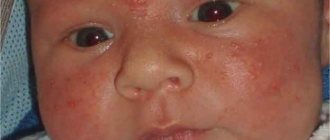
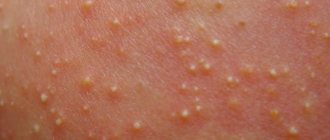
Possible reasons for the appearance
Modern medical literature does not describe the exact causes of birthmarks. But there are several assumptions and unconfirmed versions:
- Multiple pregnancy.
- The mother's age is over 40 years.
- Various maternal diseases during pregnancy.
- Maternal alcohol use or smoking.
- Hormonal disorders in the child or mother.
The most common types
Nevi
- Nevi are birthmarks in the form of moles. They may be small in size, but sometimes they cover a significant portion of the skin.
- The color of nevi varies from brown to black.
- Depending on the tissue from which they are formed, nevi are divided into three main types. It is a melanocytic, non-cellular and organoid species.
Angiomas
Hemangiomas
- Hemangiomas are benign skin tumors that form from the inner surface of blood vessels.
- They may be congenital or may appear during the first few months of life. It is important to remember that these formations appear no later than 3-4 months. If the child is older than this age, then the formation that appears in him cannot be called a hemangioma. In this case, you need to consult a doctor for advice.
- They most often occur in girls, but boys also have them.
- Hemangioma in newborns can be at the level of the skin, it can also protrude slightly above the surface of the skin or develop deeper into the skin.
- In the vast majority of cases, they resolve and disappear on their own by 7-10 years.
- The color of these formations can be varied. As a rule, these are all shades of red, from light pink to dark red.
- A red birthmark in a newborn is of a vascular nature.
- The main distinguishing feature of hemangiomas in newborns is not color or shape, but what they are formed from, that is, blood vessels.
- These formations have three phases of development: a growth phase, a growth arrest phase and a regression phase.
- Local birthmarks can be divided into superficial, deep and combined.
Lymphangiomas
- They are formed from cells of lymphatic vessels. In newborns they are faintly noticeable, and appear more clearly only after a few years of the baby’s life.
- There are cystic, capillary (simple) and cavernous lymphangioma.
- Depending on the causes of formation, all lymphangiomas have a different structure, size, shape and color.
Are they dangerous?
In most situations, birthmarks are absolutely safe and do not require specific therapy. There are varieties that go away on their own with age and do not require any therapy. If a child was born with a nevus or hemangioma, you just need to monitor them and make sure that the size and structure of the external tissues do not change. If you manage to damage the integrity of the tissues, you should consult a dermatologist for advice so as not to harm the child with self-medication.
There are birthmarks that grow quickly, change shape, and bleed. Then you should not delay treatment, since moles of this type appear due to a disorder in the body, and there is a high probability of their degeneration into a malignant form.
Vascular defects and hemangiomas
Types of lymphangiomas
- Cystic. Consists of one or more cystic formations. It grows faster than other forms of lymphangiomas due to the accumulation of fluid in it. Sometimes different cysts communicate with each other.
- Simple (capillary) . This type of birthmark is soft and elastic when pressed; in newborns it does not have clear boundaries.
- Cavernous (cavernous). It consists of cavities filled with lymphatic fluid.
Types of hemangiomas
- Flat. These birthmarks are the most common in newborns, and account for up to 96% of all skin formations of this type. They range in color from pink to brown, and consist mainly of capillaries.
- Star-shaped. They have an unusual shape: in the center of the formation there is a red dot, from which pronounced vessels extend, like distorted rays of the sun. These birthmarks in newborns are most often found on the face, head and back of the head.
- Cavernous. Hemangiomas that rise above the skin. As a rule, they are red or brown, sometimes with a bluish tint. They acquire this color due to the fact that they consist of cavities filled with blood. But sometimes these hemangiomas have the color of normal skin. This is mainly due to the deep penetration of birthmarks into the skin. To the touch, the formation is lumpy, uneven, but elastic. It can also be painful when pressed, and sometimes throbbing and warm. These formations in newborns are quite large, and they are located mainly on the face and head. Less commonly, they can be seen on the arms, legs and buttocks.
Types of birthmarks in newborns
A baby can have two main types of pigmentation - angiomas and nevi. Epidermal and melanocytic growths are dark in color, often brown, and have a round or elongated elongated shape. A common element is the "coffee stain". It forms on the baby’s skin 2-3 months after birth. The color is light brown, smooth surface, clearly defined boundaries, sizes from several millimeters to several centimeters. There is no danger of degenerating into oncology.
