Dacryocystitis is a fairly common disease in which the nasolacrimal canal in a newborn cannot independently clear the plug that protects it from amniotic fluid.
In most cases, this plug ruptures on its own during childbirth, but if this does not happen, the newborn’s tears will not enter the nasal canal, as a result of which the eyes become sour and swelling occurs in the corners.
Probing the lacrimal canal in newborns is a rather unpleasant procedure , and the child may cry at this moment, but after it he quickly calms down. If the cause of dacryocystitis is a deviated nasal septum or a congenital anomaly of the lacrimal canaliculi, there is no point in performing the procedure. In this case, surgery is indicated.
Causes of pathology in newborns
More than 7% of babies have canal blockage from the moment they are born.
The root cause may be incomplete detachment of the film that protects the eye from amniotic fluid entering the eyeball. Other causes of pathology include an anomaly of the nasal septum, as well as an anatomically narrow opening of the lacrimal duct. The disease develops gradually, accompanied by new symptoms. Initially, you should pay attention to the signs of pathology:
- Baby's restlessness;
- Increased bags under the eyelids in the corner of the eyeball;
- Purulent discharge from the eye;
- Difficulty opening the eyelids due to sticking together;
- Fever.
| Most parents mistake these symptoms for conjunctivitis and are in no hurry to contact a specialist, which is their main mistake. |
Signs of the disease can develop up to two months, and ultimately, if diagnosed untimely, turn into an infectious disease, including an abscess, which poses a real threat to the baby’s visual system.
In what cases is surgery prescribed?
When the first symptoms appear, the child should be shown to an ophthalmologist as soon as possible to determine the presence of dacryocystitis, as well as an ENT specialist to determine the depth of suppuration.
First, the doctor injects a special dye solution into the baby’s eyes and plugs the nose with cotton swabs. In a normal state, the liquid should pass through the canal, staining the nasal plug; otherwise, conservative treatment is prescribed, and then piercing the lacrimal canal.
The second way to detect the disease is to inject a coloring substance into the eye, due to which the eyeball acquires a brownish tint. With normal functioning of the tear duct, the baby's eyes return to a healthy color after 6 minutes.
Other indications for sounding are:
- Increased tear production;
- Chronic inflammation of the bags under the eyes;
- If non-surgical treatment methods do not produce a positive effect;
- Anatomical anomaly of the lacrimal canal.
Preoperative procedure
Before surgery, you should first undergo an examination by an otolaryngologist. Consultation with a doctor is necessary to determine the presence of a deviated nasal septum. Otherwise, the operation will not bring a positive result.
It is necessary to take a general blood test, determine its coagulability and undergo an examination by a pediatrician. Before surgery, you should not eat, and the baby should be carefully swaddled so that the baby does not have the opportunity to interfere with the operation with his hands.
| If there is a strong degree of suppuration, surgical intervention is postponed until the acute phase of the disease has been ruled out. |
It is important to consult a doctor in a timely manner to diagnose the disease, since the neglected condition of the tear duct can lead to complete loss of vision in the baby.
Preparing the child
Before probing the lacrimal canal, it is necessary to consult with an otolaryngologist to find out if the baby has a deviated nasal septum. You also first need to take a general blood test.
In some cases, before probing it is necessary to consult a pediatrician or therapist.
You need to make sure that the child is completely healthy and that the suppuration is a consequence of dacryocystitis and not a viral or bacterial infection.
If there is severe inflammation and a large amount of pus, the probing procedure is postponed.
To prevent the child from burping during the procedure, you should not feed him before the sounding . Therefore, before the operation, you should contact your doctor to clarify the diet, since the smaller the child, the shorter the period during which he cannot be fed.
It is better to carry out probing before one year, then the likelihood of complications is minimal.
Before the operation itself, the baby needs to be swaddled tightly, because by waving his arms, he can interfere with the doctor. The diaper or sheet used for this should be taken care of in advance.
Many parents are concerned about the question of why the probing procedure is carried out at such an early age and whether it can be postponed until the child is a little older.
How to probe the tear duct
The bougienage operation takes no more than half an hour and has its own stages and features. The procedure is unpleasant, and therefore, during surgery, the baby may cry. Probing of the lacrimal canal is carried out in a sterile office and does not require a hospital stay. After the operation, the baby is sent home for further outpatient treatment.
Initially, anesthesia is instilled into the baby's eyes. Then the doctor, at an angle of 90 degrees, inserts a special instrument - the Sichel probe - into the child’s lacrimal canal to a certain depth to widen it. Then a smaller diameter instrument with a tube is inserted into the baby to break through the clogging plug.
Using a special solution, the doctor rinses the tear duct. The doctor checks the success of the procedure, after which he monitors the patency of the lacrimal canal using a dye solution used in the process of diagnosing pathology. The best time to perform the procedure for probing the lacrimal canal in babies is 2–6 months after birth.
