In medical practice, young children are often diagnosed with helminth infections - diseases caused by various types of parasitic worms (helminths). Roundworms in children, the symptoms and treatment of which should be carried out under the strict supervision of the attending physician, since the disease (ascariasis) occurs in a more complex form than in adults and can provoke various complications. Unfortunately, dangerous endoparasites can be identified in a child’s body only after the manifestation of clinical signs, which appear during complications, and timely diagnosis.
What are nematodes?
The parasites have a round shape, white with a pinkish tint, and most often settle in the intestines, but can migrate through the liver, blood, brain and other human organs.
Cases of detection in the eyes and ear canals of people have been recorded. Their sizes are impressive, the female can reach up to half a meter in length, and the male up to 20-25 cm. The productivity of a sexually mature individual reaches 200 thousand eggs per day.
The average lifespan of microbes is from 10 months to a year. After a year of life they die, which does not mean complete deliverance. Their eggs can live in soil, water, and on foods.
How does a helminth enter the body?
Leaving the human body, feces infected with eggs end up in the soil, where they exist in favorable conditions. In the environment they are in their infancy until they are 12 years old.
The egg is covered with five layers of shell; it protects the embryo from negative factors of the flora, ultraviolet radiation, and frost. Pathogens are spread by ordinary flies, feeding on excrement. They are then picked up by fish and animals.
The main sources of infection are:
- drinking raw water or water from dirty ponds and lakes;
- raw, uncooked food;
- unwashed vegetables and fruits; Roundworms appear in a child due to a lack of personal hygiene. Therefore, it is so important to monitor whether the baby has washed after a walk or playing with a pet.
How do parasites develop?
Once in the child's body, the eggs hatch into larvae. They shed their protective shell. While the embryo is in the soil, it is protected by five layers of shell. He is not afraid of frost or ultraviolet rays. Embryos can remain in this state in the ground for up to 10 years.
Penetrating into the portal vein, they migrate throughout the body, lungs, liver, heart, stomach. This is called the migratory phase. About 4 days pass from the moment the infestations enter, then the larvae rise from the liver to the lungs. The child re-swallows them along with saliva.
For the remaining 10 or 15 days, the microbes develop into sexually mature individuals. This period can last up to three months. Then comes the intestinal stage. The female lays more than 250 thousand eggs per day, the eggs are released along with feces. Can live up to a year, then dies.
Features of paragonimiasis
One of the most dangerous helminthiases that can cause a cough reflex is paragonimiasis, caused by the vigorous activity of a flatworm (fluke) - the pulmonary fluke. Infection occurs by eating crayfish and crabs, which are carriers of the parasite. The worm penetrates the abdominal cavity, and as the disease progresses, it reaches the lungs through the diaphragm.
Once in the lung tissue, the fluke provokes an inflammatory reaction and can cause sclerosis. A fibrous layer is formed in the affected area, and a significant content of eosinophils is observed in the infiltrate. Further development spreads to the bronchioles, where the parasite eggs penetrate and a purulent and bloody mass is formed. The result is an intense cough with sputum containing these impurities.
Signs of ascariasis
At first, roundworms in children do not cause any symptoms.
A week later, starting to multiply, they release harmful substances, the following appears:
- dry cough;
- fever;
- skin rashes;
If your child has any of these symptoms, it may be a sign of hookworms.
After a month of infection, the spleen and liver increase in volume, and pain is observed on palpation. Abdominal pain and indigestion. The baby loses weight, refuses to eat, or eats poorly. Sleep is disturbed, weakness and fatigue occur. When you have a bowel movement, worms are visible in the stool.
It is important to know that with a high intake of eggs into the body, rapid intoxication of the body occurs, body temperature rises to 38 degrees, children suffer from headaches and migraines, and internal organs enlarge.
At the last stage, biohelminths cause pale skin, fever, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea gives way to constipation.
Development of giardiasis
Another common cause is Giardia. These microscopic protozoa settle in the intestines and cause the disease – giardiasis. The disease is typical for both adults and children of different ages. Infection occurs from people - carriers of parasites, animals, through dirty food and water, milk without heat treatment.
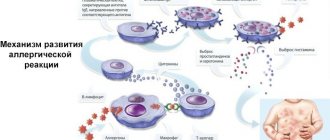
Larvae emerge from parasite eggs 10-12 days after penetration into the intestines. Then they easily pass into the blood vessels and spread throughout the body, reaching the upper respiratory tract and lungs. Dry cough with giardiasis is of an allergic nature, caused by exposure to toxins produced by microorganisms.
Attention! If measures are not taken to treat the disease, chronic forms of pathology may develop, in particular bronchial asthma.
Symptoms of advanced giardiasis often manifest themselves in the form of pronounced signs of general intoxication of the body.
Diagnostics
In order to find worms of the roundworm class in young children, you should undergo a scatological test or a general blood test. It is possible to collect sputum to determine the presence of helminths.
X-ray examination shows the accumulation of parasites in the intestines or their traces of vital activity in the lungs. Therapy is prescribed by the attending physician.
