The birth of a child is a complex and difficult process, and it can end quite unpredictably. One of the most severe injuries to the central nervous system is cerebral hemorrhage in children. This unpleasant phenomenon can occur for various reasons and the result of the therapy is not always favorable.
The sooner such a disorder is diagnosed in a child and effective treatment is prescribed, the higher the chance that the consequences of a cerebral hemorrhage in a newborn will not disrupt the normal functioning of the child’s body.
Causes of pathology and symptoms
Hemorrhage in newborns is caused by skull trauma
Any bleeding is the result of a pathological condition such as vascular rupture. Most often it occurs when the still immature cranial bones of a small child are damaged and due to fetal hypoxia. Most often, cerebral hemorrhage occurs in children born prematurely. Among babies born with a body weight of less than 1500 g, almost every second one is diagnosed with this pathology.
Brain hemorrhages are less common in babies born at full term. Medical practice shows that only one in 1000 is diagnosed with this condition.
Experts identify some factors, the impact of which on a child’s body can provoke cerebral hemorrhage:
- prematurity or, conversely, birth after term
- large size of the child’s head and its inconsistency with the birth canal
- labor is too rapid or, conversely, a protracted process
- unqualified actions of doctors
Brain hemorrhage in a child can result from a difficult pregnancy. This means that such a pathology can develop after intrauterine damage to the fetus by various infections or during hypoxia. Often the cause of the disorder is toxicosis in the second half of pregnancy, and sometimes the baby is diagnosed with two types of hemorrhage at once.
Each type of hemorrhage is characterized by the appearance of the same first symptoms:
- convulsions
- vomiting attack
- headache pain
- child's lethargy and low activity
Typically, such symptoms develop in a child completely unexpectedly and most often while he is awake. Each such manifestation allows specialists to assess the location of the hemorrhage, so it is necessary to carefully monitor the child and remember his condition.
Cerebral hemorrhage in newborns: consequences – Migraine
Pregnancy and childbirth are not easy for women. But they are not alone in their hardships: the intrauterine period and subsequent birth for the baby are considered no less difficult.
Unfortunately, everything does not always go smoothly, and certain dangerous complications are possible. One of these complications of pregnancy and childbirth is cerebral hemorrhage in a newborn. What it is and why it happens, we will tell you in this material.
Cerebral hemorrhage is one of the most severe birth injuries, which usually have an unfavorable course and prognosis. It occurs due to a violation of the integrity of the blood vessels, as a result of which blood begins to accumulate under the membranes of the brain, in the interhemispheric space, and sometimes the entire brain tissue becomes saturated with it.
Naturally, brain functions are disrupted, and the activity of the central nervous system undergoes changes, often fatal or irreversible. It is cerebral hemorrhage that is considered the most common cause of neonatal death in babies, as well as the development of cerebral palsy in survivors.
Of course, a lot depends on which vessel, in which area of the brain is damaged, how much blood has accumulated, what changes are in the brain tissue and membranes due to the pressure of the blood mass and leaching, but in general the prognosis is still, alas, considered unfavorable.
Depending on the exact location of the hemorrhage, several types of pathology are distinguished:
- epidural - accumulation of blood is observed between the skull and gray matter, brain tissue is not affected;
- subdural - accumulation of blood is present between the soft and dura maters;
- subarachnoid - bleeding is localized between the membrane and the gray matter;
- interventricular e - blood accumulates in the space between the ventricles of the brain and in them;
- parenchymal (intracerebral) - blood accumulates in the brain substance itself, saturates it.
It should be noted that all of these types are considered dangerous, but parenchymal and epidural bleeding are usually called the most severe.
They are quite difficult to establish, and therefore at the time of diagnosis the pathology may already have the scale of a global catastrophe.
According to WHO recommendations, there are three degrees of pathology. Russian doctors use a four-stage classification.
- Grade 1 corresponds to hemorrhage that affects only the walls of the ventricles of the brain, not their cavities.
- Grade 2 corresponds to pathology with blood penetration into the ventricles of the brain.
- At grade 3 , blood spreads beyond the ventricles and fills the lateral ventricles
- At grade 4, massive hemorrhage occurs with damage to the ventricles, lateral ventricles and medulla.
The size of the hemorrhage also matters.
If the affected area is no more than a centimeter, they speak of a mild form of the pathology; if the area of hemorrhage increases to one and a half centimeters, they indicate a moderate-severe form; if the affected area exceeds one and a half centimeters, we will be talking about a severe form of pathology.
Cerebral hemorrhage can develop for a variety of reasons related to the development of the child in the womb, or to the actions of doctors and certain complications during childbirth.
