A runny nose and cough in a child without fever is a problem that mothers often complain about. Such symptoms, first of all, cause concern for the baby, and also always bring a lot of trouble: cancellation of plans, absence from school (if you have a schoolchild) and often a visit to the doctor.
But perhaps it's not so scary? Let's figure out what causes a cough and runny nose without fever, how to treat it and what kind of prevention is required.
What does the absence of temperature mean?
A stable mark on the thermometer with the number 36.6 is not always a guarantee of the baby’s health. If for a day or more, parents observe snot in their child without fever, it is worth talking about the manifestation of some disease.
In this case, we can talk about bacterial, viral or allergic damage to the body.
Absence of fever with a runny nose and cough occurs in the following conditions:
- Allergic reaction.
The contact of a certain trigger on the nasal mucosa provokes excess production of mucus, always transparent in color and liquid consistency, in this organ.
This problem is especially relevant in those families where the parents already have a history of similar diseases (chronic allergic rhinitis, asthma, etc.). When coughing, a scant amount of clear or cloudy white sputum is produced.
- Respiratory infections.
In most cases, the onset of ARVI and other infectious problems in children is accompanied by a sharp increase in temperature. But sometimes this does not happen due to weakness of the immune system (temperature is the main indicator; if it is present, it means the body is fighting pathogenic flora) or for a number of other reasons.
This is dangerous due to the transition of a viral infection into a bacterial form, which in turn can take a chronic course, so the cause of a runny nose and cough should be determined immediately.
- Entry of a foreign body into the nasal cavity.
If the symptoms do not stop for a minute, it can be assumed that there is a foreign object in the nose, throat or upper respiratory tract. This condition requires immediate contact with a specialist.
- Chronic form of respiratory diseases.
Very often, diseases of bacterial origin become chronic if the child is not treated correctly. Sluggish form, characterized by periods of exacerbation and remission. The exacerbation phase is always accompanied by a runny nose, coughing or sneezing with a minimal increase in temperature. If the baby has such problems in his medical history, you should pay attention to them first.
Dry cough due to snot in a child. Can a child cough from snot?
Coughing from snot in a child is a very common occurrence. Activation of the body's defenses is characterized by the production of a large amount of mucous-serous secretions. Depending on the situation, the mucus comes out through the airways or completely covers the nasal cavity, pharyngeal ring and the back wall of the larynx. Changes in fluid output are called rhinitis. As a result of this pathology, the following may progress:
- mild rhinitis;
- outbreaks of coughing, the frequency of which increases significantly at night;
- body temperature rises;
- vomit;
- squealing in the canals.
When listening to the child's lungs, the breathing is clear and smooth. No wheezing or other extraneous noises are heard. Strong mucus discharge may be associated with the following factors:
- anatomical modifications of the osteochondral tissue of the nose;
- exposure to antigens;
- respiratory tract infection;
- the appearance of a benign neoplasm;
- changes in the regulation of blood capillary tone.
The reasons for rhinovirus infection may be difficulties with the digestive tract, suppuration of the mucous membrane of the stomach, pancreas. Quite long-term irritation of the mucous membrane provokes chronic inflammation. For this reason, the production of viscous secretion increases. The result is the development of a cough from a runny nose in a child. Predisposing factors for the disease are a state of immunosuppression, freezing, and lack of vitamins. A dry cough from snot appears due to a pathology such as adenoiditis. With such irritation, the nasopharyngeal tonsils increase in size and inhibit normal breathing. Therefore, the child will cough until the underlying illness is cured. Parents cannot independently determine what causes this cough. Only the attending physician can make an accurate diagnosis. Therefore, if symptoms appear, it is important to contact the clinic in a timely manner.
What diseases are we talking about?
A cough or runny nose without fever in a child is accompanied by many unpleasant illnesses. To determine the cause for sure, a full differential diagnosis of the following diseases is carried out:
- allergy;
- bronchial asthma;
- sinusitis;
- rhinitis;
- tonsillitis;
- bronchitis;
- ARVI;
- flu;
- pharyngitis.
First of all, in the absence of fever, the specialist assumes the allergic nature of the disease, especially if the parents have a complicated medical history.