Mongoloid spots have a light gray or blue tint. Dimensions reach up to 10 centimeters in diameter. They occur on the lower back, sacrum and back of the child. They do not cause discomfort to the baby and disappear on their own in the first two years of life. If the baby has problems with the spine or changes in education, the child should be shown to a dermatologist.
Red, pinkish, burgundy moles tend to appear in areas of the newborn’s dermis, where there is a cluster of dilated blood vessels; they represent vascular growths. They can be convex, flat, large and small, located on the legs, arms, buttocks, face and stomach.
A common red birthmark in babies is located on the back of the head, tailbone or face and resembles a triangle in appearance. It is flush with the skin, becomes more reddish when the newborn cries, and turns pale during sleep. No treatment is required; after the first year of the child’s life it goes away on its own.
Hemangiomas are red, burgundy or pale pink in color. They occur in children due to the proximity of blood vessels to the skin. They grow with the newborn’s body or remain the same size throughout life. There are several types of hemangiomas:
- Simple (berry). The point got its name because of its resemblance to a strawberry; its surface protrudes above the skin and appears on the cheeks, temples, head or neck. The diameter ranges from a couple of millimeters to several centimeters. Initially characterized by rapid growth, it becomes paler with age and disappears.
- Cavernous (cavernous) - has no clear boundaries, represents many accumulations of blood vessels rising above the skin. Color red, burgundy, crimson, purple. Pressing is painful, the temperature of the mole is higher than that of the body. The size rapidly increases within six months of the baby's life, then the growth disappears. If pigmentation causes discomfort, is located in the eyes or places where it is subject to injury, the formation must be removed in a hospital setting.
- Star-shaped. Externally, the defect looks like an asterisk with several rays formed from blood vessels. It tends to go away on its own during the first year of a child’s life.
- Flame nevus (wine stain). It looks like a trace of red wine or pomegranate juice. Color burgundy, wine. Easily confused with a bruise. The appearance of formations can be seen on the stomach, butt, back, feet, and forehead. It will not disappear on its own, it needs to be removed with a laser.
In addition to brown and red spots, light spots grow on children's skin; they are called anemic. They are characterized by a lighter shade compared to the rest of the dermis. Jadassohn's seborrheic nevus is considered common. Occurs on the scalp. Associated with damage to the sebaceous glands, the color is yellowish or light brownish. Size from five millimeters to nine centimeters. Hair in the affected area falls out. Doctors advise removing the formation due to the increased risk of developing an oncological process.
Inexperienced parents may confuse red pigment spots with erysipelas. This is an infectious disease in which, in addition to reddish marks on the skin, the following symptoms occur:
- acute pain in the affected area;
- temperature increase;
- chills;
- malaise.
Types of nevi
- Giant. This nevus occurs in newborns. From the name of the formation it is clear that it occupies quite a large space on the baby’s skin. Sometimes the nevus is covered with significant hair.
- Blue. More often appears after the birth of the baby. It comes in light blue or dark blue, as reflected in its name. The sizes of such nevi range from 0.5 cm to 2 cm.
- Halo-nevus. It looks like a mole, which is surrounded by a rim of light skin. It most often appears in adulthood, but also occurs in newborns.
- Mongolian birthmark. This is a large, benign growth on the skin that looks like a bruise. It can have shades of blue, red and black. Most often found in children of Asian and Negroid races, less common in Europeans.
When does a child get moles?
Doctors still have not decided why some children have clear skin until adolescence, while others carry marks on their bodies from birth.
Only one factor that determines the location and appearance of moles is not in doubt - heredity. Therefore, no one can say the exact time when parents will see characteristic spots on their baby.
But there are still approximate periods in life when the main activity of melanocytes is noticed:
- 6 months – 2 years – the first moles appear at an early age;
- 5 – 6 years – the second wave of marks appearing on the body;
- 12 – 15 years old – the majority of moles occur during puberty.
Let's celebrate! Along with genetic predisposition, birthmarks are formed in children and under the influence of external factors.
What is important to remember
- With the growth of birthmarks and, in particular, hemangiomas, Dr. Komarovsky advises parents to photograph the baby’s skin to record this process. This will make it much easier for the doctor to make a diagnosis.
