Why should blood clot?
This is an extremely important point.
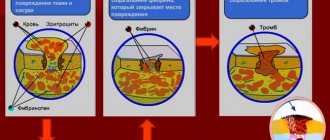
The process of blood clotting promotes wound healing and prevents significant blood loss. The formation of blood clots occurs under the influence of a protein, which combines platelets into clots, changing the consistency from liquid to more viscous, thick and curdled, which perfectly closes the resulting wound. This metamorphosis has its own name - homostasis. The duration of bleeding is already built into each organism. The norm may change slightly during life or even go beyond the limits, that is, turn into pathology. This process is regulated by the endocrine system. Accordingly, if there is a malfunction of the internal secretion organs, then we can expect problems in all functions and systems.
So, in its normal state, blood is a fluid substance. Its task is to deliver oxygen and nutrients to all tissues. Thrombosis in this case is a process harmful to the body. If the vessel is damaged, the situation changes. In this case, the clot prevents losses and reduces recovery time.
That is, when a vessel is damaged, the biochemistry of the blood changes somewhat. Substances that contribute to the formation of a blood clot are formed. In other words, platelets break down and thrombin and thromboplastin are formed in parallel. In this chain, fibrinogen is converted into fibrin, which is very similar to a mesh of threads. Blood cells enter them and fill the cells. And the duration of bleeding depends on how well the body works. The norm allows doctors to predict the course of an operation or other intervention. Now let's move directly to the issue of diagnosis.
Activated partial thromboplastin time
A study of this indicator can be prescribed to the patient along with the tests described above. The reasons for this are usually the following:
- bleeding;
- heart attack;
- intestinal necrosis;
- control of therapy in the presence of DIC syndrome;
- infertility, miscarriages, abortions;
- examination before surgery;
- diagnosis of hemophilia;
- thromboembolism;
- deep vein thrombosis;
- damage to great vessels.
Normal APTT values:
| Age | Average norms |
| for adults | 24–40 seconds |
| for newborns | 25–43 seconds |
| for premature babies | 3–5 seconds above normal |
An increase in APTT value warns of the risk of bleeding due to:
- hemophilia;
- insufficient amount of vitamin K;
- presence of lupus anticoagulant in the blood;
- genetic abnormalities;
- acute leukemia;
- DIC syndrome;
- postpartum hemorrhage.
An APVT in the coagulogram below normal indicates a predisposition to hemophilia, bleeding and thromboembolism as a result of a deficiency of antihemophilic globulin, thromboembolism, and the initial stage of DIC in a child.
When assessing the APVT indicator in combination with PTT, the decoding of the blood coagulogram can be as follows:
- a normal APVT with an increased PTT means the likelihood of liver pathologies, vitamin K deficiency and weak function of blood coagulation factor VII;
- the APVT norm + the PTT norm in the presence of a lupus anticoagulant in the sample is evidence of von Willebrand disease;
- APVT and PTT are increased, which means we can talk about serious problems with the liver, fibrinogen and prothrombin deficiency;
- a normal PTT + a slight decrease in aPTT indicates normal blood coagulation or a slight deficiency of coagulation factor.
D-dimer test These coagulogram indicators are valuable due to their high negative predictive value. The accuracy in this case is up to 98%.
How to evaluate the interpretation of the coagulogram in this case? If the D-dimer coagulation parameters are normal, then thrombosis is practically excluded with the indicated probability.
Elevated values will indicate that blood clotting is more active and the risk of thrombosis is high.
A negative result of this test is extremely rare, only in 2% of cases. First of all, when such a result is obtained, possible errors are eliminated even at the stage of collecting material, and a repeat analysis is performed. And even then, the obtained value below the normative threshold may indicate a small thrombus size, a decrease in FAP (plasma fibrinolytic activity or the ability to spontaneously dissolve blood clots) or a high level of the plasmogen inhibitor activator PAI-I. However, this is where the complex topic of genetics begins and to understand it, you will need a separate article.
