Closed
Closed fractures are divided into displaced fractures and non-displaced fractures. Such fractures can occur in infants as a consequence of birth injuries.
Most often, newborns suffer from clavicle fractures. In the event of a closed type injury, the skin remains undamaged, and treatment of fractures in children occurs faster and without complications.
How do bones heal after a fracture?
Knowing the answer to the question of how and how long a fracture heals can be a necessary aid in treatment. Healing time may vary depending on the extent of the damage. There are three degrees of severity:
- Light fractures. The healing period is about 20-30 days. This group includes injuries to the fingers, hand and ribs.
- Moderate fractures. Healing occurs within 1 to 3 months.
- Severe fractures in most cases require surgical treatment, and the period of complete healing can reach 1 year.
Based on the type of injury, open and closed fractures are distinguished.
Compression
Damage to the spinal column due to external influence is called a compression fracture. Compression-type fractures in children are rare and can be easily treated if recognized early, but due to the small size of the vertebrae in children, the symptoms of a fracture may be misdiagnosed, and the injury itself may remain hidden for a long time.
A compression fracture in a child manifests itself as compression of the entire spinal column, while some vertebrae change their original shape, lengthening in the shape of a wedge. This form of damaged vertebra has a negative impact on the lower vertebra, pressing into it and ultimately destroying its structure.
Correct diagnosis of injuries of this type allows you to avoid serious consequences and begin the necessary rehabilitation actions in time. Treatment usually occurs without complications and, in addition to standard methods, also includes mandatory exercises from therapeutic gymnastics.
Symptoms of early trauma
Complex trauma with multiple fragments and displacement in a child and an adult has common symptoms:
- The functionality of the limb is completely or partially lost;
- A state of shock or stress in a child is accompanied by loud crying;
- Swelling and redness develop on the injured limb;
- The limb is deformed;
- The temperature rises to 37.8 degrees;
- Hematomas form on the skin;
- An open fracture is accompanied by bleeding;
- The child experiences sharp pain. When you try to move the injured limb, the pain intensifies.
With pronounced symptoms, the child cannot move a limb and cries constantly. A subperiosteal fracture causes vague symptoms:
- Slight redness in the area of injury;
- A dull ache that some children can easily tolerate;
- No deformation.
The specificity is in the intact periosteal membrane, which connects the bone fragments, even after displacement. Such an injury heals quickly, since the intact membrane nourishes the tissues and blood circulation in them is not impaired. And if the displacement is not diagnosed in time, then the child develops bone curvature.
First aid
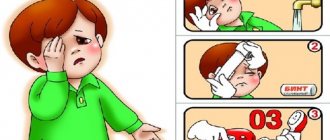
If an injury is detected, the first thing to do is to ensure the immobility of the damaged organ, for which purpose a splint is made from means that can be detected (pieces of boards, even sticks). The injured limb is placed between two straight and hard objects in such a way as to also cover the joints adjacent to the site of injury. Using any dressing material, the prepared parts of the splint are fixed and, as a result, the injured area is immobilized.
As a result of such injuries, severe pain occurs and to alleviate the suffering of the victim, pain-relieving drugs (ibuprofen, paracetamol) should be given.
It is necessary to give the child the opportunity to calm down, maintaining his own restrained behavior, and immediately call an ambulance. The ambulance team will be able to assess the correctness of the splint and transport the child to the emergency room.
For open injuries, bleeding should be eliminated before applying a fixative bandage. An open wound may become infected and should be treated and covered with a sterile dressing. When working with an open wound, the person providing assistance is required to treat their hands with disinfectant solutions.
If an artery is damaged during a fracture, bright red blood with pulsation is observed. In this case, the vessel should be clamped above the wound to reduce the flow of arterial blood. Venous bleeding is stopped by squeezing the vein below the wound location.
If there is no bleeding as a result of an open fracture, contamination should be removed from the wound site under running clean water or treated with hydrogen peroxide.
