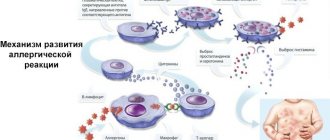
There are many diseases that cause a child’s eyes to fester – conjunctivitis, colds and viral infections (flu, ARVI), allergies, inflammation of the sinuses. The problem is especially common in newborns and infants up to 3 months of age. Ignoring lacrimation, discharge of pus, or negligent attitude to treatment provokes a worsening of the condition.
Pus in the eye signals the presence of a disease and the need for treatment, do not start the process
A child’s eyes are festering - the causes of the problem
In newborns up to one year old, pus is released due to the following reasons. The cause is an underdeveloped tear duct. Later it forms and the pus disappears, but the disease dacryocystitis occurs - a disease considered to be congenital obstruction of the lacrimal canal.
7-8% of babies have dacryocystitis. The ophthalmologist prescribes gentle treatment, which includes massage of the tear duct and instillation of antiseptic drops - Vitabact. And if it doesn’t help, antibiotics are prescribed - Levomycetin, Tobriss, Floxal and rinsing with Furacilin.
Prescribed for 10 days, 3-4 times a day, one drop in each eye. Antiviral tablets Acyclovir are recommended for children aged 2 years.
Doctors do not recommend washing with breast milk; it has favorable microflora for the proliferation of microbes, leading to suppuration. If gentle treatment does not help, a procedure for probing the tear duct in the clinic is prescribed.
Another common disease is conjunctivitis. There are viral, bacterial and allergic.
The main causes of the disease:
- lack of hygiene;
- untreated colds;
- infection during childbirth (inflamed maternal birth canal) or due to inappropriate sterilization of medical instruments,
- an eyelash in a child's eyes;
- viruses - ARVI, measles, herpes, etc.
As a result, conjunctivitis is observed in children aged 3 years and older. Less commonly observed up to 3 years of age. More often, conjunctivitis appears due to viruses and isolation from healthy children is needed.
When pus remains for a long time, maceration occurs - irritation and inflammation of the skin around the eyes. In infants this is very painful and unpleasant.
Most situations with suppuration are not considered dangerous to vision. Bacterial conjunctivitis leaves no consequences, and after a few weeks the disease disappears.
Together with pus from the eyes, the following symptoms are observed:
- redness;
- if you press on the area of the lacrimal sac, white or yellow pus flows;
- crust formation;
- lacrimation;
- redness of the sclera;
- visual impairment;
- lethargy, fatigue, drowsiness;
- fever due to intoxication.
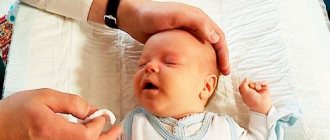
Daily morning toilet for a newborn - eye rinsing
Before starting the baby's morning toilet, the mother should wash her hands cleanly with soap to avoid infection. Before starting a newborn, it is necessary to assess their general condition.
Healthy eyes have clean eyelids, and when the baby blinks, they move without difficulty. If the baby’s eyes still fester, then it is necessary to consult a specialist to rule out any disease, for example, dacryocystitis. After the organs of vision have been examined, you can begin rinsing.
For this you will need:
- cotton pads or balls;
- boiled water, cooled to room temperature;
- gauze napkin.
Once you are armed with the necessary items, start wiping your eyes with a cotton pad or swab dipped in boiled water. The procedure must be done from the outer corner to the inner. After completing the procedure, blot your eyes with a gauze napkin.
Caring for your baby's eyes if there is discharge of pus
If in the first days of life the baby’s eyes fester, then the doctor, while still in the maternity hospital, prescribes eye drops based on antibiotics. Already at home, after discharge from the maternity ward, you can treat purulent eyes with a solution of 2% boric acid. For this, 1 tsp. boric acid is dissolved in a glass of boiled water. It is necessary to properly treat the organs of vision, from ears to nose.