About vitamin K and its role in the body
The very name of the vitamin, designated by the letter K, comes from the phrase “coagulation factor,” which directly indicates its most important function. It has been proven that blood clotting requires at least 10 active proteins, 5 of which are synthesized with the participation of vitamin K. The liver needs it to produce prothrombin, a substance that allows blood to thicken. Vitamin K is necessary not only for the circulatory system, it also helps retain calcium in bone tissue.
In adults, a deficiency of this vitamin is rare, since it is produced in sufficient quantities by intestinal bacteria, and it is also present in many vegetables without breaking down after heat treatment. But in babies, deficiency is possible for a number of reasons, then hemorrhagic syndrome develops in newborns.
How many days does a coagulogram take?
The state clinic provides the opportunity to take a test with a minimum set of indicators, as a rule, this is a coagulogram of PTI and INR. The execution time does not exceed 1 day, not counting the day of collection of the biomaterial.
Private clinics offer both a limited version of the analysis (price starts from 200 rubles) and an extended full version (from 1,500 rubles). The duration is similar to state laboratories.
Thus, to summarize, it must be emphasized that:
timely detection of hemostasis disorders can significantly reduce the risk of possible bleeding or excessive coagulation that threatens the formation of a blood clot; before submitting the biomaterial, it is important to prepare properly; These laboratory indicators are not enough to make a final diagnosis, because deviations from the norm can be caused by a number of pathological conditions. Determining the final diagnosis involves the use of additional laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods.
Treatment
In mild situations, treatment begins with the administration of Vikasol 1% (vitamin K, obtained synthetically). Unlike its natural representative, which has a fat-soluble form, Vikasol is water-soluble. Recommended routes of administration: intravenously or intramuscularly at a dose of 0.1 ml/kg per day. The course of treatment is 3 days.
If hemorrhagic effusions become life-threatening, it is suggested to administer fresh frozen plasma.
In rare cases, the use of vitamin K in oral form is prescribed, but there are currently insufficient studies to prove the effectiveness of such therapy.
Blood clotting mechanisms
Violation of the integrity of tissues and blood vessels activates the launch of a sequence of biochemical reactions of protein factors that ensure coagulation during bleeding. The final result is the formation of a blood clot from fibrin strands. There are 2 main pathways leading to blood clotting:
- internal - for its implementation, direct contact of blood cells and the subendothelial membrane of blood vessels is required;
- external - activated by the protein antithrombin III, secreted by damaged tissues and blood vessels.
Each of the mechanisms individually is ineffective, however, forming a close relationship, they ultimately help stop bleeding. Violation of the compensatory mechanisms of the hemostatic system is one of the reasons for the development of thrombosis or bleeding, which poses a threat to human life and health. This is what emphasizes the importance of timely diagnosis of the state of the hemostatic system.
Details about blood coagulogram parameters
Causes of low fibrinogen:
- donation, taking steroids, etc.
- chronically low levels of fibrinogen, impaired synthesis from birth;
- liver diseases;
- unbalanced diet.
Reduced protein concentrations characterize the inability to fully coagulate blood and a tendency to spontaneous bleeding.
Increased fibrinogen level:
- inflammatory processes, alas, the most varied - acute pharyngitis, rheumatoid arthritis, infectious mononucleosis, pyelonephritis, etc.;
- massive tissue destruction (sepsis, lung abscesses, gangrene, ulcers, etc.);
- tumor formation;
- heart attack, stroke, cerebrovascular accident;
- peripheral vascular diseases (atherosclerosis of the arteries, vascular damage in diabetes mellitus, thrombophlebitis, chronic venous insufficiency);
An increased or decreased fibrinogen level does not always indicate health problems.
A minor effect on the indicator in an adult can also be exerted by:
- smoking;
- taking hormonal-based contraceptives, estrogens;
- loads;
- stress;
- diabetes;
- cholesterol;
- obesity.
In adults, the norm ranges from 2-4 g/l, in pregnant women up to 6 g/l, in children the fibrinogen content in the blood is 1.25–3 g/l.
The aPTT concentration can also be affected by high levels of lipids in the blood and the presence of heparin impurities in the blood sample.
