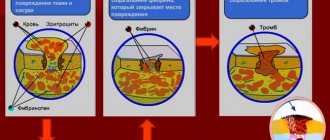
The value of glucose concentration depends on various factors, including diet, hormone levels and the functioning of the digestive system.
The main reasons affecting the indicator:
- Immaturity of the pancreas due to physiological characteristics. This condition often occurs in newborns. The organ continues its maturation during the first years of life.
- Active phases distinguished during the development of a child. Children aged 6-8 or 10-12 years experience powerful hormonal surges. In this state, body structures increase in size, affecting all indicators, including sugar levels. The increased work of the pancreas under such conditions becomes a source of production of additional amounts of insulin.
Increased glucose is most often associated with the following factors:
- incorrect analysis or incorrect preparation for the test;
- stress or nervous tension that the child experienced on the eve of the study;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland, pituitary gland or adrenal glands;
- decreased insulin production due to pancreatic tumors;
- obesity;
- long-term use of NSAIDs or glucocorticoids;
- unbalanced diet;
- infectious diseases.
Reasons for the decline:
- excessive physical stress without replenishing energy;
- prolonged fasting;
- disturbance in metabolic processes;
- lesions of the nervous system, in which tumors and injuries are observed;
- constant exposure to stressful situations;
- sarcoidosis;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- arsenic or chloroform poisoning.
A fall or increase in glycemia should be a reason for additional examination to determine the source of the pathological process.
Video from the famous pediatrician Komarovsky about diabetes in children:
Which children are at risk for diabetes?
The number of children diagnosed with this disease increases every year.
The following categories of patients are at risk:
- with a genetic predisposition;
- children exposed to nervous stress;
- with obesity;
- with metabolic disorders;
- poorly nourished children whose diet contains carbohydrates in excess.
The likelihood of the influence of these factors increases if the parents have diabetes.
The risk of developing the disease is:
- 25% in children born into a family with two diabetics;
- about 12% if there is one parent with diabetes.
In addition, diagnosing diabetes in one twin increases the risk of developing the disease in the other.
What to do if a disease is detected?
Children with elevated glycemic levels are prescribed appropriate therapy, which includes the following measures:
- taking medications;
- following a diet with limited carbohydrates;
- performing physical activity;
- timely implementation of hygiene procedures in order to reduce itching and prevent purulent formations;
- providing psychological assistance.
It is important to understand that diabetes is not a death sentence. Parents simply need to pay more attention to the child, monitor diet and therapy, and help him adapt to new living conditions.
The norm of sugar, as well as other biochemical indicators, is reduced in a newborn baby. This is due to the fact that the cycle of formation of internal systems has not yet ended. The main biochemical criterion for a baby is the amount of glucose. If children have no complaints about their health, then such tests should be taken once every six months to a year. If you need a thorough analysis, take a referral from your doctor.
Rules for preparing for research and diagnostic methods
In order for a blood test to show accurate results, it is important to follow a number of rules. Thus, a laboratory test is done on an empty stomach, so the child should not eat food 8 hours before the test.
It is allowed to drink clean water, but in limited quantities. Also, before taking blood, you should not brush your teeth or chew gum.
To determine the concentration of sugar at home, a glucometer is often used. This is a portable device with which you can quickly and accurately determine your glycemic level.
Test strips are sometimes used, but they must be stored correctly. Otherwise the result will be false.
There are certain rules for using a glucometer:
- Before the examination, hands should be washed with soap and warm water;
- the finger from which blood will be taken must be dry;
- All fingers can be pierced except for the index finger;
- to reduce discomfort, the puncture should be done in the side;
- The first drop of blood should be wiped off with cotton wool;
- the finger should not be squeezed too hard;
- With regular blood sampling, the puncture sites must be constantly changed.
To make an accurate diagnosis, a full range of tests is performed, which includes fasting blood sampling, urine testing, and determination of the level of glycated hemoglobin.
Expert opinion
Shalaeva Svetlana Sergeevna
endocrinologist, highest category, 18 years of experience
It would not be superfluous to conduct a stress test with glucose and identify ketone bodies in biological fluids.
