Skin diseases in children
Here are the main manifestations that you may notice on a child’s skin.
Acne on the face
- Babies often develop pimples on the cheeks, nose and forehead. Neonatal acne is thought to occur when the mother's or baby's hormones cause the baby's glands to produce more sebum. The rash usually goes away on its own in the first few months, but in some cases treatment may be necessary. The doctor must tell you if it is required. Childhood acne has nothing to do with whether a child will have acne problems as a teenager;
- Tiny white spots very often appear on a newborn's face during the first seven days. Most of them are located on the skin of the nose. The spots are called milia. These are small cysts containing sebum and keratin.
Keratin is a type of protein that makes up the outer layer of skin, as well as human hair and nails.
Sometimes milia are present on the gums. They are very pronounced during the first few days of life and eventually go away without any treatment.
A pediatrician tells more about what neonatal acne is and whether such a condition needs to be treated.
Baby's skin looks blotchy
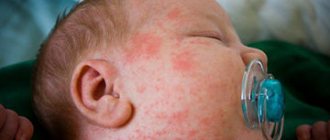
- During the first few days of life, many babies develop harmless red spots with tiny bumps that sometimes contain pus. This is called erythema toxicum. It may appear only on a limited part of the body or cover almost its entire surface. Spots may come and go. But they usually go away on their own within a week;
- The spots, called pustular melanosis by doctors, are harmless and do not need treatment. Transitional pustular melanosis is a type of rash that occurs more often in babies with dark skin. The lesions appear at birth and appear as small white bumps on the baby's neck, chest, back or buttocks. They will go away on their own, but sometimes leave slightly darker spots on the skin.
The child has a rash
- Children may develop miliaria (heat rash) when they are dressed too warmly or when the weather is very hot. This is a red or pink rash usually found on areas of the body covered by clothing. It itches and causes discomfort to the child. Doctors call this rash miliaria.
To help the rash go away, remove your child from the hot place. Dress him in light, loose clothing and bathe him in warm, but not hot, water;
- Diaper rash, red and inflamed skin on the baby's buttocks or groin is caused by wearing a wet diaper for a long time. Urine and stool irritate the skin. The rash can occur when a baby sleeps for many hours without waking up. Sometimes the rash can be caused by an infection from bacteria or fungi. If an infant has a rash in the diaper area, take special care to keep the infant dry;
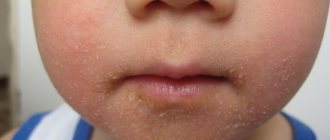
- Many children develop a rash around the mouth or on the chin. It is caused by saliva and regurgitation.
Clean your baby frequently, especially after eating or burping.
An allergist-immunologist talks in detail about what an allergic rash looks like in children, how to treat it, and how not to confuse it with ordinary prickly heat.
Your baby will sometimes develop tiny red dots on their skin
You may notice red spots on your newborn's skin. They are called petechiae.
This is blood that has leaked from the capillaries into the skin. This rash is caused by trauma as the baby passes through the birth canal. The dots will disappear within the first week or two.
Crusts on a child's scalp
Seborrheic dermatitis often occurs in children.
Scaly or hard skin on your baby's head is a normal buildup of sticky skin oils, scales, and dead skin cells. Sometimes a child's hair falls out when parents try to comb out the scales. Unlike some other rashes, seborrheic dermatitis can be treated at home using shampoo or mineral oil.
Seborrheic dermatitis usually goes away by the age of 1 year.
Useful and relevant information from a pediatrician about where this “dirt” comes from and how to remove crusts on a baby’s head.
Birthmarks on the skin of a newborn
They come in different sizes, shapes and colors. Some are flat, while others form raised areas on the skin. Most of them are harmless and do not require treatment. The spots often fade or disappear as the child gets older.
