What are the causes of chronic tonsillitis in children?
Typically, chronic tonsillitis in a child occurs after acute inflammation of the tonsils.
As a rule, this may be preceded by a sore throat and other viral infectious diseases, accompanied by inflammation of the mucous membrane.
The pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory processes in the tonsils are:
- Streptococcus pyogenes;
- Staphylococcus aureus;
- influenza stick;
- Pneumococcus.
The following can bring pathogenic microflora into an active state:
- hypothermia;
- infectious diseases;
- decreased immune defense;
- stress.
All this can provoke an exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis.
Not often, but you can find this disease in children who have never had a sore throat. In this situation, the provoking factor is diseases that cause inflammation of the tonsils, namely:
- sinusitis;
- inflammation of the adenoids;
- scarlet fever;
- measles;
- diphtheria.
Complications in the form of purulent sore throat
One of the most common types of acute tonsillitis is streptococcal. Its causative agent is streptococcus bacteria, which are activated when the immunity of children is reduced. In this case, the treatment is slightly different. The symptoms of this type of streptococcus are much more serious than its classic form:
- Purulent plaque on the tonsils;
- Enlarged lymph nodes;
- Heat;
- Diarrhea.
The disease manifests itself in children over 3 years of age. To make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment, the doctor must direct the patient to get tested for bacteria and study the symptoms. Antibiotics are prescribed first.
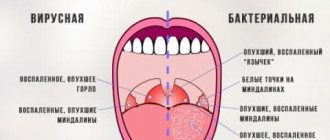
Symptoms of chronic tonsillitis in a child
Chronic tonsillitis in a child manifests itself as follows:
- Purulent plugs are formed in the lacunae, which include mucus, desquamated epithelium and microbes. They lead to inflammation in the tonsil (see photo above), irritate the ends of the nerve fibers, which causes: tickling and sore throat;
- cough;
- shortness of breath;
- pain in the ears.
When the disease worsens, the child experiences rapid fatigue, becomes moody and irritable, and complains of a headache.
How does infection occur?
Provocateurs of tonsillitis are streptococcal, staphylococcal, hemophilic, pneumococcal infections. Risk factors for the development of inflammation are acute respiratory viral infections of a recurrent nature, frequent hypothermia, weakness of the body’s protective properties.
The infection process goes through several stages:
- pathogens penetrate the tonsils and blood vessels by airborne droplets and trigger toxic-allergic reactions due to the production of toxins;
- under the influence of toxins, blood circulation is impaired, the permeability of the vascular wall increases, and immune defense mechanisms decrease. As a result, tonsillitis develops;
- long-term circulating inflammation leads to changes in the tissue of the tonsils (increase - hyperplasia, decrease - atrophy with scar deformation).
Against the background of tonsillitis, an inflammatory infiltrate accumulates in the lacunae with the formation of plugs. Thus, the anatomical features of the structure become an additional source of long-term circulation of microorganisms.
When to see a doctor
In some cases, chronic tonsillitis can cause the throat to become very swollen, causing difficulty breathing. If this happens, seek medical attention immediately.
If you experience the following symptoms, contact your doctor.
- fever, temperature 103 °F (39.5 °C);
- muscle weakness;
- stiffness and stiffness of the neck;
- sore throat that does not go away for 2 days.
Why is chronic tonsillitis dangerous for children?
This disease not only has a detrimental effect on the body’s immunity, but also leads to the following complications:
- rheumatism, with the development of heart defects and joint damage;
- diseases of the genitourinary system;
- otitis media with hearing loss;
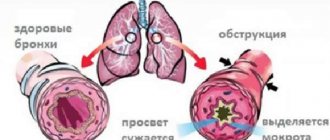
- pneumonia.
- poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis;
- obstructive sleep apnea may begin;
- rheumatic fever;
- provokes the occurrence of hyperthyroidism.
Preventive measures
- Warn your child against hypothermia.
- During an outbreak of the disease, the baby is not allowed to be in crowded places. You should not travel on public transport again.
- Don’t forget to ventilate the room where the child is and do wet cleaning.
- Teach your child to observe the rules of personal hygiene.
- Take care of the general strengthening of the child’s immunity. Hardening is of considerable importance.
Drug treatment of chronic tonsillitis in children
To relieve a sore throat, you can use over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen and ibuprofen . Be sure to check with your doctor before giving medications to children.
If an exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis occurs, prescription strong analgesics, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents are used. The following medications and procedures may also be prescribed:
- antibiotics (take into account which of them the pathogen is sensitive to, which is determined during the study of a bacteriological smear); Read: new generation broad-spectrum antibiotics list.
