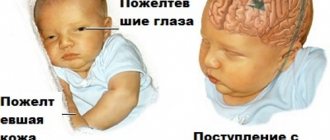
The appearance of worms in infants negatively affects their development and health. Giardia appears in infants at 1 year of age due to various reasons. Giardiasis can present with mild symptoms for a long time, and it becomes very difficult to detect. If it is still possible to identify parasites in a child’s body, a helminthic disease requires immediate treatment. How to cure giardiasis in a small child, and are there measures to prevent helminthic infestation?
Giardia in a child's stool: symptoms of the disease
When released into the environment, living individuals live for about half an hour, after which they die, so diagnosing them can be quite difficult.
Giardia cysts in a child’s stool have the following symptoms:
- Abdominal pain localized in the navel area, accompanied by vomiting and foul-smelling diarrhea (up to 10 times a day).
- Chills, temperature rise to 37.2-37.5.
- Dry cough, similar to an allergic one.
- Decreased child reaction, apathy, tearfulness.
- Sudden weight loss.
- Grinding of teeth during sleep (bruxism).
- Enlarged spleen and lymph nodes.
- Reddish rash on the skin.
These symptoms are characteristic of many intestinal diseases and only a doctor can correctly diagnose.
Differential diagnosis
Since giardiasis has a rather non-specific clinical picture, reminiscent of other diseases, differential diagnosis is necessary. First of all, it is important to distinguish giardiasis from intestinal infections, because the gastrointestinal changes are similar.
Differential diagnosis:
- salmonellosis: characteristic “swamp mud”-type stool, pain in the right iliac region. Bacteriological research allows you to isolate the causative agent of the disease;
- yersiniosis: stool mixed with blood, mucus, enlarged lymph nodes and liver. Laboratory examination of stool also helps in making the correct diagnosis;
- rotavirus infection: copious, watery stools, frequent vomiting, a combination of these symptoms over a few hours can lead to dehydration of the child’s body. Along with the above changes, catarrhal symptoms are often detected in children. Stool examination reveals rotavirus;
- amebiasis: painful abdomen in the lower parts, stools mixed with blood like “raspberry jelly”. Stool microscopy does not raise doubts about the diagnosis;
- acute appendicitis: the disease develops suddenly, the child’s condition worsens. The stool analysis will be unchanged. A consultation with a surgeon and an instrumental examination of the child is indicated for a quick and accurate diagnosis;
- shigellosis: a characteristic stool of the “rectal spit” type is observed - stool mixed with greenery, mucus, and blood. Tenesmus (false urge to defecate) appears. Abdominal pain is cramping in nature. Bacteriological examination of stool reveals the presence of Shigella.
How does Giardia infection occur?
The disease is transmitted in the following ways:
- Water , as the main method, since parasite cysts can stay in it for a long time. Using unfiltered water, a person is almost immediately exposed to the risk of infection. To avoid this, it is recommended to boil the water, since at high temperatures Giardia die.
- Food. Eating unwashed vegetables, fruits, or thermally poorly processed meat.
- Fecal-oral method , using other people's hygiene items, household items and rarely washing your hands. It is especially common in people who bite their nails.
You can often hear that the disease is transmitted through animals, in particular cats. However, this is a misconception, since parasites can only get through the interaction of a cat with water, after which a person uses it or through a kiss with an animal. Therefore, close contacts should be avoided. But it won’t be transmitted by kissing a person, because cysts cannot survive in human saliva.
Preparing the child for tests
Parents usually wonder how to get tested for Giardia in a child, so that the patient can be correctly diagnosed and appropriate treatment prescribed. It is necessary to understand that only compliance with all standards will help to obtain correct results. Before taking tests, the child must be prepared for this. There are a number of conditions that must be strictly adhered to. Before donating blood, you must consider the following rules:
- blood must be donated exclusively on an empty stomach;
- the day before the test, you need to exclude fatty, fried and spicy foods from your diet;
- Strong physical activity is not allowed before examinations;
- It is prohibited to use medications without the recommendation of the attending physician;
- you cannot drink any drinks other than water;
- It is prohibited to donate blood after X-rays, physiotherapeutic procedures and rectal examination.
