Therapeutic measures
If the baby is growing and the eye rolling continues, the doctor may prescribe therapeutic measures to strengthen the muscles. Diagnostic tests are usually performed when several warning signs are present or when the child is more than 3 months old. The eye muscles are strengthened without drugs using exercises and physical therapy.
Gymnastics for the eyes
The simplest exercises for the eye muscles are carried out for infants in the form of a game. The baby is taught to focus his gaze while following a toy
To do this, choose a bright rattle and slowly move it in front of your eyes, drawing attention to it.
It is important that the baby is healthy, well-fed and in a good mood at this time. The distance is changed, teaching the child to find an object and not look away
It’s worth playing with your baby until he gets tired. This will be a complete workout for the eye muscles.
The distance is changed, teaching the child to find the object and not look away. It’s worth playing with your baby until he gets tired. This will be a complete workout for the eye muscles.
A mobile phone that is great for independent training attracts kids with a variety of bright objects and teaches them to independently choose an object to observe.
Massage and physiotherapy
Massage has a general strengthening effect and increases muscle tone in the baby.
It is important to find a good specialist who knows how to work with infants. A special eye massage strengthens the eye muscles, improves coordinated joint movements of the eyeballs
Self-massage will not give the desired result. Parents can invite a massage therapist to their home or visit a clinic. If there are indications, other physiotherapy procedures are prescribed - therapeutic baths with soothing phytocomplexes, physical therapy exercises for muscle development, reflexology.
Causes of the phenomenon
If the newborn baby is calm, does not try to twitch, has no problems sleeping, and sucks the breast with appetite, there is no need to worry. In this case, we are talking about a normal physiological phenomenon. The fact is that the baby’s nervous system is still immature, so the baby does not know how to control his muscles and focus on objects. Therefore, eye rolling in a newborn is considered normal.
Baby with rolled eyes
If this happens after a month, attention should be paid to this fact, since at this age children already know how to control their eye muscles
While falling asleep
If a newborn rolls his eyes when he falls asleep, this is completely natural. Even adults sleep with raised pupils. This is how the brain tunes in to sleep.
When he sleeps
In children under one month old, the muscles of the eyelids are not fully developed, so they can open spontaneously. Experienced parents already know that children can sleep with their eyes open. This shouldn't be scary.
Sleeping newborn
You should be concerned about the situation when at 3 months the baby continues to roll his eyes. Here you need to consult a neurologist.
Other possible options
9 times out of 10, rolling your eyes is not a cause for alarm. The baby may try to focus his gaze on an object that is not within his vision. Newborn babies do not yet know how to hold their heads up, so they can turn their eyes to look around.
In 1 percent of cases, the sign indicates a malfunction in the functioning of the body:
- Paroxysmal tonic gaze. This is a genetically determined disease that can manifest itself after infection with pathogenic microorganisms. The condition is not dangerous, but can cause delayed psychological development.
- Otitis.
- Eye diseases.
- Inflammation of the tonsils.
- Nervous tic. It usually occurs in older children (from 4 years old), but in an infant this condition should not be excluded.
- The onset of epilepsy or a single seizure. Here, apart from rolling back their eyes, children do not react to extraneous stimuli. Babies also shake their arms and legs. The head is thrown back.
- Increased intracranial pressure. In addition to the described symptom, the condition may be accompanied by vomiting. In this case, you should definitely call an ambulance, since increased intracranial pressure can lead to death.
- Graefe's symptom. Manifests itself in rolling the eyes downward while sleeping. As a rule, this goes away on its own by six months.
- Increased or decreased tone of facial muscles.
When should you worry?
But the child does not always stop rolling his eyes by the end of the first month of life. This may happen:
- When the muscles responsible for eye movement have not developed enough or developed unevenly.
- Due to neurological problems. Eye rolling accompanies many pathological conditions. If a newborn burps profusely, cries frequently, arches, throws his head back, and the movement of his eye muscles does not return to normal for a long time, you should consult a neurologist.
Contact your doctor if:
- the baby continues to roll his eyes in the second month of life;
- despite your efforts and visual gymnastics, the baby rolls his eyes after 3 months;
- the child rolls his eyes, accompanying these movements with general restless behavior and strong crying.