If the injury is open, a tetanus vaccination must be carried out.
If a child falls from a height, it is necessary to ensure complete fixation of the body. Immobilization is carried out by laying the victim on a hard and level base (wooden flooring, hard stretcher). If there is a suspicion of damage to the pelvic bones, a cloth cushion should be placed under the knees, thus eliminating the cause of further displacement of the injured bones.
If a hand is injured, the child can be transported to the traumatology emergency room independently. If the lower limbs or spine are injured, hospitalization should be carried out exclusively by special ambulances.
Fractures in children First aid and treatment
Statistics on childhood injuries indicate that fractures in children occur due to minor trauma and trivial circumstances - at home, on the street, on the sports field, for example, when falling from a great height, while running or walking, etc. Fractures of arm bones in children are 2 times more common than leg bones. The most common sites for fractures are the elbow and forearm bones. Fortunately, severe multiple injuries in children are not common and account for 2.5% - 10% of all injuries to the musculoskeletal system.
Features of bone fractures in children
A child's bones contain more organic matter (the protein ossein) than those of adults. The shell covering the outside of the bone (periosteum) is thick and well supplied with blood. Children also have areas of bone tissue growth (Fig). All these factors determine the specificity of childhood fractures.
- Often bone fractures children occur as a “green branch”. Outwardly, it looks as if the bone was broken and bent. In this case, the displacement of bone fragments is insignificant, the bone breaks only on one side, and on the other side a thick periosteum holds the bone fragments.
- The fracture line often runs along the bone tissue growth zone, which is located near the joints. Damage to the growth plate can lead to its premature closure and subsequently to the formation of curvature, shortening, or a combination of these defects during the child’s . The earlier the growth plate is damaged, the more severe the consequences it leads to.
- Children are more likely than adults to experience fractures of the bone projections to which the muscles are attached. Essentially, these fractures are separations of ligaments and muscles with bone fragments from the bone.
- Bone tissue in children grows together faster than in adults, which is due to good blood supply to the periosteum and accelerated processes of callus formation.
- In children of the younger and middle age groups, self-correction of residual displacements of bone fragments after a fracture is possible, which is associated with bone growth and muscle functioning. In this case, some displacements undergo self-correction, while others do not. Knowledge of these patterns is important for deciding the issue of surgical treatment of fractures.
Types of fractures
Depending on the condition of the bone tissue, traumatic fractures
and
pathological
.
Traumatic fractures arise from the impact of a short-term, significant amount of mechanical force on an unchanged bone. Pathological fractures occur as a result of certain painful processes in the bone that disrupt its structure, strength, integrity and continuity. A minor mechanical impact is sufficient to cause pathological fractures. Often pathological fractures are called spontaneous. Depending on the condition of the skin, fractures are divided into closed
and
open
.
With closed fractures, the integrity of the skin is not compromised, bone fragments and the entire fracture area remain isolated from the external environment. All closed fractures are considered to be aseptic, uninfected (uninfected). With open fractures, there is a violation of the integrity of the skin. The size and nature of damage to the skin varies from a pinpoint wound to a huge defect of soft tissues with their destruction, crushing and contamination. A special type of open fractures are gunshot fractures . All open fractures are primarily infected, i.e. having microbial contamination! Depending on the degree of separation of bone fragments, fractures non-displaced
and
displaced
.
Displaced fractures can be complete when the connection between bone fragments is broken and there is their complete separation. Incomplete fractures , when the connection between the fragments is not broken along the entire length, the integrity of the bone is largely preserved or the bone fragments are held by the periosteum. Depending on the direction of the fracture line longitudinal
,
transverse
,
helical
,
stellate
,
T-shaped
,
V-shaped fractures with bone cracking are distinguished. Depending on the type of bones, fractures of flat
,
spongy
and
tubular bones
.
