Bilirubin
Bilirubin is a bile pigment found in plasma, an intermediate product resulting from the destruction of hemoglobin. Belongs to the group of yellow pigments. If there is more bilirubin in the blood than should be normal, then there are problems with the liver.
For newborns, the norm is higher bilirubin levels than for adults. And all because while the fetus is inside, oxygen does not come from outside, but is carried by fetal red blood cells containing special hemoglobin. In a newborn, they are destroyed and then excreted from the body.
Neonatal jaundice occurs when free bilirubin is not excreted into the liver to be dissolved and excreted in the urine. Therefore, bilirubin in newborns is under the special control of neonatologists.
Bilirubin in a newborn: blood test for bilirubin
Remember that when testing blood for bilirubin, three values are indicated: direct, indirect and total. Direct (free) bilirubin makes up no more than 1 quarter, it is insoluble. Indirect (soluble) bilirubin should account for three quarters of the total. Total bilirubin means the sum of direct and indirect. In the first month of a child’s life, this normal ratio may be disrupted.
A blood test for bilirubin in a newborn will help determine the level of this indicator. So, in the case of a high level of bilirubin, a negative effect can be had on the child’s nervous system, which is fraught with negative consequences in the future.
Therefore, if high bilirubin is detected in newborns, it must be reduced.
How to reduce bilirubin in a newborn?
Prevention of jaundice in newborns is early breastfeeding and frequent feeding of the newborn.
Light therapy (phototherapy) is used to reduce bilirubin in newborns. Indeed, under the influence of light, indirect (soluble) bilirubin can be converted into one that leaves the body in feces and urine within 12 hours. In case of high bilirubin, treatment will be carried out in a children's hospital with special attention from specialists.
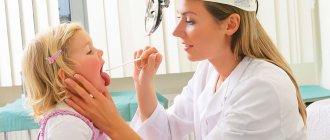
To assess the health status of newborn babies, blood is taken for analysis. The first thing that is examined is the level of bilirubin.
Approximately 60% of full-term newborns and 80% of infants develop jaundice. In this case, the skin, mucous membranes and sclera of the child’s eyes acquire a yellow tint. Parents have a question about how to quickly reduce bilirubin in the blood.
How to reduce bilirubin in the blood with choleretic and hepatoprotective drugs
To reduce bilirubin, complex therapy is required. Usually two groups of medications are prescribed: choleretic and hepatoprotectors. Only the attending physician should prescribe them after diagnosis.
Amino acids
A decrease in bilirubin requires a greater intake of amino acids into the body. These substances are the building blocks for all proteins in the body. When the number of red blood cells decreases, additional sources of amino acids are required.
Effective products whose active ingredients are amino acids:
- Heptral, Heptor, Heparetta (contain ademetionine);
- Hepa-merz (preparation with ornithine);
- Amvix, Ensil, Previn (dietary supplements).
The fact that amino acids play an important role in building protein makes their consumption beneficial. They will not only reduce the amount of bile pigment, but also strengthen the body as a whole.
Essential phospholipids
These drugs belong to the group of hepatoprotective drugs. With an increase in bilirubin associated with diseases of the gallbladder and liver, the membranes of the cells of these organs are damaged. Because of this, their functionality is reduced. Essential phospholipids are used to restore the structure of liver cells.
To reduce bilirubin in the blood, Essentiale forte N is usually prescribed - tablets for oral administration. The main advantages of the drug are that it has virtually no contraindications (except for individual intolerance and age up to 12 years), and can be used for a long time. Also assigned:
- Rezalut about;
- Essliver forte;
- Eslidin;
- Phosphogliv;
- Phosphonziale.
Bile acids
These drugs have a choleretic effect, reducing bilirubinemia levels. Medicines containing ursodeoxycholic and chenodeoxycholic acids are effective:
Preparations of animal origin
To produce medicines of animal origin, the liver of pigs and cattle is used.
Hepatosan is considered an effective preparation of animal origin that can reduce the pigment content. Available in the form of gelatin capsules taken orally. The recommended daily dose is two pieces per day, taken before meals. The duration of treatment is limited - no more than 10 days. Analogues of Hepatosan are Progepar and Sirepar.
Herbal remedies
Extracts of some medicinal plants effectively reduce bilirubin. The advantage of herbal-based medications is their safety; they have practically no contraindications, except for individual intolerance by the body. They normalize the flow of bile into the intestines, due to which they can reduce the absorption of pigment from bile into the blood.
- Effective are preparations based on milk thistle, a unique plant that contains amino acids involved in the breakdown of proteins (Karsil, Legalon, Silimar, Sibektan, Gepabene).
- Pumpkin seeds are also widely used, the oil of which is considered a particularly valuable element. Medicines that lower bilirubin: Tykveol, Peponen.
- Artichoke is another liver healer that can quickly reduce excess toxic substances. Preparations: Artichol, Artichoke extract, Chophytol, Cinacholine.
- Rosehip – found in the preparations Holosas, Hepatofit.
Choleretic
Choleretic drugs, which are divided into three groups, can effectively reduce bilirubin:
- choleretics – Allohol, Hologon, Osalmid;
- cholekinetics – Sorbitol, Flamin;
- Cholespasmolytics - Atropine, Metacin, Fubromegan.
Other medicines
Considering the general harm to the body associated with the effect of increased bilirubin, it is advisable to take vitamin complexes and dietary supplements. If the causes of the phenomenon are associated with infectious damage to the liver or gallbladder, immunostrengthening drugs are also effective.
To reduce excess bilirubin, the following are usually prescribed:
- Multi-tabs Immuno plus;
- Vitrum;
- Centrum;
- Immunal;
- Alphabet.
How is bilirubin removed from the body?
Bilirubin is a component of bile that arises as a result of the breakdown of hemoglobin, myoglobin, and cytochrome.
