Here you can calculate the child’s blood type based on the blood groups of the parents, find out how the blood type is transmitted from parents to children, and look at the table of the blood type of children and parents.
The widespread division of people into 4 blood groups throughout the world is based on the ABO system. A and B are erythrocyte antigens (agglutinogens). If a person does not have them, then his blood belongs to the first group (0). If there is only A - to the second, only B - to the third, and if both A and B - to the fourth (see the large table at the bottom of the article). Accurate determination of blood belonging to a specific group is possible only in laboratory conditions using special sera.
According to the Rh factor, the entire population of the globe is divided into those who have it (Rh-positive) and those who do not have this factor (Rh-negative). The absence of Rhesus does not affect health in any way. However, a woman has a risk of Rh conflict with her child, especially with repeated pregnancies, if this factor is absent in her blood, but it is present in the baby’s blood.
Inheritance of blood type in theory
Inheritance of blood groups and Rh factor occurs according to the well-studied laws of genetics. To understand this process a little, you will need to remember the school biology curriculum and consider specific examples.
From the parents, the child is given genes that carry information about the presence or absence of agglutinogens (A, B or 0), as well as the presence or absence of the Rh factor. Simplified, the genotypes of people of different blood groups are written as follows:
- The first blood group is 00. This person received one 0 (“zero”) from his mother, the other from his father. Accordingly, a person with the first group can only pass on 0 to his offspring.
- The second blood group is AA or A0. A or 0 can be passed on to a child from such a parent.
- The third blood group is BB or B0. Either B or 0 is inherited.
- The fourth blood group is AB. Either A or B is inherited.
As for the Rh factor, it is inherited as a dominant trait. This means that if it is transmitted to a person from at least one of the parents, it will definitely manifest itself.
If both parents are negative for the Rh factor, then all children in their family will also not have it. If one parent has the Rh factor and the other does not, the child may or may not have Rh. If both parents are Rh positive, then in at least 75% of cases the child will also be positive. However, the appearance of a baby with Rh negative in such a family is not nonsense. This is quite likely if the parents are heterozygous - i.e. have genes responsible for both the presence and absence of the Rh factor. In practice, this can be assumed simply by asking blood relatives. It is likely that among them there will be an Rh-negative person.
Specific examples of inheritance:
The simplest option, but also quite rare: both parents have a negative blood group. The child will inherit their group in 100% of cases.
Another example: mom’s blood type is positive, and dad’s blood type is negative. A child can receive 0 from his mother, and A or B from his father. This means that the possible options will be A0 (group II), B0 (group III). Those. The blood type of a baby in such a family will never coincide with the parent’s. The Rh factor can be either positive or negative.
In a family where one of the parents has a second negative blood group, and the other has a third positive blood type, it is possible to have a baby with any of the four blood groups and any Rh value. For example, a child can receive A or 0 from his mother, and B or 0 from his father. Accordingly, the following combinations are possible: AB (IV), A0(II), B0 (III), 00(I).
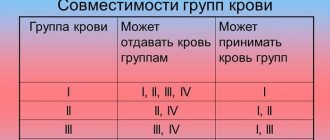
Table of the probabilities of having a child with a certain blood type given the corresponding data on the blood types of the parents:
| first | second | third | fourth | |
| first | I – 100% | I – 25% II – 75% | I – 25% III – 75% | II – 50% III – 50% |
| second | I – 25% II – 75% | I – 6% II – 94% | I – 6% II – 19% III – 19% IV – 56% | II – 50% III – 37% IV – 13% |
| third | I – 25% III – 75% | I – 6% II – 19% III – 19% IV – 56% | I – 6% III – 94% | II – 37% III – 50% IV – 13% |
| fourth | II – 50% III – 50% | II – 50% III – 37% IV – 13% | II – 37% III – 50% IV – 13% | II – 25% III – 25% IV – 50% |
It is worth remembering that blood type calculated using charts, tables or calculators cannot be considered final. You can accurately find out your baby’s blood type only from the results of laboratory tests.
How is a child’s blood type calculated if there is information about the parents’ group and Rh?
Each person has an individual set of genes, which he acquires from the moment of conception. And blood type is inherited.
You can find out your blood type and Rh factor. You can make the calculation if you have knowledge about the blood groups of the parents. The blood distribution system (AB0) does this. According to her standards, blood is divided into four groups. Each couple can independently calculate the probability of blood inheritance that their offspring will have. Tables developed based on the probability of borrowing will help with this.