You can replace boric acid with a weak solution of potassium permanganate. The solution becomes slightly pink; the potassium permanganate crystals must completely dissolve, otherwise the baby may get burned. You can also care for the eyes of a newborn with the help of furatsilin. To do this, you need to dissolve one tablet in a glass of boiled water. If a child’s purulent discharge does not go away for a long time when he washes his eyes every day, this may be a signal of the development of a disease such as dacryocystitis.
A fairly common occurrence in newborn babies is purulent discharge that accumulates in the corners of the eye. In this regard, many mothers have a natural question - how to wash their child’s eyes so as not to harm him. First of all, it is worth understanding why a baby may experience such a condition.
In the etiology of eye suppuration in infants, three main reasons can be distinguished:
- Bacterial, infectious or viral conjunctivitis. This condition usually occurs due to bacterial infection of the eyes during passage through the birth canal during childbirth or due to insufficient eye hygiene after birth.
- Dacryocystitis or congenital inflammation of the lacrimal ducts due to their obstruction. It usually occurs due to physiological underdevelopment of the tear ducts, and can go away on its own over time.
- Allergic conjunctivitis, which may be a consequence of exposure to external irritants (dust, animal hair, detergents, etc.).
In any of these conditions, the baby experiences photophobia, excessive lacrimation and the formation of purulent discharge in the corners of the eyes, which are more intense in the morning. If the cause lies in dacryocystitis, then the baby may not experience any discomfort, but with allergic and bacterial forms of conjunctivitis, the baby’s eyes may itch.
Immediately after the baby is born, obstetricians are required to treat the baby’s eyes with special antibacterial solutions. Such measures are needed to prevent bacterial infection of the newborn during the birth canal. After this, caring for the baby’s eyes falls entirely on the shoulders of the new parents.
How to wash the eyes of newborns and how to do it correctly is the topic of our conversation today.
Red eyes in a 2 year old child - what to do
What to do if a child’s eyes fester? The baby probably developed a stye. Barley is an inflammation of the ciliary sac. If purulent discharge appears, this indicates staphylococcus bacteria.
A small grain forms on the inside of the eyelid, the eyes itch and a burning sensation appears, then inflammation appears. If there are problems with the immune system, barley appears often. Redness and suppuration cause conjunctivitis.
When the disease appears:
- photophobia, redness;
- itching;
- feeling of sand.
A distinctive feature of the disease is not only eye damage, but also a runny nose, muscle pain, and inflammation of the lymph nodes. Redness of the sclera indicates the entry of a foreign body, trauma to the mucous membrane, inflammation of the choroid, allergies, and glaucoma. And also, vegetative-vascular dystonia is the cause of redness.
Dacryocystitis also causes redness and purulent discharge. More often the disease appears in infants.
The difference from conjunctivitis is swelling and redness of the conjunctiva, and with moderate pressure on the area where the lacrimal sac is located, pus consisting of leukocytes is formed. The disease affects one eye, rarely two.
If the eye is red and swollen, the eyelids itch and a crust of pus appears on the eyelids, this is blepharitis. It happens with an allergic reaction and fatigue.
The eye is red, swollen and has a runny nose
From anatomy it is known that the nasal cavity and the lacrimal sac are connected by a single duct. Therefore, the disease often affects both the nose and eyes.
This problem occurs in childhood. Redness appears with adenoviral infection, which has clinical forms: conjunctivitis and pharyngoconjunctival fever.
Red eyes and a runny nose are common with the flu. Rhinitis causes redness because the ducts are blocked, which in turn causes inflammation of the nasal mucosa. Whooping cough is also a cause of redness, but the mechanism of action is different. The sclera of the eyes turn red due to pressure on the blood vessels, as well as a long and continuous cough.
A runny nose and red eyes occur with allergic rhinitis. There is a high sensitivity to certain allergens, accompanied by a runny nose and flu.
An inflammatory process occurs in the nasal sinuses and severe discharge from the eyes, as a result of which the eyes become suppurated.
Pus can also form due to blockage of the nasolacrimal duct. For allergic rhinitis, you need to start by eliminating the source of the allergen, and also pay attention to the accompanying symptoms. Anti-inflammatory drugs and anti-allergy medications that can be used at home are needed.