- A simple nevus is a pink or reddish patch of skin between the eyes, on the forehead, or on the back of the head. People commonly call these spots "stork bite" or "angel's kiss." They are caused by dilated blood vessels, which give the skin a reddish tint. Most of these spots disappear within two years;
- Vascular malformations are another common type of birthmark. They may look different depending on the type of blood vessels involved and where they appear on the body. The most common malformations are called "port wine stains" because they appear as dark red patches of skin;
When these spots are large and close to the eyes, the doctor should check the child to make sure the blood vessels in the brain and eyes are healthy. These birthmarks remain with the child for the rest of his life.
- Mongoloid spots. Smooth, flat, blue or blue-gray birthmarks, usually on the lower back and buttocks. They often look like bruises. Very common among dark-skinned newborns. They lighten and almost disappear at school age, but traces of them often remain;
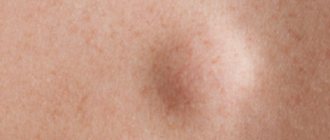
- Infantile hemangioma is the most common birthmark formed from blood vessels. This occurs when groups of blood vessels grow rapidly. Much faster than any other part of the baby's body. In the past, it was called "strawberry hemangioma" because it is bright red and raised, resembling a berry. Some hemangiomas extend deeper into the skin and may appear as a beige or bluish bump on the surface of the skin. Infantile hemangiomas are usually absent at birth or may appear as a reddish patch on the skin. However, after a couple of weeks, the spot begins to enlarge and become more noticeable. It may continue to grow for several weeks before stopping and then shrinking until it disappears. Deeper hemangiomas behave in the same way as superficial ones - they disappear over time. It is usually impossible to predict how long it will take for a hemangioma to disappear. The smaller it is, the faster it disappears, but it takes many years. Most hemangiomas do not require treatment.
But if they occur in certain areas of the body, such as the face (especially around the eyes or lips) or the genital area, they can cause disfigurement or impair body functions. In these cases, treatment should be considered. Your doctor can tell you what options are available;
- melanocytic nevi. More commonly known as moles. They are formed from cells that produce pigment and are light or dark brown in color. Many children develop tiny moles from birth or in the first months of life. Some babies have many moles (large or small) all over their body and require medical monitoring. Moles do not disappear over time.
Jaundice in newborns
Many newborns have a yellow tint to the skin and sclera of the eyes. This is called jaundice. In newborns, jaundice usually disappears within a week and does not require treatment. But in rare cases, jaundice gets worse and can lead to brain damage.
That's why you should call your doctor if you notice signs that your jaundice is getting worse. If you notice that your child's skin or eyes have become yellower or that your child is lethargic and acting differently than usual, call the doctor.
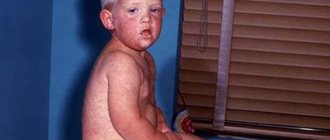
Pustules in newborns: causes and methods of treatment
Purulent-septic diseases of newborns are understood as a group of infectious diseases that are characterized by the presence of a primary focus and circulation of infections in the bloodstream. Since the clinical picture of this type of disease can be very ambiguous, it will be useful for every parent to learn more detailed information about them.
Newborn sepsis is a scary experience for any parent.
Forms of sepsis
Sepsis in a newborn can manifest itself in various forms.
Generalized
The generalized form of purulent-septic diseases of newborns refers to a general infectious process that is caused by the entry of pyogenic and pathogenic microflora from local foci directly into the bloodstream. This type of disease is accompanied by serious systemic manifestations.
The development of a generalized form of sepsis in newborns is largely determined by the pathological course of the perinatal period, the difficulty of diagnosing septic conditions in newborns in the early stages and insufficient indicators of the formation of the immune system and protective mechanisms of the infants' body.
Localized
Localized purulent-inflammatory diseases in newborns usually have a bacterial etiology. They can be caused by staphylococci, Proteus, E. coli, streptococci, or be of a mixed nature.
Clinical forms of purulent septic diseases of newborns can have the following:
Early stage
The early stage of sepsis development is otherwise called toxemia. It is at this stage that pathogens emerge from the primary focus of the disease. The symptoms of sepsis at the first stage of development may differ and depend on both the specific pathogen and the general state of the infant’s immunity.