The norm for women is 24-35 seconds, the norm for men is 14-20 seconds.
Lupus anticoagulant:
Adhesion is the adhesion of platelets to a damaged surface. A decrease indicates kidney disease, leukemia; increased – atherosclerosis, thrombosis, heart attack, diabetes mellitus. The norm for women carrying a child is usually higher (see table below).
Prothrombin and antithrombin:
Proteins involved in the formation and resorption of blood clots. Prothrombin is formed in the liver.
Thrombin time is a special laboratory generally accepted indicator that characterizes the external pathway of hemostasis activation.
Prothrombin index (PTI) - the indicator is measured as a percentage and characterizes the time of the 2nd stage of coagulation - the formation of proteins. PTI norm is 72-123%.
A PTI blood test can indicate diseases of the abdominal organs (liver and gastrointestinal tract). Increased prothrombin indicates:
- thromboembolism;
- pre-infarction state;
- polycythemia;
- malignant formation.
INR blood test allows you to systematize blood coagulogram data. The ratio (INR) was developed by the International Committee on Thrombosis and Hemostasis and the International Committee for Standardization in Hematology for ease of drug prescribing.
Using the INR indicator, doctors assess the effect of prescribed medications.
After the destruction of the blood clot (during the breakdown of fibrin), a protein fragment - D-dimer - is observed in the blood. After restoration of the affected part of the body, the protein plasmin is formed, which destroys and destroys blood clots.
The norms for indicators in adults and children are presented in the table below. Deciphering the blood coagulogram will reveal the discrepancy in each indicator: what it is and how much it should be.
Soluble fibrin-monomer complexes (SFMC):
Few people have heard of the RFMK blood test. The RFMC blood test is an additional indicator; it is included in the coagulogram and is considered an important laboratory test that characterizes the hemostatic system. Many experts consider the RFMC blood test to be an indicator of thrombinemia (the formation of small blood clots) and the onset of DIC.
Symptoms
In the early form, hemorrhages often begin in the prenatal period. The child is born with intracranial, pulmonary and skin hemorrhages. Internal bleeding into the liver, spleen, adrenal glands, as well as into the abdominal organs, and vomiting with blood are typical.
The classic reaction is characterized by the presence of blood in the stool and vomit around the 7th day of life. Poor coagulation is visible in the bleeding of the navel, in the long-term non-healing in case of circumcision of the foreskin in boys, in nosebleeds, cephalohematoma on the head and bruises on the skin. The wounds do not heal for a long time after injections. In severe cases, anemia and hemorrhagic damage to internal organs are detected.
The late form develops as a result of liver diseases and dysfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract along with breastfeeding. Leading symptoms:
- hematemesis (bloody vomiting);
- in half of the cases there are intracranial hemorrhages and cephalohematomas;
- extensive bruising on the skin and mucous membranes;
- hematuria (blood in the urine);
- melena - a disease accompanied by black stools and indicating gastrointestinal bleeding; the development of melena is possible with gastroesophageal reflux;
- the umbilical wound is bleeding.
Melena is often accompanied by hyperbilirubinemia, since red blood cells in large quantities disintegrate and die in the intestines. Ulcers appear on the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum. This condition is explained by the stress of birth, during which glucocorticoids are released in large quantities.
In severe cases of the disease, hypovolemic shock is possible - a condition characterized by a rapid decrease in circulating blood volume due to fluid loss due to persistent vomiting and diarrhea. The child's blood pressure and temperature drop, he is weak, and his skin is pale. The condition requires urgent resuscitation.
Preparing for analysis
Preparing for a coagulogram has a number of important features; you should take them seriously.
Like any blood test, hemostasis testing must be carried out on an empty stomach; stress, alcohol consumption, and intense physical activity should be avoided for several days.
It is important to notify your doctor about the medications you are taking, as they can significantly affect platelet aggregation (sticking together)
Please note that the blood is collected in a different test tube, which differs in the color of the cap from the general analysis or biochemistry. The main difference is the substance applied to the walls - an anticoagulant
You cannot use vacutainers (blood collection container) with EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetate) and heparin due to distortion of the test results. In most cases, citrate is used for coagulation analysis.