Upon completion of the operation, the child is prescribed eye drops and a special massage, then the baby is sent for outpatient treatment. Return to contents
Causes of obstruction of the lacrimal ducts and indications for surgery
Obstruction of the lacrimal canal in some newborns is formed in the following way. When the baby is still in the mother's womb, his eyes are protected by the so-called gelatin film, located just in the tear ducts. It prevents amniotic fluid from entering the tear ducts, as well as the nose and respiratory tract.
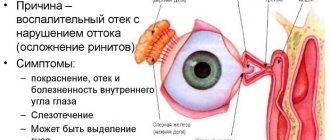
When a child is born and screams for the first time, the film bursts from tension. In rare cases, this process still does not occur. Due to the fact that it maintains its integrity, there is no way for tears to escape ; they accumulate in the lacrimal sac and cause an inflammatory process. The described phenomenon is the cause of dacryocystitis.
Symptoms of the disease
- with light pressure on the lacrimal sinus, pus flows out of the eye;
- continuous flow of tears in any condition of the child or their absolute absence;
- pus is released without stimulation.
If these symptoms are present, in order to make a final diagnosis, the doctor resorts to the following manipulations: a special coloring liquid is poured into the child’s eye . Before the procedure itself, cotton strands must be placed in the nostrils. You need to wait 5 minutes and let the solution flow down the entire tear duct.
The absence of violations is indicated by colored cotton wool, since normally the liquid overcomes the lacrimal canal and enters the nose. If staining does not occur, the doctor diagnoses obstruction of the canals and prescribes probing of the lacrimal canals. It is worth considering that it is better to carry out intervention for children who are already 2-3 months old, not earlier.
If the situation is urgent and alternative treatment methods have not helped, probing can be done earlier. Parents must definitely find out information about why the eyes of a newborn are festering. Timely implementation of recommendations will help avoid serious vision problems.
Indications for probing
- inflammation of the tear ducts and sac has acquired chronic status;
- alternative treatment methods (drops, massage) do not help;
- continuous flow of tears;
- the doctor questions the normal development of the lacrimal duct.
If all of these symptoms are present, probing of the lacrimal canals in infants is inevitable, otherwise dacryocystitis in newborns will lead to more dire consequences, including loss of vision.
Postoperative actions of parents
While undergoing home treatment, the baby’s mother and father should take care of his condition to prevent re-clogging of the tear duct. First of all, you should bury your eyes with a special antibacterial solution prescribed by your doctor.
The second stage of home care is massage of the lacrimal canal, recommendations for which parents can receive from a doctor.
| You should protect your baby from colds and other infections for 2 months, as this can trigger a relapse of the disease. |
The operation of probing the lacrimal canal has a positive effect in 85% of cases. However, if the treatment is incorrectly selected or the procedure is performed incorrectly, blockage of the canal may recur. In this case, the baby is prescribed a repeat operation according to the same scheme.
Is piercing the tear ducts dangerous?
Probing the eye for dacryocystitis can provoke the development of negative consequences. During the recovery period, you need to beware of viral and bacterial infections, as infection with pathogens can cause a relapse. Often, if the operation is carried out correctly, negative consequences rarely occur. Probing the lacrimal canal in children under one year of age can provoke an adhesive process. If the patient has a purulent eye, bleeding, high fever, excessive production or absence of tears, red eyes, nausea and vomiting, or the development of an eye infection, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor. Self-medication is dangerous, as it can worsen the course of the disease.
Massage technique after bougienage
Massage after probing the lacrimal canal is one of the ways of further outpatient treatment. Before the session, it is important to perform the following manipulations:
- Treat your hands with an antiseptic;
- Squeeze out the pus from the inner corner of the eye;
- Wipe your eyelids with a cotton pad soaked in a solution of chamomile or Furacilin;
- Apply eye drops.
Technique for lacrimal canal massage:
- The starting point of the procedure is the far tubercle at the base of the nose.
- Using light pressure with your fingertips, in a circular motion, palpate the elevation from the eyebrows to the inner corner of the eye.
- Repeat 15 times.
After the massage, the eye must be instilled with an antiseptic drug for disinfection. The frequency and duration of the procedure is prescribed by a specialist.
| Massage is prescribed by a doctor for a period of at least 7 days with a regularity of 3-5 times a day. |
Complications after probing the lacrimal duct
The operation of piercing the tear duct has its own characteristics and risks. The following complications may occur during the procedure:
- Rupture of the canal wall due to incorrectly selected probe diameter;
- Breakthrough of pus into the maxillary cavity;
- The probe enters the nasal sinus;
- Defect of the probe inside the canal, requiring surgical removal.