Eye rolling in children
Sometimes the baby’s organs of vision are rotated so that only the whites are visible, and the pupil is hidden under the upper eyelid. This condition is in most cases normal for a newborn baby.
In children under 1 month of age, eye rolling occurs due to the fact that it is difficult for them to control the following eye muscles:
- leading,
- diverting,
- lifting
- lowering.
The baby is unable to focus his gaze on any object. Underdeveloped muscles, the retina, the lack of a strong connection between the optic nerve and the brain, and the small size of the eyeball are to blame for this.
Over time, the newborn will learn to focus his gaze, thanks to the gradual development of the function of the visual organs, and the rolling will pass. Parents should take their child to the doctor if, after a month of life, he rolls his eyes.
Eye rolling in a newborn
A similar phenomenon is also observed when falling asleep - in a newborn and older children. This condition is not a sign of disease. In the initial phase of sleep, almost everyone's eyes roll upward. This occurs due to a weakening of the connection between the eye muscles and the brain. The baby falls asleep as follows:
- 1. Rubs eyes, nose, ears.
- 2. Blinks frequently.
- 3. Yawns.
- 4. Rolls his eyes upward.
During sleep, the eyelid may partially open, so part of the white is visible.
Possible diseases
The reason for eye rolling may be that the child has a disease. We can talk about pathology when the baby is more than a month old and there are accompanying symptoms:
- restless sleep,
- cry,
- excited state.
It is not normal to experience a condition in which the visual organs roll down, involuntary movements of the eyeballs in different directions (nystagmus) are observed, rhythm disturbances, convulsions and fluttering of the eyelids appear. The latter indicates a nervous tic, which is observed in 20% of children under the age of 10 years.
The ophthalmological reference book distinguishes three types of nystagmus, and each of them is accompanied by rolling of the eyes.
Types of nystagmus
Pathology often occurs with neurological diseases. Disorders that can lead to visual impairment in children include:
- mental disorders,
- inflammation of brain structures,
- increased intracranial pressure,
- poisoning with toxins and medications,
- hydrocephalic syndrome,
- neuroinfection,
- uneven muscle tone,
- gene mutations,
- fever.
The most common causes of eye rolling in children include:
- epilepsy,
- incorrect eye position,
- Graefe's syndrome.
Convulsive syndrome
Eye rolling in children occurs with convulsive syndrome or epilepsy. Minor seizures are called absence seizures. With them, in addition to problems with the organs of vision, inhibition of movements and reactions is observed.
Upon completion of minor epileptic seizures, the child’s condition returns to normal. These symptoms cannot be ignored as they develop into epilepsy
It is important to take your child to a specialist
If eye rolling began after encephalitis, meningitis or trauma, then the occurrence of epileptic seizures cannot be ruled out.
Incorrect position of the visual organs
In this case, the child experiences pain in the eye socket and rolls his eyes. Incorrect position of the visual organs develops due to reasons such as:
- neuritis of the trigeminal or facial nerve,
- ophthalmic inflammatory diseases,
- otitis,
- tonsillitis,
- adenoids,
- sinusitis.
Graefe syndrome
The pathology is called the “setting sun”, and scientifically it is called hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome. It manifests itself in an infant when the eyeball turns downward with the iris, above which the white is visible.
The cause of this condition is a violation of brain function, the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid, which accumulates in the ventricles of the brain.
Graefe syndrome
The child may have a genetic predisposition to Graefe syndrome. Causes of rolling associated with the “setting sun” symptom may be:
- over- or premature pregnancy,
- rapid labor activity,
- illnesses suffered by a woman during pregnancy,
- received birth trauma.
Why does a baby roll his eyes when he falls asleep?
At the newborn stage, the child may roll his eyes, since the muscle tone of the eyelids is still too weakened.
This is a common phenomenon in infants when falling asleep.
During the newborn period, in addition to eye rolling, other involuntary movements are observed that are not characteristic of the adult category. The pupil can move both down and up during sleep. However, there are symptoms that require consultation not only with an ophthalmologist, but also with a neurologist or pediatrician.
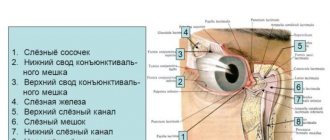
Causes of eye rolling in babies
The following factors provoke upward rolling of the pupil:
- prematurity;
- injuries to the baby during labor;
- infectious lesions of the mother during pregnancy;
- Hypoxia is common;
- hereditary predisposition.