The volume of blood in the vaccumtainer is important: it reaches the mark, since the amount of anticoagulant is calculated optimally. A tourniquet applied for a long time (more than 1 minute) before blood sampling is not allowed, as this leads to activation of the hemostasis systems, and the results will no longer be reliable. The first milliliters of blood obtained are not used for analysis, since traces of tissue thromboplastin may remain there. Blood should fill the tubes by gravity. Gone are the days when blood was drawn with a syringe. Do not shake the test tube with blood, as this will cause hemolysis (destruction), activation of platelets and release of coagulation factors.
Predictions and prevention
In most cases, the prognosis is favorable. But in order to avoid the severe consequences of the disease in the form of hypovolemic shock, it is recommended to administer Vikasol to newborns at risk for prophylactic purposes, without waiting for clinical symptoms of the disease.
Let us remind you that this group includes children:
- those who suffered from intrauterine hypoxia or suffered asphyxia during childbirth;
- injured during childbirth;
- babies born by caesarean section;
- premature birth with low baby weight;
- infants whose mother took one of the drugs that affects coagulation during pregnancy;
- if the mother suffered from dysbacteriosis during pregnancy, had liver problems, or suffered from toxicosis and gestosis.
What is the normal blood coagulogram in children?
In order to understand what a coagulogram is and why it is necessary to undergo it, you should study several concepts:
- Blood clotting is the ability of blood, when damaged and the integrity of blood vessels is damaged, to form a clot to close the site of damage and stop bleeding.
- Hemostasis is a system of the child’s body, the main function of which is to ensure blood clotting.
- Coagulogram is a blood test showing the functioning of hemostasis in a child.
This test must be taken for children before any surgical intervention, even the most minor one. A coagulogram performed before surgery will help avoid possible severe bleeding.
There are cases when surgical intervention is impossible due to increased blood clotting, which increases the risk of blood clot formation.
A coagulogram is often used to determine the diagnosis of suspected hemophilia in children.
Additional research
Coagulogram tests are taken:
- Lupus anticoagulant is a very important indicator. Determines the amount of enzyme involved in hemostasis. Designed to neutralize the work of phospholipids. It cannot be in the blood of a healthy child. The presence of this enzyme may indicate diseases such as ulcerative colitis, cancer, etc. Taking any medications can also affect a positive test result.
- Prothrombin shows the time it takes for thrombin to be formed from prothrombin in the second stage of blood coagulation. It is expressed as a percentage of this time in the blood of a sick child to the clotting time of control plasma.
Norms of coagulogram results in children
Key figures:
- The clotting time for a child in full health is 4-9 minutes.
- Thrombin time. The result should be equal to 30 minutes with an error of 3 minutes.
- Prothrombin index - the norm is 70-100%.
- Fibrinolytic activity. The result should be 180-260 seconds for a healthy child.
- Activated partial thromboplastin time. The number can vary from 24 to 35 seconds.
- Fibrinogen concentration in blood plasma. The test result for a healthy child should be 1.25-4 g/l.
- Thrombotest - IV-V stage.
- AVR or Activated recalcification time - the time indicator should correspond to 50 -70 seconds.
- Soluble fibrin-monomer complexes - the level of this substance in the blood of a healthy child should not be 4 mg\100 ml.
- Plasma tolerance to heparin should normally be 3-11 minutes.
- Fibrinogen - 5.9-11.7 µmol/l.
- Duke bleeding time. The indicator in healthy children is up to 4 minutes.
- The normal time for plasma recalcification is 90-120 seconds.
- Blood clot retraction - 30-40%.
- Prothrombin - the norm is 78-142%.
- Lupus anticoagulant - negative.
Cost of blood coagulation analysis in children
Currently, a very large number of clinics provide coagulogram testing services. Such an analysis is carried out in any hospital located near your home, which has the necessary equipment and reagents for the analysis.
