Raising a child with the syndrome is difficult, but no matter how strange it may seem, it is an interesting task. After all, courageous parents who gave birth to a child with a genetic disease, and also set themselves the task of raising a full-fledged member of society, must make repeated efforts to ensure that the baby does not lag behind in development. Of course, the lag inherent in nature cannot be avoided, but even in healthy children this process can be freely controlled, accelerating it with your own efforts. To help a child develop, you need to know month by month, year by year, how such children usually develop.
Diagnosis of the disease
It is not difficult to detect in the early stages of pregnancy. Invasive and non-invasive diagnostic methods are used. To do this, an analysis of the fluid that is taken from the umbilical cord is performed. A biopsy or specific ultrasound examination is also used. Another method is intrauterine sequencing of the DNA of a pregnant child using fragments found in the mother’s blood. These methods are carried out in women who are at risk (have a predisposition to the disease) and under 30 years of age. They provide reliable information on identifying the disease.
For pregnant women over 35 years of age, such techniques are not advisable, as damage to the uterus and fetal rejection are possible. At the end of the first trimester, they undergo non-invasive studies, which, unfortunately, do not provide a 100% guarantee.
Thanks to timely diagnosis, the number of Down children born has now significantly decreased.
Diagnostics
Treatment of Down syndrome (mosaic, translocation and standard) is carried out by a geneticist. In addition, consultation with other specialized specialists is required, since the functioning of internal organs is disrupted against the background of pathology.
It is possible to detect the disease in the fetus even before birth. Diagnosis of the mosaic form of Down syndrome involves the study of cells and blood karyotype. Already in the first weeks of pregnancy, it is possible to perform a chorionic villus biopsy.
As part of the diagnosis, the following studies are also carried out:
- Biochemical analysis of maternal blood. When receiving low levels of AFP (this is a hormone produced by the fetal liver), it is customary to talk about a high risk of having a genetic abnormality.
- Ultrasound. The study is carried out every trimester. Already during the first ultrasound, the presence of trisomy can be assumed.
- Maternal blood test for hCG and PAPP-A. These are substances that are secreted by the fetus. It is customary to talk about the mosaic form of Down syndrome in the case when the hCG level is deviated from the norm to a greater extent, and the PAPP-A indicator to a lesser extent. Upon receipt of these results, a chorionic villus biopsy is prescribed.
- Amniocetosis. This term refers to the analysis of amniotic fluid. This is the most reliable and accurate method for diagnosing the mosaic form of Down syndrome. But it is important to know that this study is associated with a high risk of infection of the body (both the child and the mother). In addition, often after the biomaterial is taken, the film breaks and a miscarriage occurs.
Particular attention is paid to differential diagnosis. It is necessary to exclude hypothyroidism and the following syndromes: De La Chapelle, Klinefelter, Edwards and Shereshevsky-Turner.
Regardless of the presence and severity of external signs in a child, the diagnosis of the mosaic form of Down syndrome is carried out even after the baby is born. This is due to the need to identify internal pathologies. The doctor prescribes a comprehensive examination for the child, which includes many laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods.
Causes of the disease
- Woman's age. In a woman giving birth over 35 years of age, the risk of gene mutation increases.
- Male age limit. After 45, a dad runs the risk of waiting for the birth of a baby with Down syndrome.
- Features of the genetic apparatus and heredity of parents.
- Closely related sexual relations. Incest leads to genome disruption.
- Scientists conducting research have determined that, to some extent, the development of the disease is influenced by increased solar activity.
However, no evidence has yet been found.
Prevention
Currently, there are no measures that can prevent the occurrence of trisomy. Prevention only slightly reduces the likelihood of developing a genetic abnormality.
Doctors' recommendations:
- All identified diseases must be treated promptly. In addition, you need to adhere to the principles of a healthy lifestyle.
- It is necessary to regularly expose the body to moderate physical activity. Against the background of physical activity, blood circulation improves, which significantly reduces the risk of developing oxygen starvation of the eggs.
