What determines the frequency of fetal movements?
The frequency of fetal movements depends on many reasons.
Women who have carried several babies will definitely tell you that each child was different in its frequency and manner of movements. Many people believe that the baby’s character is already formed in the tummy. It is important to understand what type of movements are normal for a given fetus, and what is evidence of its unusual state of health. The test for counting movements helps to navigate the “norm” for a given fetus.
Much depends not only on the fetus, but also on the lifestyle of the pregnant woman. If a woman moves a lot, this lulls the child and he is less active. When a woman rests, the child’s movements become more pronounced; at rest, the woman listens to herself more and notices movements more often. The opinion that some foods can “wake up” a baby is most likely wrong - the baby’s activity does not depend on the type of food the mother consumes, but depends on the level of glucose in the blood. After eating, within a short time, the level of glucose in the blood of the mother and fetus increases, which increases the number of fetal movements.
Often the fetus begins to move violently and painfully if the pregnant woman is in a stuffy, smoky room and experiences nausea and dizziness. Such movements occur in response to a temporary disruption in the flow of oxygen to the fetus.
The position of the pregnant woman's body is important. If the mother is positioned in a position that is uncomfortable for the child, he will definitely let you know about this with violent, intense movements.
So, if a pregnant woman lies on her back, mechanical compression occurs on the inferior vena cava (a large venous vessel through which blood from the lower half of the body returns to the heart). Compression of this vessel leads to a decrease in the venous outflow of blood, blood flow through the uterus worsens, the fetus begins to experience a slight lack of oxygen, to which it reacts with violent movements.
In addition, children react differently to loud sounds: some calm down, others, on the contrary, “rage”.
As a rule, strong, prolonged and painful movements indicate the child’s discomfort, while smooth and rhythmic movements indicate that the baby is feeling well. Increased motor activity can be observed with the threat of premature birth, polyhydramnios and the initial signs of umbilical cord entanglement. When the fetus moves, the blood pressure increases, the heart rate increases, which means blood flow accelerates, which leads to an increase in oxygen and nutrients in the blood. So, with his movements, the child can “ask” his mother to eat or go outside.
By movement, you can determine the position of the fetus in the uterine cavity. With a cephalic presentation, active movements are felt in the upper half of the abdomen, above the pregnant woman’s navel, and with a pelvic presentation, on the contrary, they are felt in the lower sections. Closer to childbirth, movements are felt mainly in the area where the baby’s limbs are located, most often in the right hypochondrium (since in the vast majority of cases the fetus is positioned head down and back to the left).
In the last weeks of pregnancy, the baby dramatically changes the way it moves. Most often, he begins to move less actively. However, when recording using ultrasound, it was shown that the number of movements remains almost unchanged, but their nature changes: the fetus turns and pushes less often, but still moves its arms and legs with the same frequency. The woman feels these movements weakly or does not notice them at all. It is precisely this fact that is associated with the erroneous idea that before childbirth the fetus supposedly freezes.
Why can't I feel fetal movements?
Pregnancy » During pregnancy » Why can’t I feel fetal movements?
The baby's movements in the womb are not only an indicator of his condition, but also a unique way of communication between the mother and the unborn child. But it happens that a woman stops feeling these movements. Panic begins. “I don’t feel any movement!” - that’s how it flashes through my head. Fear and anxiety about the baby's condition is a natural reaction to this. What causes a decrease in the frequency of movements and when do you need to act immediately?
When does a woman start to feel movements?
At just seven weeks, the baby makes its first movements, but they remain invisible to the woman. The time when you begin to feel the baby for some expectant mothers is at 14 weeks, for others at 25, but most often a woman feels the first movement between 16-18 weeks. Moreover, this happens earlier in multiparous and thin women.
Some mothers understand perfectly well that the kicks that the baby makes are just movements; some confuse them with digestive processes. Some people look forward to them, listen to the slightest changes, others don’t notice them at all because they are so busy.
In the third trimester, it is often possible to identify existing problems by the nature of the child’s movements.
After 24 weeks of pregnancy, the baby can make about 15 movements per hour, and after that sleep for several hours.
After 30 weeks, the gynecologist may ask you to keep a diary of movements: in 12 hours, the mother should feel at least 10 periods of movements. The period of movement is the period from the moment when the baby began to move until the moment of complete calm: it is possible that one period will last several minutes, and the other about an hour.
Until 32-33 weeks, the baby moves very actively and often, then the number of movements may decrease, but the periods should still not be less than 10.
For what reasons may a pregnant woman not feel movements?
1. In the first and most of the second trimester, it is normal to feel a lack of fetal movements, because the baby is still too small and has enough space in the mother’s belly.
2. Every baby has a period of activity and a period of calm when he sleeps and, naturally, at this time the mother notices the absence of tremors. If this causes concern, then to check the baby's condition, you can lie on your left side and spend about an hour in this position, or eat something sweet, hold your breath, or do some physical exercise. In any of these cases, normally, the baby will have to react with jerks. If this does not happen, then it is better to go to the maternity hospital.
3. A decrease in fetal movements or the baby completely quieting down is observed in some cases when the mother approaches the source of loud sounds.
4. If a woman is active, walks a lot, plays sports, then soothing movements help calm her and the fetus can sleep a lot.
5. The most dangerous reason is a frozen pregnancy.
When is the absence of fetal movements a bad sign?
But the reasons for the lack of movement are not always so harmless: sometimes they are a sign that not everything is all right with the baby.
The most dangerous case is when the mother does not feel movement for more than 12 hours at a period of 28-32 weeks and 6 hours at a later stage, because this may be a sign of a frozen pregnancy. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor.
It is also necessary to pay attention to poor fetal movements and changes in the baby’s activity over several days: if initially movements become stronger, more frequent or erratic, and then after a few days, on the contrary, rare and weak, then this indicates that the child is suffering from excess carbon dioxide and lack of oxygen (fetal hypoxia).
What are the movements during hypoxia?
Fetal hypoxia is a quite dangerous and common phenomenon, and there are many reasons for its occurrence. In order not to miss the first signs, women need to constantly monitor the baby’s movements. If a child suffers from a lack of oxygen, then he begins to move too actively in order to thus increase the incoming amount. In this case, his tremors become quite strong and sharp. Hypoxia often occurs if the mother takes the wrong position: she lies on her back or sits cross-legged. Often it is enough to change the position of the body for the child to feel much better.
If the situation does not change and hypoxia becomes chronic, then a decrease in fetal movements occurs, the baby begins to move less actively and not so intensely (less than 3 movements per hour), his tremors become weak, and in extreme cases, there is no movement at all.
In any case, if the expectant mother doubts whether everything is okay with the baby, there have been no movements for more than 12 hours, it is better to consult a specialist, do an ultrasound and CTG of the fetus. Perinatal psychologist Dmitrieva Veronica
If there are no movements, the baby can just sleep
At week 24, the mother notes 10-15 movements of the embryo in 60-80 minutes. If the embryo calms down for 3-4 hours, young women wonder why the baby is quiet. If this happens once a day, then you should not worry. The fetus should fall asleep for 4 hours to relax the muscles and slow down the rate of metabolic processes in the developing body. This time is necessary to normalize cellular metabolism and remove unnecessary substances.
What determines the frequency of fetal movements?
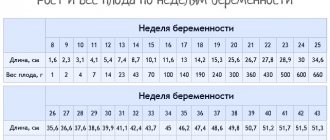
The baby in the placenta is constantly moving, making up to 200 kicks at 20 weeks of pregnancy. In the period from 28 to 32 weeks, their number increases to 600. After this time, the activity of the embryo gradually decreases, which is associated with its growth and reduction of free space in the uterus. After 7 months of intrauterine development, the baby pushes up to 8-10 times per hour of wakefulness.
The frequency of movements for each embryo is strictly individual. It depends on the woman’s diet, her activity, exercise and hormonal levels. The room in which the pregnant woman is located plays an important role. Sources of light and noise can irritate the embryo, which increases its activity as a sign of dissatisfaction.
How to properly check movements at home. 2 special tests
In the third trimester of pregnancy, a woman should keep a calendar of fetal movements. In it, the expectant mother records the number of kicks over a period of time. To assess the activity of the embryo, there are 2 tests:
- Count to 10. In this case, on a special form you need to mark the number of embryo movements every day. A woman should count her kicks for 12 hours. If the number of movements during this period is less than 10, she needs to see a doctor.
- Sadowski's method. After the evening meal, the pregnant woman should lie on her left side and count the movements of the embryo. Normally, he should push the uterus about 10 times in 60 minutes. If the number of movements is less than normal, counting continues for the next hour. In the evening, due to an increase in serum glucose levels, fetal activity increases 3-4 times, so during this period pathologies can be diagnosed in time.
How to help a very active child calm down in his stomach?
If during the day fetal movements rarely cause discomfort to the expectant mother, especially if she is on the move all day, then at night they can become the main cause of insomnia. In order to calm a child who is very active in the stomach, a pregnant woman should take the following measures:
Walks in the open air. They are needed to prevent oxygen starvation and excessive activity of the fetus. If it is not possible to take a walk before going to bed, then thoroughly ventilating the room will be enough. Gymnastics and various warm-ups are also a good way to prevent hypoxia. Change of body position. Often increased fetal activity can be caused by the mother's uncomfortable position. Sometimes simple rolls from back to side help cope with strong movements of the baby in the stomach. Eliminating the source of stress. The emotional connection between mother and baby is very close, so it is no coincidence that he reacts sharply to her mood. With a balanced mother, the baby grows calmer. Listening to calm music. Classical music and a gentle parental voice have a positive effect on the condition of the fetus. Balanced diet. The food a mother eats during pregnancy should be healthy. Preservatives, caffeine, and flavorings excite the fetal nervous system. They should be avoided during pregnancy. Drink soothing herbal teas and infusions. During pregnancy, it is better to replace black tea, rich in caffeine, with a herbal drink with mint or lemon balm. Establishing contact with the child. Rhythmic stroking movements on the belly soothe the baby
This should be taken into account if the baby is very active in the stomach at night. The warmth of his mother's hands will help him calm down faster
Test to determine the number of movements
From the 28th week of pregnancy, the expectant mother must take control of the child’s activity. This test is carried out 2 times a day (morning and evening) and consists of performing a simple sequence of actions. Mom needs to count the number of movements during a certain period of time and write them down. The test is performed in the following sequence:
- Mom records the time of the first movement (for example, 9 a.m.).
- The woman records all movements of the fetus, including light kicks and rollovers.
- As soon as 10 movements are recorded, the counting stops. As a result, the time interval from the first to the last shock should be about 20 minutes. This indicates good fetal activity.
- If a pregnant woman does not feel the baby's movements within an hour, she is recommended to have a snack with chocolate or drink sweet tea, and then continue the control count. If fetal activity remains low, you should consult a doctor.
It is worth noting that from 28 to 32 weeks the baby will move more actively than, for example, in later stages of pregnancy
This fact must also be taken into account when calculating movements.
What to do if there is no movement, and why the baby does not move in the stomach
The absence of movements heard by the mother does not indicate that the baby is not active. Quite often, movements are recorded on ultrasound, but for some reason the mother does not feel them.
There are ways to “wake up” your baby:
- Pat the belly with patting movements. If the pregnancy is over 28 weeks, the baby understands the warmth from touch and pushes to the place where the hand of mom or dad is located.
- You can enjoy the sweet hour with a chocolate bar or chocolates. The glucose present enters the baby's bloodstream and will cause his activity, but sometimes this method is ineffective.
- A glass of cold water should cause a change in internal temperature and provoke the baby to move.
- Play loud music that your child likes.
If it is not possible to induce fetal activity for two or more hours, you should go for a consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist. He will be able to listen to the fetal heartbeat and measure its activity using a CTG machine.
The most terrible reason for the absence of tremors is intrauterine fetal death.
How to wake up a baby if there is no movement for a long time?
Sometimes a pregnant woman catches herself thinking that she has not heard her baby for several hours. This is normal, the baby also sleeps for up to 3-4 hours at a time. If it seems that this period has long passed, you can try to stimulate fetal movement. You can do some physical exercises, breathing exercises, or pour a stream of cold water on your stomach. The easiest way is to hold your breath and the child will begin to worry and move in response to the lack of oxygen.
If the breath-hold test doesn't work, try the following: walk or go up and down the stairs, then eat something sweet (glucose and physical activity stimulate movement), and then lie quietly for two hours. As a rule, these events help to activate the fetus, and movements will resume. If this does not happen, you should consult a doctor within the next 2-3 hours. Also, if the situation when the child’s movements are not felt during the day is repeated too often, you need to inform the doctor who is observing you about this.
Why might a child move little or stop doing so?
It is not always bad when the baby begins to move less or does not show physical activity at all. This may be due to physiological reasons. In other cases, it is worth thinking about the abnormal course of pregnancy. One way or another, when the fetus stops pushing, you need to consult a doctor for advice.
Physiological reasons
If movements are not felt for more than 3 hours, you should try to rouse the baby - for example, eat sweets or drink sweet tea, lie on your left side for about an hour, take a walk, walk up the stairs. The child must respond to such actions.
As a rule, towards the end of pregnancy, a woman recognizes the baby’s sleep and wakefulness cycles, knows all his habits and preferences, so she is not particularly worried when he calms down. Excessive concern for movements in the abdomen, as well as an absolute lack of attention to this phenomenon, is not welcome.
Causes for concern
Sometimes the fetus does not move or moves less actively as a result of lack of oxygen. This can be indicated by the baby's calmness during the day, when the mother is awake and knows that he is usually awake at this time. In this case, you need to consult a doctor. If it is not possible to see a gynecologist right away, you should call an ambulance.
Doctors will use a special device to listen to the fetal heartbeat, which is normally 120–160 beats per minute. If the overall indicators are normal, a cardiotocographic study is performed to evaluate the contractions of the baby’s heart, its general condition and identify hypoxia.
This examination takes about half an hour. If no motor reaction was detected during the test, the pregnant woman is asked to move actively, then the study is repeated.
If hypoxia is confirmed, treatment is prescribed, which depends on the severity of the pathology. In case of minor deviations, the pregnancy is constantly monitored, and various examinations are periodically carried out. If the symptoms of hypoxia are pronounced, urgent delivery is necessary. Depending on the condition of the pregnant woman, they resort to caesarean section or induction of labor.
Fetal movement during pregnancy
Let us note right away that every pregnant woman feels the movement of the fetus in her own way. Some people equate this feeling with the fluttering of butterflies in the stomach, others associate it with a kind of bursting of bubbles, and others clearly feel the baby’s kicks.
Baby's first movements in the stomach
During pregnancy, the baby begins to move very weakly for the first time and this is not very noticeable. Moreover, this happens very rarely: several times throughout the day or once every 2-3 days.
Fetal movement activity
In this case, everything directly depends on the lifestyle of the expectant mother: if the mother is very active, then the child sleeps more and vice versa.
When does the baby move the most?
Basically, the baby in the stomach is constantly moving. When the mother is in a kind of rest mode, if you can call it that, the baby begins to move more in the womb. And this starts to scare mothers a little, which is why questions arise; the baby is moving a lot in the stomach.
The movement of the fetus is directly affected by adrenaline, which is released from the mother in various stressful situations; this adrenaline is also transmitted to the baby, who begins active movements. But this is not observed in all women. For some, it's the other way around. Each pregnancy, in fact, like any person, is individual and unique in its own way. There is no specific “instruction” for everyone.
Stress during pregnancy
The perinatal connection between mother and child plays a huge role in shaping his health, because all the feelings and emotions, the stress that a woman experiences during pregnancy, are transmitted to her fetus. If the mother is in a positive mood, then the baby will feel good and calm, but as soon as she gets a little nervous, a real disco begins in her stomach. Stress during pregnancy can harm not only the mother, but also the baby. After all, experiencing stress during pregnancy , a woman sharply reduces the delivery of oxygen and nutrition to the baby and he has no choice but to move actively, thereby massaging the placenta in order to receive a sufficient portion of blood during uterine contractions, and with it the necessary elements to maintain vital functions. It’s good if mommy immediately comes to her senses and tries to correct the current situation, otherwise she risks causing irreparable damage to the unborn little person.
Find and relieve stress during pregnancy
Hans Selye, the author of the term “stress,” believed that it is a nonspecific reaction of the body to a situation that requires its restructuring in order to adapt to changed conditions. These conditions can be internal or external. The latter are associated with sudden changes in what is happening around a person, and, as a rule, cannot be controlled. These include some crisis and emergency situations. But there are exactly as many reasons for internal experiences as there are women in an “interesting” position. This list mainly includes fears that make all mothers, without exception, nervous. Let's try to figure out together why they arise and how we can deal with them.
Evolution of sensations in the stomach of an expectant mother
As pregnancy progresses and the fetus develops, the nature and frequency of movements change accordingly. This must be monitored in order to consult a doctor in time if alarming signs are detected. It is necessary to inform the specialist when the baby began to move and how actively he does it.
In the middle of the second trimester, pregnant women begin to really feel the baby's movements (however, he makes chaotic movements already from the 3rd month). Some describe the sensation as butterflies in the stomach. As the fetus develops, it moves more and more actively, and by the 22nd week all pregnant women should feel this (see also: how often should a baby move at the 23rd week of pregnancy?).
The child does not just move chaotically all day, he performs various actions. During an ultrasound examination, they notice how the fetus swallows liquid, rotates its head, twists its arms, touches the umbilical cord, etc. If the child turns over, a change in the shape of the abdomen is observed.
Closer to childbirth, the tremors are felt more on the right side if the baby is positioned upside down. They often cause discomfort, and to avoid it, you can lean forward or lie on your side. Also, in later stages, the head or buttocks are fixed at the entrance to the pelvis, the fetus moves less, because it is cramped. However, some babies begin to push harder.
Why is it necessary to monitor your child's movements?
Doctors recommend keeping a calendar and noting there all changes associated with the activity of the fetus. Thanks to them, it is possible to obtain information about its condition, for example, what position it is in.
If the tremors are felt in the upper part of the abdomen, it lies head down; if in the lower part, the baby is in a breech position.
Of course, the movement of a child is a very individual process, and yet it has its own norms and deviations. Don't worry if the baby doesn't make itself known for several hours - he may simply be sleeping.
But if the immobility drags on, this is a reason to be wary. You need to try to motivate the baby through physical exercise and eating sweets.
If this does not help, you will definitely need to consult a gynecologist.
Norms and control over the child’s movements
From the 24th week of gestation, the average fetal kicks are 10-15 times a day.
Active movements appear in the afternoon, and often at night.
Sleep is 18 hours, and the duration of 1 sleep period is from 3 to 4 hours. At this time, the baby makes a minimum number of movements that the woman does not feel.
You can monitor the number of fetal movements yourself. There is a whole scheme for this.
- Keep a diary for notes;
- Starting at 28 weeks, perform a movement test.
The essence of the method is to count 10 fetal movements twice a day. From 9am to 9pm, and from 9pm to 9am. The test can be performed daily.
Example, the first fetal activity is at 9.20, then at 11.40, 3 - at 12.15, etc. 10 movement - at 17.35 - 1 part of the test is over, the table indicates 2 times 9.20 and 17.35. The second part of the test is counting from 9 pm to 9 am.
According to this technique, constant monitoring of the baby’s activity is possible. An alarm signal is a complete absence of movement for 12 hours, or excessive activity.
The bigger the baby gets, the stronger its movements, and it feels like the baby is dancing in the womb.
How does a baby move just before birth?
Before labor, from 32 to 36 weeks, the following changes are observed:
- the child reduces activity;
- the kicking stops, the embryo prepares for birth, contractions begin;
- During uterine contractions, the fetus actively moves, but these sensations are overshadowed by severe pain.
To track the dynamics of movements and evaluate the heart rate of the embryo, doctors connect a CTG machine.
Read further:
How does the baby behave before birth and during contractions - does he actively move or calm down?
A child hiccups in the stomach during pregnancy - what does this mean and what is the cause of hiccups?
Clicking in the abdomen during late pregnancy - natural causes and causes for concern
39th week of pregnancy: the belly turns to stone - causes, associated symptoms, reasons for concern
The child sleeps on his stomach - is it possible for a newborn to sleep with his legs tucked under?
Hard belly during pregnancy - causes in early and late stages, symptoms, reasons for concern
How does the expectant mother feel?
In order for a pregnant woman to feel the first movements, the baby must push quite hard against the wall of the uterus. In this case, the sensations of the expectant mother will be barely noticeable. They can be compared to the movements of a small fish or the fluttering of a butterfly. But it is from this moment that the woman becomes the “sensor” that allows her to monitor the condition of the baby in her stomach.
The baby's first movements are not clearly coordinated, but over time they acquire a certain meaning and meaning. In many ways, the frequency of fetal movements depends on the activity of the mother and the time of day. On average, a five-month-old baby makes up to 60 movements daily in the womb.
From about 24 weeks, the baby’s movements become clearer, and in the third trimester you can even see the belly moving. The movements feel more like the movements of a newborn. Most women call them very nice.
In the long term, the expectant mother often feels pain in the hypochondrium when the baby moves. This is not a deviation from the norm. It is enough to change the position of the body and the movements will become moderate. If active movements of the fetus in this case cause pain to the woman, it is recommended to inform the doctor about this.
Why count movements?
Experts say that the number of movements a baby makes in the womb is an important marker of his condition. If the child moves too much or too little, you must tell the doctor about this: it is possible that additional tests will be needed to understand whether everything is okay with the unborn baby. But if you don’t track movements and count them, you’re unlikely to be able to understand when the baby moves more and when less. Our perception is subjective, it can always “seem”, but the doctor needs accurate data.
Plus, counting kicks and bumps is a great way to bond with your baby before he's even born. Some even communicate with the baby by tapping on the stomach: the little man is curious about what is happening there, outside, and he responds to tapping with movements from the inside. They say that you can even teach math to a child this way!
Diagnostics
If the child does not move, what should you do - run to the clinic, or call an ambulance and go urgently to the emergency department of gynecology and obstetric pathology.
If a woman does not feel the baby in the womb, this does not mean that the child has already died. In some situations, emergency delivery saves the baby's life.
In order to establish the reasons for the lack of movement, cardiotocography is performed - if the “heart” is not detected, an emergency ultrasound is performed. It is at this stage that the sequence of actions of the medical staff is determined.
Antenatal fetal death is the death of a baby in the womb. The fetus and its location will not leave the uterine cavity on its own, so the woman will have to endure the birth of a still child.
The type of delivery is selected individually depending on the gestational age. Preference is given to natural childbirth, but in some cases a caesarean section is performed.
Causes of fading
A frozen pregnancy, regardless of gestational age, must be removed. In the early stages - curettage, in later stages - artificial birth with the help of hormone therapy. The reasons for pregnancy failure are different; they are classified according to the timing of development.
In the first trimester
- chromosomal abnormalities;
- violations in the laying of genetic material;
- maternal infectious diseases;
- alcohol addiction;
- smoking and drug addiction;
- hereditary diseases;
- chronic pathological processes.
It is possible to unambiguously identify the cause of fetal death in the first trimester using a histological examination of a biopsy of the placenta and the fetus itself.
In the early stages, a miscarriage occurs when the fertilized egg is rejected. The most common culprit is hormonal imbalance.
In subsequent trimesters
- Infectious processes, in particular sexually transmitted ones;
- Acute fetal hypoxia. These include: entanglement with the umbilical artery, oligohydramnios, polyhydramnios;
- Rh conflict with the development of severe anemia;
- cardiac pathologies, especially those that poorly supply blood to the fetal heart muscle;
- genetic diseases;
- Endocrine disorders (thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus).
The main cause can be identified after ultrasound diagnostics and pathological examination of post-mortem biomaterial.
If the baby doesn’t move much in the womb, there are several reasons:
- Short term;
- Fullness of a woman;
- Problems with the baby's health.
What determines the frequency of fetal movements?
The frequency of movements the baby makes depends on many factors. Conventionally, they can be divided into physiological and abnormal.
Physiological ones include:
- emerging character;
- desire to eat;
- mother staying in a stuffy room;
- presence of loud bass in the room. For example, when listening to high frequency music;
- the mother's position is comfortable or uncomfortable for the child.
Smooth, painless kicks are an indicator of the baby’s normal well-being. Their number depends on the duration of pregnancy and the length of motherhood.
From abnormal reasons:
- acute hypoxia;
- threat of premature labor;
- polyhydramnios;
- infection.
The tremors are rough and painful; in later stages, a pathological process can be suspected based on the baby’s violent behavior. However, the cause of activity or lull can be determined after consulting a doctor and ultrasound examination.
In the first trimester, there are no tremors due to the baby’s small height and weight.
In the second trimester, starting from the 18th week, the first weak movements appear, intensifying as pregnancy progresses. From 24 weeks the baby is active.
At the end of the second trimester, the mother is able to control the movements of the fetus by stroking the belly and talking to the unborn child.
During the trimester, activity gradually fades away - the fetus grows, enlarges and it is difficult and tight for it to make movements, but they do not disappear completely.
Why doesn't the fetus move?
It is normal for your baby to move. The small embryo begins to grow, and at the same time its skeleton and nervous system begin to develop. It begins to react to external factors and move. Therefore, when a woman does not get any sense, it begins to scare her. In this case, it is important to study it and take the necessary actions.
The baby begins to move
The baby begins to make the first pushes around the beginning of the 4th or 5th month. Since they are the first, they will not be immediately noticeable. This can be explained by the fact that at this time the fetus is small.
Important! The period of the first tremors is different for everyone, so everything here is individual.
Over time, the fetus begins to actively move. The strength of the shocks and their number increase. You need to monitor this, and if something goes wrong, contact a specialist.
Normal for fetal movement
The frequency of the baby's kicks depends on two factors: physiological and abnormal.
Physiological:
1. formation of character 2. presence of loud sounds 3. position of the mother 4. desire to eat
Such tremors are calm and painless. They are an indicator of the child’s well-being.
Anomalous:
1. diseases 2. acute hypoxia 3. threat of premature birth of a child 4. polyhydramnios.
At the same time, the shocks are rough and cause unpleasant sensations. Here it is advisable to consult a doctor.
Frequency and control of fetal movements
During the first trimester, there are no tremors. This happens due to the fact that the fetus is still very small. In the second trimester, from about 18 weeks of pregnancy, the first tremors appear and intensify. And at week 24 they become more active. But at the end of the third trimester, these movements can be controlled. To do this, the mother talks to the child and strokes the belly.
Baby moving before birth
At this time, the tremors become less intense for reasons such as: The child is already large, but at the same time continues to develop. The child takes a vertical position, although previously he was in a horizontal position. It is positioned upside down.
Causes of baby kicking
The reason for the baby's kicks is his desire to find the most comfortable position for himself, so he begins to move. This happens in the second trimester of pregnancy.
Reasons why the fetus does not move
Sometimes it happens that during an ultrasound examination the child is normal and active. Mom just doesn't notice it.
Then there are ways to help your baby wake up:
1. you can stroke or stir your belly a little 2. you can eat or drink something sweet 3. you can play loud music or make any other loud sound.
And if after this, within 2-3 hours, the child still does not show activity, then you should contact a gynecologist.
The causes of fetal fading can lead to a frozen pregnancy. Its causes depend on the duration of pregnancy.
So in the first trimester there are: 1. chromosomal abnormalities 2. disturbances in the genetic material and its formation 3. maternal diseases 4. alcohol addiction 5. tobacco and drug addiction 6. diseases transmitted by inheritance 7. chronic processes
In subsequent trimesters there are: • infectious processes, which also include those that are sexually transmitted • acute hypoxia • hereditary diseases • endocrine disruptors
Fetal activity may decrease for three reasons: • short gestational age • maternal obesity • child health problems.
What to do if the fetus does not move?
If your child has not been active for a long time, you can check his condition yourself. There is a method called the “Sadowski technique”. To do this, you need to count the number of movements the baby makes after eating, lying on your left side for an hour. There must be at least 10 of them.
Important! If you have a feeling that something is wrong with your baby and he is not active enough, you should immediately consult a doctor and not try to find out anything on your own.
In this case, it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound examination and cardiotocography. Thanks to this, it is possible to save the baby. If a miscarriage does occur, it needs to be helped to leave the mother's body.
Important! This process cannot be delayed, otherwise it could take the life of the mother.
Pregnancy is a period of maximum fusion between the child and the mother, so it is necessary to take care of your health and the health of the baby.
From the 24th week, the fetus already communicates with the mother through movements
Intrauterine movements indicate normal well-being of the embryo. From 18 to 20 weeks, its activity is low and does not appear every day. It is recommended to record kicks from the beginning of the 6th month of pregnancy, when the fetus can move its limbs or move in the uterine cavity. The child moves chaotically in response to external stimuli or the emotional state of the mother. With the help of tremors, the fetus informs the pregnant woman about its well-being. The frequency of movements may vary depending on the behavior or emotions of the fetus.
If the baby kicks, that's good
If a child kicks in the stomach, this indicates his good health and normal intrauterine development. High activity is observed from 24 to 32 weeks. With the help of pushes, the child communicates his mood or changes in it.
Can movements cause pain?
Sometimes the baby's movements cause discomfort to the mother. Thus, painful sensations can appear when a woman lies on her back or sits with a straight back, especially with her legs crossed. In this case, increased physical activity is not a pathology and is most often associated with the uncomfortable position of the expectant mother, when less oxygen is temporarily supplied to the fetus due to decreased blood flow. If pain occurs, you need to change your position: bend forward, stand up, lie on your side. Calm down, relax, take a few deep breaths. Pat your belly, talk to your baby. Usually such simple techniques are enough to change the behavior of the fetus.
If fetal movements result in pain in the right hypochondrium, be sure to tell your doctor about it. It is necessary to exclude diseases of the gallbladder in the mother, for example, gallstones. Pain under the sternum when the fetus moves may indicate the presence of a diaphragmatic hernia.
If a pregnant woman has a scar on the uterus after a cesarean section and she feels pain in the area of the scar when the baby moves, then this should also be reported to the obstetrician-gynecologist. Pain in the area of the uterine scar may be one of the signs of its inferiority.
Fetal pressure on the bladder area can also be painful. Such pain can also occur with inflammation of the bladder (cystitis). A general urine test will help rule out cystitis. If the analysis is normal, there is no need to worry.
Sometimes a pregnant woman may feel a throbbing sensation in her abdomen. This is the pulsating blood in the umbilical cord. If this phenomenon is not permanent, then there is no need to worry.
A very common occurrence is the baby’s hiccups, which a woman feels in the form of rhythmic tremors inside herself. Such episodes can last up to 10-20 minutes at a time and appear a couple of times a day. Experts say that it does not pose any danger to the baby and does not cause him any unpleasant sensations; on the contrary, it is a sign of a normally developing central nervous system of the fetus. From about 28 weeks, the fetus begins to breathe. In this process, he swallows amniotic fluid, which provokes contraction of the diaphragm. Hiccuping is an unconditioned reflex that every born child has. You should not have any cause for concern, however, just like women who do not feel fetal hiccups. It’s just that every woman has her own threshold of sensitivity, some simply do not detect small movements of the fetus. If episodes of hiccups become more frequent and longer, tell your doctor. In some cases, like increased other movements, this may be a sign of fetal distress.
The main causes of movement
Many girls complain that they are not pregnant, something is moving in their stomach. There may be several reasons for this, and some of them are quite dangerous. In thin girls, a pulse can be felt when lying on their stomach. This is due to the fact that there is practically no fat layer in the abdominal cavity, and when the muscles are tense, pulsation can be clearly observed.
However, such a manifestation may also be a sign of a serious illness, in particular, such as an aortic aneurysm. This disease is additionally accompanied by frequent urge to go to the toilet, belching and painful sensations near the umbilical fossa. In some cases, there may additionally be nausea and bloating.
In addition, movement can occur during fermentation in the intestines, which is associated with malnutrition, as well as the installation of internal organs in their original place after childbirth. If something seems to be moving in the stomach, then the reason for this may be helminths, which are found in many people and cause great harm to the body.
When does the baby start moving in the stomach?
Despite modern methods of diagnosing the fetus, movements are perhaps the main confirmation of its normal development and growth. Usually the expectant mother begins to feel them in the fifth month of pregnancy. But in fact, the child begins to move much earlier.
In the eighth week of pregnancy, the fetal nervous system begins to develop. By this moment, he already has muscle tissue, which is excited by nerve impulses. The first motor reflexes, caused by contractions of nerve endings, are observed in the fetus from the end of the eighth week of pregnancy. Thus, in the womb the baby begins to move quite early, although unconsciously. In addition, there is still quite a lot of space in the amniotic sac and the embryo floats freely in it without touching its walls.
At about 16 weeks of pregnancy, the baby begins to respond with movements to sounds, primarily to the voice of its mother. With each subsequent week, fetal movements only intensify. At 18 weeks, he is already touching the umbilical cord, covering his face with his hands and making other simple movements.
The date when a woman can say for sure that the baby in her stomach is moving very actively is individual for each pregnant woman. This happens between 18 and 22 weeks. It all depends on the sensitivity threshold of each individual woman. With each subsequent week, the movements become more intense and clear. From them, a pregnant woman can judge whether the baby is growing and developing normally in the uterus, whether he is receiving enough nutrition and oxygen.
When does a woman begin to feel fetal movements?
Most expectant mothers are interested in when the baby will start pushing. Most often, the first movements are noticed in the middle of the 4th - early 5th month. It is impossible to name an exact date, because it is individual. Sometimes the child begins to move earlier, sometimes a little later. Within the specified two weeks, the onset of movements is considered normal.
Why does the baby move very actively in the stomach?
It is considered normal when a pregnant woman feels 10 distinct movements during the day. At the same time, in recent weeks the kicks may be less obvious, their character changes. This is explained by the fact that by the end of pregnancy the baby becomes quite large and feels cramped in the stomach. If from 24 to 32 weeks a woman experiences more than 10-15 movements per day, she needs to see a doctor.
It should be noted that usually the baby in the belly is very active due to:
- hypoxia – lack of oxygen to the fetus;
- unstable emotional state of the expectant mother, overexcitation, stress;
- smoking, drinking alcohol and other bad habits;
- unbalanced diet.
Consuming caffeine, too spicy foods and other foods that have a strong taste negatively affects the baby's emotional state, which is why he may move more. To help the baby calm down, you should find out why the baby in the stomach is very active. In addition to the above reasons, the fetus reacts sharply to other factors occurring outside.
Why did the fetus stop moving in the stomach?
The baby has stopped moving - this is a very exciting situation for the expectant mother.
Does he have enough, does he feel good, is he comfortable? At the first stage of bearing a baby, you can only find out about this through tests and ultrasound. But from 18-25 weeks, the woman begins to feel the movements of her baby in the womb. Some experience this joy a couple of weeks earlier. From now on, you can monitor your baby’s well-being using these extraordinary signals.
Doctors usually indicate the need to count the number of movements during the day, starting from 24-25 weeks. At this stage, the fetus should normally be active at least 10 times a day. Before this period, movements are simply unnoticeable to the mother. And after 36 weeks, the baby becomes too cramped in the womb for frequent body movements. But their strength increases. Monitoring fetal movements is very important. After all, this is the main indicator of his condition, which is constantly available to a pregnant woman. And why the fetus has stopped moving in the stomach, you should definitely ask your doctor, and without delay, if such calmness lasts 12 hours or more. Intrauterine death is the worst thing that can cause a lack of fetal activity.