The cost of a basic coagulogram package varies in Moscow from 700 to 1300 rubles. It is possible to conduct an advanced analysis, which examines additional indicators of the blood coagulation system.
In this case, the cost of a coagulogram will increase to 3,500 rubles.
Donating blood for a coagulogram in children is most often prescribed in the following cases:
- Before surgery. Timely identified pathologies in the blood clotting system can eliminate problems with bleeding and blood loss and even save the life of a small patient.
- If your child bleeds frequently. This could be nosebleeds or bleeding from wounds that cannot be stopped for a long time.
- If you suspect hemophilia or other similar diseases associated with blood clotting disorders.
Do not forget that only a doctor should decipher the analysis. When deciphering the result, the specialist not only checks the obtained indicators with the norm, but also takes into account a number of associated factors. The results obtained as a result of a coagulogram will help identify autoimmune, inflammatory and vascular diseases.
Coagulogram
A coagulogram is a set of indicators of the blood coagulation system.
Coagulogram analysis is very important when:
- Bleeding, a tendency to thrombosis, before surgical interventions, with the development of thrombosis and their prevention, vascular diseases, liver diseases, strokes, heart attacks.
- Coagulogram parameters must be assessed during treatment with anticoagulants (warfarin, phenylin, syncumar, heparin, fraxiparin, etc.)
- A coagulogram helps the doctor select the correct dose of aspirin in the treatment of coronary artery disease and hypertension (for example, Thrombo AS, Cardiomagnyl)
- A coagulogram during pregnancy is prescribed if there is an increased risk of thrombosis and bleeding, with gestosis, or fetoplacental insufficiency.
- A coagulogram is an important part of monitoring when taking oral contraceptives (once every three months) to assess the risk of thrombosis.
- Analysis of a coagulogram is necessary when carrying out hirudotherapy (treatment with leeches) to monitor treatment and prevent severe bleeding.
Coagulogram indicators:
Prothrombin is a blood coagulation factor, one of the most important indicators of a coagulogram, characterizing the state of the blood coagulation system.
A change in its amount in the blood reflects a blood clotting disorder. Prothrombin increases with a tendency to thrombosis. Normal values are 78-142%.
Prothrombin time is the clotting time of plasma in seconds after adding thromboplastin-calcium mixture to it. The normal prothrombin time is 11-16 seconds,
INR (international normalized ratio) is a calculated coagulogram indicator that shows the ratio of the patient's prothrombin time to the normal average prothrombin time. Determination of INR is necessary to monitor therapy with indirect anticoagulants (anticoagulants - warfarin, phenylin). Such patients need to monitor their INR at least once every 3 months. An excessive increase in INR is an indication of bleeding tendency. A decrease in the indicator indicates an insufficient effect of anti-clotting agents and indicates a continued increased risk of thrombosis. The normal value for INR is 0.8-1.2. Treatment with oral anticoagulants (warfarin) requires a higher target INR level - usually above 2.5.
Prothrombin index (PTI) is the ratio of the clotting time of normal plasma to the clotting time of the patient's plasma, expressed in%.
It increases with increased coagulation and the tendency to thrombus formation, and decreases with the tendency to bleeding.
Fibrinogen is a protein that forms the basis of a blood clot during blood clotting. It increases in the blood during inflammatory processes and reflects the risk of developing cardiovascular complications due to increased blood clotting. Decreases - with a tendency to bleeding, including congenital defects, with impaired liver function, etc. Normal values - 2.0-4.0 g/l APTT (activated partial thromboplastin time) - used for screening assessment of blood coagulation, and also for monitoring patients receiving heparin. This test determines the time it takes for a blood clot to form after adding special reagents. A shortened APTT indicates increased blood clotting and a tendency to thrombosis, and a lengthening indicates decreased blood clotting and a tendency to bleeding. Normal - 24-35 s
Antithrombin III is a natural anticoagulant that inhibits blood clotting factors (inactivates thrombin) and helps reduce blood clotting. It is studied in the blood during recurrent thrombosis, during treatment with heparin. Normal values are 71-115%.
Lupus anticoagulant should not normally be produced by a pregnant woman. This is a group of antibodies (IgM and IgG) to the outer membrane of platelets.