- It is important to constantly monitor your body weight. Obesity is one of the main causes of failure in the development and maturation of germ cells.
- It is necessary to prepare for pregnancy. You need to undergo an examination in advance and start taking vitamin complexes. It is worth remembering that the older the spouses are, the higher the risk of developing trisomy.
- Responsible prenatal testing is essential. With the help of modern methods, pathology can be detected already in the early stages of pregnancy. If pathology is confirmed, the decision remains with the parents. No doctor has the right to refer a woman for an abortion without the consent of the spouses.
In addition, it is important to know that when trisomy is confirmed, there is no need to look for the culprit. The pathology is random; not a single woman is immune from it.
Distinctive features of a child
All Down children share common similarities in appearance.
External features:
- The face is particularly flat, especially the nose.
- The eye shape is oblique, a small fold is located near the inner corner of the eye.
- The head is short with a flat, sloping nape. Ears with various anomalies.
- The mouth is small, slightly open. The palate is too short, the tongue sticks out, does not fit in the oral cavity.
- Very weak muscle tone, and joints are overly mobile.
- There is a transverse fold on the palms.
- Crooked little finger.
Many patients with Down syndrome have abnormalities in the development of internal organs.
Among them are quite common:
- Congenital heart disease (more than 40%).
- Visual diseases – strabismus, glaucoma, cataracts.
- Decreased hearing.
- Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, problems with digestion of food.
- The structure of the nasopharynx is abnormal, which often results in difficulty breathing at night.
- Endocrine diseases.
Pathologies of the musculoskeletal system: absence of a rib, hip dysplasia, deformation of the chest, short stature.
Down children are similar to each other, but they also differ in the presence of certain facial features of their parents. These kids have bright sunny eyes, sincere smiles and good dispositions.
Consequences and complications
Although the mosaic form of Down syndrome is considered the mildest, it can pose a health threat. This, in turn, significantly worsens the course of the pathology and quality of life.
Negative consequences of trisomy:
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system. More than half of patients suffer from congenital defects.
- Frequent episodes of infectious diseases. Children with the syndrome often have a weakened defense system. This leads to the fact that the body practically does not resist the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Excess body weight. Persons with the syndrome are more likely than others to suffer from obesity. This, in turn, leads to the development of a large number of diseases.
- Pathologies of the hematopoietic system. The most common diagnosis is leukemia.
- Dementia. This pathological condition is associated with the accumulation of abnormal proteins in the brain. As a result, dementia sets in and the person loses the desire for knowledge. The first symptoms of dementia in persons with the syndrome usually appear before the age of 40.
- Apnea. Sleep apnea is associated with abnormalities in the development of the oral cavity and respiratory tract.
- Pathologies of the thyroid gland.
- Bone weakness.
- Visual and hearing impairment.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Infertility (in men, in women reproductive function is preserved).
- Early onset of menopause.
These are the most common complications. This list is far from complete.
General development of a child with this syndrome
Families with Down children bear a huge responsibility for the happiness and health of the child. He needs constant supervision from specialists. After birth, it is important to undergo a medical examination in order to identify any concomitant pathologies and diseases. After which the doctor can prescribe medications that reduce the impact of the syndrome.
Babies develop much more slowly than ordinary children. The baby will learn to hold his head up only by three months, will sit up closer to a year, and will be able to walk independently by two years. But qualified assistance from specialists will help reduce these deadlines to earlier ones.
Individually designed programs can help your baby’s development:
Special gymnastics aimed at developing fine motor skills. A set of exercises is done daily, which changes and becomes more complex with age.
- Massage is considered an effective method in the rehabilitation process, promoting overall health.
- Educational finger active games.
- Teaching the alphabet and the ability to count, read, learn songs and poems by heart.
- The most important thing is to instill in children with Down syndrome the skills of independence, accustom them to life in society and fully communicate with peers.
