Material tested:
Kravchenko Boris Sergeevich, surgeon - 11/12/2019
A coagulogram is a blood test to measure its coagulability. It is important for doctors to know this result when preparing a patient for surgery. It is necessary to have data on blood clotting if a person has a disorder, if there is a history of diseases of the liver, cardiovascular and autoimmune systems, or varicose veins of the lower extremities. Using a coagulogram, the causes of bleeding are determined and the condition of a woman’s blood is monitored during pregnancy.
Blood clotting in children
Blood clotting in children - coagulogram, acts as the main diagnostic test necessary to obtain information about the health status of the whole organism.
Depending on how well or poorly this process occurs, clinicians can talk about the child’s predisposition to developing internal hemorrhages or the formation of blood clots. Such values can be either high or low, which in any case is a problem that needs to be dealt with. Most often, this or that deviation is influenced by pathological reasons, however, sometimes changes in indicators can be caused by irrational use of medications.
The coagulogram in children is divided into general and detailed. In the vast majority of cases, clinicians turn to the first type of analysis, which includes only 4 factors, while the second type combines approximately 30 different indicators.
In order for the blood clotting time to be determined correctly, this category of patients must prepare for the described diagnostic test. Parents must strictly ensure that several simple preparatory activities are carried out accurately.
Since blood clotting in children is assessed by studying biological material obtained from a vein, it is quite natural that such a process has its own algorithm.
Indications for the test
In the vast majority of cases, a child’s blood clotting is assessed to confirm the occurrence of a particular disease, since deviations from the norm often have a pathological basis.
Nevertheless, such an analysis should also be carried out for preventive purposes - to monitor the hemostasis system and the general health of the human body.
Other indications for such a diagnostic procedure are:
- control over anticoagulation therapy - in some cases, treatment of a particular disease involves taking anticoagulants, which inhibit the ability of blood to clot;
- routine examination before surgery;
- suspicion of DIC syndrome;
- diseases of the hematopoietic system;
- uncontrolled use of any medications;
- chronic liver diseases;
- frequent bleeding that does not stop for a long time;
- lagging behind peers in growth, mental or physical development.
Normal values for children
The assessment of the coagulability of the main biological fluid includes an impressive number of indicators, each of which can deviate upward or downward, for which there are reasons.
The permissible values of blood clotting in children are summarized in the following table:
Activated partial thromboplastin time
Activated recalcification time
Plasma recalcification time
Plasma tolerance to heparin
Soluble fibrin-monomer complexes
no more than 4 mg per 100 ml. blood
The norm for blood clotting in children will differ depending on the calculation method:
- according to Lee-White - 5-10 minutes;
- according to Mas-Magro - 8-12 minutes.
The duration of bleeding may also vary depending on the method chosen.
Blood clotting in children is normal:
- according to Duke – 2-4 minutes;
- according to Ivy - no more than 8 minutes;
- according to Shitikova - no more than 4 minutes.
Norms of coagulogram results in children
- The clotting time for a child in full health is 4-9 minutes.
- Thrombin time. The result should be equal to 30 minutes with an error of 3 minutes.
- Prothrombin index - the norm is 70-100%.
- Fibrinolytic activity. The result should be 180-260 seconds for a healthy child.
- Activated partial thromboplastin time. The number can vary from 24 to 35 seconds.
- Fibrinogen concentration in blood plasma. The test result for a healthy child should be 1.25-4 g/l.
- Thrombotest - IV-V stage.
- AVR or Activated recalcification time - the time indicator should correspond to 50 -70 seconds.
- Soluble fibrin-monomer complexes - the level of this substance in the blood of a healthy child should not be 4 mg\100 ml.
- Plasma tolerance to heparin should normally be 3-11 minutes.
- Fibrinogen - 5.9-11.7 µmol/l.
- Duke bleeding time. The indicator in healthy children is up to 4 minutes.
- The normal time for plasma recalcification is 90-120 seconds.
- Blood clot retraction - 30-40%.
- Prothrombin - the norm is 78-142%.
- Lupus anticoagulant - negative.