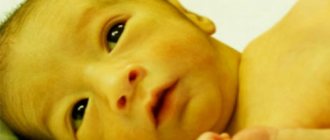
This substance often increases in newborns. There are physiological and pathological jaundice. A couple of days after birth, children's skin and eyeballs turn yellow. The state of health does not deteriorate. These are signs of physiological jaundice.
This condition does not require treatment. It occurs due to the breakdown of fetal hemoglobin. The body is gradually cleansed of toxic compounds. Excessive amounts of bilirubin are excreted in feces and urine. This process is quite long. As a rule, the skin and sclera of the eyes acquire a healthy color after 4-5 days.
But it happens that cleaning takes about 2-3 weeks. This means that the body cannot cope with the load. Pathological jaundice is caused by disturbances in the functioning of the liver and gallbladder. It is accompanied by poor health: nausea, lack of appetite, pain in the right hypochondrium, drowsiness. This kind of jaundice needs to be treated.
Diet for high bilirubin in the blood - what is possible and what is not?
Nutrition with increased bilirubin in the blood plays a key role in the treatment of this pathology.
This is due to the fact that the liver and gall bladder neutralize all harmful substances entering the body, and they get there mainly with food. Therefore, it is quite simple to ease the work of the liver - just review your diet and exclude from it dishes that increase the load on the liver. The diet for high bilirubin is divided into three parts: permitted and recommended foods, restricted and prohibited foods.
Exclude from food
You will have to completely exclude from the menu:
- all yeast products, especially those containing baking powder;
- semi-finished meat products and sausages;
- fatty meats: pork, lamb;
- fried foods;
- fatty store-bought sauces of any kind;
- alcohol in all forms, including that added to food;
- carbonated drinks;
- mushrooms and other gifts of nature containing a large amount of acid (sorrel, citrus fruits, tomatoes, berries);
- preservation of all types, including fruits.
The main enemies of the liver are fat and various acids, so these foods should be completely abandoned.
It is important to limit salt intake, but spices and herbs are allowed, but in moderation. You should not get carried away with chocolate and other cocoa-containing dishes, various sweets, especially those in the manufacture of which preservatives, sweeteners, dyes and other chemicals permitted in the food industry are used.
The list of products that reduce bilirubin levels includes:
- egg white;
- low-fat milk and all products based on it;
- fruits and vegetables;
- lean meats: chicken, rabbit, turkey, veal;
- cereals: rice, buckwheat, oatmeal;
- berry fruit drinks;
- fruit and herbal teas.
Diet principles
The diet itself for elevated bilirubin is based on the following principles:
- Homemade food. You should avoid fast food, restaurant snacks and cafe snacks. The priority is home-cooked meals prepared from approved ingredients in the correct manner. Products must be boiled, stewed or baked.
- Proper drinking. If the level of liver pigment is elevated, you need to drink at least 2 liters of fluid per day (in the absence of contraindications from the kidneys or heart). This can be pure or still mineral water, herbal teas and other permitted drinks.
- Small meals (five times a day). It is with liver pathologies that the basic principle of healthy eating “little and often” must be fully observed.
- Blanks. Many dishes can be prepared in advance or frozen: dumplings and dumplings made from lean meat, cottage cheese or potatoes, cottage cheese casseroles, cheesecakes, yoghurts - all this is easy to prepare yourself.
- Diversity. There are not very many permitted products, but you can prepare a large number of dishes from them: fruit and vegetable soups, milk porridges, casseroles - all this diversifies the diet and makes the diet not only healthy, but also tasty.
How to reduce it in a newborn baby at home?
To speed up the process of removing this substance from the body, various medications are used. They must be used as prescribed by a pediatrician.
If the child’s condition is not serious, then treatment can be carried out at home. Some parents resort to using folk remedies. Non-traditional methods of therapy have a lighter and gentler effect on the body and usually do not provoke the appearance of adverse reactions. There are also hardware methods for reducing high bilirubin levels.
Approved medicinal products
Various medications are used to reduce bilirubin. The choice of pharmacological group of the drug depends on what caused the jaundice.
Before prescribing treatment, the doctor conducts an examination. If the cause of high bilirubin is a decrease in liver function, then hepatoprotective, choleretic drugs, vitamins and sorbents are prescribed.
If jaundice is caused by an infectious-inflammatory process, then antiviral and antibacterial medications are used. Regardless of which remedy is chosen, it should be taken strictly according to the instructions and recommendations of the pediatrician.
Newborns are allowed to be given the following medications to support the liver, gallbladder and digestive function:
- Karsil . Contains milk thistle extract. Restores liver cells;
- Hofitol . The main active ingredient of the drug is artichoke extract. For young children, an oral solution is used;
- Ursofalk . Contains ursodeoxycholic acid. Activates the liver, reduces the load on the brain, and has an immunomodulatory effect. It is given to newborns in the form of a suspension;
- Ursosan. The main component is ursodeoxycholic acid. It has a beneficial effect on the liver, helps convert free bilirubin into direct bilirubin.
How to quickly and effectively reduce bilirubin in the blood at home
Bilirubin is a pigment that is formed in the blood after the breakdown of hemoglobin. Normally, this pigment is the main component of bile.
Exceeding the permissible level of pigment may indicate that the patient has jaundice, hepatitis, hereditary bilirubinemia, infectious liver damage, hemolytic anemia, etc.
Methods for reducing bilirubin depend on the underlying disease that caused the change in biochemical parameters. So, let's find out how to lower bilirubin in the blood as quickly and effectively as possible.
How to quickly and effectively reduce bilirubin in the blood at home?
The main reason for increased bilirubin levels in the blood is disruption of the outflow of bile and liver function. Therefore, for successful treatment, first of all, you will need to follow a diet, which can be supplemented with medications or traditional medicine methods.