The presence of these antibodies is accompanied by an increase in aPTT. These antibodies appear in autoimmune diseases (when the work of the immune system is directed against its own organs), in the pathology of pregnancy (preeclampsia - a complication that worsens the condition of the mother and fetus and is manifested by increased blood pressure, the appearance of edema, and protein in the urine). Such patients are characterized by thrombosis of arteries and veins.
Pregnancy against the background of such pathology is often complicated by spontaneous abortion, placental infarction, and fetal death.
Determination methods
As mentioned above, in modern diagnostic practice, mainly three main methods are used to determine the duration of bleeding.
Duque's technique
It was developed more than a century ago by the famous British scientist William Duke. The initial puncture before collecting biomaterial was made with a scarifier on the earlobe. Later, the technology was improved, and blood began to be taken from a finger using a Frank needle, which is immersed in the corresponding area to a depth of no more than 4 millimeters.
After making the puncture, the doctor prepares filter paper that is fairly large in size and blots the damaged finger with it every 15-20 seconds, taking measures until the marks on the material completely disappear.
Alternative options
Method according to Lee and White. The rate of formation of a venous blood clot in 1 milliliter of biomaterial at a temperature of 37 degrees is determined with relative corrections for the process of mixing the corresponding biological fluid in a test tube and artificially accelerating coagulation.
Methodology according to Sukharev. This approach was used widely in domestic pediatrics of the 20th century, along with the corresponding Duque technique. As part of laboratory diagnostics, capillary blood from a finger is examined. Relative general norms, regardless of age, range from 2 to 5 minutes.
Coagulogram - what is it?
Many patients needlessly begin to worry when they hear from their attending physician such unusual at first glance words as coagulogram or otherwise hemostasiogram. So what kind of coagulogram analysis is this and why is it taken?
First of all, it is worth noting that this is a fairly common method in modern medicine for studying the functioning of the hemostatic system of the human body, which is responsible for such important vital functions as stopping bleeding when blood clots or blood vessels are damaged, as well as maintaining the normal fluid state of the blood.
Hence the answer to the question of what a hemostasiogram is - a study that determines how well the body’s hemostasis system functions. A blood coagulogram test helps to study such an important blood function as the ability to clot, i.e. formation of a blood clot.
Having received the results of coagulation, the attending physician can predict in advance the outcome of surgery or childbirth. Information about blood clotting is vital in emergency situations, for example, when a person is injured, when seconds count and the bleeding needs to be stopped as quickly as possible.
Therefore, you hardly need to worry too much about how much this research costs. After all, the price of a hemostasiogram cannot be compared with the confidence that the patient will be alive and healthy.
Indications for prescribing such an analysis as a hemostasiogram are the presence of the following diseases in the patient:
- intestinal thrombosis;
- stroke;
- thromboembolism;
- vascular thrombosis and varicose veins of the lower extremities;
- chronic cirrhosis;
- gestosis;
- inflammatory processes in the acute stage;
- hemorrhagic pathologies, for example, thrombocytopenia, hemophilia or von Willebrand disease.
In addition, such an analysis is necessarily prescribed to determine the rate of blood clotting in preparation for planned operations, for example, cesarean section, as well as during pregnancy to assess the state of hemostasis and before spontaneous childbirth. Every woman in labor must have a blood test such as a coagulogram in her exchange card.
Human hemostasis system
Having determined what a hemostasis test is, it is worth understanding in more detail the concept of blood clotting. Perhaps we should start with a definition. So, the hemostasis system of the human body is the most important biological system, the main functions of which can be considered to be the preservation of basic blood parameters, as well as stopping bleeding.
It not only circulates through the vessels, but also, unnoticed by a person, restores veins and arteries throughout his life due to its ability to form blood clots or dense clots, i.e. roll.
