How does hydrocephalus manifest?
Depending on the form of development of the pathology and the age of the child, the external signs of the disease change.
For children under two years of age, in which in 95% of cases hydrocephalus is a congenital pathology, the following symptoms are characteristic:
- Severe course of the disease. A rapidly deteriorating condition caused by damage to brain structures.
- The main symptom is a rapid increase in head volume. Growth of 1.5 cm or more every month is typical, for at least three months in a row. Starting from the ninth month of life, growth drops to 8-9 mm.
- A child is born with a head whose girth is larger than the girth of the chest. If by six months the ratio does not change, and the head is still larger than the chest, there is reason to suspect hydrocephalus.
- The veins on the occipital, temporal and frontal parts of the head are clearly visible.
- At three months the child does not yet hold his head up and begins to sit up late, crawl, and walk.
- The fontanel on the top of the head is convex.
- The accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid primarily occurs in the frontal lobes of the brain. Head enlargement starts from the forehead.
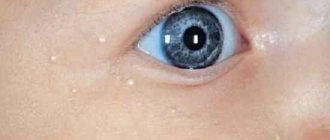
- While fixating the baby's gaze, the baby's pupil twitches chaotically.
- The scalp becomes thin and has a painful shine.
- Overhang of the brow ridges over the facial bone - the eyes appear to be very deep-set.
A number of less characteristic signs can confuse the initial diagnosis of hydrocephalus in children and complicate treatment. For example, tearfulness, poor appetite, slow weight gain, frequent regurgitation, drowsiness, legs constantly bent at the knees, head tilting - all these symptoms are characteristic of hydrocephalus. But at the same time, they can be observed in dozens of other childhood diagnoses.
In the acute form of dropsy, when the disease progresses rapidly, other signs can be observed:
- convulsions;
- long cry on one note;
- loss of acquired physical skills (sitting, following other people's movements, vocal functions);
- vomit.
For children aged two years and older, other manifestations of hydrocephalus of the brain are typical:
- Headaches that begin in the morning (after sleep) and gradually subside in the evening. Nausea and vomiting often begin at the same time.
- Migraines that appear after stress, mental or physical work. Often accompanied by nosebleeds.
- A feeling of a rush to the head when bending over and bursting headaches.
- Pain in the fundus of the eye.
- Visual impairment: loss of sharpness, double vision.
- Urinary incontinence.
- Decreased muscle strength, accompanied by rapid fatigue.
- Cramps and fainting.
- Loss of coordination and uncontrolled movements of the limbs.
What is hydrocephalus?
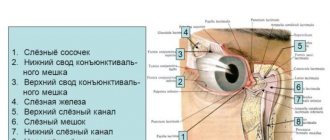
Hydrocephalus is popularly called dropsy of the brain. With hydrocephalus, the volume of the ventricles of the brain increases, often quite significantly. The child’s brain is structured as follows: it contains several cavities called ventricles, which communicate with each other. These cavities are filled with cerebrospinal fluid - cerebrospinal fluid.
If too much cerebrospinal fluid is produced, it accumulates in the cavities of the brain. It is this fact that leads to the development of dropsy of the brain, or hydrocephalus. Moreover, the greater the excess fluid, the more pronounced the disease, and the more the general health of the child and his brain suffers.
There are several types of hydrocephalus, depending on the location of the cerebrospinal fluid. In the event that cerebrospinal fluid cannot flow from one ventricle to another, hydrocephalus is called non-communicating or occlusive. If the cerebrospinal fluid moves freely from one ventricle to another, hydrocephalus is called communicating or open.
In addition, hydrocephalus can be an underlying disease - primary, or secondary: the result of other diseases, such as congenital malformations of the central nervous system, cerebral vessels, tumors of various origins. There are still quite a large number of varieties of hydrocephalus, but they are all derivatives of these basic types.
Treatment of hydrocephalus in children
Regardless of the child’s age, hydrocephalus at any stage of its development requires medical attention. Treatment of hydrocephalus in children and further tactics of patient management will depend on the severity of the patient’s condition, concomitant pathology and stage of the disease.