A decrease in bilirubin levels should always be carried out under medical supervision and with the medications and methods prescribed by a specialist. This is due to the fact that this pigment has two forms:
- direct – already neutralized by the liver and not posing a particular threat to the body;
- indirect - bound pigment, which is highly toxic and can provoke the development of serious pathologies.
Medicines
Drugs for reducing bilirubin in the blood in adults are divided into several groups and their choice depends on the reason that caused the increase in pigment levels:
- impaired outflow of bile - medications that dilate the bile ducts, reduce the viscosity of bile or increase its volume;
- inflammatory processes of the liver - in case of infectious etiology, antibiotics or antiviral agents will be required, in other cases - enzymes, vitamin complexes, hepatoprotectors.
- hereditary diseases - symptomatic treatment with sorbents, choleretic agents, immunomodulators and drugs that directly lower bilirubin.
Of the drugs prescribed to reduce bilirubin in adults, the most commonly used are:
- hepatoprotectors (Karsil, Essentiale Forte, LIV52) – restore liver cells and its proper functioning;
- ursodeoxycholic acid preparations (facilitate the outflow of bile, have antioxidant and hepatoprotective effects);
- enzymes (Mezim, Pancreazim, Panzinorm) – normalize metabolism;
- sorbents (Smecta, Atoxil, Enterosgel) – neutralize, bind and remove all toxic substances from the body, including indirect pigment;
- Barboval (used for Gilbert's syndrome, since phenobarbital, which is part of the drug, promotes the utilization of bilirubin);
- B vitamins, vitamin A, E.
Read further: Table with bilirubin norms in women by age, deviations, treatment
Alternative medicine methods
Traditional methods aimed at reducing bilirubin levels are also quite effective. However, they can only be used after consultation with a specialist. It is also necessary to understand that traditional medicine cannot replace drug therapy and can only be used with a slight increase in bilirubin.
The following recipes will help reduce bilirubin in the blood:
- Infusion of birch leaves. 1 tablespoon of dry crushed product is poured with 1 glass of boiling water and left for 30 minutes. The liquid is then filtered and taken before going to bed.
- Herbal mixture based on St. John's wort, motherwort and chamomile. Mix all the plants in equal quantities, pour 1 tablespoon of the mixture into 250 milliliters of boiling water, leave for half an hour. Divide into 2 servings and drink 20 minutes before meals in the morning and evening.
- Beetroot juice. It is recommended to drink 1/3 cup of fresh juice on an empty stomach.
- Corn silk. Pour 2 dessert spoons of the product into a glass of boiling water, leave for half an hour, strain and divide into 2 servings. Take 20 minutes before meals in the morning and evening.
- Motherwort infusion. Prepare at the rate of 1 tablespoon of herb per 250 milliliters of boiling water, infuse for 30 minutes. Drink 2 tablespoons strictly on an empty stomach.
Reducing bilirubin in the blood using folk remedies must be agreed with your doctor.
Bilirubin in newborns
Almost every young mother has been diagnosed with neonatal jaundice, and this pathology is also caused by an excess of pigment in the baby’s blood. How to reduce bilirubin in a child’s body, since most medications are contraindicated for children in the first years of life?
They will come to the rescue:
- children's sorbents;
- probiotics that improve intestinal microflora and promote the natural elimination of substances;
- taking vitamin E in the form of drops;
- decoctions of medicinal plants (corn silk);
- phototherapy.
Also, sunbathing and intensive breastfeeding are recommended for the baby, and for the mother to follow the rules of a healthy diet.
Biologically active additives
Special dietary supplements will help reduce the level of pigment - drugs that are not drugs, but have proven their effectiveness in clinical studies.
Some of the most popular pharmaceutical products that lower blood bilirubin include:
- Adliv Forte®;
- Artisonik®;
- Betulagepate®;
- Hepatrin®;
- Ovesol® and others.
Despite the exclusively natural composition and safety for the body, such products should also be prescribed by a specialist.
Diet for high bilirubin in the blood - what is possible and what is not?
Nutrition with increased bilirubin in the blood plays a key role in the treatment of this pathology.
This is due to the fact that the liver and gall bladder neutralize all harmful substances entering the body, and they get there mainly with food.
Therefore, it is quite simple to ease the work of the liver - just review your diet and exclude from it dishes that increase the load on the liver.
The diet for high bilirubin is divided into three parts: permitted and recommended foods, restricted and prohibited foods.
Exclude from food
You will have to completely exclude from the menu:
- all yeast products, especially those containing baking powder;
- semi-finished meat products and sausages;
- fatty meats: pork, lamb;
- fried foods;
- fatty store-bought sauces of any kind;
- alcohol in all forms, including that added to food;
- carbonated drinks;
- mushrooms and other gifts of nature containing a large amount of acid (sorrel, citrus fruits, tomatoes, berries);
- preservation of all types, including fruits.
The main enemies of the liver are fat and various acids, so these foods should be completely avoided. It is important to limit salt intake, but spices and herbs are allowed, but in moderation.
You should not get carried away with chocolate and other cocoa-containing dishes, various sweets, especially those in the manufacture of which preservatives, sweeteners, dyes and other chemicals permitted in the food industry are used.
Video on the topic
About the causes and treatment of jaundice in newborns in the video:
Thus, there are different ways to reduce bilirubin in the blood in newborns and infants. With a slight increase in this substance, traditional methods are used.
If herbal decoctions do not help, then drug treatment is carried out. The doctor may prescribe hepatoprotective, choleretic, and adsorbent drugs. Phototherapy helps to cope with jaundice well.
One of the important indicators of a child’s health immediately after birth is the level of bilirubin in the blood, which is not stable in the first days of life and causes anxiety in young mothers, turning the baby’s body a jaundiced color. What should be the level of bilirubin in newborns, how to distinguish normal from pathology, and also choose the right treatment tactics? Only a pediatrician can answer these questions in detail after closely monitoring the baby’s condition, but in our article you will read basic information on this topic.