In the case of newborns, the onset of sepsis is predominantly acute and is accompanied by the following frightening symptoms:
- attacks of fever that have a wave-like character are observed;
- chills appear, alternating with sweating;
- the skin becomes covered with a rash.
No doctor can give a prognosis for the course of sepsis in a newborn baby.
Late stage
At a late stage of a disease such as sepsis, the functioning of vital organs and systems occurs, and hypotension develops. If adequate help is not provided to the baby in time, septic shock will occur. With the latter, the functioning of the blood supply organs is disrupted, and death is almost inevitable.
Face, head and back
If ulcers suddenly appear on the body, their causes and treatment can be completely different.
We suggest that you read Antibiotics for oncology or not - ooncologiya
For example, on the face they arise due to the fact that the sebaceous ducts of the skin are clogged with subcutaneous fat.
In this case, pus is a product that appears after decay.
Those who have had such acne note that they are extremely painful.
They appear suddenly and grow from small, barely visible lumps. The result is a large blackhead that has a core of pus in the center.
Ulcers on the head are always accompanied by itching, discomfort when scratching, as well as peeling. Such formations appear due to the fact that the hair retains heat from.
In addition, fat production is associated with this condition. All this creates good soil for bacteria to multiply and penetrate the skin on the head.
Pimples on the surface of the back look like red inflammation. Essentially, these are edematous tissues, under which there is purulent content. Abscesses on the back have their own varieties:
- Reddish balls called papules. They represent the mildest form of such inflammation.
- Balls with purulent contents and red color are called pustules.
- Nodes - in which the inflammatory process affects the deep layers of the skin.
- , which give strong pain when touched, are called cysts. This inflammation has a bluish tint.
- Around the lips and on intimate parts of the body.
Pimples on the lips appear when bacteria enter the pores of the skin. They are not very large in size and white in color.
If the abscesses are fully mature, then their head is clearly visible. The reasons for the occurrence of these formations may be as follows:
- The skin was taken care of incorrectly or insufficiently (for example, a cream was used that was not suitable for its type).
- The habit of holding a pencil or pen in the mouth. These items can be very dirty.
- Using expired cosmetics. This also includes products with low quality.
- Poor compliance with hygiene rules. This refers to the frequent habit of some people to touch the area with dirty hands.
Acne on intimate places can be of different types. They can be serious, for example, with venereal or skin diseases, or completely harmless, which appear during puberty.
Causes of sepsis
There can be many reasons why an infant may develop sepsis. Most often we are talking about the following.
Intrauterine infection
Meconium in newborns - description of feces is normal, with deviations
The intrauterine purulent-inflammatory process develops even before the birth of the child. Infection occurs at the stage of formation of the organism, which means the location of the purulent focus outside the fetus. This form of infection occurs against the background of certain chronic and acute diseases in a pregnant woman. These can be purulent-inflammatory processes of various etiologies or infections.
Infections that enter through the umbilical cord
Often the baby gets infections through the umbilical cord or small wounds. This turns out to be almost inevitable if the maternity hospital does not comply with basic sanitary standards. If the baby's mother has a pathogen, sepsis can enter the newborn's body with her help.
Important! Sterility of the premises in which a child is kept in a maternity hospital is the best way to protect the baby from a purulent-inflammatory process.
Birth infection
Bacteria can enter the body of a newborn, both during pregnancy and during childbirth. Most often the problem is caused by:
- infection in the placenta or uterus;
- feverish state of the mother during childbirth;
- premature rupture of the membranes.
Pustules in newborns
Such unpleasant formations on the body can have different sizes (from 1 to 1.5 cm). In their shape, the ulcers resemble an oblong ball or cone.
Removing ulcers on your own may result in the appearance of a small scar on the body. In addition, pustules often form in hair follicles (follicular pustules).