You should not let the disease progress and start treatment on time. Because otherwise, nematodes lead to complications. Their local accumulation leads to damage to internal organs, for example, accumulating in the intestinal tract they gnaw through its walls, leading to peritonitis.
The migration of larvae creates mechanical damage; walking through the vessels, the microbe damages the lungs, liver, and intestines. In addition, the pathogen feeds on all useful substances and microelements, literally sucking them out of the body. While feeding, it throws out the consequences of life activity, poisoning a person. Decomposition products have severe allergic and toxic reactions.
Long-term non-treatment causes asthmatic suffocation, blindness, and obstructive bronchitis. Pneumonia, appendicitis, kidney inflammation, deafness, mental and physical retardation, this is not a complete list of serious diseases.
The child’s body becomes susceptible to infections, it becomes more and more difficult for it to fight, and the immune system weakens. Therefore, it is necessary to remove helminthic infestations as quickly as possible.
Echinococcosis in children
Echinococcus larvae enter the child’s body through contact with sick dogs or through contaminated water. Echinococcosis can develop in any organ - liver, kidneys, heart, brain, lungs, etc.
Cough from worms appears when the lungs are damaged. Invasion of echinococci into the respiratory system leads to the formation of cysts. The growth of the cyst provokes the following symptoms:
- chest pain;
- first dry and then wet cough;
- deformation of the chest (with severe growth of the cyst);
- pneumonia.
To diagnose echinococcosis, blood is taken for analysis (antibody test), sputum, and tomography and x-rays are done.
Treatment
To carry out treatment, the doctor clarifies the phase of the patient’s disease, health status, age, body weight and the presence of contraindications to medications. Anthelmintic drugs are prescribed, they are aimed at destroying and blocking pinworms, and subsequent elimination.
In case of severe infection, immunostimulating and restorative drugs, vitamins, and preparations containing iron are additionally prescribed.
It should be noted that if weak-acting medications are used during therapy, this will lead to invasion upward into the oral cavity and nasopharynx and cause suffocation.
If there is a degree of migration, roundworms should be treated with broad-spectrum anti-nematode medications. Frequently used Levamisole or another name Dekaris, Vermox, Wormin, Thiabendazole. For dosage, the weight of the infected person and the number of helminth colonies are determined.
Mintezol anti-parasitic drug is given 25 milligrams per 1 kg of weight in 3 doses, after eating, for 5 days. In the chronic phase, Medamin or Dekaris.
- The first is calculated at 10 milligrams per 1 kg of body weight in 3 doses for 1 day.
- The second dose of 2.5 mg is divided into three times. Ascariasis in infants is treated with Albendazole.
If the baby has a massive infection with worms, then Wormix cannot be used. It promotes increased activity of harmful agents, causing them to enter the respiratory tract.
Antibiotics and antiparasitic agents also destroy beneficial flora. To restore it and to avoid dysbiosis, medications are prescribed for the gastric microflora.
Tests are taken every week, and a follow-up examination is done a month later. The risk of re-infection during this period is high; weakened immunity picks up worm eggs and re-infection cannot be avoided.
Manifestation of cough due to worms
Coughing due to worms signals that parasites are actively moving and multiplying in the body; urgent measures must be taken. Cough, of course, is an unpleasant and annoying phenomenon, but most often it becomes only a symptom of the disease.
Cough due to worms is most typical for a child’s body and is sometimes mistaken for a cold. In order not to saturate the body with useless drugs, it is necessary to correctly diagnose its cause. This manifestation is a protective reaction of the body to an abnormal process within a person; and all the signs should be seriously analyzed in order to choose a treatment regimen.
The relationship between cough and worms
Despite the apparent incompatibility of the concepts cough and worms, many helminthiases, i.e. Diseases caused by the development of worms have a characteristic symptom of coughing. The manifestation of this symptom is caused by two reasons: the localization of parasites in the lungs (pulmonary form) or the migration of larvae through the respiratory tract.
The most common cause of cough due to worms is the migration of larvae or roundworms through the respiratory tract, especially when they reach the lungs. Being in the bronchi, they interfere with the air flow, to which the body reacts in the form of a dry cough. In this case, a fairly large number of microscopic eggs and larvae come out with the cough, invisible visually, and it seems completely dry, without discharge. Another symptom is an inflammatory process in the tissues of the respiratory vessels, which is caused by small helminths. In this case, the cough may contain products of the inflammatory reaction.
The most serious cough is caused by pulmonary forms of helminthiasis (especially paragonimiasis). This symptom indicates that the worms have settled directly in the lungs and have a direct effect on their functioning.
What types of helminths cause coughing?
Cough can be caused by different types of helminths through one of two mechanisms. Part of the migration of larvae that cause coughing are roundworms and giardia. The main location of worms is the intestines, but during the process of active reproduction, the larvae penetrate the cardiovascular system, migrating along with the blood, seep into the trachea and bronchi, and then into the lungs. Along the way, they vigorously feed on blood components and mucous secretions, releasing back toxins that lead to allergic and inflammatory reactions. Upon reaching the lungs, some of the larvae are removed along with a cough, some fall into a latent state, and some return to the intestines, enriched with nutrients, where they will continue to develop in the form of helminthiasis.