Treatment of jaundice in newborns at home
Jaundice is a special symptom that manifests itself in infants in the form of changes in the color of the skin and sclera of the eyes. The yellow color appears depending on the intensity of the pathology. Jaundice in newborns does not require treatment at home in all cases.
Quite often the symptom decreases as the baby grows older. However, there are other types of disease (for example, intrauterine) that require adequate therapy. Parents should know about the nature and causes of the pathology.
A pediatrician will help cure it, prescribing a course based on the patient’s test results.
Today, phototherapy, a special diet for a nursing mother, is most often prescribed. Taking sorbents and other medications and bathing in a herbal bath also have a positive effect. It is also recommended to regularly drink a special solution of glucose along with rosehip decoction.
Causes of pathology
Most often, jaundice in newborns appears immediately after birth. The situation is considered normal because it is caused by the following factors:
- The process of fetal hemoglobin breakdown continues in the skin.
- Bilirubin accumulates in the blood. This is a special substance that gives the skin its characteristic yellow color.
With jaundice, natural processes in the baby’s body are disrupted:
- The mother has a disturbance in the production of hormones. Breast milk is directly affected by estrogen. To remove it from the body, it will be necessary to use additional resources of the gastrointestinal tract.
- A woman does not adhere to a special diet during lactation.
- The baby's liver and some organs of the biliary system have not yet fully formed.
For a newborn, the manifestation of jaundice is considered normal between two weeks and a month. During this period, the color intensity may change.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D-sEj9ZiH28
Bilirubin is a special substance that tends to accumulate in the blood serum. The process occurs only if the baby’s liver has not yet fully matured. Against this background, insufficient outflow of bile is recorded. Products are absorbed into the intestinal walls without prior disinfection.
If bilirubin accumulates in the blood in large quantities, then the risk of intoxication in the child’s body increases. The symptom is serious and can lead to complications in the human body. Toxic substances negatively affect the brain and its stem, so the baby may develop a number of neurological diseases.
We recommend reading: Increased bilirubin in a newborn
Children with jaundice should be under constant medical supervision. The dynamics are analyzed within two weeks. If there is no obvious improvement, then it is advisable to start a course of drug therapy.
There are also neonatal types of pathology that pose a serious threat to the baby’s health:
- If the breakdown of hemoglobin was recorded inside the mother’s womb, then the baby develops hemolytic disease.
- The liver cells were damaged due to the woman having an intrauterine infection.
- There are abnormalities in the digestive tract. In this case, obstructive jaundice is diagnosed.
In such cases, jaundice in newborns should be treated immediately. However, at the first stage, the causes and diagnosis are established. Next, the doctor needs to track the dynamics of changes in bilirubin.
Only after this can you choose between traditional and medicinal methods. Additionally, the woman must adhere to a special diet. Foods that lead to exacerbation of pathology are completely excluded from the diet.
In this case, it is possible to prevent liver infection and disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract.
Main symptoms of the disease
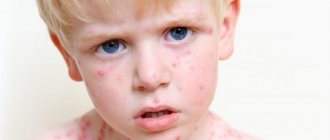
Most often, a change in skin color in a baby is recorded on the third day after birth. The baby becomes significantly darker, and the skin acquires a pronounced brown color. This is how jaundice manifests itself in infants.
The final color of the skin largely depends on the level of bilirubin in the blood. Its amount can vary from 35 to 250 µmol/l. It is impossible to avoid serious consequences if the indicator reaches its maximum.
Parents can also be guided by the color of the baby's skin. Most often, yellowness appears on the legs, feet or hands. It is easier to prevent a situation than to deal with its consequences
Physiological jaundice in newborns also manifests itself in the form of the following symptoms:
- severe anxiety;
- frequent regurgitation, which can lead to vomiting;
- general state of apathy and lethargy;
- characteristic change in urine color.
All these manifestations arise due to severe intoxication of the body. Parents are interested in the question of whether they are discharged from the maternity hospital in this condition. The feasibility of the process is assessed by the doctor. Based on tests and signs, he can prescribe treatment in a hospital setting. Here the dynamics and intensity of changes in bilirubin are monitored.
Kernicterus is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Lethargy and drowsiness in a child become more and more obvious every day.
- Spontaneous regurgitation or vomiting may be noticed from time to time.
- The sucking reflex becomes less and less.
- Periodic appearance of spontaneous muscle twitching.
Treatment of jaundice in newborns at home cannot continue in this case. The situation should be analyzed by a doctor. In some cases it is impossible to avoid hospitalization.
Determination of bilirubin level depending on skin color
Treatment methods for jaundice
Parents have a logical question: how to treat jaundice in a newborn? When choosing a course, the pediatrician takes into account the following important criteria:
- General condition of the baby.
- The presence of pathological processes in the past.
- Changes in bilirubin over time.
- Does the baby have any other illnesses?
In this case, parents at home are recommended to use the following therapeutic measures:
- Phototherapy and regular sunbathing.
- A newborn should be outdoors regularly.
- Medications should be taken only after consultation with the attending physician.
- Traditional methods also help eliminate symptoms. For this purpose, the baby is regularly bathed in chamomile decoction. Additionally, it is recommended to use rosehip decoction and glucose solution as mother's drink. These two drinks will help significantly improve liver function.
ethnoscience
If the decision was made to discharge the baby from the maternity hospital, then further treatment of the pathology will be carried out at home. Mommy should pay close attention to every symptom. Additionally, the attending physician monitors changes in the physiological state. If no improvement is observed, then it is advisable to change treatment tactics.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7Cf7ER-AL3E
During the treatment of a baby, only those products that have been previously agreed upon with the attending physician can be used.
Rosehip decoction allows you to quickly and effectively remove toxic substances. To prepare it, you need to use three dried berries, which are carefully crushed and filled with boiled water. Just a glass of liquid is enough.
To obtain the maximum amount of healing properties, the decoction must steep for at least five hours. Taking one teaspoon each time before feeding will help you get rid of jaundice.