Quite often, cerebral hemorrhage occurs in very premature babies who were born before the 32nd week of pregnancy. Their brain is immature, weak, it is not able to withstand changes in pressure during childbirth, the integrity of the blood vessels is compromised due to the premature birth of the baby.
Neurosurgeons note that the probability of cerebral hemorrhage in a premature baby weighing more than one and a half kilograms is about 50%. In babies whose birth weight is less than a kilogram, a stroke of varying severity is observed in 100% of cases.
Other reasons include the following.
- Acute hypoxia during childbirth. Severe oxygen starvation can develop during sudden rapid labor, as well as during protracted labor with a long stay of the baby in an anhydrous period (after the passage of amniotic fluid). The non-traumatic nature of the hemorrhage in this case somewhat increases the chances of a more favorable outcome for life.
- Obstetrician's actions. The application of forceps and improper extraction of the fetal head can lead to a fracture of the skull bones, and then traumatic hemorrhage develops.
- Post-term pregnancy. If childbirth occurs after 42 weeks, the likelihood of the baby receiving a cranial injury during childbirth increases, because at this stage the bones of the skull begin to lose the elasticity necessary for smooth passage through the birth canal. Birth trauma to the skull can be the main cause of subsequent cerebral hemorrhage.
- Unfavorable pregnancy. Acute hemorrhage in the brain during gestation usually leads to termination of pregnancy and fetal death. After birth, pathology may develop due to certain malformations of blood vessels, heart, and brain. The cause may also be intrauterine infection of the fetus with dangerous viruses and bacteria.
If a woman belongs to a risk group (the woman in labor is over 40 years old, the pregnancy was accompanied by gestosis, severe toxicosis, she is carrying a large fetus with a narrow pelvis, etc.), the woman is usually offered to reduce the risk of hemorrhage in the child through surgical delivery.
After a caesarean section, brain disorders and circulatory disorders rarely develop in babies.
A child who has a slight hemorrhage at birth will not immediately let you know about it. Perhaps at birth he will be more lethargic, perhaps he will cry later, but within a few hours the symptoms will appear and doctors will be able to diagnose the pathology.
Symptoms of cerebral hemorrhage manifest, acutely, suddenly. The baby's condition is deteriorating sharply. It is difficult to say what the specific signs will be; it all depends on the size and location of the hematoma inside the skull.
Most often, convulsions appear, vomiting occurs, and the child loses consciousness. Strabismus may suddenly appear (the pupils begin to “look” towards the affected hemisphere). Many babies have trouble breathing, it becomes intermittent, and then it may stop.
Usually, the maternity hospital has time to provide first aid and provide the child with a ventilator.
Constant screaming may indicate subarachnoid hemorrhage, low blood pressure and strabismus may indicate epidural bleeding.
Experienced neonatologists have many signs by which they can distinguish not only pathology, but also suggest its size and location. However, without an accurate diagnosis, no conclusion can be made.
To confirm hemorrhage, the baby undergoes emergency neurosonography and computed tomography of the brain.
Treatment of the child begins as soon as the diagnosis is confirmed. If necessary, provide resuscitation assistance. Therapy is aimed primarily at normalizing blood circulation in the brain and reducing intracranial pressure. If the hematoma is large and the child’s condition is serious, he may undergo emergency neurosurgical surgery.
If the child’s life can be saved, parents are warned about a long recovery period without any guarantees, because the consequences of cerebral hemorrhage can be very diverse.
During the recovery process, which can last several months, several years, and sometimes even a lifetime, the child will be required to undergo clinical observation by a neurologist, whose recommendations parents will have to strictly follow.
The infant brain is unique in its own way.
He has a high ability to adapt and compensate. And that is why mild cerebral hemorrhages, if treated correctly, can be managed in most cases. But even with them, the process of rehabilitating the child will take a long time.
If the degree of hemorrhage was higher than the second, and the course was severe, then there is a high probability of the child becoming disabled in the future. The degree of damage to brain functions will depend on how destructive the hematoma was to it. Common lesions in such cases are cerebral palsy, epilepsy, hydrocephalus, and dementia.
In the case of severe parenchymal hemorrhage, the survival rate of children is extremely low. Almost one hundred percent fatal outcome is recorded in the case of hemorrhage with rupture of the falx or tentorium of the cerebellum.
According to mothers, the main thing is not to lose composure when the pediatrician in the maternity hospital reports a hemorrhage in the baby’s brain. Hemorrhages occur more often than we used to think, and not every child will become disabled because of this.