Blood sugar levels in newborns
Blood sugar levels in children of different ages
| 1 year | From 3.3 to 5 |
| 2 years | From 3.3 to 5 |
| 3 years – 18 years | From 3.3 to 5 |
If the indicators deviate from the normal value, then you should understand:
- Glucose is a unique material for all tissues and organs of the body.
- Complex carbohydrates are broken down with the help of special enzymes into glucose, which quickly appears in the blood.
- Sugar regulates a large number of hormones.
- Decreasing or increasing the level should be treated very carefully.
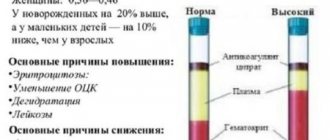
Hyperglycemia is a clinical symptom that indicates an increase in glucose in the blood serum (when compared with the norm of 3.3 - 5.5 mmol/l).
- mild (6.7 – 8.2 mmol/l);
- moderate severity (8.3 – 11.0 mmol/l);
- severe (more than 11.1 mmol/l).
With hyperglycemia, sugar levels are as follows (depending on the stage):
| Age | Degree of compensation | Glucose before meals, mmol/l | Glucose 2 hours after eating, mmol/l 4 | Glucose before bed/at night, mmol/l |
| From 0-6 years | Compensation | 5,5 – 9,0 | > 7,0-12,0 | 6,0-11,0 |
| Subcompensation | 9,0-12,0 | > 12,0-14,0 | Less than 6.0 or more than 11.0 | |
| Decompensation | > 12 | > 14,0 | Less than 5.0 or more than 13 | |
| From 6-12 years | Compensation | 5,0-8,0 | 6,0-11,0 | 5,5-10,0 |
| Subcompensation | 8,0-10,0 | 11,0-13,0 | Less than 5.5 or 10.0 | |
| Decompensation | > 10,0 | > 13,0 | Less than 4.5 or more than 12.0 | |
| From 13-18 years old | Compensation | 5,0-7,5 | 5,0-9,0 | 5,0-8,5 |
| Subcompensation | 7,5-9,0 | 9,0-11,0 | Less than 5.0-or more than 8.5 | |
| Decompensation | > 9,0 | More than 11.0 | Less than 4.0 or more than 10.0 |
What is sugar level
Blood sugar levels are calculated in mmol per liter, less often in milligrams per deciliter. The normal blood sugar level for a healthy person is 3.6-5.8 mmol/l. For each patient, the final indicator is individual, in addition, the value changes depending on the intake of food, especially sweet and high in simple carbohydrates. Naturally, such changes are not considered pathological and are short-term in nature.
How the body regulates sugar levels
It is important that your sugar level is within normal limits. A strong decrease or strong increase in blood glucose should not be allowed; the consequences can be serious and dangerous to the life and health of the patient - loss of consciousness up to coma, diabetes mellitus
Principles for how the body controls sugar levels:
| Sugar level | Effect on the pancreas | Effect on the liver | Effect on glucose levels |
| High | The pancreas receives a signal to secrete the hormone insulin | The liver converts excess glucose into the hormone glucagon | Sugar levels drop |
| Normal | After eating, glucose is transported through the bloodstream and signals the pancreas to produce the hormone insulin. | The liver is at rest, it does not produce anything, since the sugar level is normal. | Sugar levels are normal |
| Short | Low glucose levels signal the pancreas to stop secreting insulin before it is needed again. At the same time, glucagon is produced in the pancreas | The liver stops processing excess glucose into glucagon, since it is produced in its pure form by the pancreas | Sugar levels are rising |
To maintain normal glucose concentrations, the pancreas secretes two hormones - insulin and glucagon or polypeptide hormone.
Insulin
Insulin is a hormone produced by pancreatic cells, releasing it in response to the supply of glucose. Insulin is needed by most cells in the human body, including muscle cells, liver cells, and fat cells. The hormone is a protein that consists of 51 different amino acids.