Consequences of surgery:
- Bleeding;
- Inflammation of the lacrimal sac;
- Relapse of dacryocystitis.
The first complication arises as a result of incorrect preparation or a doctor’s error during the operation. Improper care of parents for the child’s visual organs can lead to adhesions in the canal.
After surgery, a small wound remains on the inside of the eye, through which, if not properly treated, infection can penetrate and cause inflammation or relapse of dacryocystitis.
After the probing procedure, the following symptoms may also be observed:
- Fever;
- Conjunctivitis;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Excessive lacrimation and others.
| If any manifestations are detected, you should definitely see a specialist. |
Preparing for surgery
Bougienage is carried out for babies starting from one month.
Bougienage of the lacrimal canal in newborns is carried out at 1-4 months; it is also recommended to clean it in adulthood. Before piercing the ducts, the patient needs to prepare for the procedure and consult a pediatric otolaryngologist to exclude pathology of the nasal septum. It is important to stop taking medications that are incompatible with medications used during surgery. Before piercing the lacrimal canal, the child should not be given any food; it is also recommended to undergo the following diagnostics:
- blood for clotting;
- West's test;
- examination by an allergist;
- analyzes of samples taken from the lacrimal sac.
What could go wrong?
Often, the disease dacryocystitis is confused with ordinary conjunctivitis, and therefore parents begin independent treatment. When therapy does not lead to a positive effect, the baby is shown to the doctor, while the disease has rapidly progressed at this time.
As a result, a large amount of purulent fluid accumulates in the child’s lacrimal canal, which inevitably leads to an inflammatory process. The baby begins to be capricious, feels unwell, body temperature rises and there is heavy discharge.
| A distinctive feature of dacryocystitis is purulent discharge from both eyes. |
If you contact a specialist in a timely manner, the doctor will accurately determine the presence of pathology and obstacles to surgical intervention, if any.
The procedure for bougienage of the lacrimal canal is prescribed to children starting from two months, however, in emergency cases, the operation can be performed much earlier. The general prognosis after surgery is generally positive, provided that you contact an ophthalmologist in a timely manner.
The operation is performed in ophthalmology centers and private clinics. The average price for the service varies from 1000 to 3500 rubles per eye. Return to contents
How the operation is performed
The probing procedure is carried out using local anesthesia and lasts no more than 10 minutes.
The operation is simple and lasts no longer than 10-15 minutes, although parents may find it scary
- Drops with an anesthetic effect are dropped into the child's eyes.
- The doctor inserts a special sterile instrument called a Sichel probe, which has a conical shape, into the tear ducts.
- Thanks to their special shape, the tubules expand.
- Then the doctor uses a “Bowman probe”, which, due to its length, is inserted to the required depth and breaks the film.
- Next, the lacrimal canal should be rinsed generously with saline and disinfected with a special agent.
- The last step is the manipulation of instilling the coloring solution into the eyes, described above. If the cotton wool in the nose takes on the color of dripped liquid, this indicates a successful operation.
Other methods of treating the disease
In addition to surgical intervention, there are also conservative methods of dealing with blockage of the tear duct. First of all, the eye should be washed with infusions of chamomile, strong black tea, furatsilin water or liquid boiled over a fire for one hour.
The method is used for both eyes to avoid the spread of infection. A separate cotton pad is used for each eye. During the procedure, make sure that the liquid does not get into the ear or other eye. This can cause bacteria to spread and the disease to progress.
The problem of blockage of the lacrimal canal can be solved with the help of ophthalmic drops of disinfectant action. For these purposes, Albucid, Vitibact, and Torbex are used. It should be understood that dripping eyes is not a very pleasant procedure for a baby. The child may be capricious and cry.
| The name of the drug and the duration of its use are prescribed by the ophthalmologist after the examination. |
You can also break through the canal yourself using a massage, the technique of which was described earlier. In any case, before carrying out the procedure, consult a specialist. The doctor will tell you about the correct technique and frequency of massaging the nasal tear.
What do mothers say about probing the tear duct in newborns?
In general, the procedure has very positive reviews. Many parents noted that after the surgical intervention, the baby’s eyes cleared up, purulent discharge stopped appearing, and the child became calmer and more balanced. The mothers of the children noted that they were glad to undergo the operation in the first months of the baby’s life, since the procedure for older children is very painful.
Parents note that they should carefully follow all the doctor’s recommendations about postoperative care, do not bathe the baby for the first days, avoid contact with other people and protect the child from various types of diseases.
Negative statements often include the baby's crying during surgery. However, tearfulness is not caused by the pain of the procedure, but by the baby’s fright. For these purposes, the mother is sometimes allowed to be present during the operation so that she can calm the child and hold him if the baby is overly active.