Mothers willingly share their stories and emphasize that long-term treatment and the recovery period have done their job - in most cases, children grow up quite normal, attend kindergartens, get straight A's in school, and don't complain about anything.
Severe forms of hemorrhages in a child are a reason to contact a psychologist. Believe me, every maternity hospital has a psychologist to work with pregnant women and women in labor. It will help you believe in the best and tune in to the baby’s wavelength.
Experienced neonatologists claim that children whose mothers cry and are nervous are worse at getting out of a difficult condition than children whose mothers gather themselves together internally and aim for the best. Children feel supported even when unconscious in intensive care.
You can learn about cerebral hemorrhages in newborns and the current world practice of treatment and care from the following video.
Source:
Types and degrees of cerebral hemorrhage in newborns: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
A cerebral hemorrhage is the flow of blood from an injured vessel into the skull and gray matter of the brain, in which quite serious damage to internal tissues and organs is diagnosed, with subsequent disruption of the entire functionality of the body.
This is mostly due to injury to the child’s skull and brain during childbirth, although damage can also be caused by medical negligence, prematurity, or, conversely, postmaturity of the fetus. The very outpouring of blood into the brain can occur in any area of the brain.
Types of cerebral hemorrhage in an infant
In accordance with the classification given by WHO, bleeding into the brain is divided into 4 subsequent types, which are determined by their location.
Types of pathology
There are several types of cerebral hemorrhages in newborns, and they are determined by the location where the blood vessels ruptured.
Epidural hemorrhages
This type of hemorrhage is usually detected in those babies who have suffered damage to the vessels located between the dura mater and the bones of the skull.
Hemorrhage is most often diagnosed in premature babies
With this pathological condition, the following symptoms usually appear:
- the pupil on the injured side dilates
- heartbeat slows down
- blood pressure decreases
- troubled by attacks of suffocation
- convulsions occur
With epidural bleeding in newborns, there is usually a calm period of several hours, after which brain compression syndrome develops, and the child’s condition sharply worsens. After about a few days, the child falls into a coma, and no treatment brings a positive result.
Subdural hemorrhages
This type of bleeding develops in a child when the vessels located between the hard and soft membranes of the brain are damaged. Most often, this pathological condition occurs when the baby is too heavy, as well as when labor is too long or too fast.
A common cause of subdural bleeding is considered to be damage or displacement of the bones of the skull, but this type of pathology is not diagnosed so often today, since the improvement of labor techniques allows timely measures to be taken.
The risk of developing this type of hemorrhage is too high in those babies who are born outside the maternity hospital without the necessary obstetric care.
With this pathological condition, the following symptoms are usually observed:
- strabismus due to deviation of the eyeballs
- coma state
- stiff neck muscles
- lack of reaction to bright light
It is important to remember that the baby’s life depends on the correct diagnosis in the future. In a situation where medical assistance is provided too late, the consequences may be pathologies of the nervous system and other disorders. With subdural hemorrhage, the condition is usually serious from the moment the child is born, and if medical care is not provided, death is possible 2 days after birth.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Subarachnoid hemorrhage ranks first among other types of pathology
The main reason for the development of such hemorrhage is prolonged labor and unqualified medical assistance. Mostly subarachnoid hemorrhage is detected in children born prematurely due to rupture of blood vessels between the cerumen and the arachnoid membrane.
With this pathological condition, the following symptoms appear:
- convulsions
- divergence of cranial bones
- negative reaction to any irritation
- trouble sleeping, meaning the eyes are constantly open
- the baby is too excited and constantly screaming
Typically, such manifestations occur immediately after childbirth or a few days later. With this type of hemorrhage, it is possible to avoid unpleasant consequences in the future, provided that treatment is started in a timely manner.
Parenchymal and intraventricular hemorrhage
The severity of symptoms in intraventricular and parenchymal hemorrhage is determined by the degree of filling of the ventricles.
Medical practice shows that this type of hemorrhage most often occurs in children born prematurely.
Such babies are characterized by slow development of the central nervous system and are born before 32 weeks. If the ventricles are not completely filled and their sizes are not increased, then damage occurs after a few days.
If the ventricles are completely filled and enter the brain substance, as well as if drug therapy is started too late, the development of cerebral palsy is possible. In addition, various mental abnormalities can be detected, but their signs become noticeable much later.
Cerebral hemorrhage in newborns: consequences
If a cerebral hemorrhage occurs in newborns, its consequences can be the most unpredictable and dangerous.
Often, such a pathology occurs during childbirth. Timely identification of the problem, provision of adequate medical care and proper care for the patient gives hope for a positive result.