The scientist K. Landsteiner tried to combine combinations of blood serum with red blood cells. For this experiment, people were needed, and he divided them into two groups: he took serum from the biomaterial of some, and erythrocytes from others. Based on experiments, I found out that in some cases cells with red blood cells stick together, but in other combinations they do not. Having fully studied those variants of serum that were bonded together with red blood cells, I saw in them substances that were absent in the non-combined variants. It was in this way that the scientist identified two categories - A and B. He soon discovered the third, and Landsteiner’s students made the discovery of the fourth, which includes the first and second categories of blood. New medical discoveries have led to the emergence of the AB0 blood distribution system, which is still relevant in the modern world.
- I (0) in the first group. antigens A and B are not detected,
- II is detected if antigen A is present,
- III – determined if there is antigen B,
- IV – antigens A and B are present simultaneously.
This was an important discovery for mankind, as it helped avoid many fatal blood transfusions. Since the 19th century, medicine has learned to transfuse blood to pregnant women; now the problem of replacing biomaterial in case of extensive bleeding has been resolved with minimal risk to women’s lives.
Until the end of the 20th century, these procedures were carried out with rare exceptions, as they could cause harm. But thanks to scientists, the transfusion procedure became safer and helped save many human lives. Scientists took a completely different look at research into the properties of blood after the creation of the ABO system, because it helped reach a new level of genetic research.
Mendel's law of heredity
How to calculate the blood type of an unborn child based on the blood type of the parents using Mendel's law?
- When I gr. two parents, then they have the opportunity to give birth to a baby with missing antigens A and B.
- For couples with grades I and II. offspring are born only with this type of group, and also in pairs of groups I and III.
- Features of people IV gr. is that they can give birth to children with II, III or IV groups, except I, regardless of the antigens in this pair.
- There is one deviation from the rules: a certain category of people have antigens A and B in their genotype, but they are not manifested in the phenotype. This is a rare phenomenon found in India.
What is Rh factor
Another important point on which the health of the pregnant woman and the unborn child depends is the positive or negative Rh factor. This is the name given to the presence or absence of the D-antigen protein on the membrane of red blood cells (erythrocytes). The Rh factor has absolutely no effect on health, but it is taken into account during blood transfusions, and special attention is also paid when carrying a fetus, so parents must be tested to determine Rh.
The fact is that if the mother is negative and the father is positive, it often happens that the father’s Rh factor is passed on to the baby. In this situation, there may be an Rh conflict in the pregnant woman’s body: when for some reason the fetal blood ends up in the mother’s blood, the mother’s immune system perceives the baby as a threat and produces antibodies to destroy it. This can lead to the destruction of the baby's red blood cells, and they will not be able to deliver the required amount of oxygen to the baby, which will cause the baby to die in the womb, premature birth or stillbirth.
If the baby is born alive, it may have hemolytic disease, which may be icteric, anemic, or edematous. Edema is considered the most dangerous, as it is characterized by an enlargement of the liver, spleen, all glands and heart, a reduced amount of protein, hypoxia (oxygen starvation), disruption of the functioning of all organs and systems, which can lead to the death of the baby.
It should be noted that the first child is in the least danger (the body fights the most before childbirth). The second will feel the full force of the attack of maternal antibodies throughout the pregnancy.
To prevent negative consequences, a pregnant woman should undergo tests throughout her pregnancy. If tests show the absence of antibodies, to prevent their production, the woman is given an injection of Rh immunoglobulin twice during pregnancy.
If, when deciphering the tests, it was determined that the body has already produced antibodies, the injection is contraindicated. In this case, the condition of the pregnant woman and baby is carefully monitored, for which the mother must not forget to take tests in a timely manner. Nowadays, medicine has reached such a level that with proper care and treatment many problems can be avoided.
How is a child’s blood type inherited from his parents: table and method of determination
While expecting a baby, all parents think about who their son or daughter will look like and whose character they will inherit. This secret will be revealed to young parents only after the baby is born or after they calculate the medical indicators of the individual structure of proteins - blood type and Rh factor. These factors are inherited and formed at the moment of conception, so it is important to know how to calculate what blood type the child will have, and why is it transmitted this way?
