The sperm and egg do not feel anything because they do not have a nervous system. These are still just sex cells that carry the genetic code. If you prick a sperm with a needle, it won't hurt, that's for sure.
But eight weeks after the egg selected the sperm it loved and took it for permanent residence, the embryo is ready to experience its first feeling. And his very first feeling will be irritation. Here it is: you thought that you had learned to get irritated while standing in Moscow traffic jams for 100 hours a day, but it turns out that you had this skill since you were eight weeks old.
At eight weeks, this is what happens: the fetus begins to respond. And the first thing he can react to is small flakes of skin or small hairs that have come off of him, but remain floating with him in the amniotic fluid. And when such a scale gets on the cheek of the embryo, it becomes irritated and begins to move its body back and forth to throw off the scale, and may even try to remove it with its hand. By this age, the hands have long been formed and even the fingers are perfectly defined.
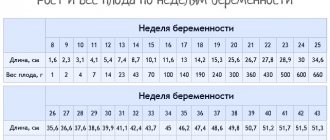
By week 16, the embryo has already completed the construction of its taste perception system. That is, in theory, if you put an apple on your child’s tongue at 16 weeks, he would feel this sweet and sour taste. But this can only be discussed theoretically. That's why. At this age, the embryo still receives all its nutrients through the umbilical cord. And only the substances themselves reach through the umbilical cord, without taste. That is, if the mother eats a chocolate bar, the embryo will not feel the taste of the chocolate bar, only glucose will reach it. If mom eats a steak, she won't be able to enjoy its taste either: only the processed protein itself will come to her. So in theory we know that a child at this age has a taste perception system like an adult, but in practice we cannot verify; To do this, it would be necessary to take the child out of the mother and put this piece of apple directly on his tongue, and this, to put it mildly, is inhumane, because the embryo at this age outside the mother’s body is not yet viable.
At the same age, at 16 weeks, the development of olfactory receptors is completed. That is, the embryo is already able to distinguish several hundred odors. But as with taste perception, this is all theoretical, because there is no smell inside the mother, and odors do not reach through the umbilical cord.
Embryology in general is a rather complex science; currently, experiments on pregnant women are prohibited for humanitarian reasons. Because any experiments are invasive in nature (that is, they invade the fragile world of the child without permission) and can terminate the pregnancy. As terrible as it may sound, a large percentage of what we know about the embryo comes from Nazi Germany, where doctors used captured pregnant women for experiments. Today, the industry uses more humane research tools, such as ultrasound.
At 16 weeks, the baby can already smile and is now ready to experience joy. By this age, the umbilical cord is ready to transport the embryo not only protein, but also endorphins, hormones of joy. If a mother sits in the sun on a park bench on a warm spring day and enjoys it, the child will also be very happy. Having sex, for example, also has a good effect on the mother’s mood.
At 18 weeks, the fetus begins to hear. That is, you can play classical music for him even from the first week of pregnancy, but he will hear it only by the 18th week. Now he is starting to react strongly to loud noises. If you suddenly turn on loud music or if someone knocks on the door too loudly, the child freezes and gets scared. In addition, he can hear his mother's heartbeat well. When a woman gets scared, her fetus senses it all well and gets scared too.
And finally, at 20 weeks, the baby can already feel how his mother strokes him. Before this, he doesn’t really understand what’s happening on the street. The fact is that the embryo is very small in size, and there is a lot of amniotic fluid and they protect it from everything that happens outside. But as the fruit grows and takes up more and more space, there is less water, and the protective layer becomes thinner. This means that if earlier, if his mother had gone out naked into the cold, he would not have felt anything, but now he may already feel cold. He can already understand whether it is day or night, because the skin transmits light one way or another, and as there is less amniotic fluid, it is easier for him to distinguish the time of day. But the best part, as I said, is that he can feel his mother stroking him. This is still not a full-fledged stroking, as in the case of skin-to-skin contact, the feeling is more like being stroked on the back through a very fluffy fur coat, but nevertheless it is still very pleasant.
When is the hearing aid formed?
In many magazines and books for pregnant women, you can find advice for expectant mothers: read fairy tales, sing lullabies or talk to the unborn child.
This may seem far-fetched to some, but modern research confirms: a child, not yet born, is already able to hear the sounds of the surrounding world, slightly muffled due to the aquatic environment around him.
The walls of the abdomen are quite thin, so scientists assume that any sounds louder than 30 decibels are accessible to the baby. Therefore, he hears quite well not only his mother’s voice, but also its intonation and mood.