Flat bones include the bones of the skull, scapula, and iliac bones (forming the pelvis). Most often, with fractures of flat bones, significant displacement of bone fragments does not occur. Spongy bones include the vertebrae, calcaneus, talus and other bones. Fractures of cancellous bones are characterized by compression (compression) of bone tissue and lead to compression of the bone (reduction in its height). Tubular bones include the bones that form the basis of the limbs. Fractures of tubular bones are characterized by pronounced displacement. Depending on the location, fractures
of tubular bones can be
diaphyseal
(fracture of the middle part of the bone - the diaphysis),
epiphyseal
(fracture of one of the ends of the bone - the epiphysis, usually covered with articular cartilage),
metaphyseal
(fracture of the part of the bone - the metaphysis, located between the diaphysis and the epiphysis) .
Depending on the number of damaged areas (segments)[1] of the limbs or other body systems, isolated
(
fractures of one segment), multiple
(
fractures of two or more segments), combined
(
fractures in combination with traumatic brain injury, organ trauma) are distinguished. abdomen or chest).
How to suspect a fracture?
to suspect a fracture in a child . Most often the child is excited and crying. The main symptoms of bone fractures in children are severe pain, swelling, swelling, deformation of the damaged limb segment, and inability to function (for example, the inability to move an arm or step on a leg). A bruise (hematoma) may develop on the skin in the area where the fracture is projected. A special group of fractures in children are compression fractures of the spine, which occur as a result of an atypical injury, usually when falling onto the back from a small height. The insidiousness of these fractures lies in the fact that diagnosing them in children is difficult even when hospitalized in the trauma departments of children's hospitals. Pain in the back is minor and completely disappears in the first 5 to 7 days. X-ray examination does not always allow making the correct diagnosis. Difficulties in diagnosing this group of fractures are due to the fact that the main radiological sign of vertebral damage as a result of trauma is its wedge-shaped shape, which in children is a normal feature of a growing vertebra. Currently, in the diagnosis of vertebral compression fractures in children, modern methods of radiodiagnosis - computer [2] and magnetic resonance imaging [3] - are becoming increasingly important. Fractures of the pelvic bones are considered severe injuries and are manifested by severe pain, inability to stand on one’s feet, swelling and deformation in the pelvic area, and sometimes crepitus (crunching, creaking) of bone fragments is observed when moving the legs.
First aid
First aid
for fractures of the limbs, it involves immobilizing the damaged segment using improvised means (planks, sticks and other similar objects), which are secured with a bandage, scarf, scarf, piece of fabric, etc.
In this case, it is necessary to immobilize not only the damaged area, but also two adjacent joints. For example: for fractures of the forearm bones, it is necessary to fix the damaged segment of the limb and the wrist and elbow joints; for fractures of the shin bones, the damaged segment of the limb along with the knee and ankle joints. To relieve pain, the victim can be given a painkiller based on paracetamol or ibuprofen. You should try to calm the child , first of all, with your calm behavior. Then call an ambulance (it can be called even before first aid begins) or go independently to the nearest children's hospital (emergency department) or trauma center. Since with open fractures there is a violation of the integrity of the skin, the wound is infected and bleeding may begin from blood vessels damaged by bone fragments, before immobilizing the limb, it is necessary to try to stop the bleeding, treat the wound (if conditions allow) and apply a sterile bandage. The damaged area of skin is freed from clothing (the hands of the person providing assistance should be washed or treated with an alcohol solution). In case of arterial bleeding (bright red blood flows out in a pulsating stream), it is necessary to press the bleeding vessel above the bleeding site - where there are no large muscle masses, where the artery does not lie very deep and can be pressed against the bone, for example, for the brachial artery - in the elbow bend . In case of venous bleeding (dark-colored blood flows continuously and evenly, does not pulsate), it is necessary to press the bleeding vein below
the bleeding site and fix the injured limb in an elevated position.