A group of diuretics - for the purpose of removing excess fluid through the renal barrier. Of the most commonly used, it is o, which helps slow down the production of cerebrospinal fluid by tissues. However, this drug actively removes potassium from the child’s body, so it is additionally necessary to prescribe Panangin or Asparkam, which contain this trace element.
Nootropics - to improve metabolic processes in brain tissue if there is developmental delay. The drug "Cogitum" is recognized as the most effective.
Only the attending physician has the right to prescribe a specific drug, taking into account the morphofunctional characteristics of the patient, the severity of his condition and the presence of possible adverse or allergic reactions to any of its components.
Conservative management of the patient is possible for no more than 4-5 months. If treatment does not give the desired effect, the patient’s general condition progressively worsens (decompensation), and according to instrumental studies there is a deterioration in the clinical picture of the disease, then it is necessary to lean in favor of surgical tactics.
The most effective and low-traumatic methods are:
- Installation of a ventriculoperitoneal shunt involves removing excess cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles of the brain into the abdominal cavity using a catheter.
- Ventriculostomy is the introduction of a device into the intrathecal space through incisions in the skin to remove excess cerebrospinal fluid. This type of invasive intervention is indicated for newborns, since the risks of complications in this situation are minimal.
- Surgical interventions aimed at restoring the natural outflow pathways of cerebrospinal fluid - removal of brain tumors, hematomas, etc.
- Surgical interventions aimed at reducing the production of cerebrospinal fluid - coagulation of the choroid plexus.
After surgical treatment, the child must be under strict dynamic supervision of the attending physician in a specialized hospital.
Signs of hydrocele in a child
Signs of congenital hydrocephalus
- Disproportionally large head. The bones of the child’s skull are soft, pliable, they are not yet tightly connected to each other, their growth continues. Therefore, due to high intracranial pressure, the skull increases in size. The diameter of the head can reach very large sizes, up to 80-100 cm.
- A large fontanelle bulges. On the front of the skull, where the frontal bone connects to the parietal bones, the child has a small diamond-shaped area that is not covered by bone. This is a large fontanel and can be easily felt under the skin. With hydrocephalus, due to high intracranial pressure, it bulges outward and is tense. Normally, the large fontanelle closes completely at 1 year of age, but with hydrocele this occurs later.
- The child is restless, irritable, or, on the contrary, constantly sleepy.
- The skin on the baby's head is thin and shiny. The veins are clearly visible through it.
- Decreased appetite. A sick child eats poorly and refuses feedings.
- Increased muscle tone in the arms and legs.
- The child is lagging behind in psychomotor development. He begins to sit, crawl, and stand later than normal for his age.
- Characteristic appearance of the eyes. The pupil is close to the lower eyelid; it covers the eye. This is called the "setting sun sign."
- Frequent regurgitation, vomiting.
- Low body weight. Children with hydrocephalus are delayed in gaining weight and often develop bedsores. This occurs due to disruption of tissue nutrition.
- Visual impairment. Up to complete blindness due to compression of the optic nerve as a result of increased intracranial pressure.
- The child's activity is reduced. It is difficult for him to hold his head, so he is less active compared to his peers, his skills are slower and difficult to form.
- With a significant increase in intracranial pressure, the child experiences convulsions.
Signs of hydrocephalus in older children (mostly all of them are associated with increased intracranial pressure)
- headache;
- lethargy, drowsiness;
- increased irritability;
- poor appetite;
- nausea, vomiting;
- visual impairment, double vision;
- urinary incontinence;
- convulsions and breathing problems (usually during an attack with open hydrocephalus).
What could be the consequences of hydrocephalus for a child in the future?
The child may develop the following problems
- decreased attention;
- autism;
- difficulties with learning at school, the child does not learn new information well;
- movement coordination disorders;
- memory problems;
- speech defects;
- visual impairment, up to complete blindness.