Parents should be extremely careful when using it if the child already has a known allergy.
Doctors advise parents to bathe their baby in calendula or chamomile
These herbs help improve blood circulation and eliminate inflammation. The process leads to the rapid removal of bilirubin from tissues and blood.
You can make the decoction yourself. To do this, 200 grams of calendula and chamomile flowers are poured with one liter of water. Brewing should continue for at least 10 minutes. Infusion must be carried out for three hours. It is advisable to add the product every time while bathing.
Lactation with jaundice
In order to quickly remove bilirubin from the blood, a woman is not recommended to give up breastfeeding. Milk contains protein that quickly and effectively binds all toxic components. Thanks to this, the body’s resistance to harmful effects increases several times. Breast milk normalizes the baby's stool and improves the functioning of his digestive system.
Sunbathing helps get rid of jaundice
Lactation should be abandoned only in case of an immunological conflict. In this case, the milk contains antibodies that will only worsen the overall situation. This clinical picture is rare, so breastfeeding specialists most often recommend continuing breastfeeding.
If the baby has been diagnosed with jaundice, the woman will have to follow a special diet. Thanks to this, it will be possible to achieve recovery within a short time. To quickly remove bilirubin from the blood, a woman should exclude from her diet foods that can lead to a malfunction in the digestive system:
- seasonings and fried foods;
- all varieties of smoked meats;
- tangerines;
- dishes that contain large quantities of dyes and preservatives;
- possible allergens;
- foods that can cause excessive gas in the baby or mother;
- ingredients that negatively affect stool.
To improve your overall well-being and health, it is recommended to regularly spend time in the fresh air. Walking improves metabolic processes and helps restore detoxification naturally.
Features of phototherapy
Exposure to light or ultraviolet rays is used to quickly relieve symptoms of jaundice. The process involves the use of a special lamp, which can have a white or blue glow. In the warm season, the tool can be replaced with regular sunbathing. However, with such an effect on the baby, he needs to cover his eyes and body with a special blanket.
Thanks to ultraviolet light, the process of bilirubin breakdown significantly accelerates, and it is quickly eliminated from the body. If the natural exposure process was chosen, then the baby should be in the open sun for no more than twenty minutes three times a day. The method has a positive effect on the immune system, as it is considered one of the hardening options.
The full course of phototherapy treatment should not exceed 96 hours
Treatment of jaundice with sorbents
Bilirubin is removed from the human body using sorbents. When hemoglobin breaks down, the color of stool changes dramatically.
- The sorbent helps the body remove bilirubin from the intestines within a short time. To speed up the process, it is recommended to use Enterosgel or Smecta. It is allowed to use only those sorbents that have been approved by the attending physician. Otherwise, their action may cause constipation or diarrhea.
- It is also possible to give the child activated or white charcoal. The daily dosage should not exceed a quarter of the tablets three times a day. Before use, they must be thoroughly diluted with boiled water.
While taking any medication, it is necessary to monitor changes in the baby’s condition. If you take activated carbon, then it is quite possible to see dark inclusions in your stool. In some patients, all stools also change color.
Jaundice is a serious disease that can only be eliminated by a professional. Parents should receive his advice on each of the therapy methods. It is also necessary to monitor changes in the baby’s general condition. If deterioration is recorded, then it is imperative to visit the pediatrician’s office.
Source: https://floragaz.ru/zdorovye/lechenie-zheltushki-novorozhdennyh-domashnih-usloviyah
What happens in the baby's body
The fact that a few days after being outside the womb, bilirubin in newborns begins to increase is explained by the physiological peculiarity of the restructuring of the body. This period is characterized by the following processes:
- as there is no need for a large amount of hemoglobin, it begins the process of decay;
- when deformed, red cells release bilirubin - a special pigment that participated in the formation of iron-containing protein - hemoglobin and is released into the blood in an abnormally large volume;
- the accumulation of bile pigment in the bloodstream increases;
- the dermis and sclera are painted in the tone of the pigment - yellow-mustard.
At the beginning of life outside the womb, the baby’s liver is simply not able to cope with high bilirubin levels, since its functionality is not yet fully developed. This condition is considered transient (transitional, temporary), and corresponds to the norms of physiological development of the child. This type of jaundice is called physiological and does not require special treatment.
So does breastfeeding jaundice. After childbirth, the concentration in milk of hormones that reduce the activity of liver enzymes is high, and during natural feeding they penetrate into the baby’s body, causing jaundice. With an increase in the amount of milk in the breast, everything returns to normal and the baby recovers.
Important! There is no need to rush to interrupt breastfeeding, which can later become a panacea for the child. However, in order to dispel doubts and make sure that the cause of yellowing of the skin is not liver pathology, you can transfer the baby to artificial feeding for several days. If during this time the color of the skin returns to normal, it is recommended to resume breastfeeding without delay.
What is the normal level of bilirubin in a newborn?
Bilirubin in the blood is presented in two fractions:
- Indirect (free), which is formed as a result of the fact that the rate of breakdown of red blood cells is higher than the ability of the liver to bind bilirubin. Free bilirubin is a substance that tends to dissolve only in lipids (fats). Due to its inability to dissolve in water, the pigment is very toxic, accumulates in the bloodstream, causing characteristic staining, and can disrupt the normal functioning of cells, easily penetrating into them.
- Direct (bound) bilirubin is formed directly in the liver. After biochemical interaction with the organic acid of the uronic acid group and liver enzymes, which reduce the toxicity of the pigment, it becomes soluble in water and is easily excreted from the body along with bile and urine.
The indicators of the two fractions add up to the total concentration of bilirubin in the blood, with direct bilirubin accounting for no more than 25% of the total volume.
In order for free bilirubin to become bound and soluble, it must be transported to the liver by certain proteins that newborns lack. As a result, the level of bilirubin in the blood increases, and physiological jaundice occurs.