Insulin performs the following functions:
- sends a signal to the muscles and liver cells to accumulate (accumulate) converted glucose in the form of glycogen;
- Helps fat cells produce fat by converting fatty acids and glycerol;
- gives a signal to the kidneys and liver to stop secreting their own glucose through the metabolic process - gluconeogenesis;
- stimulates muscle cells and liver cells to secrete protein from amino acids.
The main purpose of insulin is to help the body absorb nutrients after eating, thereby lowering blood sugar, fat and amino acid levels.
Glucagon
Glucagon is a protein produced by alpha cells. Glucagon has the opposite effect of insulin on blood sugar levels. When the concentration of glucose in the blood decreases, the hormone signals muscle cells and liver cells to activate glucose as glycogen through glycogenolysis. Glucagon stimulates the kidneys and liver to secrete their own glucose.
As a result, the hormone glucagon takes glucose from several organs and maintains it at a sufficient level. If this does not happen, blood sugar levels drop below normal levels.
Diabetes
Sometimes the body malfunctions under the influence of external or internal unfavorable factors, due to which disturbances primarily concern the metabolic process. As a result of such disorders, the pancreas stops producing the hormone insulin sufficiently, the body's cells react to it incorrectly, and ultimately the blood sugar level increases. This metabolic disorder is called diabetes mellitus.
How to prepare and pass the test?
Blood tests are performed on an outpatient basis. Blood is taken from a finger by pricking it with a special small needle. The test can also be carried out at home (with a special device - a glucometer), but its information content is not guaranteed. Blood must be donated on an empty stomach: you cannot eat or drink anything for eight to ten hours. The analysis is taken in the morning.
Sugar levels may vary depending on the severity of the disease. If there are no special indications, it is better to refrain from donating blood.
Reasons for deviations from the norm:
- Sugar may decrease for several reasons:
- If a person fasts for a long time or drinks little water.
- For severe chronic diseases.
- Insulinoma is a benign formation of the pancreas.
- For diseases of the digestive tract.
- For diseases of the nervous system.
- For sarcoidosis.
- In case of poisoning with arsenic or chloroform.
Increased rates are associated with:
- diseases of the adrenal glands, pituitary gland or thyroid gland;
- incorrect analysis: the child was full at the time of blood collection, was nervous or tired;
- pancreatic tumors - as a result, insulin production is reduced;
- obesity;
- use of anti-inflammatory drugs and glucocorticoids.
When blood glucose drops sharply, the child behaves like this: actively plays, is active, animated, then becomes worried, the activity becomes even greater. Babies who can already speak begin to crave sweet foods. After this, dizziness is observed, the child loses consciousness, and sometimes there are convulsions.
There is no need to panic if the test result deviates from the norm. If the test is taken on an empty stomach and the readings are high, you should retake the test.
IMPORTANT! There are factors that predispose a child to diabetes: genetic predisposition, obesity, weak immunity, the child weighs more than 4.5 kg at birth.
Treatment
If there are deviations from the norm, you should immediately consult a doctor. If sugar is elevated, you should follow a diet that does not contain high amounts of glucose:
- exclude chocolate;
- candies;
- grapes and other sweet foods.
If the sugar level still decreases, you need to use hormonal drugs. The pediatrician may decide to administer glucose through an IV. Once the condition has stabilized, the IV can be removed. If there is no response to the treatment, you need to find out what disease provokes the decrease in sugar.
If the conditions described above are present in a child, you need to check your sugar level daily: before bed, after meals, etc.
Preventing deviation
As mentioned above, to prevent the occurrence of such conditions in young children, they should be breastfed; for older children, the surest method is to follow a certain diet. Of course, you should go for routine examinations to a pediatrician at the clinic at your place of residence. This needs to be done once every six months. Keep your sugar levels under control at all times.
Children of preschool and school age should spend more time in the fresh air, exercise physically, and not experience stress and emotional tension.
Prevention
If the mother has diabetes, monitoring the baby will be more careful. Oddly enough, elevated sugar levels in the mother provoke the development of hypoglycemia in the child.
Blood sugar levels may vary depending on the child's age. There is no need to panic if the analysis does not meet expectations. See a doctor, donate blood, go for routine examinations to the pediatrician's clinic on time.