Decoding the coagulogram
As mentioned above, a blood coagulogram includes many parameters, each of which has its own description:
- clotting time is the period of time between the onset and cessation of bleeding;
- prothrombin index - is an indicator reflecting the ratio of normal blood clotting time to the length of time that such a process takes in a particular patient;
- thrombin time - indicates the rate of conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin;
- APTT - shows the effectiveness of stopping bleeding by forming a fibrin clot;
- AVR – allows you to evaluate the course of one of the stages of coagulation;
- GRP is a value that correlates with ABP and reflects the clotting period of citrate serum after calcium salt preparations have been added to it;
- fibrinogen - is a protein compound that is synthesized in the liver, and under the influence of clotting factors it is transformed into fibrin, which forms clots;
- RFMK - indicates a change in the structure of proteins at the molecular level under the influence of plasmin and thrombin;
- platelets are the formed cells of the main biological fluid of every human body;
- antithrombin III - is a specific protein of the coagulation system;
- thrombotest – indicates a sufficient concentration of fibrinogen in the child’s blood;
- fibrinogen B also acts as a specific hemostasis protein.
Features of hemostasis in pregnant women: research and interpretation of results
Changes that occur during the gestational period affect all body systems, including the process of hematopoiesis. During pregnancy, hemostasis norms change, and assessment should be based on compliance of gestational age with reference values. The main factor in changes in blood clotting is associated with increased risks of bleeding during termination of pregnancy, placental abruption and during childbirth, and therefore fibrinolysis is suppressed.
Hemostasis of the gestational period
Normal indicators change with increasing gestational age.
| Normal 1st trimester | Normal 2 trimesters | Normal 3 trimesters | |
| Fibrinogen | 2,9-3,1 | 3,0-3,5 | 4,4-5,1 |
| APTT | 36-41 | 33,6-37,4 | 37-40 |
| AVR | 60-72 | 56,7-67,8 | 48,2-55,3 |
| PI | 85,4-90,1 | 91,2-100,4 | 105,8-110,6 |
| RFMK | 78-130 | 85-135 | 90-140 |
| Antithrombin III | 0,222 | 0,176 | 0,155 |
| Platelets | 301-317 | 273-298 | 242-263 |
Reasons for rejection
Both an increase and a decrease in each of the above indicators has individual reasons. It follows from this that the treatment of any disorder consists of getting rid of the provoking factor.
In a newborn baby or older children, the sources of deviation will be common:
- Prothrombin increases due to the formation of blood clots, and decreases with hypovitaminosis K or irrational use of medications.
- Fibrinogen - decreases due to liver pathologies and insufficient intake of vitamins or nutrients into the body. The increase is affected by extensive burns, pneumonia and a wide range of infectious diseases, tumor processes and endocrine disorders.
- Thrombin time may decrease with excess fibrinogen. The reasons for the increase include renal failure and autoimmune diseases.
- Extensive bleeding contributes to a decrease in PTI, and the appearance of blood clots contributes to an increase.
- A high APTT is characteristic of severe DIC, hemophilia and liver diseases. At the same time, low values indicate the beginning of the development of DIC syndrome.
- A decrease in AVR is typical for thrombophilia, and an increase is characteristic for heavy bleeding.
- Plasma tolerance to heparin increases due to any liver damage, and decreases against the background of pathologies of the cardiovascular system, oncopathologies or surgical intervention.
- Lupus anticoagulant appears in cancer and gastrointestinal diseases.
- RFMC may increase with increased activity of the blood coagulation system. The reduction is often facilitated by taking heparin.
Increased blood clotting is observed against the background of:
- severe inflammation;
- late stages of DIC syndrome;
- systemic pathologies;
- extensive burns;
- cancer processes;
- peritonitis;
- pneumonia;
- pyelonephritis.
Poor blood clotting in a child is observed when:
- anaphylactic or hemorrhagic shock;
- initial stages of progression of DIC syndrome;
- myxedema.
In any case, the cause is determined not only with the help of a coagulogram, but also through a comprehensive examination of the body.
Preparation and stages of the procedure
Such a blood test involves taking biological material from a vein. In order for the hematologist to obtain the most accurate results during interpretation, even the smallest patients need to prepare for such a diagnostic event.
The main stages of preparation for children are presented:
- refusal to eat food at least 8 hours before visiting a medical facility;
- on the day of the study, black and green tea, juices and carbonated drinks are prohibited (only purified water is allowed to drink);
- One hour before the test, you should stop smoking cigarettes and drinking alcohol;
- 15 minutes before performing such a test, it is very important to eliminate physical and emotional stress.
If a child takes any medications, then parents must inform the specialist about this. If the above rules are not followed, the interpretation of the results will have errors, which is why the patient may be prescribed treatment that is completely unnecessary for him. This means that the blood test will need to be repeated, which is extremely undesirable for children.
Taking blood from a child also has some rules, namely:
- taking the test material should be carried out only with a dry, sterile syringe or using a vacuum system;
- the procedure is carried out with a wide-bore needle, and a tourniquet is not used, as in a biochemical blood test;
- filling 2 test tubes with blood, while only the second one is sent for study;
- the mandatory presence in the test tube of a special coagulant - sodium citrate.