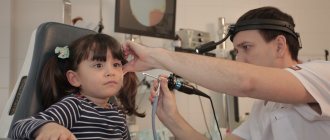
Diagnostic methods
Before proceeding to treatment of the pathological process, it is necessary to accurately establish the cause of its development. To do this, the doctor carries out standard measures, which include establishing the visual acuity and field, examining the fundus, as well as in direct and transmitted light. In addition, the doctor takes a smear from the conjunctival cavity to perform a bacteriological examination. This will allow you to accurately identify the pathogen and correctly design antibacterial therapy.
The problem arose due to a cold
If the baby begins to cough, a runny nose appears and pus comes out of the eyes, the cause is a respiratory infection or a cold. Treatment of the disease is carried out using a comprehensive method aimed at treating the underlying disease and increasing immunity.
When treating colds, drops are not used. When the runny nose stops, the tear ducts are cleared; they can simply be washed.
It is considered normal if tears flow from the inner corner of the eye through the lacrimal duct to the nose. When crying, mucus is released and the nose becomes stuffy.
If something obstructs the flow of tears, stagnation occurs in the tear duct, interfering with the removal of microbes that have entered the eyes. Due to stagnation, inflammation and pus appear.
As the child grows up, such problems go away. To treat your baby at home, you need to remove the pus using sterile cotton wool soaked in a furatsilin solution and instill special drops.
This treatment relieves symptoms, but in order to completely get rid of the cause of purulent discharge, you need to massage the nasolacrimal sac and remove the discharge from the lacrimal ducts. These procedures can be a good help in solving this problem.
If the tear ducts are anatomically narrowed, then doctors first use rational treatment. But, if a runny nose and pus continue for a long time and develop into a chronic disease, then there is a need to restore the patency of the canal surgically.
If a child coughs, has a runny nose and festering eyes, complex treatment is prescribed. To stop nasal discharge, use nasal drops and clear the nasal passages. First you need to clean the nasal cavity, since the drops may not bring the desired effect.
There may be crusts and mucus in the nose, which may prevent the medicine from penetrating further. Before cleansing, infants usually soften their nasal passages with sea water, sold in pharmacies.
Pus indicates inflammation that occurs after a cold. The reason for this may be a weakened immune system, improper treatment or lack thereof. Pus can form in both eyes or in one eye.
Often purulent conjunctivitis is quickly treated and limited to drops, ointments and rinses, but in more advanced forms it is necessary to resort to antibiotics. This disease most often affects children, since all the ducts are short and close to each other. The causative agents of conjunctivitis after a cold are bacteria, viruses and fungi.
Temperature and pus in the eyes
If the baby has pus discharge and also has a fever, this is the first sign of infection. To begin with, the causative agent of the infection is always determined, after which medications are prescribed that eliminate the cause and combat the symptoms.
It happens that after sleep, pus discharge is formed; you should know whether this is a consequence of the activity of the sebaceous glands or purulent exudate.
If you still have discharge with pus, then you should definitely contact a pediatrician, who will determine the cause and prescribe the necessary and timely treatment for the child. Often this is conjunctivitis, accompanied by fever.
Which doctor should I contact?
The child’s eyes began to fester, his eyelids were swollen - urgently show the baby to the doctor. An ophthalmologist deals with similar problems. During the examination, a consultation with an otolaryngologist (for colds, sinusitis, acute respiratory viral infections, influenza), an allergist, and an immunologist is prescribed, which allows you to accurately determine the source of purulent discharge and select effective therapy.
If pus appears in your child's eyes, consult an ophthalmologist
Main causes of swelling
Children's eyes may become swollen:
- Due to allergic reactions to pollen, pet hair, household chemicals, etc.
- For infections.
- Trauma and mechanical damage to the mucous membrane and eyelids.
- Increased intracranial pressure can also have an effect, causing them to become swollen and red. This occurs due to kidney problems and severe fluid retention in the tissues.
- For diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Frequent, prolonged crying.