Stool research has some of its own characteristics in preparation for analysis. The sample is taken over three days, after which the procedure is repeated ten days later. There are preparation rules, which include:
- You should not use antiparasitic drugs for a week.
- If the stool is characterized by high density, the use of laxatives such as Dufalac is allowed. The analysis result will be more reliable if the sample has a liquid phase.
- In cases where there is a suspicion of an acute stage of giardiasis, tests must be carried out immediately after taking samples. Analysis carried out later than twenty minutes from the moment of material selection is not reliable enough.
Another important point is that a sample that has not been processed within 24 hours after collection is not suitable for analysis. Areas of stool with a changed appearance are best suited.
How dangerous is giardiasis for a child?
When diagnosing a disease, it is important to begin treatment immediately. The younger the baby, the more difficult the consequences will be.
Consequences of giardiasis:
- Since the incubation period is at most two weeks , the cyst is covered with a special protein, interaction with which causes toxic and allergic reactions in the body, resulting in attacks of asthma, eczema, dermatitis, etc.
- In addition, parasites feed on beneficial substances that enter the child’s body, sticking to the mucous membrane of the small intestine and sucking beneficial substances from the blood. Because of this, vitamin deficiency occurs. For children under 3 years of age, this is fraught with developmental delays.
- As a result of the proliferation of Giardia, a disruption of beneficial microflora occurs in the body (especially in the intestines) due to the toxic substances released. This further disrupts the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Chronic self-poisoning syndrome occurs due to a sharp decrease in immunity, leading to damage to human systems and organs that are difficult to treat.
What is Giardia in children
Giardia are parasites that inhabit the small intestine, gallbladder, and duodenum, which lead to disruption of the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract. Such microscopic helminths are especially dangerous for the liver, as they contribute to the gradual destruction of this valuable organ. If a child has Giardia, they can be detected in the stool, with which they are partially excreted. Externally, cysts (protozoa) look like small white worms and are characterized by increased activity. If the parasites are not killed in time, the symptoms manifest themselves with double intensity.
Articles on the topic
- Face mask with aspirin
- How to get rid of subcutaneous acne on the face quickly
- At what temperature can inhalations be done?
What causes lamblia in children?
The cause of the disease may be an environmental or social factor, and infection occurs more often in people with weakened immunity and a tendency to pathological processes in the digestive system. Giardia appears in children in the intestines through the oral cavity, and moves all the way to the stomach. There they feel a favorable environment for further development and spread - giardiasis progresses. The routes of transmission of pathogenic infection are as follows:
- upon contact with toys, contaminated dishes, and everyday items;
- in case of eating unwashed berries, fruits, vegetables;
- in the absence of boiling water;
- with earth, sand;
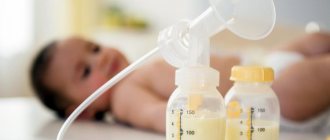
- through mother's milk during breastfeeding.
Do I need to treat and how to recognize giardiasis?
Treatment for Giardia in children is one of the most common after a cold. This is due to the fact that the transmission routes are very simple. Treatment of giardiasis in adults, the treatment regimen is covered here.
Despite this, expert opinions differ on treatment methods:
- Some do not consider giardiasis a disease as such, because without pronounced symptoms that do not cause inconvenience to the child, the body itself fights by producing antibodies.
- Others are of the opposite opinion: a fragile child’s body is too often exposed to various dangers and there is no point in putting additional stress on it.
But one way or another, any parent, if any symptoms are detected, is urgently recommended to show the child to a specialist, and in no case self-medicate, because only a doctor can correctly determine what type of pests he is dealing with.