About blood groups
The most common blood classification in medicine is the international classification AB0. Blood groups are distinguished by the internal proteins-antigens agglutinogens Alpha and Betta or agglutinin 0 (zero) and their location on the outer wall of the red blood cells of erythrocytes. These cells control the immune response to foreign proteins.
System of dividing blood into groups
What does blood type depend on? Not so long ago, at the turn of the 20th century, geneticists received information that, depending on the presence of certain individual antigenic (protein) properties of red blood cells, blood is divided into four groups. At first, only three types of blood substance were discovered - these are 1, 2 and 3, then another type was added - blood group 4.
Classification of four categories of blood flow composition:
- The first is designated 0 (I).
- The second is marked A (II).
- The third is marked B (III).
- The fourth is marked AB (IV).
The marking corresponds to the absence (0) or presence of agglutinogens in the bloodstream (A, B). Such a system received the corresponding name ABO. has no antigens at all. The second has one antigen A, the third has B. The fourth has two antigens A and B. Agglutinogens are proteins of the immune system located on the surface of red blood cells. When a pathogenic microorganism enters the human body, they immediately begin to produce antibodies, which combine with the pathogens and block their ability to move. It is possible to find out your blood type and Rh factor in a diagnostic laboratory by taking a test.
The study is not difficult and does not require special preparation.
The Rh factor can be positive or negative, that is, its absence. Rhesus positive is more common in about 80% of the world's inhabitants. Less common are people who do not have Rh, this status is called Rh negative; this pattern is observed in less than 20% of people. In humans, the lack of Rh does not affect the condition of the body in any way. Rh negative is of great importance during pregnancy. Because often the mother’s blood components do not coincide with the child’s blood flow, which is why a Rh conflict occurs, which entails adverse consequences.
Child's blood type
Blood groups
Inheritance of a child's blood type
At the beginning of the last century, scientists proved the existence of 4 blood groups. How are blood types inherited by a child?
The Austrian scientist Karl Landsteiner, mixing the blood serum of some people with red blood cells taken from the blood of others, discovered that with some combinations of red blood cells and serum, “gluing” occurs - red blood cells stick together and form clots, but with others - not.
While studying the structure of red blood cells, Landsteiner discovered special substances. He divided them into two categories, A and B, highlighting a third, where he included cells in which they were not present. Later, his students - A. von Decastello and A. Sturli - discovered red blood cells containing A- and B-type markers simultaneously.
As a result of research, a system of dividing blood groups emerged, which was called ABO. We still use this system today.
- I (0) – blood group is characterized by the absence of antigens A and B;
- II (A) – established in the presence of antigen A;
- III (AB) – B antigens;
- IV (AB) – antigens A and B.
This discovery made it possible to avoid losses during transfusions caused by incompatibility of the blood of patients and donors. For the first time, successful transfusions were carried out before. Thus, in the history of medicine of the 19th century, a successful blood transfusion was described to a woman in labor. After receiving a quarter liter of donor blood, she said, she felt “as if life itself was penetrating her body.”
But until the end of the 20th century, such manipulations were rare and were carried out only in emergency cases, sometimes causing more harm than good. But thanks to the discoveries of Austrian scientists, blood transfusions have become a much safer procedure, which has saved many lives.
Inheritance of blood in a child
For many centuries, parents could only guess how their baby would be born. Nowadays, we can lift the veil of secrecy a little by looking into the “beautiful far away.” This became possible thanks to ultrasound, which allows you not only to find out the sex of the baby, but also some features of its physiology and anatomy.
Genetics have learned to predict the possible color of hair and eyes; they can determine in the early stages whether a baby has developmental defects. It also became clear what blood type the baby would have. To better understand this and learn how to determine a child’s blood type, we suggest you familiarize yourself with the table. Blood group table for parents and children:
| Mom + dad | Possible options for the baby's blood type in percentage | |||
| I+I | I (100%) | |||
| I+II | I (50%) | II (50%) | ||
| I+III | I (50%) | III (50%) | ||
| I+IV | II (50%) | III (50%) | ||
| II+II | I (25%) | II (75%) | ||
| II+III | I (25%) | II (25%) | III (25%) | IV (25%) |
| II+IV | II (50%) | III (25%) | IV (25%) | |
| III+III | I (25%) | III (75%) | ||
| III+IV | I (25%) | III (50%) | IV (25%) | |
| IV+IV | II (25%) | III (25%) | IV (50%) | |
Many parents also want to know how to calculate the Rh factor of their unborn baby. Another table will help with this. It’s worth saying right away that the table will help you with the question of how to find out your baby’s blood type. But sometimes children can be born with “their own blood type.”