What types of cerebral hemorrhages exist, and is it possible to protect an unborn baby from them?
Causes of pathology
Brain hemorrhage in a newborn baby occurs when bones are damaged due to trauma during childbirth. As a result, the blood vessels located in the skull rupture.
Another reason for the development of this phenomenon is oxygen starvation of brain tissue.
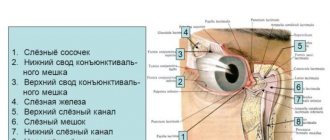
In such conditions, blood accumulates between the hard and soft membranes (membranes), sometimes entering the substance of the brain, causing disruption of its activity.
The provoking factors for rupture of cerebral vessels are:
- Difficult birth.
- Delivery after 40-41 weeks of gestation.
- Pregnancy pathologies (for example, premature placental abruption).
- Infections during pregnancy.
- Errors of medical workers.
- Premature birth. Most often, hemorrhages occur in very premature babies. The bones of their skull have not yet gained sufficient strength, so they are more susceptible to various injuries and damage.
- Anatomically narrow pelvis (discrepancy between the size of the baby’s head and the width of the maternal birth canal).
Among the most common reasons, it is worth noting an incorrect assessment of the weight and size of the fetus. If the baby's head circumference is larger than the mother's birth canal, he may become stuck or suffocate during labor.
In such situations, the doctor decides to use radical methods: vacuum or obstetric forceps. If the procedure is carried out ineptly, intense compression of the head can lead to compression of the cerebral vessels.
As a result, under the influence of strong pressure, the thinnest vessels burst.
Types of hemorrhage
In order to determine further prognosis and medical measures, it is important to understand what type of intracranial hemorrhage is. Types of violation vary according to:
- Localization location.
- Provoking reasons.
Bleeding in the brain in newborns occurs:
- Subdural . Blood accumulates between the hard and soft membranes of the brain. The causes of the pathology often lie in the discrepancy between the head circumference and the size of the mother’s pelvis. The newborn has a lack of unconditioned reflexes (partial or complete), and convulsions.
- Epidural intracranial bleeding. In this case, the blood vessels are damaged between the bones of the skull and the hard shell. The patient may experience difficulty breathing, mydriasis (dilation of the pupil) on the affected area, and a slow pulse. The pathology is associated with rapid labor, post-term pregnancy, and underdevelopment of the cranial bones during intrauterine development.
- Subarachnoid . Blood enters the brain matter and under the brain membranes. The patient experiences hyperexcitability, sleep disturbance, abnormally long wakefulness, and muscle cramps. This problem is often encountered in premature newborns. Another cause of pathology is the use of a vacuum or obstetric forceps during delivery.
- Intraventricular . In this case, the ventricles of the brain are affected: left or right. In such babies, muscle hypotonicity, absence of unconditioned reflexes, respiratory arrest, anemia, swelling of the fontanel, and impaired thermoregulation are recorded. Such hemorrhage occurs for the following reasons: pathologies of intrauterine development, deep prematurity.
Experts give the most favorable prognosis for bleeding into the subarachnoid space. Timely assistance allows the newborn’s brain to recover within several months (sometimes years). Intraventricular hemorrhage is considered the most dangerous. This type of pathology claims the lives of most newborn patients.
General symptoms
Depending on where in the brain the hemorrhage occurred, certain clinical signs appear. They allow you to suspect something is wrong in time and respond quickly.
General symptoms of pathology:
- Loss of consciousness.
- Frequent spitting up like a fountain.
- Cramps.
- Weakness, apathy, lethargy.
- Headache.
When blood enters the deep tissues of the brain, the following occurs:
- Coma.
- Lack of response to light stimuli.
- Holding your breath.
- A sharp drop in temperature.
- Paresis of limbs.
If blood gets into the gray or white matter, the baby will have the following symptoms:
- Convulsive attacks.
- Muscle weakness.
- Hyperexcitability or lethargy.
- Difficulty falling asleep.
- Prolonged monotonous crying.
Severe symptoms can be caused by blood entering the cerebellum:
- Profuse regurgitation, vomiting.
- Motor retardation.
- Stiff neck.
- Falling into a coma.
Diagnostics and therapy
The life and health of the baby depends on how quickly the injury was identified, its causes were established and therapy was carried out. To obtain reliable information and assess the baby’s condition, it is necessary to:
- Analysis of cerebral fluid for the presence of bloody elements in it.
- Computed tomography.
- Blood analysis.
- Coagulogram.