Medical and pedagogical correction
This is the main area of work with special children. Treatment of the mosaic form of Down syndrome is aimed at adapting the child to the outside world. With the right approach, we train the child; he acquires all the necessary skills to interact with society.
The scheme of therapeutic and pedagogical correction consists of the following points:
- Massage. The muscle tissue of a person with the syndrome is underdeveloped, and therefore these procedures are necessary. Hydromassage has a good efficiency indicator.
- Physiotherapy. Regular exercise helps strengthen muscles and maintain them in normal tone.
- Swimming. With the help of water gymnastics, you can also strengthen muscles and significantly improve motor skills. The psychological aspect of the disease helps to relieve swimming with dolphins.
- Diet. Individuals with Down syndrome are prone to developing obesity. A nutritionist helps create a menu so that the patient does not feel deprived.
- Consultation with a speech therapist. All forms of the syndrome are characterized by speech impairment. The specialist teaches how to express one’s thoughts correctly and clearly so that a person can freely interact with society.
- Special training program. Children with the syndrome are retarded in mental development. However, with the right approach, they can be taught all the basic skills and transferred certain knowledge.
Recently, doctors are increasingly recommending hippotherapy. This is a treatment method, the essence of which is communication with horses. As a result, the child develops attention, balance, and becomes more self-confident. In addition, the baby feels protected and warm.
One important aspect is psychomotor development. Parents must understand that this is a difficult and long process, but it is always rewarded. Having mastered a new skill, kids are always very happy about it and are even more enthusiastic about learning.
The mosaic form of Down syndrome is considered the mildest. But this does not mean that the correction will be problem-free. The thinking of children with the syndrome is more inert; it is very difficult for such children to concentrate on anything, as they are restless. In this regard, parents need to approach the learning process creatively. In addition, it is necessary to take breaks more often and alternate mental activity with physical activity.
It is important to teach children to take care of themselves in everyday life. To do this, it is necessary to develop motor skills. The most effective ways:
- Clenching of fists.
- Finger drawing.
- Modeling. You can use absolutely any material (clay, dough, plasticine).
- Tearing newspaper sheets into small pieces.
- Turning book pages.
- Sorting buttons by color or size.
- Collecting puzzles.
- Creating applications that involve working with scissors.
It is important to teach your child to dress and put on his own shoes. Working with buttons, zippers and laces is also good for developing motor skills.
Regular activities with your child contribute not only to the development of physical skills. The process of communication itself stimulates both mental and psychological development.
Currently, several methods have been developed that set the direction of training. These include:
- Zaitsev's method. Allows you to teach reading and writing. The author of the technique developed special tables and cubes, as well as devices with musical accompaniment. The result is a smoothing out of intellectual problems.
- Montessori method. Its essence is to create a comfortable environment for the child in which he will have a desire to learn. In this case, the child chooses an activity for himself from several offered.
- Nikitin's technique. Implies an emphasis on hardening and physical development. At the same time, the baby should feel freedom, the atmosphere should be relaxed.
- Glen Doman method. Its essence lies in early development. In other words, it is necessary to teach a child to read, count and speak from the age of 12 months.
- Method Cecile Lupan. The main principles are independence and curiosity. All information must be presented to the child in such a way that he becomes interested. We constantly need to offer something new.
Doctors also recommend taking children to group classes. During training, kids focus on each other, and a competitive moment appears.
Differences in physical development
Physical condition is determined by the influence of genetic material. Such children are characterized by poor physical development and low weight; they do not look their age.
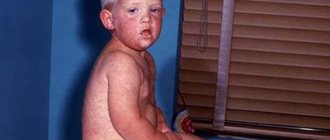
The skin is very light in color; skin rashes appear in infancy. It is dry and rough to the touch, and in winter it can crack.
Deviations in the structure of internal organs are quite common. Thus, in children born with a heart defect, high-frequency heart murmurs are heard. A malfunctioning valve or narrowing of large blood vessels causes a hole to form through which blood flows. In this case, a serious heart defect develops.
