensions of length - from the top point to the bottom, width - the distance between the side points.
The measurement formula is as follows: measure the length of the fontanel, measure the width and fold; then divide the resulting amount by 2.
The second measurement option is to find out the distance between opposite sides of the “diamond”, measuring from the middle of each side.
How to determine the closure of the fontanel
Complete closure of the fontanelle can be accurately determined by a specialist, but parents can do this too. If monthly calculations are made using the length and width of the fontanel “diamond,” then parents can use the calculations to understand how the fontanel is overgrowing. If each time the size decreases by millimeters, then it is clear that the process of overgrowing the fontanel is gradually progressing. Based on the average table of fontanel sizes by month, you can create a similar table of measurements based on your own child’s data.
- Development of children under one year old by month
- Physical development of young children
- Caring for a newborn baby