However, based on some characteristic symptoms, you can approximately determine the cause of cough and snot on your own. Of course, this does not cancel the diagnosis and is not an indication for the use of any drugs.
Allergic reaction
Accompanied by paroxysmal cough with minimal or no sputum. The child may be bothered by expiratory shortness of breath, that is, a whistling, prolonged exhalation during normal inhalation. Tickling sensation in the nasopharynx. Characterized by nasal congestion, with the simultaneous release of copious amounts of transparent snot of liquid consistency.
Read about the causes and methods of treating allergic cough in this article.
Children often experience redness of the skin and severe itching in the neck, cheeks, upper eyelids, inner arms, behind the knees, or on the stomach. There is also lacrimation, redness and swelling of the mucous membranes of the nose and throat.
Viral and bacterial infection
The symptoms of the first are similar to allergies, which makes diagnosis difficult. With bacterial or mixed damage to the body, in most cases, a general deterioration of the child’s condition develops, which is manifested by general lethargy and drowsiness of the baby.
The chest cough reflex may be accompanied by the release of a small amount of sputum. In this case, the child has yellow or greenish, thick snot that does not pass well. Sneezing is episodic. The baby complains of pain in the nasopharynx and refuses to eat for this reason.
Foreign body
Cough barking, unproductive, incessant. There is swelling of the neck veins. The child coughs and waves his arms. A runny nose is characterized by clear mucus. Subsequently, cyanosis (blue discoloration) of the nasolabial triangle and other parts of the body develops.
After the parents have suggested the main reason for this condition in the baby, it is necessary to act according to the situation.
If, in general, the child’s condition does not cause concern, it is recommended to contact your local pediatrician. When more serious illnesses are suspected, an ambulance should be called.
Allergic reaction
A cough without a runny nose (or with a weak one) may appear due to allergies.
If a child coughs dryly and harshly, and a runny nose is accompanied by tears, redness of the eyes and face, and swelling, then most likely this is the problem.
In this case, the snot will be either completely transparent or slightly whitish.
Allergies can be triggered by anything:
- polluted city air;
- detergents, perfumes;
- smoke from cigarettes;
- plants (pollen);
- pets.
It will not be possible to isolate the allergen without the help of a specialist. After you receive recommendations from your doctor (the allergen is detected using laboratory analysis), it is worth removing from the child what triggered the allergic reaction.
The doctor will also prescribe how to treat it - antihistamines and, possibly, diet.
If your baby is prone to allergies, it is important to keep the house clean, do wet cleaning and take immune-strengthening medications.
Also, allergic rhinitis can be seasonal: in the spring, when most of the plants that cause allergies bloom, and in August (at this time, ragweed, which is the strongest allergen, blooms), it is necessary to constantly monitor how the child is feeling.
Another way to help a child with an allergic cough is breathing practices. Try:
- Game of "cow". It's simple - you need to imitate the mooing of this animal. While the baby is humming, lightly pat him on the back. You will hear the baby's voice change. This exercise helps train the ligaments and airways.
- Singing children's songs in the voices of different animals. It also has a beneficial effect on the respiratory system.
- The most common deep breaths and exhalations also contribute to recovery.
Drug treatment regimen
Therapy with medications is prescribed depending on the cause of the runny nose and cough. Treatment for allergies is significantly different from treatment for a viral or bacterial disease.
If the symptoms are of allergic origin, the following are prescribed:
- Antihistamines. Zyrtec, Tavegil, Claritin, Zodak, Suprastin and others are highly effective.
- Glucocorticosteroids. Indicated in cases where there is expiratory shortness of breath and signs of bronchial asthma. The most commonly prescribed medications are those based on salbutamol and budesonide.
- Symptomatic medications to help relieve cough and runny nose.
If the symptoms are of bacteriological or viral origin, the following are prescribed:
- General strengthening drugs. Includes vitamins, dietary supplements, and immunostimulating medications.
- General spectrum antibiotics. Indicated in the absence of positive dynamics after appropriate symptomatic therapy for 3-5 days. Only a specialist can determine the appropriate medicine.