If your eyes roll downwards, you should visit a neurologist, as the baby may develop Graefe syndrome. Additional symptomatic signs of pathology are:
- not expressed reflexes;
- convulsions;
- problems with swallowing;
- weakness of muscle fibers;
- strabismus.
The syndrome develops against the background of weakening of the ocular muscles, which occurs due to the accumulation of cerebral fluid in segments of the brain.
Symptoms to worry about
The norm for the pupil to roll up is when the baby is under 1 month old and when falling asleep. It is recommended to consult a pediatrician if you have additional symptoms in addition to the phenomenon:
- child over 3 months old;
- sleep is accompanied by attacks of apnea;
- when falling asleep, the eyes move down;
- convulsive states are observed;
- the baby periodically throws his head back;
- the child has hypertonicity of the extremities;
- Recession of the pupil is observed not only during falling asleep or sleep;
- restless behavior.
Manifestations signal the possible development of pathologies:
- dysfunction of the nervous system;
- epilepsy;
- hydrocephalic syndrome;
- dystonia of the muscle fibers of the visual apparatus;
- epilepsy;
- delay in psycho-emotional development;
- Grafe's symptom;
- increased intracranial pressure.
Helping a child - what Komarovsky says
If there are additional symptoms, Komarovsky insists on the following diagnostic methods:
- consultation with an ophthalmologist;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- neurosonography;
- CT scan;
- neurosonography through the fontanel.
The pediatrician also debunks the myth that rolling the eyes downward does not always indicate the presence of a pathology of the central nervous system or increased intracranial pressure. In babies under 3 months of age, this pupil movement is normal.
You should pay attention to additional symptoms in infants:
- active head growth;
- bouts of vomiting;
- non-fusion of sutures on the skull;
- decreased appetite;
- avoiding bright light;
- severe anxiety in the child;
- fear of loud sounds;
- additional signs of meningeal pathology.
In case of decreased tone of the muscles of the visual apparatus, the following methods are suitable:
- Massage. Manipulation is permitted only after consultation with a pediatrician. It is forbidden to carry out the procedure yourself, as eye injuries may occur. It is recommended to visit a clinic or call a massage therapist at home.
- Gymnastics. To increase the tone of a child's eye muscles, the use of bright objects or toys is recommended. Initially, it is necessary to interest the child in the object, after which it is moved to various distances vertically or horizontally. When the baby becomes uninterested in the toy, it is advisable to replace it with another item. It is useful to use a mobile above the baby's crib.
- Physiotherapy. With the help of a course of physiological procedures, the muscle fibers will become stronger, and the baby will stop rolling his eyes upward.
If there are neurological disorders in young children, independent use of nootropics or vitamins for brain activity is unacceptable. The diagnosis can be made by a neurologist who will prescribe subsequent competent rehabilitation.
During the period of falling asleep, a newborn may move his eyes upward, which does not always signal the development of pathologies of the nervous system. Consultation with a pediatrician is necessary if the child is over 3 months old and has additional signs of illness.
A common cause of decreased tone of the extraocular muscles is injury during pregnancy or labor. Hereditary predisposition plays an important role in the development of diseases of the nervous system in a child.
Was the article helpful?
Helping a child - what Komarovsky says
If there are additional symptoms, Komarovsky insists on the following diagnostic methods:
- consultation with an ophthalmologist;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- neurosonography;
- CT scan;
- neurosonography through the fontanel.
The pediatrician also debunks the myth that rolling the eyes downward does not always indicate the presence of a pathology of the central nervous system or increased intracranial pressure. In babies under 3 months of age, this pupil movement is normal. You should pay attention to additional symptoms in infants:
- active head growth;
- bouts of vomiting;
- non-fusion of sutures on the skull;
- decreased appetite;
- avoiding bright light;
- severe anxiety in the child;
- fear of loud sounds;
- additional signs of meningeal pathology.
In case of decreased tone of the muscles of the visual apparatus, the following methods are suitable:
- Massage. Manipulation is permitted only after consultation with a pediatrician. It is forbidden to carry out the procedure yourself, as eye injuries may occur. It is recommended to visit a clinic or call a massage therapist at home.