To confirm or refute giardiasis, the following activities are carried out:
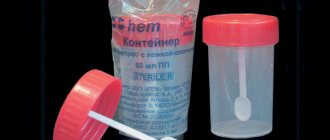
- Stool collection and examination. To do this, collect the morning material in a sterile jar purchased at the pharmacy. If collected in the evening, stool should be kept in a cool place and should be taken to hospital as soon as possible. But at the same time, the analysis results can decrease by up to 70%. However, sampling does not provide an exact guarantee, because these parasites are so small that they are difficult to detect. And they don't come out every day. Therefore, they may prescribe treatment for food poisoning, and not for helminths.
- Blood test for Giardia . After two weeks, antibodies characteristic of parasites appear in the blood. This method is the most informative and can answer the question with 100% probability.
Main stages of treatment
The child's body is most susceptible to various diseases. Therefore, infection with giardiasis in them is much more difficult than in adults and often requires long-term drug treatment. But in the case of a large concentration of parasites in the child’s body, taking pills at the initial stage leads to a deterioration in the patient’s general condition and the appearance of abdominal pain. And parents, frightened, try to stop taking medications. This cannot be done, because the appearance of these symptoms indicates that the medications have begun to act.
Typically, treatment for giardiasis consists of the following steps:
- Preparatory
- Medication
- Immunostimulating therapy.
Stage No. 1: Maintaining a balanced diet
The first stage lasts for two weeks. At this time, it is necessary to follow a balanced diet, which will help eliminate the intoxication of the child’s body with waste products of parasites. It is allowed to eat foods with a high content of protein and pectin.
Diet: plenty of protein (proteins inhibit the growth of Giardia), sour juices and berries are recommended
Doctors also recommend daily consumption of mineral water. At the same time, tubing can be performed once a week. In this case, the child is given 100 ml of warm mineral water to drink, to which a teaspoon of sorbitol or xylitol has been added.
During the entire preparatory stage, it is unacceptable to eat milk-containing products, as well as those containing easily digestible simple carbohydrates.
If necessary, the attending physician may prescribe the child to take medications containing pancreatin. You should not skip this stage and immediately start medication. Since this is fraught with a decrease in the effectiveness of treatment and can lead to complications.
Stage No. 2: Drug treatment
The drug phase lasts 20 days. During this period of time, the patient takes the following medications sequentially:
- Choleretic
- Antispasmodic
- Antiparasitic.
Most often, doctors prescribe treatment according to the following scheme:
- The first 10 days of taking Flamin and No-shpa
- Then Intetrix or Macmiror.
Medication stage: choleretic, antispasmodic and antiparasitic drugs are taken
Since taking antiparasitic drugs can lead to disruption of various body systems, during treatment for giardiasis the following may be prescribed:
- Gepabene or Odeston - to restore normal functioning of the biliary tract
- Smecta or Laktofiltrum - to reduce intoxication.
After a course of treatment with antiparasitic drugs, the doctor prescribes sorbents to the child.
Stage No. 3: Immunostimulating therapy
In parallel with the main treatment, immunostimulating drugs can be taken. And in severe cases of the disease, it is possible to repeat the medication stage with replacement of the main antiparasitic drug.
Treatment
After diagnosing the disease, a specialist can prescribe two treatment methods:
- Gentle - if the helminths have just entered the body and are in the state of a cyst, i.e. they cannot reproduce. In this case, medications are used that paralyze the work of Giardia, preventing it from functioning, and after 24 hours, they are excreted along with the feces.
- Potent - when the parasites have managed to emerge from the cyst state and move to other organs. It is necessary to destroy not only adults, but also larvae, which is not so easy. The course takes about two weeks, after which restorative medications are required for the child’s fragile body.
Giardia blood test
Parents are usually interested, having been tested for Giardia, how can they be detected? In fact, the microorganism itself cannot be seen, but its presence can be established by finding antibodies in the blood that are actively synthesized by humans to fight the parasite. Therefore, the researcher’s task is to determine the relationship between Giardia antigens and human antibodies.
The analysis detects two types of antibodies: IgG and IgM, which are also called single and total immunoglobulins, respectively. They are detected directly in the blood serum after sampling. This method helps not only to diagnose the patient (or to refute giardiasis), but also to establish when the child approximately fell ill, what form of the disease occurs at this stage, as well as the duration of the invasion. This is what the enzyme immunoassay (ELISA) of blood is based on.