- If the symptoms are a manifestation of influenza or ARVI, a group of drugs based on interferons is prescribed. For example, Tsitovir.
It is advisable to use any medications only after appropriate diagnosis. Otherwise, you may miss time for treatment. Often in such cases the chronic stage of the disease develops.
The child has a wet cough and a temperature of 37. Cough with temperature 37 in children
Cough in children is a common manifestation of various diseases. Parents should pay close attention to their child’s cough, especially if it is accompanied by the absence or slight increase in temperature to 37 degrees. In this case, a cough indicates ongoing inflammation in the airways. It irritates the throat, causing pain and a lot of other inconveniences to the child.
A temperature of 37 is called subfebrile and is considered normal in children under one year of age. When measured in the mouth or rectum of a healthy child, the temperature may be higher than normal. If a cough is added to its increase, you need to pay attention to the accompanying symptoms: • Intermittent breathing, wheezing in between coughing attacks; • Cough spasms, absent all day, intensify in the evening and at night, preventing the baby from falling asleep; • The sputum takes on a green tint.
The presence of such symptoms requires immediate medical attention, even if the temperature is below or equal to 37 degrees.
Do not try to relieve your baby's cough on your own. After examination, the specialist will identify the cause and help you choose the right treatment.
If you choose the wrong treatment regimen, you can seriously harm your baby.
Most parents are sure: a child’s cough and temperature of 37 degrees are an indicator of recovery or residual effects after inflammation. You can go to kindergarten with him, go for walks and not see a doctor. This is a misconception. With the help of a cough, the child’s body tries to get rid of accumulated phlegm, inflammation or allergens that have penetrated inside. Also, a prolonged wet or dry cough with a minimal increase in temperature to 37 degrees may indicate the onset of serious diseases: tuberculosis, pneumonia, etc.
Means for relieving cough syndrome
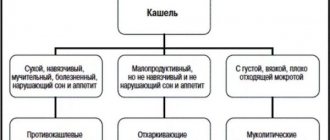
Cough can be dry or wet, so it needs to be properly treated based on this. Expectorants should not be used up to 2 years of age, mucolytics up to 5 years of age. Most drugs are also prohibited until the age of three; some drugs are not allowed for use until the age of 12.
The use of expectorants for dry cough is completely unacceptable. Such an action can cause acute bronchial obstruction (destruction of the bronchial tree). It is also prohibited to take antitussive medications for the wet version of the symptom - excessive accumulation of sputum will seal the alveoli, which will complicate gas exchange and can lead to suffocation of the patient.
Medicines for dry cough:
- Sinecode;
- Stoptussin;
- Bronchicum;
- Libexin.
Medicines from this list belong to the group of antitussives; they effectively suppress the cough reflex both at a generalized level (they block the areas responsible for coughing in the medulla oblongata) and locally (they reduce the sensitivity of receptors in the trachea and lungs).
The classification of children's expectorants is here.
Preparations for wet cough:
- ACC;
- Doctor Mom;
- Bromhexine;
- Ambroxol;
- Mukaltin.
You will find a complete list of expectorants and recommendations for their use in this article.
It is not advisable to treat asthmatic cough due to allergies (allergic bronchitis) using the above remedies. For these purposes, a special group of drugs is used to help relieve spasm and swelling of the bronchi.
Cough in asthma is eliminated using the following medication regimen:
- glucocorticosteroids - Budesonide, Mometasone, Fluticasone (The most powerful drugs. Used in a hospital setting, they eliminate allergy symptoms most effectively);
- mast cell stabilizers - Ketotifen, cromoglycic acid and others;
- leukotriene receptor antagonists - Montelukast.
Such drugs are prescribed by a pulmonologist only for serious indications. Most of them have age restrictions for use, so self-medication is unacceptable.
Cough relief for allergies
The basis of therapy is antihistamines. There are four generations of them. For the treatment of acute, paroxysmal cough, without an asthmatic component, first generation antihistamines are used: Tavegil, Suprastin, Pipolfen, etc.
If the cough is mild, preference is given to third-generation drugs Cetrin and its derivatives. Second generation antihistamines are prohibited because they have a toxic effect on the heart.