If the bleeding does not stop, cover the wound with a large piece of gauze, a clean diaper, a towel, or a sanitary pad (clamp the wound until a doctor arrives). If there is no bleeding with an open fracture, then dirt, scraps of clothing, and soil should be removed from the surface of the skin. The wound can be washed under running water or poured with hydrogen peroxide (the resulting foam should be removed from the edges of the wound with a sterile gauze pad). Next, apply a sterile dry bandage to the wound. An open fracture is an indication for vaccination against tetanus [4] (if it has not been administered previously or the period has passed since the last revaccination), which must be done in an emergency room or hospital. First aid for a fall from a height consists of immobilizing the spine and pelvis, which are often damaged. The victim must be laid on a hard, flat surface - a shield, boards, hard stretcher, etc. If a fracture of the pelvic bones is suspected, a bolster is placed in the popliteal areas of the legs. All this leads to muscle relaxation and prevents secondary displacement of bone fragments. If a child arm is injured and he can move independently, he must go to a children’s trauma center, which, as a rule, is located at every children’s clinic and hospital. If a child has an injured leg, spine or pelvic bones, he cannot move independently. In these cases, it is advisable to call an ambulance, which will take the injured child to the emergency department of a children's hospital. Hospitalization
to the hospital is carried out in cases of displaced bone fractures requiring reposition (comparison of fragments) or surgery, as well as with fractures of the spine and pelvis.
Diagnosis of
bone fractures in
children is carried out in emergency rooms or emergency departments of children's hospitals by traumatologists or surgeons. Of great importance for the correct diagnosis is an examination by a doctor, interviewing parents, witnesses or the child about the circumstances of the injury. An X-ray examination is required. Computed or magnetic resonance imaging is also often performed (especially if a spinal fracture is suspected). In case of combined injury, ultrasound examinations (ultrasound), blood tests, urine tests, etc. are performed to diagnose the condition of internal organs.
Treatment
Due to the fairly rapid fusion of bones in children , especially under the age of 7 years, the leading method of treating fractures is conservative
.
Fractures without displacement of bone fragments are treated by applying a plaster splint (a version of a plaster cast that does not cover the entire circumference of the limb, but only part of it). As a rule, non-displaced bone fractures Outpatient treatment is carried out under the supervision of a traumatologist. The frequency of visiting a doctor during the normal course of the fracture healing period is 1 time every 5 - 7 days. The criterion for a correctly applied plaster cast is the subsidence of pain, the absence of impaired sensitivity and movement in the fingers or toes. “Alarming” symptoms that the bandage is compressing the limb are pain, severe swelling, impaired sensitivity and movement in the fingers or toes. If these symptoms appear, you must immediately consult a traumatologist. Treatment of fractures by applying a plaster cast is a simple, safe and effective method, but, unfortunately, not all fractures can be treated only in this way. In case of displaced fractures, in case of severe comminuted or intra-articular fractures, an operation
under general anesthesia - closed reduction of bone fragments, followed by the application of a plaster cast.
The duration of the surgical procedure is several minutes. However, anesthesia does not allow the child home immediately. The victim should be left in the hospital for several days under the supervision of a doctor. For unstable fractures, transosseous fixation with metal pins
, i.e.
bone fragments are fixed with knitting needles and additionally with a plaster cast. As a rule, the doctor determines the method of reposition and fixation before performing the manipulation. When fixing the fracture area with knitting needles, subsequent care and ligation of the places where the knitting needles exit the limb are necessary. This method ensures reliable fixation of the fracture and after 3 - 5 days the child can be discharged for outpatient treatment. In pediatric traumatology, the method of permanent skeletal traction
, which is most often used for fractures of the lower extremities and consists of passing a pin through the heel bone or the tibial tuberosity (tibia bone) and traction of the limb with a load until the fracture heals. This method is simple and effective, but requires hospital treatment and constant monitoring by a doctor until the fracture heals completely.