And in such an environment, sounds of low frequencies are picked up especially clearly, so many child psychologists advise not only the mother, but also the father to communicate with the unborn baby.
As for when exactly a child begins to hear in the womb, opinions differ. Some studies suggest that the hearing aid, and therefore the ability to hear the outside world, is formed in the fetus by the 16th week of pregnancy.
Most scientists believe that hearing is fully formed by the 20th week. That is, starting from the fifth month of pregnancy, expectant mothers are recommended to communicate “with their tummy,” sing to it or read fairy tales.
Hearing studies in unborn children are quite interesting in their own right. In these experiments, mothers read certain nursery rhymes in late pregnancy and then read them again to their babies after birth. Psychologists observing the experimental situation recorded a recognition reaction in the children to these lines: the children began to actively move their arms and legs and smile.
Fetal hearing: how does the fetus react to noise?
Already from the 6th month of pregnancy, mothers feel which sounds the child does not like. Someone next to you suddenly screams or slams a door, a car honks or a dog barks and a child suddenly pushes, giving you a powerful kick. This is a clear signal that the sound was not pleasant for the baby. It happens that babies cry in the womb. This is confirmed by ultrasound: when children heard the noise, they turned their heads away, opened their mouths, breathed deeply, and their cheeks trembled, which suggests crying. But this does not mean that these sounds harm him.
There are no studies showing that loud noise, for example, can damage the hearing of an unborn baby because it is unethical and too risky. But there are scientific reports showing that children whose mothers worked during pregnancy, for example in the textile industry, and were exposed to prolonged noise, had worse hearing at the age of 6-9 years. Therefore, as a preventive measure, doctors recommend that pregnant women not work in positions where the noise level exceeds 85 decibels.
But attention!
The child can get used to the sounds, and over time stops responding to them. How a baby adapts to the sounds it receives was shown in studies by Lester Sontag and Helen Newbery, who played a loud sound in the area of the mother's belly. At first the fetus reacted with an accelerated heartbeat, but after a while this reaction disappeared.
Experts from the American Academy of Pediatrics note that the “noise” that accompanies a baby in the womb can be louder than the noise of a vacuum cleaner. But they don't see anything strange here. The fetus is certainly worse affected by an unexpected loud sound, i.e. a door slamming or a gunshot. In response to an unpleasant noise, the fetus reacts with an accelerated heartbeat, makes nervous movements, and even makes a “pee-pee.”
How does a newborn hear?
After birth, for the first few days, the baby can hardly hear anything due to water in his inner ear. Then, gradually, the hearing aid begins to adapt to the changed environmental conditions, becoming more and more sensitive.
Due to the fact that a newborn baby’s hearing is somewhat dull in the first month of life, many parents begin to worry whether everything is okay with him, noticing that the baby does not react even to fairly loud sounds, and does not wake up from the noise of the TV or washing machine.
In fact, such a gradual adaptation is physiologically determined and serves for the benefit of the child: after the rather calm and quiet environment in which he developed in his mother’s womb, the sounds of the outside world in all their quantity and variety would seem like a cacophony to the baby and would overload him.
The hearing aid adaptation process lasts on average up to 4 weeks and is completed by the first month of life. After 4 weeks, the baby begins to clearly hear the sounds around him, and by 9-12 weeks, parents can notice how he tries to determine where they are coming from, moving his eyes and head.
Doctors do not recommend being too strict about ensuring silence while a child sleeps - he does not need it. After all, all nine months before birth, the baby continuously listened to how the mother’s organs worked. And after birth, the roar of the washing machine, noise from the street or the muffled voices of his parents will not disturb him.
At what month of pregnancy does the baby begin to hear?
All mothers look forward to the birth of a child, to see and hug their long-awaited baby! I wonder how the fetus develops during this period of waiting? And how does the baby grow week by week in the mother’s belly?
What the baby does, sees, hears and feels while staying in his mother’s tummy for 9 long months. Fetal development by week.
The very first sensations appear in the fetus at 6–7 weeks . It is almost impossible to grasp the child’s state at such an early stage, to understand what he feels and perceives, since he still does not give any feedback and cannot tell his mother what he likes and what he doesn’t. But at 6 weeks, the fetus has already developed the main parts of the brain, called the brain vesicles, and nerve cells begin to form. Let's see how the fetus develops, its sense organs, how its ability to perceive the environment improves.