As a quick relief for bronchospasm, Salbutamol and Berodual are used in inhalation form. The drugs relax the smooth muscles of the bronchi and relieve cough symptoms well.
Dry cough in a child Komarovsky. Cough in a child under one year old without fever treatment Komarovsky
10.22. Symptomatic therapy. Cough
Let's start with the main and obvious. Cough is not treated, the disease that led to the cough is treated. There is something that irritates the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract and leads to the formation of sputum. If we eliminate this “something”, the cough will stop. How can we eliminate it? For a bacterial infection, we will prescribe an antibiotic, for allergies, an antiallergic drug, for a viral infection, we will simply wait until the body copes with the virus itself. What is so important and obvious about this? First of all, a statement of the fact that cough will not go away until the cause of the cough is eliminated. That is, if you or your child cough because the room is very dry, you will continue to cough either until you buy a humidifier, or until spring comes and the central heating turns off. Obviously, we can destroy bacteria in bacterial infections, we can significantly reduce the body’s reaction to an allergen in allergic diseases, but we are not able to do anything with viruses. Thus, with ARVI, i.e. in 99% of all acute respiratory infections, we cannot eliminate the cause of the cough! We patiently wait until the body forms antiviral immunity, the virus stops its harmful effects on the mucous membranes and the cough goes away on its own. At the same time, the cough significantly interferes with the existence of the sick child and the relatives around him. Therefore, simply “waiting patiently” does not work. Need to do something! And it really is necessary! After all, coughing during acute respiratory infections is not just a symptom that interferes with life, it is the main, key mechanism for actively clearing the respiratory tract. Hence, in fact, the main principle of symptomatic treatment of cough follows - not to eliminate the cough, but to increase its effectiveness! The most important feature of an effective cough is that it is not frequent. Sputum accumulated, coughed, cleared the airways. We got a break until a new portion of sputum requires a new cough impulse. “Coughed, cleared” is a model of an ideal situation. But this does not always happen - sometimes, in order to clear it, you have to cough twenty times... What determines the answer to the question: “How many times is it necessary”? What factors determine the effectiveness of a cough? • The ability to cough - that is, the strength of the cough impulse and the ability to cough consciously. It is clear that the older the child, the stronger the respiratory muscles, the greater the volume of exhaled air, the stronger the cough impulse, the more effective the cough. An obvious “disadvantage” of infants is that you cannot ask them to cough, they are still unconscious... • Quality of sputum. Liquid sputum - easy to cough, effective cough; thick sputum - it is very difficult to cough: we cough, cough, cough, but all to no avail... We cannot influence the ability to cough in any way. Therefore, the leading, strategic direction in the symptomatic treatment of cough is to influence the quality of sputum, improve its rheological properties and thus increase the effectiveness of cough. Where does the effect on sputum rheology begin? From the main thing that we have already talked about many times, what we are forced to talk about again and again, to which we will constantly return - from compliance with the most important organizational principles of treatment of acute respiratory infections, which turn into the main rules of symptomatic treatment of cough: 1. Mode of cool, moist air - prevention of drying out of sputum and mucous membranes. 2. Drinking plenty of fluids - maintaining and restoring sputum rheology by ensuring normal blood rheology. It is possible to name and discuss medications that affect cough only after the two main rules we formulated are implemented. Dry, warm, refuses to drink - nothing will help. Therefore, before you run to the pharmacy for “cough medicine,” you need to clearly set priorities, understand what is primary (air and liquid) and what is secondary (potions, drops, syrups, tablets, etc.).
Remedies for runny nose
Medicines for the common cold should also be used correctly. Drugs are divided into several groups, each of which solves a specific problem or has a complex effect at once.
As a rule, a runny nose caused by an allergic reaction quickly disappears after oral administration of the above antihistamines. For a complete list of medications and treatments for allergic rhinitis, read this article.
To speed up the effect, you can use drops based on xylometazoline. This active substance has a vasoconstrictor effect and quickly stops the flow of mucus from the nose and removes swelling.