Symptoms
The manifestation of hydrocele is different in newborns and children over two years of age. In order not to miss the symptoms of the disease, you need to know what hydrocele looks like in newborns. The problem can be identified by the fact that the child’s condition is deteriorating and there is a slowdown in development. An open fontanel and soft bones of the skull create favorable conditions for the accumulation of additional fluid in the head. Therefore, the main sign of hydrocephalus in newborns is considered to be an increase in head circumference.
We recommend additional reading: What to do and how to treat it if a child’s forehead swells due to a blow and a lump forms
The diagnosis can be confirmed by other symptoms: loss of appetite, disturbed sleep, the baby does not hold his head up at the right time. Drooping eyelids and squinting may also be observed. But you shouldn’t wait for the child’s condition to worsen. Any of the listed symptoms is a reason for urgent hospitalization. Because the disease can only be treated in a hospital.
In older children, the pathology has different symptoms. Patients in this age category complain of poor sleep, nightmares, and headaches. Parents may notice that the child has poor coordination, he walks on tiptoes, irritability, and apathy have appeared.
Types and reasons
Dropsy of the brain can be either a congenital pathology or an acquired one.
In the first case, the development of the disease is influenced by unfavorable intrauterine factors: an acute infectious disease in the mother during pregnancy (most often this affects the child), developmental defects that arise due to genetic “errors.”
Acquired hydrocephalus most often affects children under one year of age who were born much earlier than expected, as well as babies who received a brain injury during childbirth.
The cause of the pathology can also be a traumatic brain injury or a previous infectious disease or brain tumor. The most dangerous combination of risk factors is if, for example, a premature baby develops meningitis, encephalitis or meningoencephalitis. The disease can also develop after surgical procedures.
Dropsy is divided into several types, depending on where exactly the cerebral fluid accumulates:
- external;
- internal;
- mixed (combined).
With external dropsy, the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid is concentrated only under the membranes of the brain, it does not affect the deep areas. This condition usually occurs in newborns and children who have suffered birth trauma.
Internal hydrocephalus is a situation in which cerebral substance accumulates in the brain ventricles, through which it cannot flow normally. Such a lesion can be a congenital pathology, as well as acquired - in toddlers older than one year.
According to the assessment of true obstacles that interfere with the full circulation of fluid, dropsy is divided into:
- open (communicating);
- closed (occlusive).
In the reported form of the disease, there are no objective obstacles, the ventricles are sufficiently dilated, and there are no mechanical barriers to the flow of cerebrospinal fluid. Occlusive hydrocephalus occurs as a result of improper development of the cerebrospinal fluid ducts themselves, pathologies in the structure of the ventricles, tubules, tumors in this system, neoplasms, and adhesions. This form of the disease is almost never external; it is characterized by the accumulation of fluid inside the brain.
According to the time of development of pathology, three types of hydrocephalus are distinguished:
- spicy;
- subacute;
- chronic.
Acute develops rapidly, the pressure inside the skull increases literally in 2-3 days. Subacute pathology can develop up to six months, gradually, almost imperceptibly for parents. Its consequences can be more devastating. With chronic dropsy, the cerebrospinal fluid accumulates very slowly, for more than six months, which at first does not affect the baby’s well-being in any way, because the pressure also increases at a very slow pace. And only then, when it reaches a critical level, the diagnosis becomes obvious.
The child's body has very high compensatory abilities. If something is wrong somewhere, the body tries in every possible way to compensate for it using other resources. Therefore, it happens that when a diagnosis of “dropsy of the brain” is established, the child does not show any deterioration in well-being or change in behavior. In this case they talk about compensated hydrocephalus.
If all the body's forces are not enough to compensate, the child's well-being worsens, there are pronounced disturbances in his development, then they speak of decompensated dropsy.
A minor compensated disruption in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid sometimes does not even require serious medical support, which cannot be said about decompensated disorders.
According to the degree of damage, doctors also divide the disease into stages. There are two of them:
- moderate;
- expressed.