Always in moving
6–7 weeks The little man already has his first sense organ – the vestibular apparatus. It helps maintain body balance even in unsupported spaces. The child spends his entire intrauterine life in motion: firstly, he constantly moves himself (observing the development of the fetus using ultrasound, you can see that he never remains motionless); secondly, the mother also moves, and the baby moves with her relative to the earth's axis. This is the first information about the outside world that the fetus receives. By the end of the intrauterine period, the child masters the mother’s movements so well that he distinguishes when she is calm, when she is excited, when she is tense, and also reacts to this with her movements.
The baby responds very well if he is moved in space (after all, he is so used to this after 9 months!). He quickly calms down when he is carried in arms or carried in a stroller. Parents often ask the question: is it necessary to rock a child so that he calms down and falls asleep? Yes, if he needs it, because movement is a normal state for a baby.
Touch everything
7.5 weeks The fetus develops skin sensitivity. First, it appears in the mouth area - this is preparation for the formation of the sucking reflex. From 8 weeks, the baby’s face and palms become sensitive, and from 10 weeks – the entire surface of the body. In the mother's tummy there is a lot of material for the baby to develop tactile sensations. With the help of ultrasound, you can see how the baby touches his own body, the umbilical cord, and the walls of the amniotic sac. The child begins to use his sensitivity not only to study the internal space of the uterus, but also to master the external world. If the mother puts her hand to her stomach, the baby tries to touch her “from the other side.” In the same way, even before birth, a child can “get to know” both his father and his brothers and sisters. The fetus also reacts very interestingly to the ultrasound sensor: at first, feeling the touch of an unfamiliar cold object, it tenses and moves to the side, but then, if the mother does not worry and relaxes, it calms down and begins to study the new object - it tries to touch the sensor with its palms or heels.
From the second half of pregnancy, when you already feel the baby moving, you can arrange a “mother’s session” for him. At the same time of day, place your hands on your stomach and sing a lullaby or any children's song to your baby. At this time, the baby will try to touch your hands “from the other side.” Every day you need to sing the same song - then the baby will get used to it and after birth he will recognize it and calm down when he hears a familiar melody. Such a session should last no more than 10 minutes so that the child does not get tired, but this must be done daily. You can arrange not only mom’s, but also dad’s “session”.
Secrets of taste
9 weeks The fetus develops taste buds on the tongue and develops taste sensitivity. The fetus swallows amniotic fluid, and its composition and, accordingly, taste changes depending on the conditions. So, for example, if something bitter gets into the amniotic fluid, for example, a disinfectant that is used when collecting amniotic fluid, the baby begins to wince, sticks out his tongue, and makes fewer swallowing movements, as if he is trying to spit out something he doesn’t like. But the introduction of glucose into the amniotic fluid accelerates the swallowing movements of the “sweet tooth.” What the mother eats also enters the amniotic fluid in microdoses. And if a pregnant woman eats, for example, garlic or lemon, the taste of the water becomes more bitter or sour, causing the baby to wrinkle.
Even before birth, a mother can accustom her child to her favorite dishes, even if they have a specific taste. So, for example, if dishes with garlic are part of your daily diet, you shouldn’t give them up completely. Over time, the baby will get used to them and begin to perceive them calmly. There are facts confirming that after birth a child often shows preferences for those dishes that the mother loved to eat during pregnancy.
Normal reactions to sounds in newborns
As soon as the baby's hearing system has adapted to environmental conditions, the child begins to respond to sounds, which sometimes gives parents a new reason for concern. Namely: which reactions are normal and which are not.
The fact is that at first, when the child is already receiving information from the auditory analyzer, but is not yet able to respond to it, his responses may be strange. For example, a reaction to even a quiet, but unexpected sound for a child can be fear and crying.
Also, loud or unexpected noises can cause a convulsive reaction, which, no matter how strange it may look, is normal and allows us to conclude that the hearing aid is developing normally. This just goes to show that babies are extremely sensitive to their environment.
After some time, usually by two months, the baby adapts to the sounds around him and stops reacting so sensitively to them.
Involuntary and convulsive reactions in the first month of life are replaced by voluntary and orderly ones. The baby enjoys listening to speech addressed to him, poetry, rhythmic or classical music. You can see how he tries to find the source of the sound with his eyes.
Fetal hearing: the fetus develops by listening to music
You've probably heard about the “Mozart effect”? This is an incentive to play classical music for your child even before birth. Thanks to this, the baby will have a higher IQ and will study better in the future.
Scientists (led by Alfred Thomas) prove that stimulation by music affects the development of the fetal nervous system.