When the child’s course of treatment is completed, the examination must be repeated. In case of recovery, the number of antibodies should be minimized.
Treatment with synthetic antibacterial agents
Treatment is selected in such a way as to have:
- greatest safety and effectiveness,
- the least side effects, especially if a person suffers from other diseases.
Furazolidone
Furazolidone is an antibacterial drug used in the treatment of infectious diseases, as well as giardiasis. For giardiasis, Macmiror or its analogues are also used.
By reducing the dosage, it has a bacteriostatic effect, and by increasing it, it has a bactericidal effect. Thanks to the ability to increase the efficiency of leukocytes, the body actively fights harmful organisms. It is recommended to take with weak immunity.
However, you should not drink alcohol while undergoing treatment. Interacting with ethanol increases sensitivity, which causes severe nausea and vomiting.
Like many medications, this drug has a number of contraindications:
- children under 1 month;
- nursing mothers;
- pregnancy;
- liver and kidney diseases;
- individual intolerance to components.
Side effects include:
- itching;
- vomit;
- anorexia;
- hives;
- nausea;
- Quincke's edema
To avoid negative effects, you should take the tablets with plenty of water, and also take vitamin B and antihistamines.
Metronidazole
Metronidazole is a budget antibacterial drug intended for:
- for the treatment of duodenal and gastric ulcers;
- for the treatment of various types of infections (vaginitis, amoebiasis, giardiasis, urethritis, etc.);
- for the prevention of postoperative infections.
Contraindications:
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- liver failure;
- lactation;
- hypersensitivity;
- epilepsy.
Side effects:
- diarrhea;
- anorexia;
- dry mouth;
- depression;
- irritability:
- confusion;
- cystitis, urticaria, nasal congestion.
Drinking alcohol is also highly discouraged due to the possibility of developing neurological symptoms. In case of pronounced side effects, it is recommended to replace the drug with a similar one.
Nifuratel
Nifuratel is an antibacterial agent. Prescribed for infectious diseases of the genitourinary tract, intestines and digestive tract, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, giardiasis, amoebiosis.
Contraindications:
- pregnancy;
- lactation;
- childhood.
However, some specialists make exceptions for these groups, but under careful supervision.
Chronic giardiasis in adults
In adults, symptoms are periodic. A person experiences diarrhea, which alternates with constipation.
There may be disturbances in digestive functions, elevated temperature that does not go away on its own, and changes in the structure of feces.
Due to the vital activity of the parasite, the body’s protective functions are reduced, it is less resistant to infectious diseases, and the condition of the hair and skin deteriorates.
During their life activity, Giardia negatively affects intestinal functions and provokes dysbacteriosis with weight loss.
The disease may be accompanied by serious disturbances in the functions of the digestive system and a general deterioration in health.
How to neutralize the negative effects of lamblia metabolic products?
You can neutralize the negative effects of lamblia metabolic products as follows:
- Increase the amount of protein consumed and reduce fast carbohydrates.
- Avoid whole milk products, as enzymes do not work well with giardiasis. Instead, give more pectin-containing decoctions and jelly, which contain enterosorbents.
- It is recommended to eat apple pudding, rice water, and blueberry jelly.
- Formula-fed (or mixed) infants are given protein foods and lactose-free formulas.
- The doctor may prescribe antispasmodics or cholekinetics to increase the concentration of bile, in which parasites cannot survive.
Analysis for Giardia stool
This diagnostic method is based on a slightly different principle: the presence of the disease is indicated by an increased number of vegetative microorganisms in the feces. This ensures a more reliable research result. However, there are times when the result is negative. If this happens, you need to repeat the analysis in a week.