Attention should be paid to the concentration of nasal drops. 0.05% is used in children from 2 years of age, and 1% is suitable for use in children after 6 years of age.
The list of drugs includes:
- Rinorm;
- Galazolin;
- ForNose;
- Rhinotaiss;
- Xylene;
- Rhinostop;
- Snoop and others.
A complete list of vasoconstrictor drugs and their classification by age can be found in this article.
A child has a cough at night. How to calm a child's cough at night
It is difficult to remain calm when a child wakes up at night in a coughing fit, cries and then cannot fall asleep for a long time. In panic, adults forget that coughing is primarily a protective reaction of the body. It “evacuates” all foreign microparticles and microorganisms from the respiratory tract. Thus, a child’s cough at night is a blessing, even if it is a symptom of some disease.
Why does the cough get worse at night?
Any cough worsens at night. After all, the child is in a supine position. The mucus does not dissolve and clogs the nasopharynx. The sputum in the lungs is worse diluted, since their blood supply is slowed down in a supine position. As a result of all this, a reflex cough occurs. In addition, air, cold or overheated, can irritate the laryngeal mucosa. The body's response will be adequate. But it is also more difficult to cough while lying down than in an upright position. Therefore, a child’s cough at night is longer and more intense than during the day.
Healthy cough at night.
The next morning, responsible parents take the child to the doctor, even if there are no other symptoms of the disease. In most cases, it turns out that the baby is absolutely healthy, it’s just that the air in the room is overheated. In this case, cough in children is a physiological reaction of the body. Eliminating the cause is simple: adjust the microclimate in the house and give the child plenty to drink. During the heating season, it will not hurt to install an automatic humidifier. In the evening, the child’s room must be ventilated. And clean out the nose of the little ones so that they can breathe well at night. If mucus has accumulated, rinse with sea salt solution.
Pathological causes of night cough
But you can't ignore a cough. After all, it is not a disease in itself, but a symptom. The cause of a child's night cough should be determined by a doctor. And as soon as possible. After all, the body signals to them about some kind of disease. It could be:
- upper respiratory tract infections, bacterial and viral;
- whooping cough;
- emotional stress;
- exposure to any allergen on the body;
- toxic irritation of the respiratory tract (the child may have inhaled harmful gas);
- pathologies of cardiac activity;
- some gastrointestinal diseases;
- helminths.
Only after diagnosis can treatment begin. But not the cough, but the illness that accompanies it.
- Allergic cough. Sometimes it happens that a child behaves cheerfully all day and evening, looks healthy, but as soon as he gets into bed, he starts coughing. This could be an allergic reaction of the body to something present in the bed. Feathers, down, sheepskin from a pillow, paint from a bedding set, varnish from trim, mattress stuffing, poorly rinsed linen - whatever. Look for the allergen and get rid of it as quickly as possible. Often in this case, a cough is accompanied by a runny nose.
- Difference between cough in ARVI, whooping cough and asthma. A cough caused by ARVI will torment the baby around the clock, but not debilitatingly. And especially at night. If the night cough takes the form of an attack that does not go away until vomiting, the baby’s face turns red, it is difficult for him to breathe, his tongue sticks out, then the reason is much more serious. Bronchial asthma may develop. A cough that gets worse in the morning is the most likely symptom of this. Or the baby got whooping cough. Or he was given a DTP vaccine and the body reacted inadequately to the pertussis component. Prolonged use can lead to laryngospasm.
- Cough due to gastrointestinal diseases. It is easier in older children to suspect that a child’s severe cough at night is associated with gastrointestinal reflux. They also complain of heartburn. Very young children are unlikely to be able to explain their condition in this case.
- When teeth are being cut. Babies may cough when they are teething. At the same time, salivation increases, the child chokes on saliva, and therefore coughs. If this is the cause of the cough, place your little one on its side to sleep. Or place a cushion under the mattress so that the head is higher.
Reasons for the development of pathology
The presence in a child of a cough with a runny nose without fever is a sign of an incipient cold or allergy
The main signs of a cold, which can occur when various viruses enter a child’s body, are a runny nose and cough. The baby’s immune system begins to react to pathogenic microorganisms and enter into a peculiar reaction with them.