A child's brain learns to accept and process sounds. It is best stimulated by classical music, which affects the proper functioning of the brain waves and heart of the fetus. Children love the works of Vivaldi, Bach, Mozart, Schumann and Gregorian chants. Listening to this music, he moves calmly.
And when he hears high-pitched and low-frequency sounds that are unpleasant to him, he may even turn his back on the sound wave. For example, the music of Beethoven and Brahms causes anxiety in a child (maybe this is too monumental and dramatic for him?).
However, before you develop your baby with music, check out the findings of scientists from Columbia University. Developmental psychologist William Feather, who works there , warns pregnant women about playing music in close proximity to the fetus, that is, by putting headphones on their stomach, for example.
This can disrupt the unborn baby's sleep and, as a result, disrupt its growth and development, he said. He explains that the child does not need such “artificial” acoustic stimulation, the baby should accept sounds naturally. In addition, it is enough to play music for your child for 5-10 minutes twice a day. The same recordings should be listened to after the birth of the child. When you turn them on, the baby will calm down, as if by magic. Familiar music will give him a feeling of security. Soon you will be able to find out for yourself.
Source of the article: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/5a880f8b9b403cdd1c766b2e/chast-iii-sluh-u-ploda-kogda-malysh-nachinaet-slyshat-chto-slyshit-rebenok-v-utrobe-materi-i -kakie-zvuki-liubit-5ab53fdc77d0e620019bc042
When to be wary
Since hearing in a newborn child develops gradually, many parents experience anxiety when they notice that the baby’s reactions are absent or very weak. They want to make sure that everything is fine with the baby’s hearing, because according to statistics, two children out of a thousand are born with congenital hearing loss.
We will not describe all possible variants of the norm, since the development of each child is very individual and can be completely different in two different children, although this will not mean that one of them develops with pathologies.
However, the following patterns will help worried parents understand that something may be going wrong during hearing development:
- If at 2-3 weeks the baby does not pay any attention to fairly loud sounds.
- If a child older than a month does not try to turn his head towards a sound coming from out of sight.
- If a three-month-old baby does not calm down from the mother’s voice.
- If, around four months of age, your baby does not notice voices or an unusual sound that he has not heard before, such as the noise of a new toy.
- If a child between the ages of two and four months does not try to make sounds, imitate intonations, or pronounce the first syllables.
If parents, while observing their newborn, notice any oddities, they should show the baby to an otolaryngologist.
To diagnose hearing, specialists use modern equipment that makes it possible to determine the presence of disorders even a few days after the baby is born.
How to test your child's hearing yourself
However, before visiting the doctor, parents can try to figure out if there are problems themselves.
There are several ways to test a child’s hearing at home within the first month of his life:
- To check, you need to take some kind of toy that is unfamiliar to the child - a rattle or a pipe, and make noise with it, while standing behind the baby so that he does not see you. In this case, you should carefully monitor his reaction.
- You can also test your hearing not only while you are awake, but also during REM sleep. At the same time, you will notice how the eyeballs move through the eyelids. A sleeping child's reaction to the sound will be a change in facial expression or a sigh.
Under no circumstances should you frighten your baby with loud noises. To create enough noise, you just need to cough or rub your palms together.
It is also worth paying attention to the process of speech formation in a baby, since it is closely related to the formation of hearing and cannot proceed normally if there are any problems with the hearing aid. Already at two months of age, the child begins to make the first vowel sounds.
One of the signs of healthy hearing is the constant gradual development of speech skills: the child begins to make sounds with a certain mood in which he is, and then form simple syllables.
If this does not happen, you should consult a doctor.
How does the hearing aid develop?
In accordance with the norms of fetal development, a tiny person in the womb, at about the seventh week, two barely noticeable tubercles appear on the sides of the head. These are the future ears that we can see on every person. However, the inner ear begins to develop 14 days earlier. This occurs in the fifth week, and in the eighth week the formation of the middle ear begins. The process of development of the structure of the hearing aid lasts until the beginning of the fifth obstetric month. At about 18 weeks of age, your baby's ear labyrinth becomes hard.
Embryogenesis of the hearing organs
The process of developing hearing organs in a baby is one of the most difficult. At 4-5 weeks of pregnancy (when the mother just begins to miss her period), the embryo develops a rudiment that will later become the inner ear. At 7-8 weeks of pregnancy, the structures of the middle ear begin to form. The outer ear is finally formed in the third trimester, and hardening of the cartilage tissue of the ears occurs shortly before childbirth.