To carry out the analysis, you need to buy a special test tube into which the child’s feces are collected with a stick. The research is carried out quite quickly - in some cases it can be done within half an hour. Material that has not been processed within 24 hours is no longer suitable for analysis. In this case, you need to take the test again. But if the study was carried out 2-3 hours after the test, it is quite possible to detect cysts. To increase the reliability of the result, experts recommend doing the analysis three times.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies for giardiasis:
- Horseradish balm. Take 3 medium-sized horseradish roots, first brushing them and removing small roots, leaving the skin intact. Using a sharp knife, make shavings. Place in a glass jar and fill with cold boiled water, carefully seal with a lid. Leave at room temperature for 3 days. Then strain and mix the extract with honey in a 1:1 ratio. Leave the prepared mixture for another 3 days, shaking occasionally. Take the product 20 minutes before meals. Children 1 dessert spoon twice a day, adults – 3 tablespoons. The course is 10 days with a break of a week, after which it is repeated again, since Giardia cysts may remain in the body.
- Vodka with garlic. Crush 50 grams of garlic in a mortar. Transfer the pulp into a dark glass container, pour in 200 grams of vodka and seal the jar. Store at room temperature for a week. Take 3 times a day, half an hour before meals, 20 drops, preferably diluted with milk or water.
- Corn silk. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over a tablespoon of crushed stigmas. Leave for 3 hours and take 1 tbsp. 4 times a day.
Treatment of giardiasis
The goals of treatment of giardiasis: elimination of intoxication, removal of lamblia, increasing local and general immunity, combating dysbacteriosis, as well as restoring impaired metabolic mechanisms.
Basic principles:
- Diet. Completely exclude fast carbohydrates and sugar, because they create a breeding ground for parasites. Introduce foods rich in fiber: bran, vegetables, fruits, dried fruits. The diet should also be lactose-free. Such recommendations should be followed for 3 to 6 months.
- Antibacterial therapy is a mandatory principle of treatment. Drugs that destroy Giardia: Metronidazole (Trichopol) - course of treatment for 10 days, Macmiror - course of 7 days, Nemazol - course of 5 - 7 days, Ornidazole - course of treatment of 1 - 2 days, Tinidazole - this drug is contraindicated in children under 12 years of age. The effectiveness of antibacterial therapy for giardiasis is no more than 30%. Therefore, in the absence of effect and in the chronic form of the disease, a combination of several drugs is indicated.
- Choleretic therapy. To eliminate stagnation of bile, choleretic drugs are prescribed - Ursosan, Halidor.
- Detoxification therapy. Enterosorbents - Polyphepan, Smecta, Enterosgel - will help reduce intoxication of the body for a course of 7 - 10 days.
- Vitamin therapy. To combat hypovitaminosis, vitamins B, C, A, and E are prescribed (parenteral administration is recommended).
- Antispasmodic therapy. This type of treatment is prescribed to improve bile secretion - No-shpa, Papaverine.
- Improved liver function. For this purpose, drugs from the group of hepatoprotectors are prescribed - Heptral, Essentiale.
- Enzyme therapy is prescribed according to indications when there is damage to the pancreas.
Prevention
To avoid infection, the following measures should be taken:
- Purify and filter drinking water.
- Be careful with pets.
- In children's institutions, periodically carry out parasitological control with further treatment of the child or the entire team.
- Wash your hands after using the toilet and before eating, as well as after going outside.
- Attend preventive examinations.
By following preventive rules, you can easily protect yourself from the disease.
Prevention of giardiasis in children under one year of age
To prevent the occurrence of giardiasis in children, you should adhere to the following preventive rules:
- Wash your child's hands more often before eating and after walking.
- Make sure that while walking on the street, the child does not pick up anything from the ground or touch stray animals.
- Regularly clean the room in which the baby is located, wash toys with disinfectant.
- Carry out preventive maintenance for pets once every 3 months.
- Do not let your child eat poorly washed vegetables and fruits.
Timely detection of Giardia in an infant will allow for effective treatment and relieve the baby of unpleasant symptoms caused by parasitic organisms. Compliance with preventive measures will help avoid the occurrence of helminthic infestation and negative consequences for the baby’s health.