An attack of false croup usually begins unexpectedly. The child is sleeping peacefully in his crib, and suddenly he develops a hoarse cough with a whistling component, hoarseness in the throat, and he begins to choke. Of course, parents get scared, even if the child has coughed or snotted a little before. These symptoms have no comparison with signs of ARVI.
This is how a viral infection of the upper respiratory tract begins - false croup. There is another name - stenosing laryngitis. Doctors make the diagnosis very quickly based on the resulting laryngeal stenosis.
Pathogenic microorganisms invade the submucosa of the trachea in the area of the subglottic space around the vocal cords, causing swelling and an increased amount of viscous discharge.
In most cases, an attack of false croup in children ends on its own, but 7-12% of children require urgent medical attention and hospitalization.
Actions at the first symptoms of false croup
If you suspect false croup in your baby, you should immediately call an ambulance. First aid for false croup, until the ambulance arrives, should be the following:
- open the windows in the room or car, providing access to fresh air to the patient;
- free the child from clothes that are constricting the chest and throat;
- put vasoconstrictor drops into the child’s nose;
- do inhalations (saline), if it is not possible to do inhalations with false croup, you can breathe in hot steam from a saucepan or emanating from a stream of hot water from a tap in the bathroom;
- provide the baby with the amount of drinking water he needs, but do not force him to drink a lot to avoid vomiting;
- if there is a fever, give an antipyretic;
- if the child stops breathing, press on the root of the tongue, thereby causing vomiting;
- Give antihistamine tablets to reduce swelling.
How to alleviate a child's condition
A big mistake parents make is to give their child cough medications, especially those that have an expectorant effect. They will only worsen the child’s condition, since the swollen larynx will not cope with the large amount of sputum discharge and will block access to air. For the same reason, you should not use inhalers, especially steam ones: under the influence of steam, mucus increases in size and softens, which again can lead to blockage of the larynx.
Therefore, it is extremely important not to treat croup yourself. All you need to do is call a doctor and try to alleviate the child’s condition. In the meantime, the doctors are traveling, it is important to ensure the baby’s comfort as much as possible:
- During an attack, the main task of parents is to calm the child: crying and panic intensify muscle spasms of the larynx, making breathing even more difficult.
- If the body temperature is very high (more than 38.5°C), give an antipyretic.
- Maintain your child's drinking regime. Give him plain warm water more often, which will thin out the mucus and make it easier to remove.
- You can relieve an attack with cool, fresh air. Therefore, open the windows without fear or go outside with him, having previously dressed him in warm clothes.
Causes
This disease is caused by a virus or infection. Croup becomes more active against the background or after influenza and other viral infections of the upper respiratory tract, due to damage to the larynx by various types of viruses. Rarely - due to injury to the larynx. Various kinds of cocci and E. coli also provoke the occurrence of this disease.
Why do children suffer from this disease? Because ideal conditions for the occurrence of edema have been created in their nasopharynx:
- unique sizes and structure of the children's trachea and larynx (easily and quickly compressed by surrounding tissues);
- the vocal cords are placed high in children, therefore they are vulnerable to infection that penetrates through the nasopharynx;
- The nervous system in children is not yet fully formed, the functioning of reflex zones is imperfect.
But not all children suffer from croup, but those who are at risk due to:
- gender of the child - boys get sick more often;
- predisposition to allergic reactions to food or certain medications;
- birth trauma;
- overweight;
- frequent illnesses that do not go away for a long time;
- period after vaccination.
Signs of laryngitis
◉ Mild malaise
◉ Temperature rises to 38 degrees
◉ Voice becomes hoarse, hoarse
◉ Complete loss of voice in severe form (aphonia)
◉ Dry cough, barking at the beginning of the disease, wet after a few days
◉ Scanty sputum
◉ Sore throat, sore throat
◉ Baby's anxiety due to difficulty breathing
◉ Blue lips of a child are a sign that the child is beginning to suffocate!
Upon examination, the pediatrician sees swelling of the larynx and the area near the vocal cords. Severe redness of the mucous membrane (hyperemia) is also observed.
In most cases with laryngitis, the disease does not take a severe form. The duration of this ailment in children is several days. The treatment is not complicated, the prognosis is favorable.
The consequences of laryngitis are complications such as laryngotracheitis, aphonia, otitis media , bronchitis.
Classification of false croup
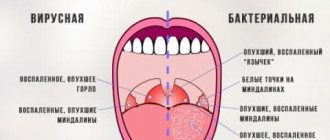
There is a gradation of this disease into viral and bactericidal croup - it all depends on the cause of its occurrence (etiology). If, in addition to signs of croup, there are signs of other concomitant diseases, this is complicated croup; if not, it is uncomplicated. There is a classification of croup according to the degree of stenosis (narrowing) of the larynx:
1st degree – compensated;
2nd degree – subcompensated;
3rd degree – decompensated;
Grade 4 – the most severe, hypoxia.