The table shows the norms of bilirubin levels in infants (table of bilirubin in newborns by day)
Jaundice develops in newborns if bilirubin levels are above 50 µmol/l and is expressed, in addition to the concentration of pigment in the blood, by changes in the condition of the infant’s skin: initial color, capillary tone, the extent of the pigment distribution area.
To assess the intensity of changes in indicators, the Cramer scale is used, which can be used to assess the severity of the child’s condition:
- The head area turns yellow (eye sclera, face, palate, tongue below) - 100 µmol/l.
- Yellowness descends to the upper area of the body above the navel - 150 µmol/l.
- The area below the navel is added, including the buttocks and thighs - 200 µmol/l.
- The upper and lower extremities are painted with pigment - 250 µmol/l.
- Skin changes color throughout the body, including fingers, toes, palms and feet - over 250 µmol/l.
How to lower bilirubin in the blood of a newborn
Bilirubin is formed in the baby's blood after birth due to the destruction of special fetal hemoglobin. Active formation of this substance occurs, and if there is too much of it, bilirubin can have toxic effects on the nervous tissue and the entire body of the child.
An increase in bilirubin levels above the normal limit threatens the child with the development of a special condition - bilirubin encephalopathy (kernicterus). This is damage to the cortex and brain substance by toxic doses of bilirubin.
This leads to irreversible damage to the structure of the brain; such a child may remain disabled for life.
Therefore, it is important to promptly notice the development of pathological jaundice and begin adequate treatment. In the maternity hospital, a neonatologist will tell you how to treat bilirubin in newborns. Based on the level of bilirubin in your blood, he will determine what methods can be used in your case; these will not always be medications.
How to lower bilirubin in newborns?
If we remember that excess bilirubin in babies is formed due to the fact that they have not yet matured special liver enzymes that can process bilirubin, in treatment it is necessary to stimulate the maturation and activation of this enzyme. Therefore, answering the question of how to reduce bilirubin in a newborn, first of all, it is worth prescribing drugs that help activate enzymes - these are phenobarbital or zixorin. These drugs are prescribed in strictly calculated dosages and for a short course; they help in the maturation and activation of the enzyme for processing bilirubin.
As an additional therapy in treatment to quickly reduce bilirubin in a newborn, folic acid and B vitamins, vitamins E, D and A, as well as glucose solutions are used. These drugs help in the treatment of increased bilirubin in newborns. Intravenously administered solutions of glucose with vitamins activate metabolism in the liver, due to which it more actively captures bilirubin from the blood plasma and processes it into non-toxic compounds.
How else can you reduce bilirubin in the blood of a newborn? For mild degrees of jaundice in newborns with non-critical bilirubin levels, a special treatment is used - phototherapy. This is a dosed stay of a completely naked child in a special incubator with an ultraviolet lamp. Irradiation with ultraviolet light is a kind of “tanning” for a newborn, helping to actively break down bilirubin in the blood. In this case, the skin gradually turns pale, and bilirubin is excreted from the body. The dose is calculated individually based on weight, several sessions of several minutes are carried out per day, and special glasses are put on the child’s eyes to prevent retinal burns.
Additionally, doctors tell the mother how to reduce bilirubin in the newborn’s blood upon discharge home. A lot of bilirubin remains in the intestines, therefore, sorbent preparations can often be recommended to reduce bilirubin in newborns - Smecta, Polysorb, Enterosgel are used. Sun and air baths, breastfeeding and the use of special substances - probiotics - are useful. These are special living microbes that help normalize the intestinal microflora and actively break down bilirubin through it.
In cases of severe jaundice in newborns, when the bilirubin level reaches critical levels and brain damage threatens, a replacement blood transfusion procedure is used for the baby. In this case, a portion of blood is taken, which contains a lot of bilirubin, and compatible blood, completely free of this substance, is injected into it. Up to 70-75% of a baby’s total blood can be replaced over the course of several days, this helps in most cases to cope with severe toxicosis. This procedure is resorted to extremely rarely, in especially severe cases, and blood for transfusion is taken from transfusion stations that are strictly compatible both by cut group and by Rh factor.
Rate the material:
thank you, your vote has been accepted
Get to know yourself
More on the topic
detstrana.ru
Causes and consequences of high bilirubin in newborns
More than half of full-term babies and ¾ of premature babies suffer from jaundice in the first days. The risk group also includes:
- twins;
- children whose mothers have diabetes.
In order to recognize the pathology in a timely manner, blood from the umbilical cord is immediately taken from the newborn for analysis at the time of birth and again on the third day of life. This allows doctors to keep the situation under control and, if necessary, take emergency measures to preserve the health and life of the baby.
If after 2-3 weeks signs of jaundice continue to actively appear, doctors may suspect pathological jaundice, as a result of an increased concentration of bilirubin in the blood. The reasons for this condition may be:
- Hemolytic disease of newborns. This serious disease occurs against the background of rhesus - conflict between mother and child. It manifests itself as congenital internal edema of the subcutaneous tissue, an enlarged spleen and liver, and damage to the central nervous system.
- Genetic failure. In this case, the newborn may experience one of the following conditions: a defect in the formation of liver enzymes (Gilbert syndrome), decreased enzyme activity (Crigler-Najjar syndrome) and a deficiency of essential enzymes (Lucey-Driscol syndrome). With timely treatment, full compensation is possible, provided there is no severe damage to the brain nuclei.
- Damage to the liver by dangerous infections while the child is in the womb. Toxic agents and viruses reduce the ability to bind bilirubin and provoke parenchymal jaundice. This condition is characterized by prolonged jaundice, enlarged lymph nodes, darkening of urine and lightening of stool, and changes in biochemical blood tests.
- Blockage (obstruction) of the bile ducts, which occurs due to intrauterine cholelithiasis, the presence of a tumor in the body that compresses the bile ducts, bile thickening syndrome. This type of jaundice is called obstructive. The problem is solved by surgical intervention.