The rate of blood clotting is the most important indicator, so such a study must be carried out on a regular basis. Early detection of deviations will protect children from the development of complications and death.
source
How to take a blood test?
A very important factor when donating blood for a coagulogram is following certain rules. It is recommended to take blood tests in the first half of the day, preferably in the morning, since blood counts may change during the day. Before taking the test, you should limit your food intake for 24 hours and completely abstain from eating 12 hours before the test. This also applies to juices, sweet drinks, coffee, tea. Pure still drinking water can be consumed in any quantity.
Before taking the test, you should calm the child down and distract him so that his pulse returns to normal.
Blood for analysis will be taken from a vein from a child, so explain to him that it is not painful and not scary. If you are taking medications that affect the blood clotting system, or have previously had blood transfusions or surgical interventions, you should inform your doctor. The more the doctor knows about the child’s health, the more accurate the coagulogram results will be. After taking the test, you should not strain the arm from which blood was taken for 1 hour. It happens, although extremely rarely, that a hematoma forms at the puncture site. It does not pose any danger, but to prevent its occurrence, you must follow the instructions of medical personnel.
Coagulogram: what kind of analysis is it, deciphering hemostasis indicators
Coagulogram is a comprehensive analysis of blood clotting indicators. Studies of venous blood using the coagulometry method help assess the condition and efficiency of functioning of various parts of such blood systems as coagulation, anticoagulation and fibrinolytic.
Indicators of a coagulogram, or hemostasiogram, are studied to assess the possible risk of hyper- and hypocoagulation, respectively, increased and decreased blood clotting ability, the likelihood of blood clots or bleeding.
In what cases is a blood test for coagulogram prescribed?
Regardless of the presence of any symptoms and signs of blood coagulation pathologies, a hemostasis test is prescribed in preparation for surgery and during the gestational period. In this way, the likelihood of life-threatening risks of bleeding and thrombosis during surgery or delivery (naturally or by caesarean section) is assessed. Other indications for this analysis include:
- gestosis of pregnancy, as well as repeated miscarriages;
- injuries accompanied by internal and/or external bleeding;
- the presence of a tendency to thrombus formation, thrombosis, varicose veins of blood vessels, a tendency to thromboembolism;
- heart attack, history of stroke, pre-infarction conditions, ischemia, arrhythmia;
- pathologies of the circulatory system;
- liver dysfunction;
- monitoring the condition during anticoagulant therapy;
- hemorrhagic pathologies, chronic anemia, frequent nosebleeds, heavy menstruation, inclusions of blood in discharge (urine, feces), sudden loss of vision, etc.;
- long-term therapy with anabolic drugs, glucocorticosteroids, oral contraceptives;
- routine medical examination.
How to prepare for a blood clotting test
This study is carried out strictly on an empty stomach, with a break after the last meal of at least 12 hours. At the last meal, it is recommended to exclude spicy, fatty, canned foods with a lot of spices from the diet. As for drinks, only pure, non-mineral water is allowed; juices, compotes, drinks and alcohol are excluded.
Immediately before the analysis, it is recommended to avoid physical, emotional and mental stress (fast walking, excitement), as well as smoking, for 30 minutes. If you are currently or have recently completed a course of treatment with anticoagulant drugs, you must inform the specialist of the name, dosage and duration of use. If during blood sampling you experience nausea, dizziness, or deterioration in health, you must immediately inform medical personnel.
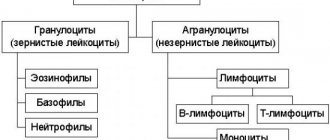
Components of the hemostasis system
The hemostatic system includes biological substances and biochemical mechanisms that maintain blood in a liquid state, as well as prevent and stop bleeding. The main function of the hemostatic system is to maintain a balance between coagulating and anticoagulant factors. An imbalance is realized by hypercoagulation (increased blood clotting, leading to the formation of blood clots) and hypocoagulation (decreased coagulation, threatening prolonged bleeding).
Blood clotting is ensured by two mechanisms: external and internal. When tissue injuries and violations of the vascular walls occur, tissue thromboplastin (factor III) is released, which triggers the external process of blood clotting. The internal mechanism requires contact between the collagen of the endothelium of the vascular walls and blood components.
Extended coagulogram and its meanings
In some cases, the doctor needs to examine not only the blood clotting ability, but also the activity of the opposite process - fibrinolysis. Based on these parameters, a conclusion is made about low or high foldability.
When is it worth taking an extended coagulogram?