The lungs are formed according to the norms, only in some they show slight underdevelopment. Down children with congenital heart disease have high blood pressure in the lungs and are prone to pneumonia.
The abdominal muscles are poorly developed, causing the stomach to protrude slightly. Most people experience an umbilical hernia that does not require surgical intervention. As the child grows gradually, the hernia heals on its own.
The spleen, kidneys, and liver develop normally, without pathologies. The genitals may be slightly smaller than those of normal children.
The limbs are characterized by short, wide feet and hands. The little fingers on the hands are bent forward. The lines on the palms have a characteristic, pronounced pattern caused by the disease. On the feet, the distance between the first and second toes is increased, and there is an unusual fold on the sole. Flaccid tendons cause the development of flat feet. Therefore, orthopedists advise wearing special shoes with orthopedic insoles.
There is abruptness, uncoordination and inconsistency in the movements. The swings of the arms are abrupt, and varied movements are observed at the legs. Weakness of muscle tone and bone tissue contributes to dislocations, bruises, and fractures.
Not all children with Down syndrome have the disorders listed above. Some may have more pronounced these features, while others may have them to a lesser extent.
Mental development
Modern research studies refute the mental retardation of Down children. The mental retardation of such children is mild or moderate. Only a small percentage of Downs experience profound intellectual delay.
Unlike an ordinary baby, who at the age of three months develops a reaction to the mother’s voice, he begins to smile, turn and hold his head, such a child does not have the so-called “revival” complex. He does not react at all to sounds, to tactile sensations, to who picks him up - a stranger or a loved one.
Intellectual development is inhibited and stops at approximately the seven-year level. The vocabulary is minimal, memory is greatly weakened, attention is scattered, reflex relationships instantly fade away. He can cry for a long time without any reason, while being fed, dry, and warmly wrapped.
It is difficult to communicate with Down children due to poor concentration; they hear, but do not want to answer just like that. They are interested in watching bouncing sports balls for a long time, without practicing with hoops or jump ropes.
For society, a child with Down syndrome, unfortunately, cannot become a full-fledged and equal member, but after appropriate correctional work, he can be taught to comply with basic sanitary standards and self-hygienic care. In addition, among them there are excellent scientists in mathematics, since these people are able to concentrate on one specific task and remember all its sequential actions.
This syndrome is no longer characterized by difficulty in developing intellectual abilities, but rather by the upbringing of a normal personality.
An appropriate environment should be created for these children in which they will feel comfortable and communicate with others without inhibitions. Qualified specialists with medical education will help you adapt to society and find childhood happiness.
Prevalence
The mosaic form is the rarest, occurring in only two cases out of a hundred. The trisomic variant, when all 21 chromosomes are tripled, occurs in 94 percent of cases of Down syndrome. If the pair of chromosomes number 21 fuses, then the human cell has 45 chromosomes, this form occurs in four cases out of a hundred and is called translocation or Robertsonian translocation.
In terms of the severity of developmental delays in people, the mildest form of Down syndrome is considered to be Robertsonian translocation, in which children may not differ too much from their peers. Carriers of mosaic syndrome are slightly more behind in development, but in general they can adapt well socially. Trisomic, the most common variant, requires the greatest effort to socialize children and adults.
Preschool development
Staying in kindergarten has a huge impact on a child with Down syndrome. The activities of the kindergarten are aimed at the comprehensive development of children. They acquire certain skills, abilities, and knowledge.
Every child has to adhere to standards of behavior, maintain discipline, learn to play and communicate with other children. At this age, the leading position is occupied by outdoor play, during which acquired knowledge is consolidated, direct contact with peers occurs, and coordination of movement is formed.
At such moments, the caring attitude of educators and their assistance in normal adaptation in the group is important.
During joint play processes, kids imitate and copy movements, learn to think, draw conclusions, manage events, and share toys and things with others. Games allow you to form a common model of behavior for everyone and solve assigned problems.