By observing the baby and knowing the signs of jaundice, mothers will be able to recognize the pathological or safe course of the disease and seek help from a doctor in time. Only in this case will it be possible to avoid such severe complications as:
- acute intoxication of the body;
- albuminemia, when albumin levels decrease and do not allow plasma to fully transport vitamins and nutrients;
- deafness, mental retardation, convulsions due to the penetration of bilirubin into the brain;
- involuntary motor reflexes that cannot be controlled;
- limb spasms.
Very rarely, but still there are cases when the most undesirable and very dangerous complication occurs - kernicterus, which symptomatically passes from one phase to another:
- Braking. The baby becomes lethargic, practically unable to suckle, all his reflexes are depressed.
- Irritation. The child is in hypertonicity, bends his back, twists, and screams heart-rendingly.
- Imaginary recovery. A safe stage at first glance, when it seems to everyone that everything is over and the child has completely passed the illness. However, this is only a temporary lull, during which you need to show special attention to the child and try not to miss a single symptom.
- Complication. Bilirubin attacks the brain, affecting the nuclei, affecting the nervous system, causing serious disorders in the body, which can result in cerebral palsy.
To diagnose complicated jaundice, biochemical, radiological methods, as well as biopsy are used.
Important! Timely diagnosis and correctly chosen medical tactics determine how severe the health consequences of jaundice will be.
how to quickly reduce bilirubin in a newborn
Very often, after the birth of a baby, doctors diagnose him with high bilirubin. This phrase is very scary for many young mothers, because everyone knows that high levels of this substance in adults can mean the development of a serious disease. Increased bilirubin in newborns, is there a danger and how to treat the baby. What mothers should know about the first days of their child’s life, and what bilirubin levels are acceptable for newborns.
Why is the baby yellow?
Long months of pregnancy have already passed, the baby was born. But on one of the first days of his life, his mother suddenly notices that the baby has turned yellow. Why does bilirubin increase in newborns and how to get rid of jaundice? With these questions, mothers attack doctors in the maternity hospital, but most often specialists assure that this phenomenon is normal and their child is healthy.
Why does a newborn have increased bilirubin? The thing is that in the first days after birth, the baby’s body begins to actively restructure itself in order to adapt to the environment. At the same time, red blood cells, which are responsible for transporting oxygen to the child’s organs in the womb, begin to be destroyed en masse. Now they are simply not needed, their function is completed, and they must collapse and leave the baby’s body. When red blood cells break down, they release fetal hemoglobin, which is converted into bilirubin under the influence of enzymes.
It will also leave the baby’s body, but first it needs to undergo a neutralization procedure in the liver and exit with feces and urine.
However, bilirubin levels in newborns need to be monitored. Doctors in the maternity hospital take the baby’s blood for analysis several times in order to promptly notice high bilirubin in the newborn, which may signal the development of pathology. This allows specialists to assess the degree of functioning of the liver and biliary tract
Source
Jaundice (also known as hyperbilirubinemia) is the cause of the yellow discoloration that appears on the skin and eyeballs of newborn babies in the first week or two. Jaundice occurs because babies are born with more red blood cells than they need. When the liver breaks down these extra cells, a yellow pigment called bilirubin appears. Since the immature liver of a newborn cannot quickly dispose of bilirubin, excess yellow pigment is located in the eyeballs and skin of the newborn. This type of jaundice is called physiological jaundice because it is part of a normal process in the body. As the newborn's bilirubin elimination system matures and the number of excess red cells decreases, the jaundice will subside (usually within a week or two) and will not harm the baby. Jaundice is more common in prematurely born babies, who are less able to cope with excess bilirubin.
In some cases, with certain blood types or Rh incompatibility, jaundice may result from problems that go beyond simply having too many red blood cells. Very rarely, bilirubin levels can rise so high that they affect the baby's brain. For this reason, if the healthcare provider suspects that the cause of the baby's yellow skin is something more than normal physiological jaundice, then bilirubin levels should be monitored more closely using special blood samples. If bilirubin levels become too high, your doctor may try to lower them using phototherapy, which breaks down extra bilirubin in the skin, helping it to be eliminated from the body in urine.
By a biochemical quirk not yet fully understood, jaundice tends to manifest itself
Source
Promotions all promotions
New items all new items
Read
How to reduce high bilirubin levels in a newborn.
Have you had a baby? Read the most important things about jaundice and bilirubin, so as not to faint over trifles, but also to prevent problems in advance.
The level of bilirubin in the blood of a person, including a child, should normally not exceed 20.5 µml/l. At this level of bilirubin, human skin has the usual pink color.
The exception is newborn children. We can say that the normal level of bilirubin in newborns for each day of life is “their own.”
Bilirubin is a bile pigment, it is present in the blood of each of us. Jaundice of newborns develops as a result of an increased content of bilirubin in the blood of a child, which is formed as a result of the destruction of red blood cells (blood cells, and in the first days of life a newborn has much more of them than older children), which is also a physiological feature of a newborn child.
When jaundice appears in a newborn, a large amount of bilirubin is formed, and the child’s liver cannot quickly process and remove it from the body. This is due to the fact that the child’s liver is not yet mature and cannot fully cope with such a load.
Jaundice in newborns becomes visible when the level of total bilirubin is 60 µml/l. At home, we usually do not determine the child’s bilirubin level every day.
IMPORTANT. How can you visually determine the level of bilirubin in the blood of infants by the stages and areas of distribution of icteric staining?
zospono.ru
Treatment of elevated bilirubin in the maternity hospital and with home remedies
Doctors in the maternity hospital are required to monitor bilirubin levels in the blood of newborns. To get a complete systemic picture of pigment concentration, they prescribe biochemical blood tests throughout the baby’s stay in the hospital (2-3 times) and monitor the tendency for bilirubin levels to increase or decrease.