- Gymnastics. To increase the tone of a child's eye muscles, the use of bright objects or toys is recommended. Initially, it is necessary to interest the child in the object, after which it is moved to various distances vertically or horizontally. When the baby becomes uninterested in the toy, it is advisable to replace it with another item. It is useful to use a mobile above the baby's crib.
- Physiotherapy. With the help of a course of physiological procedures, the muscle fibers will become stronger, and the baby will stop rolling his eyes upward.
If there are neurological disorders in young children, independent use of nootropics or vitamins for brain activity is unacceptable. The diagnosis can be made by a neurologist who will prescribe subsequent competent rehabilitation.
Pathological causes
Eye rolling is considered a normal physiological process in a newborn, but it can also be a sign of dangerous diseases. It is necessary to study the reasons why a child rolls his eyes in order to react correctly to this phenomenon and, if necessary, consult a doctor.
Immediately after birth, some of the newborn's body systems are not yet fully developed; their final formation occurs during the first year of life. This is also true for the organs of vision. Infants have poorly developed extraocular muscles, a small size of the eyeball, an underdeveloped retina, and a weak neural connection between the optic nerve and the visual nuclei in the brain.
Parents themselves may notice this, since the newborn is not able to focus his gaze on objects. This ability, like the friendly movement of the eyeballs, begins to form by the end of the second month of life. The functionality of a child’s eyes develops gradually in the process of strengthening connections between the organs of vision and the brain.
We invite you to read: How to quickly and easily make a fur pompom with your own hands
The physiological causes of eye rolling are weakness of the eye muscles, which should hold the eyeball in its normal position, as well as poor development of the nerve centers responsible for their control. Since the muscles are controlled by the brain, you will most often see a newborn rolling his eyes when falling asleep, and this control is weakened.
Eye rolling is a normal state of a child in a borderline state of sleep.
Normally, when falling asleep, you can see the following: the baby blinks frequently, rubs his eyes and nose, fiddles with his ears, looks for his mother’s breast, yawns, his head falls back, the child rolls his eyes up. You can also see that when the baby sleeps, his eyelids open slightly and part of the white is visible.
If a newborn baby rolls his eyes, but does not have other unusual symptoms, then this condition is normal, corresponding to the level of development of his nervous system.
However, if the unusual position of the eyeballs in an infant is not associated with sleep and the child is older than three months, then you should pay attention to the possible presence of other symptoms. A condition is considered dangerous when a newborn child rolls his eyes down, there is nystagmus (involuntary small movements of the eyeballs from side to side), nervous tics (fluttering of the eyelids), convulsions and irregular breathing rhythm.
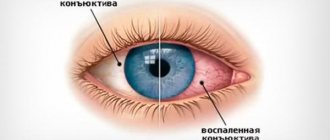
In neurological disorders, eye rolling is accompanied by nystagmus
Visual impairment in preschool children
- inflammatory or traumatic damage to brain structures such as the pons, labyrinth, cerebellum, cerebellum and pituitary gland;
- poisoning with drugs or toxic substances;
- neuroinfection;
- fever;
- genetic mutations;
- epilepsy or seizure disorder;
- hydrocephalic syndrome;
- increased pressure inside the skull;
- mental development disorder.
Nervous tension can also be expressed in children in the form of small epileptic seizures – absence seizures. In this state, the baby rolls his eyes and seems to “freeze” - all other mental functions stop (movement, humming, any reactions). After the attack ends, the child returns to his normal state. An absence seizure can turn into a grand mal seizure, so you should consult a doctor without waiting for it.
Also, the eyes may take an incorrect position if the child has pain in the eyeball or orbit due to various ophthalmic inflammatory diseases, adenoids, sinusitis, inflammation of the tonsils or otitis media, neuritis of the facial or trigeminal nerve.
The photo shows Graefe's symptom, the iris is directed downwards
An indicative appearance of the eyeball in children with hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome takes on pathological rolling. The so-called Graefe symptom or “setting sun” occurs when the eyeball is turned with the iris downward, so that a stripe of white is visible above it. This situation is caused by damage to the brain and the pressure of cerebrospinal fluid accumulated in its ventricles.
