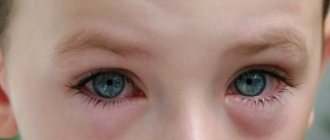
Nowadays, there are many common diseases that bring discomfort to a person’s life. One of these diseases is conjunctivitis, which can affect both children and adults. If an adult gets over the disease quite easily, a child will have to suffer. Rather, various ointments for conjunctivitis for children will help relieve him of discomfort, and we will talk about them in detail in this article.
Which ointment for conjunctivitis should I choose for children?
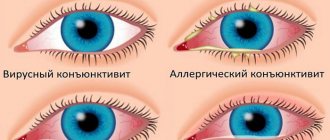
What is conjunctivitis
It is important to note that conjunctivitis comes in various forms; each form of the disease requires an individual approach and course of treatment. The most effective drug in the fight against conjunctivitis are ointments; they have a wide spectrum of action, contain many useful components and practically do not cause irritation or other side effects in children.
Before starting a course of treatment, undergo a detailed examination of your child’s eyes by an ophthalmologist in order to receive an accurate diagnosis and a detailed course of treatment; it is strictly forbidden to decide on your own which drug is suitable for your child.
Approved drugs for children
In children, allergic conjunctivitis is also common, like any other form of allergy. Their immunity is not strong enough, and many substances and objects are not yet familiar to them, so it is unknown how the immune system will react to them. Very often, allergic conjunctivitis in childhood appears during travel abroad, when joining a group of peers, in the summer.
Children can experience both mild and severe forms of the disease. In the first case, parents sometimes do not immediately notice that something is wrong with the child, because the symptoms are too sparse.
If there is redness, tearing, swelling, or accumulation of pus in the child’s eyes, it is imperative to show him to a specialist. An ophthalmologist, having made a diagnosis, often prescribes eye drops:
- tear substitutes: Lakrisin, Oftagel, Systane, Visin “Pure Tear”, Natural Tear;
- vasoconstrictors: Visin, Okuklia, Afrin;
- antihistamines: Levocabastine, Azelastine;
- mast cell membrane stabilizers: Optikrom, Highkrom, Lecrolin, Cromohexal, Alomide;
- combined: Allergodil, Nedocromil, Opatanol, Cyclosporin A.
In some cases, corticosteroids are prescribed (for advanced disease), antibiotics are prescribed when an infection occurs, vitamin drops can be part of complex therapy or used for prevention.
Ointments for bacterial conjunctivitis for children
The best ointments for conjunctivitis for children: list
Erythromycin ointment
Erythromycin eye ointment is an antibacterial agent that is actively used in ophthalmology.
The most popular drug in the fight against bacterial conjunctivitis. Produced in denominations of 3, 7, 10 grams.
A huge plus is that the ointment has an antibacterial effect on the affected area, which allows it to be used even by newborn babies.
Tetracycline ointment
Also used in the case of bacterial conjunctivitis. The ointment is based on an antibiotic, but is allowed for use in children over 8 years old.
Tetracycline eye ointment is available in bottles of 3, 5, 7, 10 and 15 ml
Tobrex
The ointment is actively used for bacterial and infectious conjunctivitis. Produced in packs of 3 grams. Application can be started for children from two months.
Colbiocin
Antibacterial drug, produced in denominations of 5 grams. Includes:
- Colistimethate sodium.
- Chloramphenicol.
- Tetracycline.
Active use for purulent conjunctivitis; use is not recommended for pregnant women; children are allowed to use from 8 years of age.
Eubetal
Produced in packs of five grams. Very effective in fighting bacteria and inflammation. Active in the fight against chlamydia, mycoplasma, amoeba, rickettsia. It is prohibited for use by people with diseases of intracranial pressure, and people who are allergic to the components of the drug.
Types and symptoms of conjunctivitis in children 2 years old
The clinical picture of conjunctivitis in a 2-year-old child directly depends on the type of this pathology.
A 2-year-old child may experience one of three types of conjunctivitis, classified by etiological factor (cause):
- Allergic conjunctivitis occurs quite often, which is associated with high sensitization (hypersensitivity) of the body. Symptoms of this type of disease are: lacrimation; mucous discharge from the eyes in moderate quantities, itching, redness of the eyes, swelling of the orbital area. Both eyes are affected;
- Viral conjunctivitis. Often, a 2-year-old child is diagnosed with catarrhal (signs of inflammation of the eyes and symptoms of damage to the ENT organs and upper respiratory tract) and membranous (formation of films on the mucous membrane of the eyes, which are easily separated) conjunctivitis. The appearance of this type of conjunctivitis is preceded by a viral disease of the ENT organs, bronchi and lungs. Symptoms: photophobia, lacrimation, sensation of a foreign body in the eye, discomfort, discharge from the eyes is light, viscous, formation of films on the mucous membrane. The child experiences an increase in body temperature up to 38 degrees, and in the film form - up to 39 or more. Only 1 eye may be affected;
- Bacterial conjunctivitis is characterized by a severe course. It is characterized by a persistent increase in body temperature, itching, redness and discharge of pus from the eyes, which forms crusts on the eyelashes and eyelids and can stick the eye together. Inflammation develops in both eyes, first on 1, and after 2–3 days it spreads to the other.