Worms that form pulmonary forms, i.e. The lungs, which have chosen the lungs as their place of development, are very dangerous types of helminths that can cause severe pulmonary diseases. These worms include Toxocara and pulmonary fluke, which are flatworms. Having established themselves on the lung tissues, they cause diseases - toxocariasis and paragonimiasis, which begin to destroy lung cells and disrupt the functioning of the lungs. Diseases begin to manifest themselves in the form of a dry cough; As the blood vessels are damaged, it turns into a cough with sputum, and then with traces of blood.
Cough and roundworms
Cough due to worms in young children is almost always explained by the migration of roundworm larvae during the course of the disease - ascariasis. This parasitic worm is a nematode (roundworm) up to 15 cm long; when a person becomes infected through contact with domestic animals, getting soil particles into the mouth, or consuming dirty vegetables. The disease is more common among children due to the fact that the immune system has not yet fully developed and hygiene is not always observed.
The main development of ascariasis occurs in the intestines, where their active activity disrupts metabolism, depresses the nervous system, and releases toxins that lead to poisoning of the body. Excessive consumption of vitamins and minerals leads to a decrease in immune defense. Against this background, the process of migration of roundworm larvae often reaches the lungs, where a local inflammatory reaction develops.
The clinical picture of the process is manifested by a dry cough. It usually occurs unexpectedly in attacks. As inflammation develops, mucoid sputum begins to appear. If treatment measures are not taken, then the active movement of the larvae leads to mechanical damage to small vessels, which can be expressed in the appearance of blood traces in the secreted sputum. Due to the weakness of the child’s body, such processes can cause respiratory failure. Externally, ascariasis is characterized by pale skin and blue lips.
Cough and paragonimiasis
In older children and adults, a severe cough due to worms may indicate a more serious disease - paragonimiasis, caused by worms such as the lung fluke, which belongs to the class of flukes (flatworms). Having settled in the lung tissues, such a helminth causes inflammation and sclerosis. Eosinophils are concentrated in the infiltrate, and a fibrous membrane is formed around the affected area. The process penetrates the bronchioles, and helminthic eggs, purulent exudate and blood rush there. All this comes out with a cough. The disease is accompanied by bouts of coughing with sputum.
The main carriers of parasites are freshwater crustaceans and crabs. Through water, the infection reaches animals, incl. domestic, and from them it is introduced to humans. Consequently, the main sources of infection are animals and river mud.
Cough and toxocariasis
Another source of cough due to worms is toxocariasis, which is a consequence of the penetration of toxocara (dog roundworms). The disease can appear at any age; especially dangerous for young children. Roundworms up to 18 cm long actively reproduce, the larvae concentrate in the lungs, bronchi and trachea. They cause a severe allergic reaction of the respiratory system, expressed in coughing attacks. The disease is accompanied by fever, whistling breathing, and blurred vision. The process threatens to develop into bronchial asthma.
The main source of infection is too close contact with the dog.
A cough in a person, especially in early childhood, can be caused by worms activated in the body. Such diseases should not be treated by eliminating the cough - it is only a symptom of the disease. Treatment in this case should include antiparasitic drug therapy aimed at destroying and removing worms.
Folk remedies
From the article we learned the symptoms and treatment with medications. Below we will consider the effectiveness of traditional medicine. Let's look at how to remove roundworms with garlic. Peel the vegetable and pour a glass of boiling water. Cook for about 30 minutes. Cool the solution, strain through gauze and administer it internally through an enema. This is done in the evening.
Remember that it is prohibited to give alcohol tinctures with the plant. Alcohol has a negative effect on a fragile body.
Expulsion of nematodes with onions. Onions have disinfectant and bacterial properties. Pass one large onion through a meat grinder. Mix the resulting gruel with honey in a one to one ratio. Take one teaspoon orally, three times a day, until the worms leave the child.
Walnuts help better at the initial stage of the disease. All you need is green walnuts. Pour boiling water and add a little salt.
Let it brew for half an hour. Strain and drink. In total, it is worth including medications with a laxative effect. A large number of pinworms, when removed from the lumen of the stomach, sometimes lead to their accumulation in balls, forming constipation.
Pumpkin seeds help well in the fight against illness. They should simply be eaten raw in unlimited quantities. Before taking, you should consult a specialist.
You cannot use celandine juice, although it is an effective medicine, but it can be difficult to calculate the dose. In addition, it will destroy the worms in the stomach, causing a blockage of the body. It will be difficult to remove them from the liver, lungs, and heart. New biohelminths will breed again.
Preventive measures
It is always better to prevent a disease than to treat its consequences:
- always wash your hands after visiting the street, the toilet and after contact with pets;
- strictly monitor your baby to see if he washes fruits and vegetables before eating;
- does he drink raw water?
- eliminate flies in the house in a timely manner, they are carriers of infection;
- protect the child’s communication with family members who have been diagnosed with a pathological condition;
- Do not give your child medications to prevent helminthiasis;
Compliance with these rules will protect parents from infecting their children with roundworms.