Cytomegalovirus in children (CMV) is an infectious disease caused by a specific microorganism, Human betaherpesvirus 5. In most cases, the pathogen is detected by examining blood and urine using the polymerase chain reaction method. In many children, cytomegalovirus infection does not manifest itself with severe symptoms, and only when exposed to a number of factors do the first signs develop.
Causes of infection↑
Despite the fact that the primary infection acts as a vaccine, one should not neglect the manifestations of the disease. Most often, children “bring it” from kindergarten, from holidays and children's events. Children with congenital cytomegalovirus infection in the first five years are active carriers of the virus. Infection occurs during play, through dishes, clothing, and common items.
In newborns, the mother becomes the source of cytomegalovirus. Infection can occur during childbirth, breastfeeding, and through household contact. It is especially dangerous if a woman gets sick in the third trimester. In this case, the risk of infection during natural childbirth is very high. If infected in the first days of life, a diagnosis of neonatal cytomegalovirus infection is made.
How do children become infected with cytomegalovirus?
Cytomegalovirus spreads between people through airborne droplets. This infection is also found in all human fluids: sweat, saliva, urine, blood, sputum, genital secretions.
For this reason, it is quite easy to become infected with cytomegalovirus. This infection occurs in most people on the planet; it is not considered dangerous to health.
Typically, children are infected with cytomegalovirus without any symptoms. It is impossible to say exactly at what point the infection entered the body.
In such cases, the virus does not pose any danger. However, certain difficulties are caused by cytomegalovirus, which entered the child’s body in the first months of his life.
The infection that the fetus receives while in the womb is especially dangerous. It can negatively affect its development, as well as provoke miscarriage or death of the child.
Symptoms of the disease↑
In strong, healthy babies, cytomegalovirus infection is asymptomatic in 90% of cases. In the remaining 10%, symptoms and treatment are similar to mononucleosis infection. An accurate diagnosis is required if:
- sore throat;
- increased temperature;
- headache;
- a runny nose began;
- rashes appeared on the skin;
- loss of appetite;
- the child is weakened, does not play, does not show interest in anything.
In serious cases, slight bleeding begins from the navel. Symptoms characteristic of jaundice appear; there are spots of blood in the stool. If these alarming signs occur, the child should be seen immediately by a doctor. Cytomegalovirus in children can lead to developmental delays, neurological disorders, and visual impairment.
Prevention
Prevention of infection includes the child observing the rules of personal hygiene, since the virus is transmitted by contact. Walks in the fresh air, a varied menu, a rational daily routine - all this will strengthen the baby’s immunity and make it easy to survive the attack of the virus.
To protect the child from congenital cytomegaly, a woman must be tested for antibodies when planning pregnancy . If antibodies are not detected, the doctor will prescribe a preventive vaccination for the expectant mother.
The vaccination will form immunity to the pathogen and protect the woman during pregnancy from infection.
Treatment with folk remedies for acute infection during pregnancy is ineffective ; you should definitely consult a doctor if you have any symptoms of acute respiratory viral infection. The consequences of congenital cytomegaly are too serious to neglect the possible danger.
Forms of cytomegalovirus infection in children↑
In early infancy and preschool children, primary infection develops. It does not require emergency hospitalization. Symptomatic treatment is acceptable. After 1-2 weeks, the body overcomes the disease. During this period, antibodies are formed naturally in children. The infection may be:
- acute;
- chronic;
- latent;
- generalized.
A child with a weakened immune system is likely to have complications. Recurrent infections can lead to bronchitis, pneumonia, and retinitis. If untreated, kidney, adrenal, liver or spleen diseases are likely. The lymph nodes become inflamed, the infection can affect the gastrointestinal tract and cause the development of encephalitis.
In some cases, a recurrent form of congenital cytomegalovirus infection develops. Sometimes it is asymptomatic, which is why regular preventive examinations and clinical laboratory tests for children up to one year old are so important.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing such a disease in children is not easy, since the manifestations are nonspecific and resemble the course of many other diseases. The doctor will examine the child and then prescribe the necessary tests and studies to confirm cytomegaly.