According to the dynamics of manifestations, hydrocephalus can be:
- progressive (with noticeable deterioration of the condition);
- stable (when new symptoms do not appear, but there is no improvement);
- regressing (with a gradual decrease in symptoms).
Classification
There are several criteria by which hydrocephalus in children is divided. The International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision, adopted by modern medicine (ICD 10), identifies class G91 for this disease, which includes 6 types. At the same time, congenital hydrocephalus and caused by other external causes are classified under other headings, and G91 includes communicating, obstructive forms, as well as normal pressure hydrocephalus, which occurs against the background of normal cerebrospinal fluid pressure.
For ease of use, clinicians distinguish congenital and acquired forms of hydrocephalus by origin, acute (up to 3 days), subacute (from 3 to 6 months) and chronic (from 6 to 12 months).
According to the formation mechanism, there are 2 main forms:
- communicating (open, non-occlusive) - too much cerebrospinal fluid is produced or it is not absorbed enough, although it circulates freely, which happens with tumor metastases, sarcoidosis, meningitis, hemorrhages;
- closed or occlusive hydrocephalus - caused by a mechanical block of the cerebrospinal fluid pathways, occurs when there is a blockage with a cyst, a scar after hemorrhage, narrowing or stenosis.
Depending on the place of development, external and internal hydrocephalus are distinguished. External hydrocephalus is the accumulation of fluid in the subarachnoid space and special expansions at the base of the brain or cisterns, and internal hydrocephalus is in the ventricles.
For prognosis, the degree of compensation is especially important, which ultimately determines the course of the disease in the child. A good prognosis is given by moderate and small degrees of disorders, but only with timely treatment.
The severity of hydrocephalus is determined by the MR image. Moderate is considered to be the degree in which the cerebrospinal fluid spaces are expanded, but the changes in the medulla are insignificant. Parents often underestimate the threat and ignore treatment. Meanwhile, the degree of hydrocephalus increases, the consequences sometimes cannot be eliminated.
A pronounced degree is a combination of expansion of the cerebrospinal fluid pathways and spaces with increasing atrophy of the cortical substance of the brain.
Treatment of the disease
Dropsy in the head in infants and newborns is treated in two ways: drug therapy or surgery. The use of drugs is aimed at maintaining the body and preventing the increase in head fluid. It is not possible to cure a child in this way.
If the identified cause of the pathology cannot be cured with conservative methods, a shunt is inserted into the brain or a hole is made in the ventricle. In any case, the liquid will be able to escape and will not accumulate. However, bypass surgery is performed every 2-3 years, and endoscopy will eliminate the problem for life.
Medication
To slow down the development of dropsy, reduce symptoms and improve the general condition of the child in the first stages of the disease, you can take medications.
Depending on the testimony of the specialists examining the child, a course of use of the following drugs is determined:
Diuretics, which help remove excess fluid.
Drugs to improve intracranial circulation.
Medicines with magnesium and calcium.
Nootropics.
This treatment will prepare the weakened body of the newborn for surgery and prevent serious disorders. Only a doctor can prescribe medications, because the age and condition of the baby must be taken into account. The patient's condition must be constantly monitored so that if complications threaten to develop, surgery can be performed.
Surgery
Removal of fluid from the brain is done through shunting or endoscopic surgery. Liquor from the ventricles or subcranial space is artificially removed to another place in the body that is free for fluid.
Types of operation:
Ventriculoperitoneal shunt insertion. Silicone shunts move fluid from the brain into the peritoneal cavity.
Lumboperitoneal method. The excretory canal connects to the channels of the abdominal cavity.
Ventriculoarthrial method. The cerebrospinal fluid is transferred to the right atrium.
Operation according to Torkildsen. Transportation of cerebrospinal fluid into the cerebellomedullary cistern.
Ventriculostomy using an endoscope. Physiological restoration of blood flow using an artificially made hole in the ventricles.
