Adenoviral conjunctivitis is a fairly common ophthalmological disease in children, especially in those who attend kindergartens, schools, clubs and sports clubs. In this article we will talk about the specifics of this form of conjunctivitis, the features of its manifestation, possible methods of treatment and prevention in children.
In this article
- Brief information about the disease
- Development of adenoviral conjunctivitis: causes and risk factors
- In what form can the disease manifest itself in a child?
- Symptoms of adenoviral conjunctivitis
- Features of the diagnosis of adenoviral conjunctivitis
- How to treat adenoviral conjunctivitis in children?
- Is it possible to prevent the occurrence of conjunctivitis?
Brief information about the disease
Adenoviral conjunctivitis is an acute infectious and inflammatory pathology of the eyes, which is provoked by a special group of viral pathogens - adenoviruses. The disease is often accompanied by fever, inflammation in the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx and symptoms of inflammation of the visual organs.
Adenoviral conjunctivitis can affect both adults and children of any age. The only exception is breastfed children of the first year of life, who are protected by special antibodies. Such babies very rarely suffer from conjunctivitis.
The disease is highly contagious: simply put, it is highly contagious and easily transmitted from sick people to healthy people. Doctors usually register massive outbreaks of viral conjunctivitis in the fall and winter, when the body is especially susceptible to various infections. Often, an epidemic begins in preschools or other educational institutions, where a large number of children are always in close contact with each other.
Development of adenoviral conjunctivitis: causes and risk factors
The main cause of adenoviral conjunctivitis in children is the penetration of various types of adenoviruses into the body. The infection can be transmitted in two main ways - airborne droplets (for example, when coughing or sneezing) and contact (for example, if a healthy child takes a sick toy). The disease does not manifest itself immediately: the first symptoms may appear only on the third or even tenth day from the moment of infection. During the incubation period, the child is already contagious, but there are still no external manifestations of the disease, so he often continues to attend school or kindergarten. Because of this, adenoviral conjunctivitis can become an epidemic in children's groups - an infected child, before being on sick leave, manages to transmit the infection to dozens of other children.
The following categories of people are at risk for the incidence of adenovirus-type conjunctivitis:
- those who have been in contact with an infected person;
- children who have been injured or who have had eye surgery;
- contact lenses;
- people after hypothermia or sick with ARVI;
- those who are experiencing stress.
These factors increase the likelihood of developing adenoviral conjunctivitis, but do not necessarily mean the development of the disease.
In what form can the disease manifest itself in a child?
There are three forms of adenoviral conjunctivitis, each of which can occur in childhood. The catarrhal form of conjunctivitis is characterized by minor inflammation, slight redness and a small amount of discharge from the eyes. The disease is quite mild, rarely accompanied by complications and usually resolves within seven days.
The follicular type of conjunctivitis is distinguished by the fact that gelatinous transparent follicles (vesicles) of different sizes form on the mucous membrane. This form of the disease is otherwise called pharyngo-conjunctival fever, because it is accompanied by an increase in body temperature and inflammation of the nasopharynx.
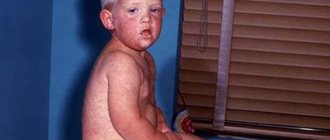
Adenoviral membranous conjunctivitis, unlike the first two types, usually only affects children. The infectious process in this case occurs with the formation of thin whitish-gray films on the mucous membrane. In some cases, they are easily removed from the surface of the eye, in others they “grow” tightly to the conjunctiva and are difficult to remove. A concomitant symptom of membranous adenoviral conjunctivitis is high body temperature (about 39 degrees Celsius). Scar changes may also occur on the mucous membrane.
Symptoms of adenoviral conjunctivitis
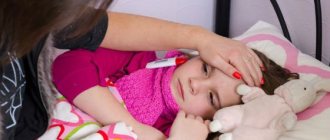
Quite often, viral conjunctivitis is mistaken for a common cold at an early stage. It may start as an acute infection or develop gradually. In case of any ailment, parents should pay attention to the child’s condition and see the symptoms of the disease as early as possible.