However, Graefe's symptom is not an accurate diagnostic sign of hydrocephalic syndrome. The reasons that a child rolls his eyes downward may be illnesses of the pregnant woman, rapid labor, birth trauma, prematurity or postmaturity, as well as hereditary predisposition.
Therapeutic measures
The treatment regimen is always selected individually, depending on the diagnosis. The following medications may be prescribed:
- anticonvulsants;
- sedatives;
- vitamin and restorative preparations.
For children who experience muscle weakness, physical therapy and various physiotherapeutic procedures are recommended. Thanks to this treatment, good results can be achieved. Swimming will also help eliminate the problem.
For younger children, massage is recommended, which helps eliminate excessive muscle tone and normalize their function. This type of massage should be performed by a qualified massage therapist.
Low muscle tone
It is necessary to contact specialists not only if the newborn has a rolling gaze, which is accompanied by crying. You should also go to the doctor for an examination if, at an older age (after three months), the rolling of the eyes does not stop.
An experienced specialist will conduct full research and prescribe the necessary measures to eliminate this phenomenon. If the problem is low tone of the eye muscles, the doctor prescribes special massage sessions, physical therapy and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Leading experts recommend that if muscle tone decreases in infants, hang many movable structures above the crib. The baby will watch moving objects, thereby strengthening muscle tissue.
You can strengthen the muscle tone of your eyes with the help of colorful toys and objects. To do this, it is enough for the baby to simply show them. The fact is that objects of bright colors contribute to the concentration of the baby’s gaze. Regular exercises will not only help you get rid of eye rolling, but will also give rise to the development of a healthy visual system.
It is necessary to do special exercises. Move the toys left and right, up and down, so that your child moves his gaze. At a more conscious age, if the child’s rolling has not disappeared, you can try to make the baby blink frequently and close his eyes tightly. Take your baby to a special pool and give him a massage.
If you follow all the recommendations listed, the baby's eye rolling will disappear in the near future.
Children roll their eyes
Parents often turn to pediatricians with the question of why their infant rolls his eyes or opens them during sleep. We need to figure out where is the norm and where is the pathology.
Newborns
During the period when a child is born, his muscular system is still very weak. The baby is not able to independently control his muscles. Newborn babies do not know how to focus their gaze, so if a similar symptom occurs in the period after birth, there is no need to panic and sound the alarm.
In most situations, eye rolling is the norm for a baby who has just been born. The baby may try to focus on an object that is located above it. Sometimes a child who is not holding his head will roll his eyes just to look the other way or behind him. And since his eye muscles are not yet formed, the eyelids can open a little on their own during sleep.
After a month, this should normally go away on its own, when the baby learns to control the movements of its muscular system. If by the age of three months this phenomenon remains, a mandatory consultation with a pediatric neurologist is necessary.
Up to a year
When a baby turns one month old, he should already be able to concentrate his vision on specific things and images, and control his eye muscles. If a child older than 1 month begins to roll his eyes, the reasons may lie in:
- improper maturation of the muscular system;
- in the absence of muscle tone;
- that intracranial pressure increases;
- such a phenomenon can be a dangerous signal of an epileptic seizure;
- Graefe syndrome may develop.
A symptom of Graefe's syndrome may also be the baby's eyes rolling downwards during sleep. Such pathologies are very rare, but if parents have doubts and suspicions, it is better to contact a pediatrician and neurologist to exclude the development of serious diseases.
Older
If such a symptom appears in children older than one year, this is not the norm. This is a sign of existing disorders in the body. For example, diseases of the upper respiratory tract or hearing organs may develop, and there may be pain in the facial muscles. Eyes roll as a result of natural reactions to stimuli - the child is simply trying to alleviate his condition in this way.
Sometimes parents notice when a child often squints his eyes and rolls them up and to the side. This most often occurs between the ages of 4 and 10 years. This is called a nervous tic. You should not scold your baby, since he cannot control such reactions of his body, and you should not ignore such symptoms.
Another cause of this symptom may be intracranial hypertension or epilepsy. In such cases, you need to visit a doctor for help as soon as possible and begin timely treatment.
About the work of the eyes and visual muscles of a newborn
A newly born baby still has poor control over his own limbs, and almost all of his systems are unstable, including his organs of vision. In the first month, the group of muscles that control them works unstably and often incorrectly coordinates the movements of the eyeballs of newborns.
The most common time when parents notice their child rolling his eyes is in the last few minutes before bed, when the baby is falling asleep. In the borderline state between wakefulness and sleep, the baby's eye muscles relax, and at this time the pupil and iris rise under the upper eyelid. Sometimes a newborn may roll his eyes while eating, when active sucking occurs and all the forces of the still weak body are directed towards this process.
Only in the second month of life does the baby begin to focus on objects, recognize you and your family, and before that, if the baby rolls his eyes or squints slightly, this is considered the age norm. You should keep an eye on the child and sound the alarm if the problem does not resolve itself after a month.
Advice and recommendations from doctors
A newborn can communicate all worries, pains and inconveniences only by screaming. Frequent crying, reaching the point of hysterics, when the baby twitches and cannot calm down for a long time, indicates serious problems. Another alarming sign is poor sleep, inability to relax or fall asleep soundly.
Anxiety should be caused by erratic movements of the pupils, their movement in different directions, not only upwards, when falling asleep. Unnatural twitching and uncoordinated eye movements should be reported to your doctor.
A tilted head in a baby may be a sign of certain diseases.
Developmental delay
Developmental delays - insufficient weight gain, inconsistency with other age norms - should be a cause for concern.
Strabismus
Strabismus becomes noticeable in the first months of life and requires timely treatment.
A disproportionately growing head may be a physiological feature and gradually straighten out or require serious treatment for hydrocephalus.
Vomiting, nausea
Frequent regurgitation and vomiting are a sign of an underdeveloped digestive system in a newborn. Sometimes they indicate the development of dangerous diseases.
If the baby does not eat well, regularly does not meet age-appropriate feeding standards, or the sucking reflex is poorly developed, you should consult a pediatrician.
The baby must gradually learn to coordinate his movements - pull the arms, follow the object with his eyes, turn his head towards the sound. If coordination is impaired, nervous system disorders may be diagnosed.
A dangerous sign is an increase in temperature. This is a reason to urgently call a doctor without trying to knock it down yourself.
Parents, together with doctors, must determine in time when eye rolling is not a physiological feature of young infants, but indicates the development of pathologies. An alarming sign is that the baby is already more than 3 months old, but the rolling of the eyes does not decrease; it occurs not only before falling asleep, but also while awake.
Increased intracranial pressure in an infant is characterized by many signs, including rolling and protruding eyes. Hypertension can be suspected by a disproportionate increase in head size and severe anxiety in the infant, as he suffers from headaches.
ENT disease
Severe diseases of the nasopharynx (also otitis media) can negatively affect the eye muscles and provoke their weakening. As a result, the rolling of the pupils of an infant may last longer than physiological norms.
Graefe syndrome
Eye rolling may be a partial or isolated manifestation of Graefe syndrome, caused by excess cerebrospinal fluid in the brain. In this case, rolling up is called Graefe's symptom.
It is characterized by the movement of the eyeballs down to the lower eyelid, slight mobility of dilated pupils. In this case, the baby throws his head back. Usually the muscle condition returns to normal by 6 months.
Muscular dystonia
Increased or decreased tone of the eye muscles, causing the pupils to roll back, may be a sign of muscular dystonia. This is one of the syndromes of central nervous system damage.
We suggest you read: How to rid a child of hiccups, the most effective and safest ways
Some advice from doctors for young parents:
- In the vast majority of cases, eye rolling is simply a physiological feature of infant development. Don't worry ahead of time.
- Do not skip preventive examinations by specialists - they will notice problems in time.
- Pay more attention to your baby. Talk to him while moving around the room. Let him watch his mother with his eyes - this is an effective training of the eye muscles.
- Follow the recommendations - do gymnastics for the eye muscles, massage, if prescribed.
You should not come up with your own methods of treating infants or use traditional methods without the recommendations of a pediatrician. Parents should know that a baby may roll his eyes for completely harmless reasons - due to simple underdevelopment of muscles. But it is necessary to monitor the baby’s condition and notice problems in time to help the child strengthen his muscles and stimulate his immune system. Early detection of pathologies of the eyes and nervous system will help the baby quickly cope with the disease.