Recovery period
The timing of fracture healing in children depends on the patient’s age, location and nature of the fracture. On average, fractures of the upper limb heal within 1 to 1.5 months, fractures of the lower limb - from 1.5 to 2.5 months from the moment of injury, fractures of the pelvic bones - from 2 to 3 months. Treatment and rehabilitation of spinal compression fractures depend on the age of the child and can last up to 1 year. The active recovery period begins after removal of plaster immobilization or other types of fixation. Its goal is to develop movements in adjacent joints, strengthen muscles, restore the supporting ability of an injured limb, etc. The means of rehabilitation treatment include physical therapy (physical therapy), massage, physiotherapy, and a swimming pool. Physiotherapy and massage are carried out in courses of 10 - 12 sessions and help improve microcirculation of blood and lymph in the damaged area, restore muscle function and joint movements. of particular importance for fracture healing in children . In this regard, it is advisable to include vitamin-mineral complexes containing all groups of vitamins and calcium in the treatment regimen. For severe open fractures complicated by circulatory disorders, treatment with oxygen under high pressure in a pressure chamber is recommended - the method of hyperbaric oxygenation (used to prevent infection and helps activate metabolic processes in the body). Rehabilitation treatment begins in a hospital setting and then continues on an outpatient basis. In case of severe injuries accompanied by severe dysfunction of the damaged segment, treatment is carried out in rehabilitation centers, as well as sanatorium-resort treatment.
Complications of fractures
With complex fractures, severe dysfunction of the injured limb and pain syndrome are possible. Open fractures are often accompanied by poor circulation. The consequences of undiagnosed compression fractures of the spine in children lead to the development of juvenile osteochondrosis - a dystrophic (associated with tissue malnutrition) disease of the spine, which affects the intervertebral discs, which is accompanied by their deformation, changes in height, and dissection. Also, such fractures can lead to spinal deformities, poor posture and persistent pain. Fractures of the pelvic bones may be accompanied by damage to hollow organs, such as the bladder.
[1] Limb segment - anatomical and morphological unit of a limb (for example, shoulder, elbow, lower leg, thigh).
[2] Computed tomography (CT) (from the Greek tomos - segment, layer + Greek grapho - to write, depict) is a research method in which images of a certain layer (section) of the human body are obtained using X-rays. Information is processed by computer. Thus, the smallest changes that are not visible on a regular x-ray are recorded.
[3] Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is one of the most informative diagnostic methods (not associated with x-rays), which allows obtaining layer-by-layer images of organs in various planes and constructing a three-dimensional reconstruction of the area under study. It is based on the ability of some atomic nuclei, when placed in a magnetic field, to absorb energy in the radio frequency range and emit it after the cessation of exposure to the radio frequency pulse.
[4] Tetanus is a deadly infectious disease caused by the bacterium Clostridium tetani. Its spores can enter the body through a wound contaminated with soil. Tetanus is characterized by progressive damage to the nervous system, convulsions, and paralysis.
Treatment
The regeneration capabilities of infants and children up to seven years of age are very effective and therefore a conservative approach is used in treatment to eliminate the consequences of injuries. Places of injury in the absence of displacement are fixed with a plaster splint (it does not cover the entire surface of the injured limb). In this case, hospitalization is not required, and treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis with regular visits to the doctor. Observations are made approximately once every five days.
Proper application of the splint is confirmed by a reduction in pain in the patient. Conversely, if the pain does not go away, swelling and numbness of the fingers appear, you should immediately contact a traumatologist and check the quality of the plaster.
In cases of displaced fractures, in the presence of bone fragments in the muscles, it is necessary to perform a surgical operation to place the fragments. Reposition of fragments is performed under general anesthesia and usually lasts no longer than half an hour, but in order to monitor the body’s reaction to anesthesia, the baby should be observed in a hospital setting for up to a week.
To fix unstable fractures, in addition to a plaster cast, metal knitting needles are used to fasten the fragments together. An X-ray photo allows you to perform this operation with proper accuracy. When healing occurs, the wires are removed, and the exit sites must be treated for some time to ensure wound healing.
If the lower extremities are injured, the method of skeletal traction with the use of a load can be used. The method shows its effectiveness for injuries of the tibia.