Nosebleeds
If the patient is undergoing extensive surgery, the administration of anticoagulants or hemostatic drugs, to establish a diagnosis of increased bleeding or vascular pathology, an extended research technique is prescribed, which includes:
- lupus anticoagulant,
- protein C and S,
- D-dimer.
A detailed study of the blood condition is necessary for bleeding from the nose, gums, frequent skin hemorrhages, heavy periods, and anemia. A coagulogram study is not carried out for acute infections or inflammations, autoimmune processes. When examining a patient, a biochemical and general analysis of blood and urine is simultaneously performed to obtain complete information.
What will the INO tell you about?
The international normalized ratio is equal to the obtained prothrombin time, which is divided by the average value. Used in anticoagulant treatment. If it is below 0.8 - 1.1, then this is a sign of a risk of vascular thrombosis. A high INR indicates a tendency to bleed.
What is APTT and why is it prescribed?
APTT shows how the blood clots when reagents are added. It is prescribed to patients who receive Heparin or Fraxiparine. A low APTT occurs with high coagulation activity and a tendency to form blood clots, and an increased APTT occurs with a risk of bleeding.
D-dimer indicator and its meanings
D-dimer appears in the blood when a fibrin clot breaks down. If this indicator is below 248 ng/ml, then this means that there is the formation of blood clots and the breakdown of fibrin fibers in the body.
Fibrinogen and features of its indicators
This substance is the basis of a blood clot. It increases during inflammatory and necrotic processes in the tissue and can serve as a diagnostic sign of myocardial infarction. Low fibrinogen is found in hereditary syndromes of increased bleeding and liver diseases.
To learn how coagulometry is carried out and deciphering the indicators, watch this video:
Indicators and norms of hemostasis
When studying indicators, different laboratories may use different techniques. Thus, the speed rate of the coagulation process varies from 5-10 to 8-12 minutes depending on the chosen technique (according to Lee-White or Mass and Margot). The assessment of compliance of results with the norm must be carried out in accordance with the standards of the specific laboratory.
| Indicator name | Accepted notation | Norms, units of measurement |
| Prothrombin time | PT | 11-15 s. |
| INR | INR | 0.82-1.18 |
| Prothrombin index | PTI | 72-123 % |
| Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time | APTT | 23-36 s. |
| Thrombin time | TV | 14-21 pp. |
| Activated Recalcification Time | AVR | 81-127 p. |
| Antithrombin III | ATIII | 76-126 % |
| D-dimer | 250-500 ng/ml | |
| Soluble fibrin-monomer complexes | RFMK | 0.36-0.48 units |
| Fibrinogen | 2.7-4.0 grams |
Each norm of a coagulogram and its components in the table is given without taking into account gender and age indicators and individual characteristics. To decipher hemostasis indicators, you must contact a specialist.
Low blood clotting
It happens with hemophilia, hereditary deficiency of clotting factors, vitamin K hypovitaminosis:
- High numbers: PTI, thrombin time, APTT, proteins C and S.
- INR, fibrinogen and D-dimer levels are below normal values.
The coagulogram allows you to accurately determine the coagulation system, fibrinolysis and anticoagulant properties of blood. The results are used in surgery, cardiology, and hematology. The assessment of indicators is carried out in combination with data from other research methods and clinical signs.
Interpretation of hemostasis indicators
What is included in a coagulogram study? A basic hemostasis study includes several indicators assessed together.
Blood clotting time indicator
This indicator assesses the rate of formation of a fibrin clot at the site of injury and is assessed by the time interval between the onset of bleeding and its cessation. For venous blood, the reference rate of thrombus formation is 5 to 10 minutes.
Exceeding the indicator often indicates the presence of diseases and conditions such as thrombocytopenia, hemophilia, vitamin C deficiency, liver pathologies, and also occurs during therapy with indirect anticoagulants (Trental, Warfarin, Aspirin, etc.). A reading below normal indicates an accelerated ability to form clots, and may also decrease after extensive bleeding. In women, a decrease in clotting time is observed while taking contraceptive medications.
Changes in indicators with increased clotting
A high risk of blood clots forming inside a vessel occurs when there are such changes in coagulogram parameters:
- Above normal – INR, fibrinogen, D-dimer.
- Low level – PTI, thrombin time, APTT.
These signs give reason to suspect thrombosis, thromboembolism, intravascular coagulation; such tests are typical for the last months of pregnancy, in the post-traumatic or postoperative period.
We recommend reading about the abdominal form of myocardial infarction. You will learn about the types of atypical necrosis of the heart muscle, clinical symptoms and diagnosis of the abdominal form of MI, treatment. And here is more information about how an ECG is done.