A sick child may complain of a headache, develop a fever or develop a fever. When examining the throat, you can see red areas of inflammation; breathing is difficult due to a runny nose, which can lead to inflammation of the pharynx, soreness and pain in the throat. A sick child is distinguished by a lethargic, drowsy state, poor appetite, and general malaise. A few days after the onset of the disease, abdominal pain, nausea, and a painful cough may be added to the listed symptoms.
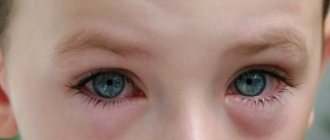
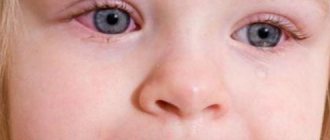
The symptoms of conjunctivitis may not appear immediately, but on the second or third day after the appearance of general signs of illness. When the visual organs are inflamed, a child may experience a burning sensation or “sand” in the eyes, tearing, and itching may occur. Some children with adenoviral conjunctivitis experience such severe discomfort from bright light that they even refuse to open their eyes until their parents close the curtains tightly. In the morning, crusts may form on the eyes, which stick together the eyelashes. Parents should help the child carefully remove them using a cotton swab. If you do not do this, the baby will rub his eyes with his hands, which increases the risk of a bacterial infection and the development of purulent conjunctivitis.
Other complications of the disease may include:
- “dry eye” syndrome, in which the production of tear fluid is disrupted and the visual organs experience discomfort from dryness;
- inflammation of the cornea;
- diseases of other organs - tonsillitis, otitis and adenoid growths, which can lead to adenoiditis.
It is worth noting that adenoid growths are dangerous because they interfere with breathing through the nose.
Symptoms and forms of adenoviral infection
Symptoms of adenovirus infection:
- Increased body temperature. It can persist at low-grade levels, and sometimes reaches febrile levels. Body temperature drops quickly.
- Headache.
- Increased fatigue and weakness.
- Rhinitis.
- Sore throat and other catarrhal symptoms. They develop from the first day of illness.
- Swelling of the mucous membranes.
- Dry cough, which becomes wet on the 3rd or 4th day of illness.
- The appearance of purulent plaque on the tonsils, their soreness.
- Swelling of the mucous membranes.
- Pain in the eyes, watery eyes.
- Lack of desire to eat.
- Insomnia.
- Pale skin, irritability.
- Abdominal pain, diarrhea and vomiting.
- Increased size of lymph nodes.
Since adenoviruses belong to ARVI, people often confuse the manifestations of the disease with the flu. A marker that allows one to determine that a patient is developing an adenoviral infection is conjunctivitis. This symptom cannot go unnoticed. A person gets the feeling that sand has been poured into his eyes, they become watery and can fester. Moreover, the pathological process can spread to both one and two eyes.
Intoxication of the body with adenovirus infection is not as intense as with influenza. It lasts no longer than 1-2 days. While with the flu this period extends for 1-7 days.
Body temperature rises to 38 °C. Within a day it begins to decrease and stabilize. If the patient has the flu, then the fever is intense. The mark on the thermometer remains at 39-40 °C.
Symptoms characteristic of adenovirus infection include:
- Conjunctivitis and keratoconjunctivitis.
- Rhinitis and inflammation of the tonsils.
- Inflammation of the bronchi.
- Pharyngitis.
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the abdomen (mesenteric lymphadenitis).
These symptoms are often combined with each other.
In childhood, the infection has a pronounced course. In a child of the first year of life, adenoviruses can cause pneumonia. Moreover, the disease develops quickly. Breathing becomes hoarse, convulsions, shortness of breath, and vomiting may occur. Pneumonia manifests suddenly, while in adult patients this complication is expected if he does not receive the necessary treatment.