Treatment of the disease with surgery allows the child to develop normally
However, it is important to notice the symptoms of the disease in time. Otherwise, the child will become incapacitated or die from intracranial pressure
Traditional methods
Treatment with traditional recipes will not lead to the baby’s recovery. However, it can relieve the symptoms of the disease without affecting the liver and gastrointestinal tract. Alternative medicine is not suitable for newborns, as there is a risk of developing allergies and digestive disorders.
For dropsy, it is recommended to drink freshly squeezed black radish juice, raw onion and pumpkin juice, a decoction of elderberry, clover or parsley. It is useful to eat more grapes and drink teas with lemon balm. These recipes help remove excess fluid from the child’s body, some have sedative properties.
Conservative treatment
Conservative therapy is used in the following cases:
- the disease was detected at an early stage;
- hydrocephalus of newborns and older children is in acute form after an inflammatory process in the brain;
- There are errors regarding the mental and neuralgic state caused by the activity of bacteria.
The recovery rate with drug treatment is no more than 50%. There remains a high probability of psychomotor and mental retardation. For a more successful result, several methods are used aimed at non-surgical reduction of intracranial pressure, drainage of excess cerebrospinal fluid and minimization of complications. Auxiliary methods include physical education, massage, physiotherapy.
| Procedure name | Target |
| Taking diuretics | Reduced rate of cerebrospinal fluid production |
| Antibiotic therapy | Destroying harmful bacteria in excess liquid |
| Taking blood vessel stabilizers | Regulating blood flow in brain tissue |
| Taking vitamin complexes | Regulation of cellular metabolism |
| Taking absorbable medications | Removing stagnant fluid from the body |
| Physiotherapy | Stabilization of the course of the disease |
| Physiotherapy | Facilitating the removal of excess cerebrospinal fluid from the brain |
| Taking glucocorticoids | Promoting healthy brain function |
| Massage | Toning the blood vessels of the head |
What is a disease?
In congenital hydrocephalus, cerebrospinal fluid accumulates in the brain. At the same time, it puts pressure on the newborn’s brain, which can cause damage to this important organ and, as a result, lead to physical and mental retardation. A huge role is played by timely diagnosis and adequate treatment - all this helps to eliminate the risk of complications. The development of these long-term complications also depends on the cause of the disease, the dynamics of the disease and the child’s response to the treatment methods taken.
According to research, congenital hydrocephalus of the brain is diagnosed in approximately one newborn out of a thousand. The disease often occurs in babies who, after birth, were diagnosed with an open brain tube defect. There is also acquired hydrocephalus, the development of which can begin in a child after birth.
Useful tips
- There is no need to look for those to blame; sometimes this illness does not depend in any way on the parents and their correct or incorrect actions.
- During pregnancy, you should definitely visit an antenatal clinic. Many studies and tests that are prescribed to expectant mothers will help you learn about risk factors in advance.
- Before pregnancy, a woman should visit an infectious disease specialist at least once to find out, by donating blood, what diseases she has suffered from, and what antibodies to what dangerous infections she has in her body.
- If during pregnancy (especially in the early stages) a woman gets sick with rubella, measles or another infection, she should definitely agree to additional studies of the fetus’s condition and visit a geneticist in order to make a further (very painful) decision about bearing a child. You need to know about the risks of pathologies and treatment during pregnancy.
- If a child was born prematurely, you should not miss a single mandatory medical examination or routine visit to the doctor.
- Babies over one year old should be protected from head injuries. If you bought him a bicycle, be sure to give him a helmet. If a child is transported in a car, then it is imperative to use a car seat.
- All viral infectious diseases that infect a child cannot be treated independently - according to grandmother’s recipes, viburnum and burdock. You should definitely consult a doctor, get tested, and take medications only as prescribed by a qualified doctor.
You will learn more about this disease from the video below.
Prevention of congenital hydrocephalus
Children whose mothers were diagnosed with at least one TORCH infection during pregnancy are at risk of being born with hydrocephalus. To prevent the development of pathology in the unborn child, you need to avoid infectious diseases during pregnancy and avoid taking any medications, except for those prescribed by the doctor.