- If your child is diagnosed with a fast-growing nevus or other problem, you will need to see your doctor about every week. Your doctor will determine more precisely how many days later you need to see your next appointment.
- Don't ignore your pediatrician's advice. If he has scheduled the next appointment for a specific time, then you must definitely show up with him.
What is a birthmark
A birthmark is a formation on human skin that is visible to the eye. The spots vary in structure, color, size and appearance - brown, red, smooth to the touch, visible on the skin, covered with hair, and others.
Basically, such formations on the skin are divided into two groups:
- Nevi (these include moles, freckles and other brown spots).
- Angiomas (red spots of vascular nature).
Nevi are the most common type of spots on the body, which is familiar to everyone and almost never causes concern. They are caused by the accumulation of cells in the epidermis - melanocytes. Melanin is a natural brown pigment found in melanocytes. It is this that gives birthmarks their brown color. Sometimes nevi can be found on a child’s body from birth. But in most cases, they appear closer to two years, and also in adolescence, when puberty begins.
The number of moles or nevi varies from person to person, but most often there are at least a dozen of them throughout the body. In some cases, the location and size of moles is inherited
Angiomas or vascular formations on the skin are also divided into two groups:
- Hemangiomas are formations that are located in the dermis and consist of small vessels. They are most often congenital.
- Lymphangiomas are spots that are formed from vascular cells of the lymphatic system. They can form in the womb, but will only appear closer to the age of three.
There are many types of angiomas:
Strawberry angioma. Occurs in 6% of newborns
Wine (capillary) angioma
Cavernous or cavernous hemangioma
In addition to these, there are more than ten types of vascular neoplasms. They all have a characteristic red color and can be located anywhere on the body. Such spots can be congenital or form during a certain period of human life.
Treatment and removal
- Hemangiomas located near physiological openings, such as the eyes, ears, nose, mouth, genitals and anus, require mandatory observation and, in some cases, treatment.
- If you have problems with birthmarks in newborns, you should contact not a dermatologist or cosmetologist, but a pediatric surgeon.
- The decision to treat or remove birthmarks should not be made by parents, but by an experienced and competent doctor. In this case, there should be no doubts or multiple opinions. There are specific indications for the removal of these formations.
Treatment methods
- Laser therapy. Effective only in the case of stellate hemangioma.
- Cryosurgery. This procedure is done using liquid nitrogen.
- Surgical intervention. This effective method is used only if necessary, for example, if a birthmark threatens the life and health of a newborn baby.
Localization Features
Mongolian spots are localized on the back, lower back and buttocks of the child. Less common is a formation on the leg of a newborn.
Vascular nevi are located on the nose, cheeks, forehead, eyelids, and rarely on the stomach, chest, arms and legs.
Anemic birthmarks are found on the knees, back, fingers and palms. You can distinguish light spots from the rest of the dermis by pressing on them with your finger - the skin around them turns red and then takes on its usual shade.
Jadassohn's nevi form on the head, temples and neck of children during infancy, and sometimes develop in adolescents and adult patients.
Related topics
- When parents are faced with a child’s illness, they are very worried, and any, even minor, problem seems dangerous to them. Find out what conjunctivitis is in a newborn, how to treat it, and are there possible complications after it?
- It seems to us that only an adult can catch pneumonia, but this is not so. Read about the signs of pneumonia in newborns and treatment methods for this difficult disease.
- Hemorrhagic disease in newborns is not very common. But if your baby has been diagnosed with this, then find out more about this pathology.
- When a baby has a stuffy nose, it causes a lot of trouble for his mother, and causes inconvenience and discomfort to the child himself. Sometimes a simple runny nose can develop into a more serious pathology, but this can be avoided. Find out how.
Dear mommies, answer a few questions in the comments. Tell us, does your baby have moles or similar problems? What do you do with them: treat them, or just observe?
When should nevi under hair be removed?
To remove a nevus on a baby’s scalp, the laser method is most often used. But only those tumors that pose a danger due to degeneration into melanoma need to be removed.
Also, a mole should be removed if it bleeds , peels and itches, or noticeably increases in size.
Despite the fact that moles in children are not uncommon, the appearance of each of them must be treated with full responsibility. It is important to listen to the advice of doctors and prevent the appearance of moles on the head and other parts of the body.
The study of nevi will allow you to understand which of them are dangerous and which will not harm the small organism.