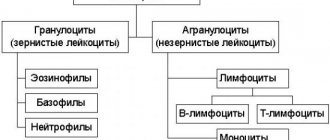
There are three main components of the human hemostasis system:
- Vascular endothelial cells (the inner layer consisting of flat cells lining lymphatic and blood vessels, as well as the cavities of the heart), which, when vascular walls rupture or other damage, are capable of releasing biologically active components such as prostacyclin, thrombomodulin and nitric oxide. They, in turn, trigger the process of blood clot formation.
- Platelets or blood platelets that have the ability to “stick together” with each other in order to subsequently form a primary hemostatic plug.
- Plasma factors (15 plasma factors in total, most are enzymes), which, due to chemical reactions, form a fibrin clot, which should finally stop the bleeding.
Summarizing all of the above, we can clearly answer the question of what a blood test for hemostasis shows during pregnancy, in preparation for a planned operation, or during diagnostics. This test gives an idea of how well or poorly a patient's blood is clotting. In other words, how quickly doctors can stop bleeding when it occurs.
Antithrombin
Antithrombin III is an extremely important protein that regulates the level of blood clotting, preventing its excessive thickening and the formation of blood clots. To assess the general condition of the blood, it is necessary to know the level of antithrombin.
The content of antithrombin in the blood varies greatly depending on age: in infants it is the lowest - 60-90%, in children from one to six years old it reaches a maximum value - 101-131%, then gradually decreases, in adults reaching 66-124% .
An increase in antithrombin levels is observed when:
- acute inflammatory processes in the body;
- acute viral hepatitis;
- lack of vitamin K.
A decrease in antithrombin levels may accompany:
- liver diseases;
- DIC syndrome;
- sepsis;
- congenital disorders of antithrombin synthesis.
How to donate blood for analysis
To get the most reliable results, you need to properly prepare for the study.
Preparation
Before screening, the patient must follow all the recommendations given by the specialist:
- Avoid eating 12 hours before the session. If you cannot avoid having dinner the night before, preference should be given to light dishes.
- Stop taking all medications that require minor breaks.
- Eliminate any drinks from your diet, especially alcohol. You are allowed to drink clean water.
- Reduce physical activity.
- Do not expose the body to stress.
- Do not smoke at least one hour before the procedure.
If you do not follow these rules, the likelihood of receiving unreliable data increases.
Carrying out
They donate blood for analysis exclusively on an empty stomach. You can take it from a finger or a vein.
After all the instruments and the place from which the biomaterial is taken are disinfected, the laboratory technician makes a puncture in an area of the skin with minimal trauma, which must also be observed to prevent data distortion as a result of penetration of thromboplastin tissue.
To eliminate this possibility, it is necessary to fill two test tubes with the material. The latter is sent for research. If blood is taken from a vein, then a tourniquet is not used.
In addition, a special substance – a coagulant – must be added to the test tube.
The procedure itself is painless. Unpleasant sensations arise only at the moment of puncture of the skin. After a coagulogram, slight weakness may be observed in the arm.
Data interpretation
The interpretation of the results is carried out exclusively by a specialist. In this case, all the indicators that were described above are taken into account.
When making a final diagnosis, it is also necessary to take into account the medical history, the results of the patient’s examination, and a general blood test. Generally speaking, exceeding the parameters of normal values will indicate thickening of the blood fluid, and a decrease will indicate a deficiency of platelets in the blood.
Generally speaking, exceeding the parameters of normal values will indicate thickening of the blood fluid, and a decrease will indicate a deficiency of platelets in the blood.
How many days does the study last?
The length of time required for the study will depend on many predisposing factors.
In most cases, a coagulogram is done for a maximum of 1-2 days. Sometimes this can take a maximum of ten days. Everything will depend on the serviceability of the equipment, the workload of the laboratory and the employee. If there is an additional charge for urgency, test results are issued on the day of delivery.
Forms of the disease
There are primary and secondary hemorrhages. Primary is said to be when the fetus initially had a deficiency of the vitamin, and its supply through mother’s milk is minimal. By the 5th day, the deficiency can be compensated for by its intestinal production.
The secondary form is diagnosed if liver lesions are present, when the synthesis of polypeptide precursors of plasma factors (PPPP) is impaired.