A woman must remember that during the period of bearing a child she needs to strictly adhere to the right lifestyle and categorically give up bad habits. It is important that a pregnant woman's diet is balanced. For normal fetal development, you need to introduce foods containing vitamins into your diet. A woman can get advice on other measures to prevent congenital hydrocephalus from a qualified doctor.
Treatment methods for hydrocele in newborns
Unfortunately, the disease in question cannot be completely cured even using the most modern methods. An already grown child, even with successful treatment, will have to be regularly observed by a doctor and follow some rules of “cohabitation” with this disease.
There are two directions of treatment - therapeutic and surgical.
Therapeutic method of treatment
It is intended only to alleviate the condition of the newborn, to relieve acute attacks of pain that arise against the background of cerebrospinal fluid pressure on certain areas of the brain.
Conservative treatment begins with the prescription of diuretics - Hypochlorothioside is often used. At the same time, it is advisable to use in treatment specific drugs designed to reduce the production (formation) of cerebrospinal fluid - these include Diacarb. Doctors often recommend undergoing a course of treatment with hormonal drugs. Please note: most often, therapeutic treatment gives only short-term results and simply alleviates the child’s condition, but does not eliminate the problem. Only surgical treatment can provide the baby with a normal/active life in the future.
Surgical treatment
Surgery has been and remains the only effective treatment for hydrocele in newborns. Both before and now, ventriculo-peritoneal shunting is actively used. The essence of this operation is to drain excess cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles of the brain into the abdominal cavity (this is where the cerebrospinal fluid is quickly absorbed without creating problems). The drainage system for bypass surgery consists of silicone tubes that are “laid” under the skin. This system is equipped with special valves, which allows you to control the process of outflow of excess cerebrospinal fluid.
Please note: ventriculoperitoneal shunt surgery is characterized by frequent relapses and complications - for example, too rapid removal of cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles of the brain may occur, often immediately after the operation the development of an infectious process begins, and epilepsy may be diagnosed. But that’s not all - the child will be left with an altered head shape for the rest of his life, and his future life will depend on the work of the shunt
Among the modern methods of surgical intervention for hydrocele in newborns, endoscopic ventriculoscopy stands out. The essence of this method of surgical treatment is as follows: ducts are created in the bottom of the third ventricle, through which the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid occurs into special tanks and from them the cerebrospinal fluid is absorbed naturally.
Please note: endoscopic ventriculoscopy does not involve the implantation of any foreign objects into the brain or other parts of the body. This reduces the risk of developing infectious diseases
It is the endoscopic treatment of cerebral hydrocele in newborns that gives the newborn a chance to lead a normal life in the future: get an education, engage in socially useful activities, and start a family. But according to statistics, ventriculoscopic endoscopy helps only in 12% of cases of diagnosing hydrocele of the brain in newborns - to obtain permission for such surgical intervention there must be a classic/standard development of the pathology, without any concomitant diseases and complications.
In case of successful endoscopy of the ventriculoscopic type, the pathological process stops development, the physiological flow of cerebrospinal fluid into the ventricles of the brain is restored within normal limits.
What you need to know about the postoperative period
Parents should know that after surgery to treat hydrocele in newborns, it is necessary to closely monitor the child’s condition. Any fluctuations should alert:
- increase in head circumference;
- increased irritability of the child;
- unmotivated whims;
- drowsiness during a full night's rest;
- loss of appetite or complete refusal to eat;
- blurred vision.
If a shunt has been installed, it may become infected - in this case, the child will experience an increase in body temperature and a bright red edging will appear around the shunt channel.
If the symptoms described above occur, then parents should immediately call a doctor - most likely, the amount of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles began to increase again for various reasons.
Reasons for the development of the disease
They vary depending on the age of the baby.
The reasons that affect the development of the brain and nervous system of the fetus are diverse:
- chromosomal disorders (Down syndrome, triploidy, Turner syndrome and others);
- Rh conflict between mother and fetus (so-called immune dropsy develops);
- infections (tonsillitis, leptospirosis, syphilis, as well as primary maternal disease during pregnancy with herpes, toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, rubella, chickenpox and measles, infection with Coxsackie viruses);
- impaired metabolism in the fetus;
- pregnancy with severe anemia, gestosis and preeclampsia, as well as against the background of uncontrolled diabetes mellitus and thyrotoxicosis;
- cardiovascular congenital diseases of the fetus and blood diseases (tachyarrhythmia, malformations of the cerebrospinal fluid tract, vascular thrombosis, leukemia, other developmental anomalies);
- during pregnancy with twins - transfusion syndrome between children (blood flow from one fetus to another);
- brain tumors;
- fetal trauma, including perinatal;
- defects of the placenta, as well as lesions of the umbilical cord;
- pulmonary, renal and intestinal diseases of the fetus;
- chondrodysplasia (impaired development of the skeletal system and cartilaginous growth zones in the child’s joints).
Malformations of the nervous system can be combined with other disorders. The most common is when the volume of brain matter is greater than the size of the posterior cranial fossa, which causes descent into the foramen magnum. Because of this, the circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid is mechanically disrupted. Stenosis, or narrowing of the Sylvian aqueduct, is common.
There may be underdevelopment or absence of openings between the ventricles and the subarachnoid space. It occurs when the IV ventricle is dilated, a cyst from the cerebrospinal fluid is formed in the posterior cranial fossa, and the cerebellar vermis cannot form normally. Dropsy of the brain interferes with the normal functioning of all systems.
In 15% of cases, the factor that influenced the development of dropsy cannot be determined. The risk of intrauterine death is quite high, so the pregnant woman is under constant medical supervision.
Hydrocephalus in a newborn is most often a consequence of an intrauterine infection, birth trauma, or intracranial hemorrhage. During childbirth, those children who were born prematurely and with low weight (up to one and a half kilograms) are more at risk. It is dangerous if the woman in labor has a narrow pelvis or the fetus experiences hypoxia or oxygen starvation during labor.
In children older than one year, the disease develops due to brain tumors, hemorrhages, inflammation of the membranes, traumatic brain injuries or genetic problems.
Diagnosis of the disease
In order to identify the disease, the first examination of the brain is carried out on the fetus while still in the womb of a pregnant woman. Based on the results of the ultrasound scans that a woman undergoes during pregnancy, the doctor determines the size of the head and its compliance with existing standards. If the growth of the fetal head is too fast, then this is evidence that the development of the nervous system is not going well, and fluid accumulates in the brain structures.
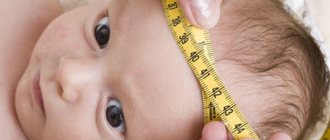
If after birth the baby has symptoms inherent in hydrocephalus, then he should be examined by a pediatric neurologist who takes measurements of head and chest circumference, assesses muscle tone and checks infant reflexes. The child should then be examined by an ophthalmologist, who will examine the fundus of the eye to determine whether a congestive disc is present in the area of the optic nerve.
Neurosonography, a screening method of ultrasound examination, is carried out in early infancy, until the large fontanel is overgrown. Thanks to this method of studying the brain, you can find out the size of the ventricles, but based on its results, a diagnosis is not made.
During a computed tomography scan, which examines the structures of the brain, it is possible to identify various pathologies that provoke the formation of dropsy in the brain. Using MRI, if hydrocephalus is present, its type can be determined. An infectious disease specialist is involved in identifying the type of infection or virus if they provoked the development of the disease.
To determine the level of ICP, a puncture (ventricular or lumbar) is performed, which involves taking cerebrospinal fluid through the cranial foramen or from the intervertebral part of the lumbar region.
Electroencephalography, echoencephalography and rheoencephalography, which are considered ineffective diagnostic methods for suspected congenital hydrocephalus, are not recommended.