Analyzes
The following tests will help detect an infection in a child:
- Blood tests for antibodies to the pathogen - the protective protein Ig M indicates an acute infection, and IgG indicates a chronic or latent form.
- PCR of urine and saliva - allows you to detect the pathogen itself in the material.
- Complete blood count - the child has a reduced number of red blood cells (anemia), platelets and leukocytes.
- Biochemical blood tests - liver enzymes ALT and AST increase; with kidney damage, the concentration of urea and creatinine will increase.
The urine sediment must be examined under a microscope for the presence of giant cells with a nucleus in the form of an “owl’s eye”, which will confirm the diagnosis of cytomegaly.
Instrumental methods
They are prescribed depending on which system is affected in the child:
- chest x-ray – if the lungs are damaged, the image will show signs of pneumonia;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity - will reveal an enlargement of the liver and spleen, possible hemorrhages in them;
- Ultrasound or MRI of the brain will detect foci of inflammation or calcifications.
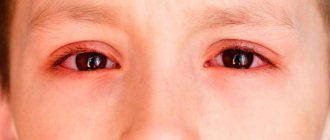
For a generalized infection, the doctor will order a fundus examination by an ophthalmologist. This will allow timely detection of damage to the structures of the eye and, possibly, preserve vision, subject to proper treatment.
Be careful - complications are possible↑
Complications of cytomegalovirus occur in both newborns and older children. As a rule, they are the result of a weakened immune system or are superimposed on other, most often chronic, diseases. Complications take the form of:
- pneumonia (requires intensive treatment);
- encephalitis (convulsions, hearing loss, drowsiness);
- chorioretinitis (impaired ability to concentrate, leading to loss of vision).
In serious cases, complications of cytomegalovirus infection can be fatal.
What is cytomegalovirus in children
Cytomegalovirus in a child is able to penetrate the tissues of all organs, but it shows the greatest activity in the salivary glands, quickly multiplying and integrating its DNA into the nuclei of cells. When an infectious agent is introduced, lymphocytes and monocytes are damaged. The disease leads to an increase in the cells of the salivary glands, which gave rise to the name of the virus (translated from Latin as “giant cells”).
The infection damages not only blood vessels, but also the tissues of the child’s internal organs, disrupting their blood supply and leading to hemorrhages. The virus causes a significant change in the shape and structure of leukocytes and phagocytes, resulting in the development of signs of immunodeficiency. When the child’s body’s defenses are healthy, the virus is not active.
With a decrease in immunity, the disease begins to manifest itself with various symptoms.
How dangerous it is for a child
The congenital form of cytomegalovirus infection can cause the development of mental retardation in a child. The risk of death in infants is 30%. The disease leads to vision impairment and blindness. In 18% of cases, damage to the nervous system occurs. Children develop convulsive symptoms, high anxiety, weight loss, and skin reactions.
Diagnostics↑
If an infection is suspected, the doctor will order a series of tests. Three diagnostic methods are used:
- enzyme immunoassay - detection of antibodies;
- cultural method;
- polymerase reaction - detects viral DNA in the blood.
If any alarming signs appear, it is necessary to show the child to a doctor and strictly follow the recommendations for treatment and relief of symptoms of the disease. According to the international classification, cytomegalovirus disease has ICD code: B25. In accordance with this code, the therapist prescribes antiviral drugs and immunomodulators.
Treatment↑
Treatment with antibiotics is required only in cases of complicated infection. For mild forms, symptomatic treatment is sufficient. The temperature is taken only if it remains above critical values (they differ by age). Interferon drugs are prescribed only to patients over 5 years of age.
A number of drugs with a more gentle mechanism of action have been developed for infants. These are drugs based on human immunoglobulin:
- Megalotect;
- Cytotect;
- NeoCytotect.