Symptoms of false croup
Depending on the degree of stenosis:
1st degree . Orthopnea and difficulty breathing occur with even minor experiences and physical stress;
2nd degree . Permanent shortness of breath, during inhalation the jugular fossa and the skin located between the ribs collapse. The voice sits down.
3rd degree . Whistling breathing, barking cough, confusion, lethargy, when inhaling, the jugular fossa and the skin located between the ribs fall in, the pulse is barely audible;
4th degree .
No coughing, no loud breathing. There is very low blood pressure and confusion. The patient may fall into a coma and die from suffocation (asphyxia). The larynx is so narrowed that it is unable to let air through; a patient with this degree of stenosis no longer coughs, and heart sounds are barely audible.
False croup in children
The diagnosis of “false croup” is made by a pediatrician based on a visual examination of the child’s larynx and listening to the lungs with a stethoscope. Since treatment must be prescribed and measures taken immediately, there is no time to wait for test results.
An experienced doctor can diagnose the etymology of false croup (whether it is viral or bacterial) without special equipment and laboratory measures, such as rhinoscopy, x-ray, etc. All these measures will be needed to diagnose possible complications after false croup.
How to recognize false croup in a child at the onset of the disease? False croup develops against the background or after ARVI or influenza. An attack of false croup usually begins in the evening or even in the middle of the night, with a barking cough, accompanied by wheezing, difficulty breathing. The child’s nasolabial triangle becomes bluish in color, the voice becomes hoarse or disappears altogether. The child is frightened, breathing quickly and shallowly.
In infants, the symptoms of false croup are the same as in older children, however, if not treated in a timely manner, the outcome of this disease in infants can be fatal, as it progresses more quickly. If the swelling of the larynx is not removed, the baby may die from asphyxia (suffocate).
Many parents wonder: is it possible for a child to walk with false croup? If the child does not have a fever and if you do not communicate with peers so as not to infect them, then you can and should go for a walk. Fresh air is healing and speeds up recovery. Another common question from parents is: at what age can a child develop false croup? We answer – up to 7 years. After 7 years of age, due to anatomical features, the child is less likely to develop false croup.
What is OSLT
If a child in the middle of the night (there are also attacks during the day, but less often) suddenly begins to cough, and his cough is barking or croaking, and his breathing is difficult when inhaling and is accompanied by wheezing, we can assume that he is having an attack of false croup.
With diphtheria, the patency of the airways is impaired due to the formation of specific dense films in the upper part of the air duct. And with false croup, the child’s breathing becomes difficult due to swelling of the mucous membrane and loose tissue of the larynx and trachea.
In the depths of the larynx, under the vocal cords, the connective tissue is quite richly supplied with lymphatic and blood vessels. Therefore, the larynx tends to react very actively with swelling to any irritants: be it viral diseases, bacterial infections or allergic reactions.
Laryngeal stenosis is popularly called false croup. Depending on its location, there is acute stenosing laryngitis (OSL) and acute stenosing laryngotracheitis
False croup (stenosis of the larynx) or subglottic laryngotracheitis, or ASL (acute stenosing laryngitis), or OSLT (acute stenosing laryngotracheitis) - depending on the location of inflammation and edema - is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract (larynx, trachea), as a result of which there is a narrowing of the lumen of the larynx.
This inflammation develops as a result of a viral or bacterial infection entering the baby’s respiratory tract. It is the infection that causes the inflammatory process, swelling and increased production of mucous secretion in the subglottic space, vocal cords and trachea.
But an important role is also played here by the factor of the child’s physiological predisposition to diseases of the upper respiratory tract.
False croup is, rather, a consequence or complication of an infectious disease or an allergic reaction of the body
When can a child get false croup?
It is the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the respiratory tract of young children that explain the fact that they are most often exposed to attacks of false croup.
- Short vestibule, funnel-shaped and small diameter of the lumen of the larynx.
- Softness of the cartilaginous skeleton.
- Disproportionately short vocal folds, located, moreover, too high.
- Increased sensitivity, hyperexcitability of the muscles that close the glottis.
- Functional immaturity of the respiratory system, etc.
All these are objective factors in the development of OSLT. Among the subjective reasons are:
- IUGR (intrauterine growth retardation).
- Prematurity.
- Birth injuries.
- Childbirth by caesarean section.
- Anomalies of the constitution.
- ARVI, acute respiratory infections and other infectious diseases.
- Allergic reactions.
- Post-vaccination period.
- Entry of foreign bodies into the respiratory tract.
- Laryngeal injuries.
- Laryngospasm.