However, in some cases, problems arise with recognizing the virus and it easily penetrates into the cells of the body. If a bacterial disease develops, an increase in body temperature is immediately noted, but with a viral infection, the indicators remain normal.
In the absence of effective treatment for viral rhinitis, the risk of developing a severe inflammatory process in the sinuses increases, that is, sinusitis develops.
Parents need to understand that pathogenic microorganisms may enter the throat and trachea area.
In such a situation, in the absence of effective treatment, complications may develop in the form of:
- sore throat
- bronchitis
- tracheitis
- pharyngitis
- pneumonia
The penetration of various viruses into the child’s body significantly disrupts the functioning of the immune system, so the course of such a disease can be supplemented by a bacterial infection. With ARVI, other pathogenic microorganisms present in the child’s body are also activated, which leads to the development of an inflammatory process in the ENT organs.
Parents need to understand that even in the absence of fever with a cough and runny nose, it is imperative to show the child to a specialist who will find out the causes of this condition and prescribe effective treatment.
Useful video - Cough in children: causes, types and treatment
In some cases, the cause of cough and runny nose without fever may be the development of allergic rhinitis. Most often, this pathology is diagnosed in children and adults who spend a long time in a dusty room. Allergic rhinitis can occur as a reaction to chemicals, pollen, children's cosmetics and animal dander. In some cases, even healthy children may experience a runny nose and cough without fever due to too dry air in the children's room.
If a cough and runny nose without fever bother a child for a long time, this may be a dangerous signal. An allergic reaction can lead to the development of such a complex disease as bronchial asthma. It is for this reason that it is necessary to show the child to the doctor in time, which will avoid the development of many complications.
Drug treatment
It is important to remember that in childhood it is necessary to use various medications only after consultation with a specialist.
To combat a viral infection, antiviral drugs are usually used, since without their help it is unlikely to achieve a positive result.
Features of treatment:
- The following drugs have a good effect in the treatment of viral diseases: Ingavirin, Remantadine, Isoprinosine, Ribavirin, Arbidol.
- Such antiviral drugs can be used in children from the first day of their birth. In order to activate the body's strength to fight the disease during drug therapy, interferonogenesis inducers are prescribed: Laferon, Cycloferon, Viferon, Anaferon.
- A severe cough and nasal congestion cause children a lot of inconvenience and anxiety, so it is necessary to get rid of unpleasant symptoms. To eliminate nasal congestion and restore breathing, experts prescribe the use of the following medications: Tizin, Farmazolin, Nazivin, Galazolin. It is important to remember that such vasoconstrictor drops are allowed to be used for no more than 5 days, otherwise the risk of developing allergic rhinitis increases. If a child is bothered by a wet cough, treatment should be carried out using medications that help dilute mucus and remove it from the respiratory tract.
- The following drugs have a good effect in the fight against wet cough: ACC, Mucaltin, licorice root tincture.
- If a child is bothered by a dry cough, drugs such as Libexin, Pertussin and Tusuprex are usually used to eliminate it.
- In some cases, a child may suffer from a prolonged cough combined with nasal congestion, but without fever. In such a situation, it is recommended to give the child herbal breast milk, however, this must be done after consulting a doctor. The fact is that such a collection has a suppressive effect on cough, which can disrupt the process of sputum discharge and cause the development of an inflammatory process in the lungs.
- Often a cough and runny nose without fever is a manifestation of an allergic reaction against the background of an inflammatory process in the body. In such a situation, to eliminate tissue swelling and relieve an allergic reaction, the following antihistamines are prescribed: Loratadine, Zaditen, Suprastin, Tavegil.
Problem Definition
A cough, like a runny nose, is just an indication of a problem in the body, for example, an infection, a cold or an allergy. If there is an inflammatory process in the body, then such a symptom as fever will not be long in coming. But if it is not there, it can be difficult to determine how dangerous the disease is for the child.
Let's consider the probable causes, ranking them according to the degree of possible threat. By the way, the term “runny nose” used by doctors is often changed to the colloquial “snot”. In the article, both concepts will be used equally, as they are found in everyday life.