Prescribe with extreme caution:
For mild forms of the disease, herbal medicine helps well. Use products that strengthen the child’s immune system. These can be decoctions or teas based on thyme, yarrow, and string. Children willingly drink infusions of oregano, rose hips or raspberries. To relieve a sore throat, use a decoction of flax seeds, preparations of licorice root, marshmallow, violet, elecampane, and cinquefoil.
Treatment
When prescribing treatment, the doctor must consider the following factors:
- Type of cytomegalovirus infection. Determined by enzyme immunoassay. With the acquired form of the disease, there are often no symptoms or changes in the baby’s organs and systems. The presence of the virus is not dangerous if the child’s immune system is functioning normally.
- The nature of the course of the disease. When an infection occurs, the severity of symptoms is taken into account.
- State of the immune system. Not only the course of the disease, but also the speed of recovery depends on the functioning of the body’s defenses.
Dr. Komarovsky about cytomegalovirus infection
Pediatrician E. Komarovsky believes that the use of antibacterial agents in detecting cytomegalovirus infection is not justified, since such drugs are not able to help with this disease.
An antimicrobial drug is prescribed to a child when signs of complications appear, manifested by the development of inflammatory processes in the internal organs.
The antibiotic is selected individually, taking into account the child’s body weight and the presence of chronic pathologies.
Treatment of the disease is carried out in the same way as therapy for herpesvirus. Children are prescribed the drugs ganciclovir and cytoven. The dosage is calculated taking into account the child’s weight (10 mg/kg); after 21 days it is reduced to 5 mg/kg. Therapy with an antiviral drug is carried out until signs of the disease disappear and laboratory parameters, which indicate the degree of infection activity, decrease. For the congenital form, ganciclovir is used for one and a half months at a dosage of 10 mg/kg. If signs of intolerance to the drug appear, another antiviral agent is selected for the child. If an exacerbation occurs, an antipyretic medication (ibuprofen) is prescribed. During this period, the pediatrician recommends drinking plenty of fluids and multivitamin complexes. To normalize nasal breathing, naphthyzine and sanorin are prescribed. When swelling of the mucous membranes occurs, an antihistamine is prescribed.
The use of immunostimulating agents is of great importance in the treatment of CMV. The child is injected with a drug containing immunoglobulins against cytomegalovirus. Course - 10 injections.
After the symptoms of the disease subside, the child is recommended to undergo physiotherapy (massage, UHF).
ethnoscience
The basis of most recipes that help cope with the disease are herbal preparations. When using folk remedies, you need to remember that the child may develop allergic reactions. If a sign of intolerance to herbs appears in the baby’s body, treatment using unconventional methods should be abandoned.
For cytomegalovirus, you can use a collection consisting of the roots of licorice, kopeck, leuzea, alder fruit, string and chamomile flowers. The dry mixture is thoroughly mixed, take 2 tbsp. plants and pour ½ liter of boiling water. For infusion, it is better to use a thermos. The healing agent is given to the child 50 ml four times a day.
Prevention↑
The main measures to prevent infection with cytomegalovirus are carried out during pregnancy. They are indicated when there is a high risk of infection for the expectant mother and fetus. For infants in the first year of life, protection against infection is the intake of immunoglobulins by a nursing mother. Together with milk, they enter the baby’s blood.
If the baby is sick, during the exacerbation of the disease it is necessary to limit his contacts with other children. It is important to carefully ensure that no one uses his dishes, clothes, or toys. It is especially important to monitor the contacts of children with weakened immune systems.
For healthy children, as a preventive measure, walks, hardening, an active lifestyle, fruits, vegetables, and vitamins are useful in the diet.
Types and forms of childhood cytomegalovirus
There are two main types of CMV:
- congenital;
- acquired.
Often infection occurs during pregnancy. The virus penetrates the placenta and enters the amniotic fluid, when ingested it is introduced into the cells of the developing body of the child.
Doctors consider the first two weeks after conception to be the most dangerous period.
In this case, the risk of developing irreversible changes in the fetus is extremely high. Infection can cause miscarriage in early pregnancy. Cytomegalovirus is considered acquired if it is transmitted from the mother. The risk of infection increases with kissing and skin-to-skin contact.