Laryngeal stenosis can be of varying degrees of severity and is characterized by paroxysmal progression.
Degrees of subglottic laryngotracheitis
Laryngeal stenosis, depending on the severity of its occurrence, can be:
I degree or compensated. Lasts from several hours to 2 days. There is an increase in the depth and frequency of inhalations during physical activity or anxiety. There are no signs of excess carbon dioxide in the blood. The gas composition of the blood is maintained due to the compensatory efforts of the body.
II degree or subcompensated. Lasts up to 3-5 days. There is constant shortness of breath and increased clinical symptoms of laryngeal stenosis. Compensation for the lack of oxygen occurs by increasing the work of the respiratory muscles by 5-10 times. The child is restless and excited. The first signs of oxygen deficiency appear: blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle, pale skin, tachycardia.
III degree or decompensated. Increased work of the respiratory muscles no longer compensates for oxygen starvation. There is constant shortness of breath. Rough wheezing can be heard over the lungs. The voice is hoarse. Signs of hypoxia intensify: tachycardia, arterial hypotension, loss of pulse wave during inspiration.
IV degree or asphyxia. Extremely serious condition. Obstructive respiratory failure leads to toxicosis of the body. Breathing becomes frequent and shallow. Convulsions may occur and body temperature drops. Bradycardia occurs. The child may fall into a coma. Deep combined acidosis develops.
Symptoms of false croup in children: barking cough, hoarse voice, shortness of breath, restlessness
False croup in adults
In adults, the diagnosis of “false croup” is made by an otolaryngologist based on the clinical picture typical for this disease. As an option, if in doubt, a throat smear and microlaryngoscopy are performed to identify and determine the causative agent of the disease. A number of specific laboratory tests can determine whether the croup is viral or bactericidal. A general analysis, acid-base blood test and blood gas analysis determine the severity of hypoxia - an indispensable component of false croup.
Treatment of false croup
If you suspect false croup, you should immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment. In medical diagnostic treatment of false croup will be quick and effective, without complications. A staff of qualified physicians, the latest medical equipment and a laboratory with all the necessary reagents and instruments will help make the correct diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment for false croup in both children and adults.
And in order to avoid getting sick at all, you need to prevent false croup. To prevent false croup in children, hardening is used; the child must lead a healthy lifestyle, regularly visit seaside resorts, swim in the pool, and eat right. The child should be dressed according to the weather, so that he does not overheat, but also does not freeze.
The air in the baby's room should be humid. But the most important thing is to prevent the baby from getting viral infections, then false croup can be avoided. Do not visit public places during mass epidemics of influenza and other diseases; make sure that your child’s diet contains all the necessary microelements and vitamins - without preservatives or food additives.
Treatment with folk remedies
Traditional medicine recipes used to treat stenosing laryngitis:
Inhalations:
- The herbal mixture, consisting of medicinal chamomile flowers and common lenka, needs to be filled with 300 ml of hot water. Leave for 45 minutes, strain, bring to a boil. Remove from heat and place on the table. The child needs to bend over the pan, covering his head with a blanket, and inhale herbal vapors for 10-14 minutes.
- ½ tsp. baking soda should be dissolved in 250 ml of boiling water. The baby (can be with his mother) needs to breathe the steam emanating from the solution for 5-7 minutes.
- Crushed blackcurrant leaves are brewed with hot water. They are infused, filtered, brought to a boil, and used for inhalation.
- 1 tsp. sequence is steamed with boiling water (350 ml). The suspension is cooled, infused (50 minutes), filtered, and brought to a boil. The child leans over the bowl and inhales the warm steam. Duration of the procedure is 8-10 minutes.
Under no circumstances should a child be forced to breathe hot steam. At least 2-3 minutes should pass from the moment of boiling to inhalation.
It is recommended to take the medicinal drink 3-4 times a day. The liquid should be consumed warm.
Any hot drinks are prohibited.
- Chamomile flowers are brewed with boiling water. The herbal infusion is infused for 30 minutes. Used after meals.
- ½ tsp. ground wild rosemary herb is poured with 2 tbsp. cold water. The suspension is placed in a dark place and kept for 8 hours. The prepared infusion is taken to relieve swelling and maintain immunity.
- Melt 20 g of butter in 200 ml of warm milk. This drink is consumed warm 2 times a day.
- Mineral alkaline water without carbonation is heated to a temperature of 37-39⁰C. Drink 5-7 times a day to improve sputum discharge.
You can instill 2 drops into the baby's nasal sinuses. any vegetable oil. After the procedure, the child should lie on his back for 3-5 minutes. The oil enters the neck, disinfecting the respiratory tract, softening fibrous films.
You should eat warm porridge with added butter. Food warms the throat, fat is a natural antioxidant that relieves inflammation.