If bleeding in the brain of a newborn is intense, then he needs emergency help related to normalizing the heart rate, stabilizing the functioning of the respiratory system and nervous system, which will avoid serious complications. For this, the patient is taken to the intensive care unit, where:
- Removing excess fluid from the affected area. This will reduce intracranial pressure and relieve compression of brain tissue.
- The use of diuretics to eliminate swelling and relieve the body of excess fluid.
- Blood and plasma transfusion (if necessary).
- Use of hemostatic and anticonvulsant medications.
- Hormone therapy to stabilize the adrenal glands and normalize hormonal levels.
- Antibiotic therapy to prevent infection of the affected areas.
- Vitamin therapy as an auxiliary measure.
The child must be prescribed:
- Massage sessions that improve blood flow in the central nervous system.
- Classes with a speech therapist (at older ages).
When discharged from the maternity hospital, the baby is registered with specialized specialists (neurologist, orthopedist).
It happens that premature babies experience several types of hemorrhages at once. The main therapy is aimed at removing blood from the brain structures.
In general, treatment of hemorrhage (if started on time) is successful, since the infants’ brain is plastic and recovers quickly.
The main thing is to exclude any damaging factors that could again provoke rupture of the vessel and cause complications.
Possible consequences
The severity of clinical manifestations associated with complications of hemorrhage depends on the degree of damage to brain structures. Sometimes severe damage cannot be repaired even with adequate therapy.
If a young patient:
- If massive and voluminous bleeding is detected, accompanied by a rupture of the tent or falx of the cerebellum, then his condition sharply worsens, which leads to death immediately after birth.
- If a massive hemorrhage localized in the cerebral cortex is diagnosed, the newborn may develop a large hematoma inside the head, which subsequently resolves, leaving behind a porencephalic cyst.
Minor cerebral hemorrhages will not cause serious harm to the child if medical care was provided in a timely and professional manner. Often a consequence of a cerebral hemorrhage in infancy is the occurrence of a stroke in young people.
Possible consequences of severe forms of pathology are as follows:
- Cerebral palsy.
- Falling into a coma.
- Hydrocephalus.
- Episyndrome.
- Noticeable developmental delay.
- Brain swelling.
- Strabismus.
- Aggressiveness.
- Speech impairment.
Whatever the bleeding (epidural, subdural, intraventricular), it often leaves consequences.
No woman going into labor can be insured against medical errors, but the risk can be minimized if you follow the recommendations of the gynecologist leading the pregnancy.
It is necessary to give up bad habits, undergo testing for toxoplasmosis, and take a responsible approach to choosing a maternity hospital and a doctor who will deliver the baby.
16.04.2018
(2 2,50 of 5) Loading...
Source: //BolitGolova.info/mozg/krovoizliyanie-v-mozg-u-novorozhdennyh-posledstviya.html
Possible complications and consequences
Brain hemorrhage can cause cerebral palsy
The peculiarity of the brain of a newborn child is the fact that it has excellent self-healing abilities. With a little treatment and proper treatment, it is possible to completely get rid of the pathology.
In addition, in the future the child will not experience negative consequences of hemorrhage, but full recovery may take from several months to 2 years.
Unfortunately, the prognosis is not always favorable and with serious brain damage the following complications may develop:
- cerebral palsy
- hydrocephalus
- epilepsy
- developmental delay
In addition, death cannot be ruled out as a consequence of cerebral hemorrhage.
Diagnosis and treatment methods
Such an unpleasant diagnosis as cerebral hemorrhage is made to the child in the maternity hospital by neonatologists, and subsequently the baby is monitored by a neurologist. A specialist may suspect a pathology based on some external signs, but additional examinations may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
The child may be prescribed the following diagnostic procedures:
- CT scan
- blood analysis
- coagulogram
- cerebrospinal fluid examination
- EEG
Pathology can be diagnosed using CT
Often, several types of hemorrhages are diagnosed in newborns, but there is no single treatment regimen. This or that therapy is selected taking into account the type of pathology, the symptoms that appear and the degree of brain damage.
The main task of the acute period is to restore the functioning of the central nervous system, breathing and heart. In addition, the treatment involves the restoration of metabolic processes in the child’s body, as well as the normalization of blood circulation and the functioning of the adrenal glands. If necessary, the child is given resuscitation measures.
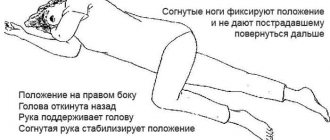
A child with a cerebral hemorrhage requires careful care and constant monitoring by doctors.
On the first day, the baby should be positioned so that his head is slightly elevated. A heating pad is placed near the legs, and ice is placed at a distance of 20 cm from the head.
From the video you can find out why newborns need to have an ultrasound of the brain: