Causes of splenomegaly in children
The spleen responds to any disease. The causes of splenomegaly lie in the immune reaction to pathological processes in the body. According to research, together with the organ of the immune system, the pancreas changes its volume upward. The increase is caused by:
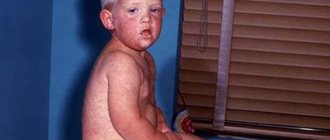
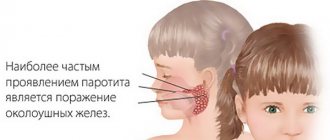
- childhood infections of bacterial and viral origin, including chickenpox, measles, mumps, rubella;
- infections of bacterial origin, including sepsis;
- tuberculosis, chronic HIV;
- metabolic disorders;
- blood diseases;
- acute inflammation of the abdominal organs;
- cysts and neoplasms in the organ, including malignant ones;
- liver diseases;
- bruises and injuries to the spleen;
- systemic diseases.
An increase in size is noted with infection with worms and advanced forms of rickets. Splenomegaly is often diagnosed in premature babies. Rh conflict between the blood of mother and child is also one of the causes of pathology.
Possible reasons for the increase
There are many reasons why a baby's spleen may be enlarged. Enlargement of this organ is medically called splenomegaly. In order to understand the cause of this condition, it is necessary to examine the child.
The most common causes of an enlarged spleen are:
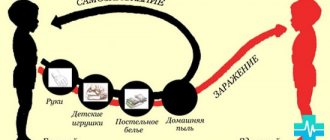
- infectious diseases . They lead to disturbances in the functioning of the spleen and its enlargement. As a rule, this applies to severe infectious diseases (for example, diphtheria, rubella, measles, toxoplasmosis, mononucleosis, tuberculosis). Some of these pathologies can be protected by vaccination;
- mycoses . Fungal infections cause histoplasmosis, blastomycosis. Such conditions lead to lung damage, fever, yellowing and blanching of the epidermis, and foamy, loose stools. Not only the spleen, but also the liver increases in size;
- metabolic hereditary disorders . These include hemochromatosis, Wilson's disease, essential hyperlipidemia, glycogenosis;
- disturbances in the functioning of the circulatory system . May be caused by leukemia, lymphogranulomatosis, osteoporosis, chronic hemolysis. An enlarged spleen is associated with inhibition of metabolic processes;
- focal lesions . These are cysts, benign tumors, suppurations. In infants, the spleen may become enlarged when infected with worms (schistosomiasis, echinococcosis).
To identify the cause of an enlarged spleen, ultrasound diagnostics, scintigraphy, MSCT of the abdominal cavity, and plain radiography are performed. Laboratory tests are also performed (general and biochemical blood tests, study of urine and feces).
Normal size of the spleen in children by age
As the child grows, the spleen also grows. This is a natural process and cannot be considered a deviation from the norm. When working with young patients, doctors rely on the ratio of the length and width of an organ at a certain age. All data can be viewed in the table.
This is interesting: Moderate hepatomegaly: causes, echo signs, symptoms and treatment
| Age | Length | Width |
| Up to a year | 5-6 cm | 1.7-3.8 cm |
| 1-3 years | 5.6-6.8 cm | 2.4-3.5 cm |
| 3-7 years | 6.1-8 cm | 3.1-4.8cm |
| 8-11 years | 9 cm | 3-6 cm |
| 11-14 years old | 8.5-10 cm | 3.5-6 cm |
| 14-18 years old | 9-11 cm | 4-6 cm |
Diagnosis and treatment of liver and spleen diseases
Diseases of the spleen are diagnosed using ultrasound.
An adult cannot diagnose diseases of this kind himself, so a visit to the attending physician is urgent.
The doctor will examine the symptoms, refer you for the necessary tests and draw up a proper treatment plan if a problem does arise.
After the examination, the first thing it will be recommended to do is take a blood test for the biochemical composition, on the basis of which the next stage will be known.
If the doctor has reason to believe that an infection is to blame for the malfunction of the liver and spleen, he will issue a referral to an immunologist. Next, an ultrasound will be prescribed to identify the problem, if there is one; extremely rarely, a puncture may be taken.
It also happens that the solution to the problem is only possible through surgical intervention, although such a result rarely happens, it still takes place. Surgery is necessary if internal bleeding or organ damage is detected. The faster the functioning of these organs is restored, the better, because until this happens, the body is terribly susceptible and vulnerable to infection.
Why is an enlarged spleen dangerous?
In a growing body, an enlarged spleen causes gastrointestinal dysfunction. The organ puts pressure on the stomach, pancreas. Regardless of the underlying disease, digestive problems appear:
- upset stomach accompanied by diarrhea;
- feeling of constant heaviness in the stomach;
- nausea and moderate vomiting;
- sharp pain in the left side;
- significant (up to 40 degrees) increase in temperature;
- the skin turns pale and appears bluish.
Such manifestations require immediate medical examination. The consequences can be the most tragic. Due to the accumulation of venous blood, the enlarged organ can rupture. The presence of growing cystic formations in combination with increased size also leads to organ loss.
If splenomegaly in a child progresses without inflammation, symptoms may be smoothed out. Temperature values do not exceed 38 degrees against the background of mild or moderate pain in the left hypochondrium. Palpation is painless or causes slight discomfort to a small patient. In this case, you cannot do without a visit to the pediatrician. The reason for smoothed symptoms often lies in autoimmune diseases and blood diseases.
In addition, the unnatural size of the organ leads to a change in its functions. The hypertrophied spleen processes its own blood cells. This leads to anemia, and in severe cases hyperspelenism is diagnosed. Large-scale destruction of blood cells is dangerous:
- leukopenia, when white blood cells die inside the organ;
- thrombocytopenia is caused by the processing of one's own platelets;
- anemia - massive death of red blood cells.
Functions of the spleen
An important function of the spleen is hematopoiesis.
The spleen in the medical community is called a “fine filter”. This organ helps remove components from the body that can harm it, disrupt normal functioning, or are simply unnecessary.
This vital organ is also responsible for the process of hematopoiesis. The spleen is responsible for filtering blood and also for its clotting.
Blood clotting is extremely important, because if not for this function of the body, a person could die even from a minor scratch, through which he could lose a large amount of blood, and it is the spleen that helps it clot and the bleeding stops. Children, as we know, often get injured and fall, which means the role of this function in childhood is much higher than in an adult.
Protection of the immune system from harmful bacteria and microorganisms also lies “on the shoulders” of this organ.
From all of the above, the conclusion suggests itself that disruption of the spleen and its enlargement is extremely dangerous, since the immune system is weakened and the body can easily be attacked by harmful elements. Pathology associated with an increase in the size of the spleen entails disruptions in the functioning of nearby organs, since they are compressed purely mechanically.
Sometimes it happens that a baby is born with an already enlarged spleen, in which case a special approach and non-standard treatment are needed, but it is impossible to compare such a pathology with an enlargement of the spleen during life (that is, it was normal before), since these are two completely different diseases .
The liver works in tandem with the spleen; these two organs are, so to speak, companions and perform very similar functions. The processing and removal of cells of foreign origin from the body is the work of two organs of the same system: the liver and spleen, so if an enlarged spleen is detected, then an enlarged liver will certainly be present.
Diagnostics
Palpation and percussion, which are informative for adults, do not have diagnostic value when it comes to a child. In adolescents, it is most often impossible to palpate. And in newborns, moderate enlargement of the organ is not considered a pathology. Listening with a phonendoscope (auscultation) is effective. During the process, sounds of the spleen rubbing against the ribs are heard. Sometimes you can notice a protrusion of the organ.
A combination of laboratory and instrumental examination methods helps to establish the true cause of splenomegaly. They take from the child:
- general blood analysis;
- blood for biochemistry;
- blood for tumor markers (enzyme immunoassay) if cancer is suspected;
- general urine test and coprogram (feces).
This is interesting: What to do if the liver is enlarged and how to treat it?
Simultaneously with laboratory tests, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound of the abdominal organs. This method is considered the most reliable for identifying the causes of splenomegaly. Echo signs make it possible to accurately determine the size and structure of an organ. All tumors are visible on ultrasound. Pathologies of other organs are clearly distinguishable during the study.
Based on test results and ultrasound data, the pediatrician can decide whether to prescribe an MRI or CT scan. Other specialists are also involved in the work. Oncologists, gastroenterologists, and hematologists take part in diagnosis and treatment, if necessary.
Treatment
Having discovered an enlarged spleen in a newborn child, the doctor will not rush to conclusions. In infants, the size of the spleen is directly related to how intense the blood circulation is - the more the organ is filled with blood, the larger its size.
In all other cases, splenomegaly requires medical attention. Since diagnostics are carried out not so much to determine the size of the spleen, but to find the true cause of its pathological growth, by the time treatment is prescribed, the doctor will know exactly what disease caused the symptoms.
The efforts of doctors will be aimed at treating the underlying disease. If the basis of splenomegaly is a bacterial infection or a strong inflammatory process caused by microbes, then a course of treatment with antibiotics will be prescribed.
Diseases associated with tumors will be treated depending on the size and location of the tumor - with antitumor drugs or surgery. Doctors always add vitamin therapy. For autoimmune causes of splenomegaly, immunosuppressants are prescribed - drugs that suppress the activity of the immune system.
As a rule, the problem can be successfully resolved in a conservative way. If, during the treatment of the underlying disease, the size of the spleen does not decrease during recovery, if there is a tendency for further growth of the organ, then a decision may be made to remove it.
The spleen is removed immediately (without prior treatment) in case of lymphogranulomatosis , a malignant disease of lymphoid tissue, and almost always when its size is so large and the tissue is so thin that there is a risk of sudden rupture of the organ.
The operation to excise the spleen is splenectomy. Most often, for children, it is performed using the laparoscopic method, which is the most gentle, almost bloodless and favorable (from the point of view of further recovery). There are also other methods of surgical intervention, but they all involve direct access to the spleen through a direct incision in the peritoneum.
After the operation, the child’s immunity sharply decreases, the baby becomes extremely susceptible to infections - both bacterial and viral in origin. Bacteria pose a particular danger to it, so children after surgery to remove the spleen must be vaccinated against meningococcus, pneumococcus and Haemophilus influenzae.
It should be noted that the decrease in immunity will be temporary; usually the body manages to compensate for the absence of an organ in one and a half to two years.
The child will get sick much less often, his life will be completely full, without significant restrictions.
Signs of splenomegaly in a child
Signs of abnormal enlargement depend on its cause. Therefore, there is no single clinical picture. Depending on the provoking disease, the following may appear:
- hematomas and pale skin;
- the child becomes lethargic and apathetic, loses interest in favorite activities;
- insomnia;
- frequent acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections due to decreased immunity;
- pain in left side;
- temperature increase;
- nausea, vomiting, headache;
- decreased appetite;
- flatulence (increased gas formation);
- sweating;
- weight loss.
Before the examination, the doctor will necessarily collect a complete history and take into account all complaints of the patient or his parents.
First symptoms and signs
It is impossible to quickly determine that a newborn has splenomegaly. As a rule, the pathological process itself does not have any clinical symptoms. The baby may be worried about signs of other diseases that are primary. Most often, adults learn about splenomegaly only during examination:
- Non-inflammatory processes often cause pain during palpation. Body temperature, as a rule, does not increase. The skin may have a pale tint, and the baby may be more tired. You may experience excessive sweating at night.
- The inflammatory process may have symptoms such as frequent and very prolonged diarrhea, periodic vomiting, slight nausea, fever, pain in the hypochondrium.
However, all these symptoms are considered ambiguous and indirect, and it is impossible to establish a definite diagnosis only by a combination of signs in this case.
The baby may feel quite healthy, however, the organ may grow. This also happens quite often.
How to treat splenomegaly in a child?
Treatment tactics are chosen after the cause of splenomegaly is determined and an accurate diagnosis is made. If the patient's condition is close to critical, the organ is removed. Indications for splenectomy include lymphogranulomatosis and other serious diseases. Conservative therapy will not help in this case.
Drug treatment
Drugs are selected taking into account the underlying disease. The infectious nature of an enlarged spleen requires the use of antibiotics. They are administered intravenously. There are also tablet preparations. If the size of the liver changes simultaneously, the child will have to take hepatoprotectors.
When the cause of splenomegaly is a neoplasm, the use of anti-blastoma drugs and a course of vitamins is indicated. Chemotherapy is another method of fighting a tumor. When it has grown and it is impossible to cope with the help of pharmacology, you will have to undergo surgery.
Diet
Therapeutic nutrition provides the body with nutrients without creating unnecessary stress on the gastrointestinal tract. Diet enhances the effect of drug therapy. To speed up recovery, a sick child’s diet should contain:
- lean meats, including chicken and turkey;
- lean fish and seafood;
- chicken and beef liver;
- vegetables and fruits;
- chicken eggs;
- cereals, especially buckwheat.
This is interesting: Enlarged right lobe of the liver: causes, symptoms and treatment in adults and children
Porridges and soups should be present in the diet of a sick child every day. They are boiled in water or diluted milk. The recommended water/milk ratio is 1:1.
Whole milk, butter, and cheeses should be limited.
Ice cream, chocolate, fast food and all types of sweet soda are prohibited.
Folk remedies
The use of traditional methods of treatment is possible only under the supervision of a doctor. Your child will love cucumber seed powder. The preparation is simple. Wash green cucumber seeds, dry and grind in a blender. Take cucumber grains 30 minutes before meals. Recommended dosage is 2 teaspoons.
Honey-ginger ointment gives good results. To make the product, grated ginger root is mixed with honey at a ratio of 1:1. At night, apply the mixture to the area from 9 to 11 ribs on the left. The course lasts one and a half months.
Exercise therapy
The physical activity of a child with splenomegaly is limited due to the child's weakness and fatigue. Simple exercises will tone the spleen.
- Lying on your back on a flat, hard surface, take a deep breath. Exhale in portions, saying cha-cha-cha. The exercise is repeated 20 times.
- Inhaling air, draw your stomach in as much as possible. As you exhale, it is pushed out. The exercise is designed for 10-20 repetitions.
Features of nutrition during treatment of the liver and spleen
For diseases of the spleen, you need to eat often, but little.
The main and golden rule is to eat often, but little. It is absolutely forbidden to overeat, it is unacceptable to eat a huge portion of lunch at once, this will not allow the treatment to proceed correctly. Therefore, parents should carefully monitor their child’s diet.
Consuming freshly squeezed juices (but not packaged ones, but squeezed at home from natural products) contributes to a faster recovery. The technologies of our time allow us to squeeze the juice ourselves at home without any hassle. Juices from fresh carrots, beets, radishes and pomegranates are very useful.
As for traditional medicine and self-medication, you definitely need to consult your doctor. You should not take risks and treat a child at your own discretion, without practical knowledge; it is unlikely that you will be able to help, but that’s okay, because you can also seriously harm your own child.
After consulting with your doctor, you can try (if he approves, of course) to enhance the healing process with the help of traditional medicine. Practice shows that the following methods help with an enlarged spleen:
- drink a hot decoction of hop cones or a glass of chicory in the morning on an empty stomach;
- After eating, give your baby a decoction of calendula or yarrow leaves to drink.
As with any other disease, there is no need to delay diagnosis; if you discover problems with your child’s health, immediately consult a doctor, there is no need to aggravate it, take care of your baby’s health. As a rule, there is no treatment for the spleen and liver as such, because it is often accompanied by another serious illness that requires immediate treatment.
You can learn more about the spleen from the video:
Tell your friends!
Share this article with your friends on your favorite social network using social buttons. Thank you!
In children, the size of the spleen depends entirely on their age. In the first days of life, if a child’s spleen is enlarged, this is considered a normal indicator. Subsequently, the organ gradually grows. When conducting a size study, specialists always compare the age, height and weight of the child and determine the spleen norms using ultrasound.
The normal size chart for the spleen in children looks like this:
| 1 year | 50 – 65 | 17 – 25 |
| 2 years | 56 – 72 | 24 – 34 |
| 3 years | 61 – 79 | 27 – 37 |
| 4 years | 64 – 84 | 27 – 39 |
| 5 years | 68 – 88 | 27 – 39 |
| 6 years | 71 – 91 | 27 – 41 |
| 7 years | 74 – 96 | 27 – 41 |
| 8 years | 76 – 100 | 29 – 43 |
| 9 years | 78 – 102 | 29 – 43 |
| 10 years | 79 – 103 | 30 – 44 |
| 11 years | 80 – 108 | 30 – 44 |
| 12 years | 85 – 113 | 31 – 45 |
| 13 years | 88 – 118 | 32 – 46 |
| 14 years | 90 – 120 | 33 – 48 |
| 15 years | 90 – 120 | 34 – 49 |
| 16 years | 91 – 121 | 35 – 51 |
Ultrasound examination allows you to determine the size of the organ, its structure and shape.
This part of the body cannot be detected by palpation. It is possible to detect an organ by palpation when it is significantly enlarged. The spleen has the ability to perform several functions:
- to fight various infections - produces antibodies;
- cleanses and filters blood;
- regulates hematopoietic processes;
- actively participates in protein synthesis.
Consequences and prevention
To prevent splenomegaly in newborns, pregnant women should stop smoking and drinking alcohol. Paying attention to your own health will create a strong foundation for the health of your unborn baby.
All children from infants to teenagers must be taught an active lifestyle. Monitor their diet. It is important that children drink enough clean water.
Timely medical examinations will help identify pathology at an early stage. The disease is easier to cure at the very beginning. Early diagnosis is the key to a favorable outcome of the disease.
Since splenomegaly is not a disease, but a symptom, there are almost no prognoses. It all depends on the initial illness.
Cyst on an organ: what to do, how to help with rupture
A splenic cyst in a child is usually detected completely by accident during an ultrasound scan. The treatment method for this pathology depends on the size of the formation. If a small cyst is detected, the child is monitored by specialists, and control examinations are done 2–3 times a year.
If a large or medium-sized cyst is detected, inflamed or ruptured, surgical intervention is performed. In this case, the cyst is removed, and in some cases the entire organ is removed.
An enlarged spleen in a child entails the destruction of blood cells. In turn, this condition can provoke rupture of the enlarged organ. How to determine pathology and what could be the cause? A fairly serious illness requires urgent medical attention.
Most often, a break does not occur suddenly. First, a hematoma forms, then under certain conditions it ruptures. In children, the organ is not sufficiently covered by the ribs, and therefore is poorly protected from external influences. In newborns, rupture occurs due to infectious diseases.
Characteristic symptoms of splenic rupture:
- in the upper part of the tummy, on the left, internal push;
- feeling of discomfort;
- a dull pain that gradually spreads throughout the abdomen.
Due to increased bleeding, other signs also appear:
- weakness and dizziness;
- child's pose: knees tucked to the stomach, on the side;
- a feeling of darkening and bright flashes in the eyes;
- nausea, vomiting, bloating, increased pain;
- when palpating the left side of the abdomen, pain radiates to the left shoulder blade.
What should parents do if they find signs of a rupture? This pathology requires surgical intervention, so you need to call an ambulance as soon as possible.
Prognosis after a child has had his spleen removed varies and depends entirely on the presence of concomitant diseases. Patients who do not have problems recover after 3 to 6 months. Children after splenectomy are prescribed a course of antibiotics to prevent possible infections, since the risk of their occurrence is high.
An extra slice is a reality
It is not very rare that during an ultrasound, a doctor discovers two spleens. This is a common developmental anomaly and many people live with it and do not even suspect its existence. What does this mean and why does an additional lobe of the spleen appear? Experts explain this pathology as follows: a violation of the development of the organ occurred during intrauterine life. The different locations of the accessory lobule indicate an impact specifically on the embryonic organ in different phases of development.
The accessory spleen is most often found in the area of the main hilum. Less often, it is located away from the main organ. The additional spleen may be small in size, or may be equal or even larger than the main one. Often the dimensions of the additional one reach 12 centimeters.
Timely detection of pathology in a child, treatment and strict implementation of specialist recommendations allows you to avoid serious consequences and save his life.
Diet for childhood splenomegaly
With an enlarged spleen, portioned (fractional) meals are recommended. The child should eat often, but in small portions.
It is prohibited to use:
- preservatives;
- semi-finished products;
- fatty, spicy foods;
- cakes and flour;
- sour vegetables and fruits;
- ice cream.
Consumption of salt and butter is limited.
The following products and dishes are recommended:
- vegetable and milk soups with the addition of cereals;
- lean meats (chicken, rabbit);
- liver;
- sea oily fish and seafood;
- low-fat dairy products;
- porridge;
- legumes;
- vegetables and fruits, berries;
- honey;
- greenery.
- Drinking enough water;
- Food should be at room temperature;
- Divide meals into 5 times a day;
- The diet includes natural freshly squeezed fruit and vegetable juices (carrots, beets, pomegranates, radishes), fruit drinks;
- Consume juices slightly warmed 1-1.5 hours before meals, at least 3 times a day;
- Use foods rich in copper, pectin, vitamin C and other components that normalize metabolic processes in the body, improve the functioning of the hematopoietic system and strengthen the immune system.