As soon as the baby is born, the level of glucose in his blood decreases sharply; after an hour and a half, the value reaches its minimum. From the second hour of life in a healthy child, sugar begins to rise and within 24 hours reaches a value of 2.5 mmol/l. This indicates a normal state of the body, but if the glucose concentration level stops at a level below 2 mmol/l, then doctors talk about a pathological condition called “hypoglycemia in newborns.” Let's look at why children suffer from this phenomenon, what its consequences are, what are the treatment options and preventive measures.
Factors affecting blood sugar
To obtain reliable glucose test results, the following facts should be considered:
- Low physical activity increases glucose levels. Conversely, vigorous physical activity (exercise, jogging, etc.) promotes the breakdown of all glycogen (sugar reserves in the liver) in 30 minutes, thereby reducing sugar. Before donating blood for glucose, a woman is not recommended to increase physical activity and work at night. Insufficient sleep and fatigue will distort the result of the study.
- Before the analysis, you cannot limit your usual diet (avoid sweets) or adhere to a diet. Fasting leads to a decrease in glucose: all glycogen is broken down within 12 hours after the last meal, but the true picture of the pancreas will be distorted.
- Alcohol, even in small quantities, increases blood sugar. Smoking, affecting all metabolic processes in the body, also leads to deviations of sugar from the norm.
- In obese people, the blood sugar level after 60 years, as at any age, is slightly increased. Obesity is often accompanied by diabetes.
- Taking diuretics-thiazides and beta-blockers prescribed for hypertensive patients increases sugar. Corticosteroids, some oral contraceptives and psychotropic drugs have the same effect.
Important! If the sugar level is too high, in order to avoid errors, the analysis should be repeated on another day, preferably in the clinic. ul
ul
What are the dangers of low glucose levels?
Hypoglycemia is especially dangerous for babies born prematurely. The shorter the fetus is in the womb, the less adapted it is to the environment and the greater the risk of developing various pathologies it is exposed to.
A low blood glucose value is not only an indicator of hypoglycemia, it may indicate other disorders of the body. Blood sugar levels below 2.2 mmol/l should cause concern. This pathological condition often causes death in newborns, because babies with severe hypoglycemia do not survive childbirth.
Treatment of the child must be started immediately as soon as the diagnosis is made based on the results of a blood test, otherwise the consequences for the newborn may be dire. Possible complications include cerebral palsy, childhood underdevelopment, mental and physical retardation, which will progress over time.
Causes of low blood sugar in a newborn baby
Possible reasons leading to the birth of children with low sugar levels:
- poor maternal nutrition during pregnancy, abuse of foods high in sugar;
- maternal consumption of alcoholic beverages during pregnancy;
- unhealthy lifestyle of the mother, poor diet;
- excessive physical activity;
- diabetes mellitus, which was diagnosed in the mother during pregnancy;
- difficulty breathing in the baby immediately after birth;
- the newborn was exposed to temperature changes;
- birth several weeks ahead of schedule;
- low birth weight;
- infectious diseases of mother and newborn.
If your baby has already been diagnosed with type I or type II diabetes, the development of hypoglycemia may be associated with the use of:
- increased dose of insulin;
- an old-style drug with many side effects.
Blood sugar may decrease due to concomitant diseases:
- pathologies of the nervous system;
- problems in the gastrointestinal tract;
- poisoning with toxic substances;
- exacerbation of chronic ailments;
- insulinomas, etc.
There is no need to worry if a deviation from the normal sugar level is detected in the newborn's first blood test. His body has not yet adapted to the new conditions, so the results of many tests will differ from standard indicators. However, if the value is still low when the blood is drawn again, this should be a cause for concern.