Many experts confidently declare that if the father’s blood type is higher than the mother’s, then the baby will inherit not only the parent’s character (as the grandmothers assure), but also health, the baby will be born strong and healthy.
It is also worth saying that conflicts due to incompatibility in the blood type of parents occur quite often, but they are not as dangerous as with incompatibility of Rh factors. Therefore, timely examinations are the key to ensuring that the baby born will be healthy. Science does not stand still, and now parents can promptly learn about possible problems with the baby, and it is also possible to prevent infertility and miscarriage. Indeed, today doctors, knowing that the mother has a negative Rh factor, can prevent Rh conflict between the fetus and mother by introducing a special drug into the body - anti-Rh immunoglobulin. The study of blood and how it is inherited has made it possible to save hundreds of lives not only of children, but also of mothers.
The blood type of children and parents may be different. It is impossible to make an accurate calculation using tables. The only option that will help you find out for sure the blood type of a child born into the world is a laboratory analysis.
Parents of an unborn child usually tend to try to predict the gender of their desired child, who they will be like, and some individual features of appearance, such as hair or eye color. Of course, it will not be possible to obtain a complete portrait of the baby before his birth. But thanks to research by geneticists on the likelihood of borrowing, it is possible to actually calculate some characteristics of the unborn baby, namely, find out the child’s blood type and his Rhesus. The science of genetics studies the inheritance of blood groups in humans. A table created on the basis of the theory of inheritance will be useful in determining which blood type can be passed on to a child from his parents.
Specific examples of inheritance:
The simplest option, but also quite rare: both parents have a negative blood group. The child will inherit their group in 100% of cases.
Another example: mom’s blood type is positive, and dad’s blood type is negative. A child can receive 0 from his mother, and A or B from his father. This means that the possible options will be A0 (group II), B0 (group III). Those. The blood type of a baby in such a family will never coincide with the parent’s. The Rh factor can be either positive or negative.
In a family where one of the parents has a second negative blood group, and the other has a third positive blood type, it is possible to have a baby with any of the four blood groups and any Rh value. For example, a child can receive A or 0 from his mother, and B or 0 from his father. Accordingly, the following combinations are possible: AB (IV), A0(II), B0 (III), 00(I).
How to determine the sex of a child using a calendar (table) based on the blood type of the parents?
A woman with blood type 1 will most likely give birth to a girl from a partner with type 3 and a boy from partners with type 2 or 4. A woman with blood group 2 can give birth to a son from men with blood group 1 or 3, but if the partner has group 4, then this couple will have a girl. A woman with group 3 may have a girl from a partner with blood of group 1, but if her man has group 2 or 4, then she should expect a son. Men with the 1st or 3rd blood group, in order to acquire an heir, should create an alliance with a woman who will have the 4th group. A woman with blood type 4 and a partner with blood type 2 are most likely to conceive a girl. Of course, the reliability of this method cannot be considered 100%, because the same couple quite often gives birth to children of different sexes. Table for determining the sex of a child based on the blood type of the parents|Conception calendar
Next table
to calculate
the sex of the child
based on
the Rh factor of the parents' blood
.
Table for determining the sex of a child based on the blood type of the parents|Conception calendar
History of the 0AB system
In the cold winter of 1900, an unknown assistant at the department of pathological anatomy at the University of Vienna, Karl Landsteiner, takes blood from himself and five colleagues. The samples are placed in a centrifuge, the blood plasma is separated from the red blood cells and the experiment is undertaken... and it turns out that none of the plasma materials react to their red blood cells. However, Dr. Pletching's plasma stuck to itself the red blood cells of Sturli's colleague. The same thing happened in reverse. This circumstance allowed Landsteiner to think that there are two types of antibodies in nature.
The experimenter did not find such a quality in his material and concluded that there is another type of human blood, different in its properties from the first two samples; for himself, he assigned it the name C.
Later, together with his colleague A. von Decastello and student A. Sturli as a donor, he discovered the fourth type of blood, calling it “typeless.”