The disease is classified according to the time of onset:
- early - bleeding makes itself felt on 1, maximum 2 days after birth;
- classic - appears on days 3-5;
- late - occurs at any time during the first 8 weeks of life.
Key indicators for the study
Conducting the research and deciphering the analysis will require an analysis, in which it will become clear whether the indicators reach their norm or not. Moreover, if the general mechanism is disrupted and there are not enough particles or none at all, they do not perform their functions. There is a high risk of severe blood loss. Another sign of improper functioning of particles - platelets in the blood is that during active work, “plugs” can form, which later develop into a blood clot.
As a result, organs and tissues receive less nutrition and oxygen. This is especially dangerous for women during pregnancy, and therefore they are tested for blood clotting during pregnancy. It is for this reason that the difference between healthy and sick people lies in the balance between blood thinning and clotting. And the slightest pathology can lead to its disruption. It is for this reason that it is necessary to take a blood clotting test, the norm of which will show how liquid it is.
In order to find out what blood clotting ability is, you will need to undergo a special examination - a blood clotting test or coagulogram. Some doctors call it a hemostasiogram. Decoding the results obtained will allow you to obtain various parameters. Among them, the most important are:
- Prothrombin (prothrombin time);
- Thrombin time;
- Fibrinogen.
A blood clotting test will allow you to decipher and understand the extent of the deviation from the norm.
A blood clotting test will be necessary if:
- when it is necessary to determine the cause of uncontrolled bleeding;
- to find out the cause of blood clots;
- detection of DIC syndrome;
- when diagnosing the development of thromboembolism, hemophilia, antiphospholipid syndrome;
- to check the body’s reaction rate to the use of heparin and other similar drugs, the use of which has a great impact on coagulation processes;
- before starting or after completing a surgical operation;
- during pregnancy before childbirth;
- carrying out manipulations with thrombolysis, coronary angiography, etc.
In this case, the first place comes to deciphering the time, the duration of clotting and the number of platelets in the blood. It is for this reason that, to check the coagulability and general composition of platelets, the time required for their accumulation, a detailed examination of both men and women, especially pregnant women, is prescribed.
In this case, you need to donate blood for a coagulation test for people who:
- if there is a suspicion of blood pathology in the body;
- women when registering for pregnancy;
- sick if there are varicose veins;
- if there are cardiovascular pathologies;
- with liver disease;
- when autoimmune diseases occur.
Analysis of the transcript carried out during the study will show the result of the blood coagulogram. In some cases, tests may be prescribed to monitor long-term treatment with anticoagulants that have an indirect effect. Studying the time required for platelets to clot, as well as the duration of the reaction, can complicate deciphering. Especially if a study is carried out on pregnancy and childbirth.
Under these conditions, take a blood clotting test, the price of which will only depend on where he will undergo the platelet clotting test.
Causes of hemorrhagic disease
Let's look at the situations in which K-hypovitaminosis occurs:
- Intestinal dysbiosis. It is associated either with taking antibiotics, or with physiological reasons, when the bacterial intestinal flora simply did not have time to develop. Its production begins only on the 4th-5th day of life, provided that the colonization of bacteria occurs unhindered.
- The fetus has a small supply of the vitamin. Vitamin K passes through the placental barrier poorly, so its content in a newborn is half that of an adult.
- Its content in milk is low. The fact is that both breast and cow's milk do not cover the daily requirement for the vitamin. Therefore, breastfeeding can become a provoking factor in the development of hemorrhagic disease. But this does not mean that you need to give up breastfeeding, there is simply a need for a small nutritional correction.
The following factors can aggravate the situation:
- during pregnancy the woman took anticoagulants or anticonvulsants;
- presence of liver or intestinal diseases;
- prematurity of the child;
- gestosis and toxicosis of a pregnant woman;
- the baby was put to the breast late;
- if the baby has been on parenteral nutrition for a long time;
- malabsorption syndrome was detected - when the process of absorption of nutrients in the intestine is impaired; the main symptom is diarrhea for more than 7 days;
- pathologies of the biliary tract (obstruction or complete absence).