An abscess appears only if the body's immune cells interact with bacteria. This means that if such a formation appears on the skin, it does not need to be attributed to a viral or fungal disease.
After all, the most common pathogens of purulent infections are Staphylococcus aureus, as well as epidermal streptococcus. But such bacteria do not cause any special problems for humans.
A baby's skin is extremely thin and sensitive, lacking the dense layer of subcutaneous tissue that adults have. That is why skin rash is often a reaction of the child’s body to certain external factors. The main reasons for the appearance of pustules on the skin of a child:
Source: https://medicprof.ru/simptomatika/bolezni-kozhi-novorozhdennyh.html
When should you see a doctor?
Always call a doctor if there are any problems, signs of skin disease, or if your child is acting differently than usual.
These signs may include:
- tenderness, swelling, or warmth in the affected area;
- red (inflamed) branches extend from the affected area;
- pus;
- enlarged lymph nodes in the neck, armpits or groin;
- body temperature from 38° C and above;
- restless behavior of the child.
If you have questions about what lotions or other products to use on your baby's skin, talk to the doctor at your next visit. Not all newborn skin conditions need to be treated with lotions and creams.
Diaper dermatitis
An inflammatory and irritable process on a child’s skin that occurs when there is insufficient air circulation and moisture accumulation. Symptoms: rash, blisters, redness and inflammation of the skin, in advanced cases: cracks and wounds, suppuration. In mild form, this is one of the most common childhood illnesses, which can be treated by adjusting the child care program. Dermatitis complicated by an infectious disease requires the use of ointments and antibiotics.
Most often, the disease occurs due to prolonged exposure to tight diapers or diapers. A humid environment without air flow stimulates the proliferation of pathogenic organisms that cause skin infections. Typically, diaper dermatitis is observed on the buttocks, lower abdomen, and crotch of the child - places that the diaper covers.
Factors that increase diaper dermatitis:
- prolonged wearing of clothes and diapers that impede skin breathing;
- prolonged skin contact with urine and feces;
- Rarely bathing a child.
It has been established that diaper dermatitis often occurs with a complication – a fungal infection that affects the skin.
Baby skin and nail care
Skin care
A child's skin is thinner and more vulnerable than that of an adult. Therefore, it is recommended to take care of it as carefully and delicately as possible.
Bathe your baby gently with mild soap and warm water. You can use the same soap to wash your scalp.
Using the wrong shampoo can cause hair loss.
After bathing, apply a mild moisturizer all over your skin and a barrier cream under your diaper to prevent diaper rash.
There are no preferred brands for bathing or moisturizing your baby's skin. The most important thing is that the products used are mild and as flavorless as possible.
Infections of newborns
Published: 10/10/2016
Infections of newborns are acute infectious, purulent-inflammatory and septic diseases of newborns that developed as a result of infection in the postnatal (early neonatal) period.
Most often, Newborns experience acute respiratory viral infections (influenza, respiratory syncytial infection, adenoviral infections, parainfluenza), acute intestinal infections (escherichiosis, salmonellosis, viral enteritis), as well as purulent-inflammatory and septic infections (see.
Sepsis) diseases (localized and generalized purulent-septic diseases - PSS) in the form of pustular lesions of the skin and subcutaneous tissue (pyoderma, abscesses, inflammation of the umbilical vessels, phlegmon, mastitis), mucous (conjunctivitis), and other localized processes.
This group of infections in newborns is of particular importance due to the possibility of outbreaks of these diseases in maternity hospitals and in hospital departments for infants. The leading ones in the structure of infections in newborns are the NHS.
Causes of newborn infections
The causative agents of DSS are, as a rule, opportunistic pathogenic microorganisms (OPMs), widely distributed in the environment; are found periodically in various loci of the body of practically healthy people. UPM include: some types of staphylococci, streptococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus, enterobacteria, etc.
These microorganisms are characterized by a high degree of variability and the development of resistance to antibiotics, disinfectants, and antiseptics. In hospitals and maternity hospitals, so-called “hospital” strains of UPM are formed, and their carriers appear, especially among people with chronic pathology of the nasopharynx.