If a newborn child is infected, there is no significant increase in body size and conjunctivitis may develop. Lymph nodes remain normal. This is explained by the fact that infants have innate immunity received from the mother. Therefore, the disease does not gain intensity in them.
Young children often suffer from intestinal disorders. The stool becomes frequent and mucus appears in it. Sometimes children complain of severe abdominal pain that resembles acute appendicitis.
If there is no treatment, this can lead to serious complications. The patient may develop tonsillitis, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, bronchitis with obstruction, sinusitis, and otitis media. Existing chronic diseases often worsen. Therefore, symptoms of adenovirus infection require contacting a doctor.
Features of the diagnosis of adenoviral conjunctivitis
Doctors note that diagnosing the adenoviral type of inflammation of the outer membrane of the eyeball is not always easy. This is explained by the fact that the general symptoms of any adenoviral conjunctivitis are characteristic of a number of infectious diseases, in particular influenza. It is the characteristic lesions of the eye tissue that help make the correct diagnosis.
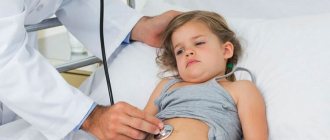
A diagnostic examination of a child is usually carried out by at least two specialists - a pediatrician and an ophthalmologist, who, based on the results of a comprehensive diagnosis, decide how to treat conjunctivitis.
When collecting anamnesis, doctors must take into account whether the patient has had contact with a person infected with adenoviral conjunctivitis. Also, a medical examination allows you to establish a set of signs that may indicate this disease - a combination of ophthalmological symptoms, inflammatory processes in the respiratory tract and enlarged lymph nodes. Using laboratory tests, cytology and other methods, the presence of adenovirus in the body is determined. There is also a way to diagnose the disease using a smear of the eyeball. This method is called immunofluorescence. Once the correct diagnosis has been made, treatment can begin.
Diagnostics
Symptoms of adenovirus infection in children are a reason to seek treatment from specialists at the CELT multidisciplinary clinic. Before prescribing certain treatment and rehabilitation measures, a clinical and laboratory examination is carried out, which will allow diagnosing the disease.
In addition, our specialists carry out differential diagnostics that allow us to distinguish adenoviral infection from:
- flu;
- diphtheria of the pharynx;
- other diseases.
The results of the diagnostic search become the key to adequately prescribing therapy and obtaining the desired result.
How to treat adenoviral conjunctivitis in children?
If a child is diagnosed with any form of adenoviral conjunctivitis, treatment should be started as quickly as possible. This will avoid a number of complications. The treatment regimen for ophthalmological symptoms is usually selected by an ophthalmologist; general therapy can be prescribed by a pediatrician. With uncomplicated adenoviral conjunctivitis, there is no need to go to the hospital; the child receives the necessary medications at home and, as prescribed by the doctor, comes to the clinic for repeated examinations.
Sometimes, as an alternative to drops, the ophthalmologist may prescribe treatment with ointments with a similar effect, which must be placed behind the child’s eyelid several times a day. To minimize the risk of complications such as a bacterial eye infection, your doctor may prescribe eye medications with an antibacterial effect. Additional use of moisturizers recommended by a doctor helps to exclude the development of dry eye syndrome due to the disease.
We told you how to treat adenoviral conjunctivitis in children from an ophthalmological point of view. But treatment is also necessary to combat other symptoms - lowering the temperature, fighting inflammation, cough, sore throat. For this purpose, antipyretic, anti-inflammatory and other drugs are used.
Treatment of adenovirus infection in children
In most cases, treatment of adenoviral infection in children is carried out on an outpatient basis, that is, at home.
Placing a child in a hospital may be necessary in case of severe disease or the development of serious complications, in particular when the process generalizes. Specific treatment methods have not been developed, and standard antiviral drugs are ineffective.
In this regard, only symptomatic therapy is carried out. Bed rest is necessary for the child until the fever passes. Indications for the prescription of antipyretics (antipyretic drugs) is a rise in body temperature above 38.5˚C. At lower values, these drugs are used if there is a high probability of developing seizures against the background of a febrile reaction (for example, in young children).
Pediatricians recommend giving children Nurofen or Paracetamol, strictly observing age-specific dosages.
In addition to pharmacological means to reduce temperature in the treatment of adenoviral infection, you can use physical methods, such as cold rubbing and applying a heating pad with ice to the projection of large blood vessels. To speed up the removal of toxins from the body, the patient is advised to drink plenty of warm drinks.
Milk with a small amount of baking soda and alkaline mineral waters help soften a dry hacking cough. It is not advisable to use antitussives! To reduce inflammation of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract, the child is recommended to inhale with the drug Lazolvan, as well as with a physiological solution of sodium chloride. To thin bronchial secretions (sputum), it is recommended to give Bromhexine and ACC. To improve sputum discharge during a wet cough, mucolytic and expectorant drugs (Ambroxol, Mucaltin) are indicated. Remember that only your doctor can prescribe the optimal medications.
Inflammation of the conjunctiva requires regular eye rinsing. To carry out the procedure, you can use a weak (pale pink) solution of potassium permanganate, or furatsilin. Natural remedies are also effective - a decoction of chamomile flowers and weak tea leaves. Among the drugs for the treatment of conjunctivitis in case of adenoviral infection, Ophthalmoferon drops (even with unilateral inflammation should be instilled in both eyes) and Oxolinic ointment (placed behind the lower eyelids) are also indicated.
For nasal congestion, you can use vasoconstrictor drops Nazivin or Galazolin (in “children’s” concentration). You can use these drugs 3-4 times a day and preferably no more than 3-5 days in a row to avoid the development of drug dependence.
For gargling a sore throat, products with an antiseptic effect are indicated - furatsilin solution and chamomile decoction.
The presence of complications due to the addition of a bacterial infection is an indication for treatment with a course of systemic antibiotic therapy.
With an adenovirus infection, it is difficult for a child with a sore throat to eat regular food, so his diet should include pureed and semi-liquid foods. To strengthen the immune system, vitamins are necessary, which the baby should receive both with fresh vegetables and fruits (or juices), and in the form of complex preparations.
The room where the sick child is located must be wet cleaned twice a day. The room should be ventilated more often. Until the symptoms of conjunctivitis subside, it is important to provide dim lighting.
Walking in the fresh air is allowed only as symptoms disappear and general health is normal.
Is it possible to prevent the occurrence of conjunctivitis?
Sometimes the best alternative to treatment is proper prevention of adenoviral conjunctivitis. It involves monitoring the incidence of children in educational institutions and timely exclusion of virus carriers from the team, frequent wet cleaning of premises, and ventilation. Also, the task of parents is to teach the child the rules of personal hygiene and explain why compliance with them is so important for health. If a child is involved in swimming, then it is better to choose a pool that meets sanitary standards and in which increased attention is paid to the quality of water purification.
Thus, adenoviral conjunctivitis is a fairly common disease among children and adolescents, who are often in children's groups. If detected in time and treatment is started, the pathology is treated within a few days and goes away without complications. Compliance with preventive measures can sometimes help avoid illness even during seasonal epidemics.
Prevention
A specific vaccine has not yet been developed.
During seasonal outbreaks, you should visit crowded places (including public transport) with your child as little as possible. The baby needs general strengthening of the body, which involves hardening and proper nutrition.
During the cold season, additional intake of multivitamin complexes can be recommended. The child must be taught to strictly observe the rules of personal hygiene.
A good prophylactic agent is leukocyte interferon (diluted with water and instilled into the nasal passages).
To get more information about the treatment of infectious diseases in children, in particular, about the treatment of adenovirus infection, we recommend watching this video review - Dr. Komarovsky gives advice to parents:
Chumachenko Olga, pediatrician
55, total, today
( 45 votes, average: 4.11 out of 5)
Blood test for measles: how to take it, norms and interpretation
Epstein-Barr virus: symptoms and treatment