Factors influencing the rate of bone fusion
The healing of a broken bone depends on a number of factors that either speed it up or hinder it. The regeneration process itself is individual for each patient.
First aid is critical to the speed of healing. With an open fracture, it is important to prevent infection from entering the wound, because inflammation and suppuration will slow down the regeneration process.
Healing occurs faster when small bones are broken.
The speed of recovery is affected by the age of the victim, the area and location of the bone lesion, as well as other conditions.
Fusion proceeds more slowly if a person has bone tissue diseases (osteoporosis, osteodystrophy). Also, muscle fibers getting into the space between bone fragments slows down bone recovery.
The bone begins to heal better in the presence of the following factors:
- compliance with the doctor's instructions;
- wearing a cast throughout the entire prescribed period;
- reducing the load on the injured limb.
Rehabilitation
Removing the cast does not mean the end of the process of treating the consequences of the injury. Rehabilitation after fractures can take considerable time. The main effect on the restoration of damaged tissues is special therapeutic physical training complexes. Such exercises are carried out with the child two to three times a day. Initially, physical therapy is carried out by an instructor, and later these exercises can be performed at home on your own.
As a result of injury and prolonged immobilization, muscle tissue at fracture sites can be significantly reduced compared to normal volume due to muscle wasting. In rare cases, lengthening of the limbs affected by injury may occur. In such cases, in addition to traditional methods of physiological influence, constant monitoring by a traumatologist is necessary for at least six months.
What do frequent fractures mean?
Features of fractures due to physiological predisposition can be expressed in the following signs:
- Lack of microelements such as calcium and phosphorus in the child’s body. Children who refuse to consume dairy products and fish are at risk. The lack of calcium during a fracture is especially noticeable, since it is what gives the bones strength;
- The use of hormonal drugs in the fight against other diseases can lead to weakening of bone tissue;
- Lack of vitamin D, produced by the body when exposed to sunlight. If a child often sits indoors and does not walk outdoors, especially on sunny days, he does not receive enough ultraviolet radiation through the skin, and therefore his bones become less elastic.
In adolescence, the cause of injuries and fractures in children is rapid growth, during which the skeleton and individual bones do not have time to adapt to the increased load and are much easier to break than at an earlier age. Teenagers more often violate a balanced diet and lead an active lifestyle, and it is for these reasons that injuries of varying severity are not uncommon among them.
Characteristics of the fracture
A fracture is a complete or partial disruption of the integrity of bone tissue that occurred under the influence of external forces. Depending on the cause of their occurrence, they are:
p, blockquote 4,0,0,0,0 —>
- pathological, caused by diseases of bone tissue (tuberculosis, osteomyelitis, sarcoma);
- traumatic if the damage is caused by a blow, fall, push.
Characteristic features of any fractures are:
p, blockquote 5,0,0,0,0 —>
- resulting deformities or shortening of the bone;
- abnormal mobility in the area of injury;
- pain at the site of injury;
- unnatural position of the limb;
- audible crunching of bones when palpating the damaged area;
- rapidly growing swelling;
- inability of a limb to perform its functions.
As a rule, after a bone injury, the victim experiences a painful shock; with the open type, signs of blood loss are observed; closed fractures are accompanied by hematomas. When the back is injured, fractures are accompanied by pain and loss of sensation. Broken bones of the skull make themselves felt by loss of consciousness, clear or bloody discharge from the nose and ears.
Possible complications
There are two types of complications. The first type is related directly to the location of the injury. Not only the bone itself is injured, but also the surrounding tissues. The consequences of damage include:
p, blockquote 8,0,0,0,0 —>
- ruptures of blood vessels;
- muscle damage;
- trauma to internal organs caused by bone fragments (marrow, pleura, bladder);
- damage to nerve processes and plexuses.
In some cases, complications are more serious than the fracture itself. They affect how long it takes for the fracture to heal, significantly complicate the patient’s recovery or provoke further deterioration of his condition.