Clinical analysis
To obtain accurate data, blood sugar testing must be done at a medical facility. The procedure is always carried out in the morning on an empty stomach. Parents also need to remember the following points:
- the last meal should be taken no later than 10 hours before the collection of biomaterial;
- the day before the test, the child should refrain from increased physical activity;
- eliminate stress and emotional distress;
- The day before the procedure, it is strictly forbidden to consume sweets, fruits, and foods high in carcinogens. Potatoes and pasta are also prohibited;
- on the day of donating blood for sugar, it is forbidden to brush your teeth, since the components included in the toothpaste can affect the test result;
- Before taking blood, you should not give your child chewing gum;
- If the procedure is performed on an infant, you can breastfeed only 3 hours before the test. The mother herself also needs to adhere to a diet the day before.
Decoding the analysis usually takes a couple of days, after which a form with the results is given to parents. As practice shows, even a blood test does not always show a reliable result, which is most often a consequence of ignoring the preparation rules. It is also worth considering that the result is accurate only at the very moment at which the blood was taken.
It happens quite often that the test shows incredibly high blood sugar levels. To identify the general clinical picture, confirm or refute the presence of diabetes, the child is prescribed additional studies and tests, on the basis of which more accurate conclusions can be drawn.
Features of the treatment of hypoglycemia in newborns
To determine hypoglycemia, a specialist uses special test strips that show the glucose concentration within a few seconds. If the indicator is below 2 mmol/l, then a more detailed blood test is performed. After the diagnosis of hypoglycemia is confirmed by laboratory tests, intravenous glucose can be administered.
Since the pathological condition occurs in the first few hours of a child’s life and often goes away on its own, we speak of transient hypoglycemia. With timely relief of an attack of low sugar, the symptoms disappear and subsequently do not manifest themselves in any way.
Rules for treating hypoglycemia:
- After the start of glucose administration, the supply of solution should not be abruptly stopped. The reduction in the level of the incoming substance should occur gradually and only under the supervision of a physician.
- The initial glucose level should be from 6 to 9 mg per 1 kg of body weight, then it is increased, bringing it to 80 mg.
- It is unacceptable to inject a glucose solution with a concentration higher than 12.5% into the peripheral veins of a newborn.
- Breastfeeding should not be interrupted during injections.
- When glucose is administered during pregnancy, to prevent hypoglycemia in the newborn, it is important to maintain the sugar level no higher than 11 mmol/l. Otherwise, an increase in glucose can lead to a coma in the pregnant woman.
How to donate blood for diabetes mellitus
When taking this test, it is extremely important to fulfill all the preparation requirements for it. This will help reduce the risk of an erroneous result and accurately determine the real state of the baby’s health. Proper preparation for donating blood means abstaining from eating 12 hours before the procedure.
Since in most cases doctors take the test in the morning, you only need to have dinner, and you can have breakfast after the blood is taken. Doctors allow you to drink regular water
Proper preparation for donating blood means abstaining from eating 12 hours before the procedure. Since in most cases doctors take the test in the morning, you only need to have dinner, and you can have breakfast after the blood is taken. Doctors allow me to drink regular water.
It is not recommended to brush your teeth with toothpaste in the morning so that the sugar from it, getting through the mucous membranes, does not affect the reliability of the results.
In the laboratory, a young patient's ring finger is pricked with a lancet, and a drop of blood emerges and is applied to a prepared test strip. The result is obtained using a glucometer.
Glucose tolerance test
You can more accurately determine your glucose level by using a glucose tolerance test. It will show the rate of glucose absorption after excessive consumption, that is, how long it takes for the sugar level to return to normal levels.
This test involves ingesting glucose powder (1.75 g for every kilogram of the child’s body weight) with a small amount of liquid. Then every half hour they measure the sugar level and draw a graph of its concentration decreasing. If after 2 hours the value is less than 7 mmol/l, then this is normal.
Surprisingly, a child's body has the ability to lower glucose levels faster than an adult. Therefore, children have their own requirements for sugar levels after a glucose tolerance test. This indicator should not exceed 7.7 mmol/l. A higher level already indicates the presence of the disease.
In adults, everything is different: with a value of up to 11 units, doctors assess the condition as preceding diabetes, and more than 11 is already a disease.
If diabetes does develop in a child, this is not a death sentence. But such a baby requires more attention and affection from his parents, as well as adequate treatment and diet. A friendly family atmosphere will help the child quickly adapt to new living conditions.