Mothers can keep this topic under control and ask the doctor whether such a test was taken from the child and what the results of the laboratory test are.
It is this approach that makes it possible to timely identify jaundice and prescribe measures appropriate to the child’s condition to treat this disease.
Important! If the baby has mild symptoms of jaundice, is active and breastfeeds well, no treatment is required! With continued breastfeeding, after a week the skin, mucous membranes and sclera are completely normalized.
Experienced specialists, as a rule, accurately determine the severity of the disease and all kinds of risks, in contrast to the advice of friends and general information on the Internet
In this case, young mothers should be patient, and if the child needs to remain under the supervision of a doctor for some more time, do not refuse this, do not take responsibility, and do not put the life and health of your child at risk.
Jaundice in newborns: home treatment with decoctions and baths
Jaundice is a disease that causes yellowing of the skin and eye sclera. Color saturation may vary depending on the form of the pathology and the degree of its development.
If the simplest form of the disease is observed - physiological jaundice in newborns, treatment at home will consist of taking baths with the addition of herbal decoctions. For other forms of pathology (hemolytic, mechanical or infection acquired inside the womb), the therapy will be slightly different.
In any case, every woman planning to have a child needs to have a general understanding of how to identify jaundice and what actions need to be taken if it appears.
Causes
The physiological form, or postpartum jaundice, is a natural condition for a child. The main reasons for its occurrence are the breakdown of hemoglobin or bilirubin accumulated in the infant’s plasma, which changes the color of the skin and sclera to a yellowish tint.
In addition, jaundice can also be caused by:
- prolonged disruption of the mother’s hormonal levels: excess estrogen negatively affects the quality of breast milk, and the baby involuntarily receives the hormone during feeding;
- unbalanced diet of the mother;
- pathologies and delay in the development of the baby’s liver and gall bladder.
When bilirubin accumulates in the blood, a normally functioning liver disinfects it.
Therefore, the development of jaundice in newborns occurs due to underdevelopment of the liver, dysfunction of the biliary tract, or pathological reabsorption of the final products of disinfection in the intestinal tract.
If the level of bilirubin is excessive, the baby's body becomes intoxicated, which leads to complications in the form of a more severe form of jaundice - nuclear.
Other types of jaundice are also dangerous:
- hemolytic - occurs due to the breakdown of hemoglobin inside the womb;
- mechanical – for digestive pathologies accompanied by dysfunction of bile flow;
- caused by intrauterine infections when liver cells are affected.
If the baby has jaundice of the skin, then it is necessary to urgently seek medical help, since jaundice in newborns must be treated immediately.
Therapy is usually complex - medications and traditional methods of treatment. The diet for jaundice is especially important for a nursing mother.
Products that affect the functionality of the newborn’s liver and the ability to disinfect bilirubin are excluded from the diet.
Manifestations
Postpartum jaundice usually appears on the third day; The defining signs are yellowing of the baby's skin and sclera. The more intense the color, the higher the bilirubin content in the blood. You can notice yellowing of the skin when the level of the substance in the blood exceeds 35 µmol/l. This value can reach 250 µmol/l.
The degree of danger can also be judged by the location of yellowness on the child’s body. The wider the area of skin damage, the more serious the consequences will be.
The main treatment for jaundice in newborns takes place at home, after the attending physician has prescribed a treatment plan.
But in the case of the development of kernicterus, when the child exhibits dangerous symptoms in the form of vomiting, weakness, darkening of urine, the baby is left in the hospital, where he is under the constant supervision of medical workers.
In addition to the above symptoms, kernicterus in children is accompanied by:
- pronounced lethargy, loss of activity of the newborn;
- frequent regurgitation;
- disorders of sucking function;
- body tremors, tics, convulsive seizures.
As a rule, a severe form of jaundice is accompanied not by one sign, but by several.
It is quite easy to notice the pathological condition of a child during this period, but in no case should you endanger the baby’s life by self-treating jaundice at home; you must consult a doctor!
Sorbents for the treatment of jaundice
Bound bilirubin can be removed from the intestines by regularly taking sorbents, most often Enterosgel or Smecta . But you should not give your child medications without first obtaining the doctor’s approval, as they can cause bowel problems or, conversely, constipation, which can lead to even more serious complications.
Another natural sorbent is activated carbon; It can be given to newborns without fear. You need to dilute a quarter of a charcoal tablet in clean water (one teaspoon is enough) and give the product three times a day. It should be noted that natural sorbent can turn baby’s stool black - this is normal and does not pose any danger.
Home treatments
Since jaundice can be treated at home during its normal course, gentle methods of therapy are used using herbs and infusions, which significantly speed up the healing process. It is also necessary to adjust the daily routine of both the baby and the young mother.
Light therapy
Bilirubin is sensitive to ultraviolet light, so sun exposure is one of the best ways to cure jaundice.
Medical institutions use special equipment to conduct treatment sessions throughout the entire therapy. Babies born in summer can be taken outside for a short time to sunbathe. You should not go out into direct sunlight; it is better to use diffused light with an exposure duration of no more than 10-15 minutes.
Diet of a young mother
There is no better cure for jaundice than breast milk. It contains all the useful and nutritious substances necessary for the baby's health. But if the mother’s diet is improper, the newborn also receives harmful components that can aggravate the course of the disease. Need to exclude:
- smoked meats;
- spicy foods;
- foods high in fat;
- marinades;
- semi-finished products;
- allergens;
- foods that promote excessive formation and accumulation of gases in the intestines.
It is preferable to eat fruits and vegetables, provided that the child is not allergic to them. It is quite easy to determine this by eating a small piece of the product and feeding the baby with breast milk. You need to observe the baby’s reaction throughout the day. If the child does not have any rashes, then the product can be introduced into the daily diet.
Particular attention should be paid to drinking - a young mother needs to drink at least two liters of water per day.