The intensity of movements depends on several factors. The greatest activity of the baby can be felt when in certain positions - lying on his back or crossing his legs. That is, in those in which the supply of oxygen through the blood to the child’s place slows down. The baby massages the placenta, accelerating blood flow. These body movements are felt. The “bellies” also behave restlessly when the mother is in a stuffy room. Or when sitting indoors for a long time.
Your baby may react to certain foods. So, sour lemon and sweets can provoke a series of body movements. In addition, an unborn little person already has his own temperament and develops a certain daily routine. Most often during the day, when the mother is active, the child is rocked to sleep by her movements and sleeps for 3-4 hours with short breaks. Mom’s emotions are also a reason to show her position. External stimuli, such as loud sounds and bright lights, will certainly cause a reaction from the little man.
Thus, the child usually does not move in a state of sleep or simply at rest. This may indicate that he is happy with everything and feels good in the womb. Among other things, this may be a sign of fetal distress. Do not feel embarrassed under any circumstances and call an ambulance if you realize that there are no or very few movements during non-working hours. The specialist will listen to the child’s heart or prescribe an extraordinary ultrasound or CTG examination. Timely measures taken will protect you from sad consequences. This is the case when it is better to play it safe so that the pregnancy ends well.
source
When should you see a doctor?
Minor movements should normally be regular; as a rule, the baby is “at the peak of activity” up to ten times a day.
If the movements are sluggish
If the movements are sluggish, or you have stopped feeling them altogether, this is a reason to consult a doctor.
This condition may be associated with serious diseases that need to be diagnosed urgently. Doctors prescribe ultrasound and CTG to identify the cause.
Most often it is hypoxia, which, in turn, is caused by various complications and diseases in both the mother and the fetus. Among them are cardiovascular diseases, anemia, diabetes, abnormal position of the fetus in the uterus and more. With oxygen starvation, excessive activity is most often replaced by lethargy of tremors. If the diagnosis is confirmed, pregnancy should proceed under close medical supervision.
anka1020
What should you pay attention to?
The common opinion that a baby’s activity is a sign of hypoxia is unfounded; most often the opposite is true. With sluggish movements, the fetus experiences hypoxia, although it may simply be little active today. However, if after thirty weeks of pregnancy your baby moves infrequently, sluggishly and weakly, this is a reason to contact an obstetrician-gynecologist. The doctor will examine the mother, measure the abdomen and the height of the uterine fundus, and listen to the fetal heartbeat.
To accurately clarify the circumstances, CTG is prescribed. Which is carried out as planned from 34 weeks. But if necessary, at an earlier date. Normally it is carried out once a week. For 30-60 minutes, the heartbeat is recorded and fetal movements are noted. After this, a 5-point assessment is carried out. The baby's heart rate should be from 120 to 160 beats and vary over time. In addition, it must change in response to external influences and movements. During active movement it intensifies to 17-190 beats. But monotonous contractions or periods of decreased heart rate to 90-60 beats may be a sign of severe lack of blood circulation and hypoxia. This requires immediate action, up to and including a caesarean section. In addition to CTG, an ultrasound can be performed to determine the degree of blood flow in the placenta and umbilical cord using Doppler.
What could a baby’s unusual “behavior” mean?
As mentioned above, the main disorders may be a decrease in the baby’s motor activity. You may need to walk and move more, but if movements are inactive, an examination to rule out hypoxia is necessary. There are many causes of hypoxia - pregnancy complications, diseases - anemia, heart and vascular disease, diabetes. Hypoxia can also be caused by bleeding, placental insufficiency, prolapse of umbilical cord loops or their compression, diseases of the fetus itself - infection or Rh incompatibility.
Among pregnant women, there are still myths about fetal movement. One of them claims that the baby, located in the mother's tummy, can distinguish between day and night. He must be active during the day and sleep at night. Therefore, if the expectant mother lies down to rest during the day, then the baby begins to push and twirl vigorously. This myth is unfounded; children do not distinguish between day and night. It's dark in my tummy all the time. The baby has his own personal sleep and wakefulness routine, which may not coincide with the mother’s routine. Sometimes babies can still cough and hiccup in the stomach, and mothers perceive these actions as active movements. Such actions are not dangerous for the baby. He trains to live outside the tummy and develops his skills. And hiccups can also occur due to swallowing a large volume of amniotic fluid.
Sometimes, by the baby’s movements, you can determine the temperament of the future baby. There are calm babies who behave peacefully in their tummy, but the mother begins to worry about the child’s health. And there are restless people who kick their mother so hard that they don’t let her sleep peacefully. A child in the womb can distinguish between the head, the mood of the mother, and the hands of the father, so you need to communicate with your unborn baby as early as possible and as often as possible, sing to him, listen to music, talk to him, stroke him. Then the baby will respond to you with a cheerful tapping of his hand or foot. The baby does not like sharp sounds, roar and excitement of the baby - he reacts to them either by freezing or persistent kicks so that the mother eliminates the source of the noise.