Therapeutic physical education and music lessons develop hearing, organicity and accuracy of motor reflexes. Classes with speech therapists help to get rid of speech disorders, create unpronounceable sounds, and learn to pronounce words clearly.
Oligophrenopedagogues are involved in the training, integration and social adaptation of Downs.
Being in a preschool institution, the individual approach of teachers and parents is an ideal way for specific children to be involved in an interesting child’s life, in communication, develop speech functions and gain the necessary experience.
School years of development
After kindergarten, it is much easier for first-graders with Down syndrome to join the classroom and get used to the lessons. Those who have not attended kindergarten may have difficulties. Teachers bear a special responsibility here, who must help children tune in to school and adapt to a new life.
The school stimulates the discovery of character traits and continues to develop the abilities of students, arouses interest and curiosity in understanding the world around them. Children with the syndrome learn self-expression and self-respect, and discover their individuality.
Practical classes and academic disciplines are difficult for such children. They lack perseverance, reaction speed, and basic skills. Along with others, they do not have quick thinking, absent-minded attention, and weakened memory.
What makes the learning process difficult?
Poorly developed fine and gross motor skills.
Visual impairment. Most have reduced vision or eye diseases. But visual methods of explaining new material are well accepted by the Downs.
Hearing problems. Sensorineural hearing loss, caused by complicated development of the nerves and ear, makes it difficult to hear information.
General speech underdevelopment (GSD) of varying degrees. Inability to correctly compose sentences, poor pronunciation of sounds, stuttering, small vocabulary, fast or sluggish speech - do not make it possible to express thoughts orally and in writing.
Difficulty in thinking. Simple tasks (counting, writing down) are performed at the level of typically developed children. Drawing a conclusion, generalizing, building a logical chain, coming from simple to complex, and vice versa, is not possible for children with Down syndrome. They lack abstract thinking and do not know how to adapt to situations.
Memory is short-term. The memory capacity is not significant; it takes a long time to memorize and assimilate new things.
Unstable attention, inability to focus, concentrate, rapid fatigue and distraction from the desired object of study.
There is no perception of a holistic image: they cannot create a whole picture from individual details.
Emotional behavior. They are obedient, obey instructions, affectionate, friendly, and readily carry out orders. They are happy to make contact with teachers and classmates, showing positive emotions. Failure from an incorrectly completed task does not upset them at all, which is not acceptable for studying.
Success and praise from a job well done serves as an incentive in the educational process and gives dynamics in development. A teacher's positive approach to a special child makes his learning effective.
How does a child develop?
How do helpless newborns develop into children who exhibit the knowledge and skills of five-year-olds? For all children, development is a process of growing and learning new skills and knowledge. The nature of this process depends on the child’s innate potential, the quality of the environment and the learning opportunities it provides him. Each child is unique, each has their own potential and experience. Psychologists such as Sameroff and Chandler (1975) have emphasized that development occurs in interaction, i.e. Children are active explorers and learners; they influence and are influenced by the world around them, especially by the people with whom they interact (see Sameroff, 1987). A child's mind - what a child knows, what he thinks and reflects on - develops over time; Each child's brain is unique, it contains certain experiences and knowledge that he had the opportunity to acquire, but the development of a child, among other things, depends on how well he remembers his experiences and how well he can use them. Psychologists call thinking, remembering and deliberation a cognitive process, and it is the ability to do this that determines a child’s intelligence. Psychologists Vygotsky and Bruner illustrated the social nature of children's cognitive development by showing that most learning occurs during social interactions with adults and children, and the quality of these interactions influences the child's progress (see Schaffer, 1992). Like the development of all young children, the development of children with special needs depends on the quality of their experiences, social relationships and learning opportunities they receive. Some authors argue that the development of such children is even more dependent on the quality of the early environment because they are less able to compensate for lack of experience on their own (e.g., Rauch et al., 1990). Now, keeping in mind the fact that development is dynamic and based on interaction, we will look at the main aspects of development and the impact that Down syndrome has on them.