At the slightest violation of the sanitary and hygienic regime, “hospital” UPM are found on items caring for newborns.
Infections of newborns are characterized by a variety of pathogens, sources of infection and routes of infection, forms of manifestation and varying severity of the disease.
The leading role in the development of most infections in newborns, in particular the NHS, is played by endogenous factors: the age of the child, insufficient barriers, and failure of the immune system.
By the 6th day of life, in healthy full-term newborns with good lactation in the mother and early breastfeeding, the anaerobic bifid flora characteristic of the period of newborn and infancy is established - a reliable factor in the fight against exogenous opportunistic and pathogenic infections.
The risk of developing pathological colonization (dysbacteriosis), intestinal infections and purulent-septic infections is higher in children with perinatal pathology, immature at birth, born to sick mothers, late breastfeeders or those deprived of breastfeeding in the first days of life, nursed in wards intensive care patients undergoing infusion therapy and instrumental examination for health reasons. A factor and source of infection can also be postpartum mastitis in a nursing mother with the release of bacteria in milk (bacteriolactia).
Symptoms of newborn infections
The clinical picture of infections in newborns is largely determined by anatomo-physiology. characteristics of the body, the associated frequency of generalization of the process, damage to many organs and functional systems.
In Newborns with ARVI, intoxication, widespread respiratory tract damage, and frequent bacterial complications are observed; intestinal infections (CI) are accompanied by impaired water-salt metabolism and dehydration; pneumonia occurs with severe oxygen deficiency syndromes and damage to the nervous and cardiovascular systems.
The diagnosis of infections in newborns is established on the basis of the clinical picture, microbiological diagnostic methods, and immunological diagnostic methods.
Herpes virus
Herpes is a general term for viral pathologies caused by various herpes viruses. Children are most often affected by primary herpes, characterized by the appearance on the lips. Primary infection with the varicella herpes virus causes the child to develop chickenpox. Secondary infection with the virus manifests itself in the form of herpes zoster. Infantile roseola is caused by herpes type 6 and is characterized by pink maculopapular rashes. The child's temperature rises, which subsides on days 3-5 of the disease, and the skin becomes covered with a pink rash. If you press on the rash, it turns pale, this is a hallmark of infantile roseola. Herpes is accompanied by fever, muscle pain, and general fatigue.
As a rule, subsequent rash and wound formation are observed. Children, unable to withstand the itching, scratch and tear off the resulting crusts, which prolongs the healing process. The goal of treating herpes in children is to suppress the activity of the virus and reduce the symptoms of the disease. Antiviral drugs, ointments and tablets are prescribed to relieve itching and pain. Drinking plenty of fluids and antipyretic medication is also recommended. It will be necessary to strengthen the child’s immunity with immunostimulants and vitamins.
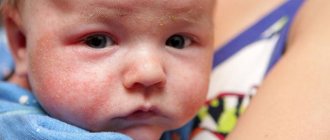
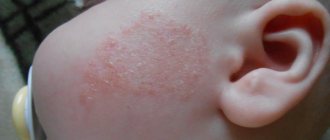
Pediatric atopic dermatitis
It is a chronic inflammatory disease caused by genetic factors. Therefore, the risk of developing this disease is higher in children whose close relatives suffer from atopy.
Factors that increase atopic dermatitis:
- increased sensitivity of the skin to external factors;
- disorders of the nervous system;
- infectious skin diseases;
- smoking tobacco in the presence of a child;
- high content of dyes and flavor enhancers in the child’s food;
- use of cosmetics that are unsuitable for child care;
- bad ecology.
This dermatitis most often affects children under 12 years of age; at older ages, the disease appears extremely rarely. With atopy, children's skin becomes very dry, begins to peel and become covered with spots. Most often, the rash is localized on the neck, elbows, face, and knees. The disease has a wave-like course, periods of exacerbation are replaced by long remissions.