If we talk about the surgical method of treatment, then the tonsils are removed only in those situations when they are no longer able to perform their protective functions and it is also impossible to restore them. Once infected, they bring nothing but harm to the child’s body, and removing the tonsils is all that can be done.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis includes blood tests. The doctor pays special attention to the presence of signs of an inflammatory process.
In-person examination is important. Sometimes, to make an accurate diagnosis, it may be necessary to culture a smear from the pharynx onto a nutrient medium. Although this analysis takes a lot of time, it allows the child to be treated correctly.
If antibiotic treatment is required, a sensitivity test is performed. If necessary, an ultrasound of internal organs may be prescribed.
Surgical treatment methods
Surgical intervention is indicated in the following cases:
- inflammatory processes in the oropharynx with the release of pus;
- due to tonsillitis, other organs were affected;
- tonsillogenic sepsis;
- there is no reaction from the drug therapy, as indicated by frequent exacerbations of tonsillitis (the doctor will especially insist on surgery if the disease manifests itself more than four times in a year).
Previously, tonsils were removed with a scalpel - a painful method accompanied by significant blood loss. Now new modern technologies are being used, so you can get rid of tonsils using laser radiation.
Laser removal has the following positive qualities compared to other methods of surgical intervention:
- the method is highly accurate and less traumatic;
- it is possible to remove not the entire amygdala, but only a part of it that does not fulfill its functional task;
- blood loss during surgery is minimal due to cauterization of blood vessels;
- complications are unlikely;
- the recovery period after surgery is shorter than usual;
- the risk of relapse of the disease is minimal.
Inhalations and rinses
In addition to basic drug therapy, pediatricians recommend rinsing with furatsilin, miramistin, and iodinol. Very young children do not yet know how to rinse on their own, so they can treat their tonsils with a gauze swab dipped in the solution.
Inhalation using a nebulizer is used to treat inflammatory processes. You can pour a decoction of medicinal herbs (sage, eucalyptus, chamomile) into the device, which has a bactericidal and analgesic effect.
Methods for treating chronic tonsillitis using traditional medicine
In folk medicine, to treat childhood tonsillitis at home, they usually use:
- inhalation with a nebulizer and regular steam from infusions of medicinal herbs;
- herbal teas;
- gargling with solutions.
It should be immediately noted that it is best to buy ready-made preparations, since they take into account the interaction between the medicinal herbs included in the composition.
Herbal teas
The herbal compositions from which teas are prepared can have different effects on the body. For example:
- herbal tea that has an anti-inflammatory effect: you need to mix currant leaves, St. John's wort, thyme, coltsfoot, cinquefoil and peony roots, dill, chamomile and calendula flowers, pollen, sage in equal quantities, then pour one teaspoon of the resulting mixture into 200 ml . boiling water Leave for 4 hours, bring to a boil, filter and give to a sick child 50 ml-100 ml twice a day;
- herbal tea that strengthens the body's immune defense: mix rose hips, horsetail, calamus and licorice roots, sweet grass, St. John's wort and wild rosemary in equal quantities, then take one teaspoon of the resulting composition and add it to a glass of boiling water; Can be taken instead of regular tea.
As a general tonic for the body, prepare the following mixture: beet juice, freshly squeezed lemon and rosehip syrup are mixed in a ratio of 5:1:3 and left in a cold place for a day, taken after meals, a couple of teaspoons three times a day.
Gargling with home remedies
To gargle, it is recommended to use the following compositions:
- add one teaspoon of salt and five drops of iodine solution to a glass of warm water (provided that the child does not have an allergic reaction to this component), then stir and rinse every 3 hours;
- two large garlic cloves are crushed, the juice is squeezed out and added to a glass of hot milk. Afterwards, let it cool and gargle 2 times a day.
Prevention
If you have the disease, you must visit an ENT doctor at least 2 times a year to prescribe preventive therapy. As a preventive measure, they use: gargling with antiseptic solutions, taking medications to strengthen the immune system, and attending physiotherapy.
Particular attention should be paid to hardening and compliance with some simple rules:
- Walk outdoors as much as possible;
- Provide mouth rinse after meals;
- Monitor your child's nutrition;
- Ensure normal humidity and air temperature in the apartment;
- Carry out wet cleaning as often as possible;
- Follow a daily routine;
- Avoid hypothermia;
- Accustom your tonsils to cold drinks (start with small portions, gradually increasing them);
- Holiday on the seaside for at least 2 weeks every year.