Until the fifth month of pregnancy, a very important process of formation and formation of the structures of the inner ear lasts. The labyrinth finally becomes hard by the 18th week of pregnancy. The auditory ossicles begin to harden at approximately 3 months of pregnancy and this process is completed closer to childbirth.
The outer ear is imperfect even at birth. The ear canal remains soft, and its final formation is completed only during the first year of the baby’s life.
Since the process of embryogenesis of hearing in a child has not yet been fully studied and is very multi-stage, at any stage an unforeseen situation may arise that can lead to the birth of a baby with impaired hearing functions.
What do they hear
Of course, not a single person remembers how he was in his mother’s womb, what he did there, what he felt. Scientists say that at that moment the baby is as if in a cocoon, through the walls of which hundreds of sounds reach him. This cacophony does not stop for a second. The child hears the beat of the mother’s heart, the movement of blood through the vessels, breathing, the work of the stomach and intestines. Try to catch something else through such a background noise, coming from outside.
However, the fetus still recognizes sharp sounds. What could it be? A barking dog, a sharp ringing of an alarm clock, the operation of a circular saw, jackhammer or electric drill, a sharp horn of a car. Many women notice that with these sounds, the baby in the tummy begins to behave restlessly.
When should children start reading fairy tales?
Fetal development actively continues in the second trimester. At 20 weeks, almost all women already feel the movements of their baby. But for now these movements are most likely spontaneous. Around the 22-23rd week, the little man begins to turn his head towards the source of sounds. All. From that moment on, he already reacts to them. Therefore, read fairy tales to your kids, sing lullabies to them, talk to them, but avoid scandals and noisy showdowns.
True, some doctors postpone the fetus’s ability to hear until the 26th week of pregnancy. But no one forbids starting to communicate with the baby much earlier.
American experts are confident that by the 22-23rd week a child is capable of responding to very sharp sounds by turning his head. Doctors warn that too loud sounds (more than 115 decibels) can cause hearing loss. This should be taken into account by all ladies who are in an interesting position.
Dangerous sounds
American doctors have determined what pregnant women should stay away from. This:
- Concerts with loud music.
- Crowd noise.
- Sirens (police, fire and others).
- Working trucks.
- Airplanes taking off and landing.
- Operation of all kinds of devices, such as a chainsaw, lawn mower.
- Fireworks.
- Gun shots.
If a pregnant woman works in a workplace where the noise level exceeds 115 decibels, she must ask management to transfer her to another job, for example, from a workshop to an administrative building, before going on maternity leave. It's usually much quieter there.
Music
By about the 25th week, the hearing of babies in the womb is so developed that they can clearly distinguish the sounds of music. They especially like calm classics, lullabies, and romances. Doctors advise letting their children listen to Vivaldi, Tchaikovsky, Chopin, and Mozart more often. Melodic compositions performed on the guitar, harp, and flute are also suitable for them.
They also react quite calmly to modern instrumental music, the main thing is that it does not sound too loud. But rock, especially heavy metal, has an extremely negative impact on them. Children not only begin to show increased activity, they experience anxiety. Therefore, it is not advisable for pregnant women to be in places where such music is played.
But maybe it’s better to do without any sounds at all, that is, to provide the expectant mother with absolute peace and quiet? Scientists think this is wrong. Before birth, the baby must hear gentle, pleasant sounds, as they stimulate the development of his hearing system. This is especially important in the third trimester.
Ability to hear
The baby acquires the ability to hear in the womb at the 15th week of pregnancy. It is at this moment that the main stages of the formation of the inner ear are completed and the processes of formation of the middle ear are already underway. At first, a baby’s perception of sounds is not the same as yours and mine. He hears them, but the cerebral cortex has not yet matured and is not able to analyze the signals. The hearing of the fetus at 15-16 weeks of pregnancy is more reminiscent of the auditory perception of the world by reptiles. With his inner ear he only picks up the vibration created by sound waves .
The beating of a mother’s heart is one vibration, the loud sound from the fall of a heavy object next to her or the ringing of an alarm clock is a completely different vibration.
The mother's voice already has a special meaning for the baby, since its vibrations are different from the voices of other people.
Almost like us, the baby begins to hear only at 26-27 weeks of pregnancy. This means that at this stage the fetus no longer just hears, but reacts to sound. He gradually learns not just to hear something, but also to analyze what he hears. The newborn turns his head towards the sound source. He learned this in the womb.
During the last three months of intrauterine development, the baby listens to sounds with pleasure. Hearing for him in the third trimester is another way of understanding the world around him.