You can learn more about high fever due to conjunctivitis in children here.
With any type of conjunctivitis, a 2-year-old child’s general condition suffers. He becomes capricious, irritable, refuses to eat, fatigue, body aches, and chills are noted (as the temperature rises).
Treatment of viral conjunctivitis
When treating viral conjunctivitis, it is worth performing a set of procedures aimed at actively influencing and destroying viruses. Before using ointments, it is important to rinse your eyes with various tinctures, which will help clean the retina. Medicines for conjunctivitis for children are in demand, because every parent wishes their child a speedy recovery.
The list of ointments for viral conjunctivitis for children is as follows.
Miramistin
Miramistin should be used only as prescribed by a doctor because you need to know the exact consistency of the drug so as not to get a burn to the retina.
Algorithm
Any violations in the technique can lead to additional infection. Drops fall on the mucous membrane, which is very sensitive to various influences. And, conversely, if you do everything carefully and correctly, a person will feel a minimum of discomfort and recover faster.
It can be especially difficult to carry out medical procedures on very young children, to whom it is impossible to explain why it is necessary. Since it is very dangerous to develop infections in infancy, not only health workers, but also all parents need to know the method of instilling drops.
The sequence of actions that must be performed by the nurse or the baby’s parents can be divided into several stages. Each of them is important to achieve the desired result. Let's look at them one by one.
Preparatory stage
At this stage, it is important to do everything that will help carry out the procedure in one place, without risk or discomfort for the patient. In terms of time, everything takes very little time, especially if the procedure is carried out in a medical office, where there are all the necessary tools
What to do before starting the procedure:
- Make sure you have everything you need: drops, a sterile pipette with a blunt end, at least two sterile wipes and cotton pads or pieces of sterile cotton wool. All this must be clean, you must be careful not to touch it with unwashed hands.
- Carefully read the name of the drops, the doctor’s recommendations regarding dosage and frequency of use, check the expiration date and integrity of the bottle.
- Warm the drops, especially if they were stored in the refrigerator. This can be done in two ways: by holding it in your palms for 15 minutes or in a water bath. If you decide to use the second option, you need to make sure that the water is not hotter than body temperature.
- Place the patient on his back on a couch or bed, or sit him up and ask him to tilt his head back. It is advisable that the face and eye area be well lit.
- Wash your hands with antibacterial soap and, if possible, wear disposable gloves.
Psychological contact is very important. If a child has not encountered such a procedure before, it can be very scary for him.
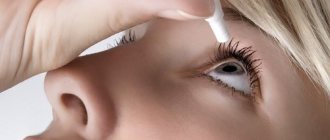
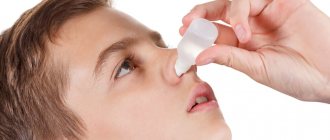
Eye drops
When all preparatory steps have been completed and the patient is ready, you can begin the procedure. The procedure is performed one by one for each eye, that is, the second one needs to be instilled only when the procedure with the first one has already been completed.
Directly instilling drops into the eyes, algorithm:
- Pipette drops. It should be kept in a vertical position. You need to collect the number of drops that need to be instilled into both eyes.
- The pipette should be taken in the right hand, and the sterile napkin in the left.
- It is necessary to ask the patient to look up and try not to close his eyes. At this time, use a napkin to slightly pull the lower eyelid and drop the medicine without touching the mucous membrane (there should be a distance of about 2-3 cm between the eye and the tip of the pipette).
- After a drop of medication enters the eye, the eye reflexively closes. It is necessary to ask the patient to make circular movements with the eyeball.
After the first eye has been instilled, everything is repeated in the same sequence with the second. You should try to do this quickly and accurately, because usually the second eye reflexively closes faster, so it is more difficult to hit it without letting a single drop slip by. Be sure to take another, sterile napkin.
After the procedure
Final steps are very important to avoid infection during subsequent procedures. Also, after instillation, you need to calm the child down if the drops cause discomfort, the baby did not like the procedure or was scared.
What you need to do right away:
- Throw away all disposable materials: cotton wool, napkins, disposable pipettes, if used.
- Carry out chemical or thermal treatment of instruments that are intended for reusable use (regular pipettes, a removable dropper on a bottle of medicine, if provided for in the instructions).
- Cover the drops and hide them in the refrigerator or other place in which they should be stored.
- Remove gloves if you were wearing them, wash and dry your hands.