- Insomnia, including during teething, are also factors affecting the swelling of the eyes.
- Eyes may become swollen and watery due to conjunctivitis, barley, phlegmon, and also due to insect bites.
How to wash your eyes
If a child's eyes become infected, pediatricians recommend rinsing them. It is necessary to moisten a sterile cotton wool with furatsilin and wipe them from the outer corner to the inner. For each eye you need to use a separate cotton swab.
Chamomile decoction helps well, rinse as described above. Pediatricians do not recommend the use of breast milk, as this creates a favorable environment for the proliferation of microorganisms.
Washing should be done every 2 hours. Thorough hand washing is necessary before rinsing.
How to treat pathology at home
How to treat pus in a child's eyes? To begin with, you can rinse your eyes with furatsilin; it must first be dissolved in warm water. Chamomile helps, then drip Albucid drops (usually 10% is used for newborns, and 20% for older children). It is recommended to drip every 2-4 hours.
Use Levomycetin or Vitabact. Some people find it more convenient to use ointments. It is worth trying Tobrex, Erythromycin and Tetracycline ointments.
If no improvement is observed, then treatment should be stopped and see an ophthalmologist, rather than self-treating your child.
The appearance of purulent discharge in any area indicates the body’s active resistance to infection with the help of leukocytes and such a phenomenon cannot be left without attention.
Before treating a child, parents need to consult a doctor. He will select suitable treatment methods. If it is not possible to go to a hospital at your place of residence, you can visit a specialized eye clinic.
According to statistics, purulent discharge from the orbits is more often diagnosed in children and the elderly, since their immunity is weakened. Nature has come up with a unique and optimal organ of vision.
A person receives 80% of information through vision, which in later life affects education and performance. Health must be protected from infancy. Parents who monitor their child help with this.
conclusions
A child’s eye can fester for a variety of reasons. So you can start treatment only after accurately identifying the underlying factor. Parents should regularly monitor the condition of their eyes, perform good hygiene and consult a doctor as soon as the first symptoms are detected.
Also read about what drugs are used to treat allergies in children, and why strabismus occurs in children.
If the baby has red eyes, purulent discharge, swelling of the eyelids, lacrimation, and in the morning he cannot open his eyes because of the eyelids glued together with yellow crusts, then most likely the child has conjunctivitis. In addition to everything, the baby becomes lethargic, restless, often cries and is capricious.
.
Older children complain of blurred vision, a feeling of a foreign body in the eyes, burning and discomfort
. This disease can be caused by viruses, bacteria, colds and allergies.
As a preventative measure, it is necessary to observe the rules of personal hygiene, keep the child’s bed and toys clean, wash hands with soap more often, walk in the fresh air, ventilate the children’s room, avoid contact with sick children and take more vitamins.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine recipes help remove swelling on the eyelids, reduce inflammation and redness, and have an antiseptic and antibacterial effect.
Anti-inflammatory decoction of calendula flowers
Place 1 tbsp in a small enamel container. l. calendula flowers and pour 450 ml of boiling water. Simmer the broth over low heat for 7 minutes, cool, strain. The product is suitable for compresses and rinsing. Do the manipulations 4 times a day, alternating lotions with eye irrigation.
Black tea compresses
Compresses with black tea effectively relieve symptoms of suppuration. Brew 1 tsp in 1/2 cup boiling water. large-leaf black tea (without flavorings, dyes), infuse and pass through 2-3 layers of gauze. Soak cotton pads in the infusion and apply to eyes for 5 minutes. Do the procedure up to 6 times a day.
Series
Place 1 tsp in 200 ml of boiling water. chopped herbs and boil for 3 minutes, let cool. Wash your eyes with the decoction in the morning and evening for 3 days.
Celandine decoction
Wipe your eyes with a decoction of celandine several times a day. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over the crushed flowers and leaves of the plant (1 tsp) and boil in a water bath for 5 minutes. Use the warm, strained decoction to rub the eyes 3 times a day.
Compress with essential oils
Soak a towel in hot water and drop 3-5 drops of lavender, rose and chamomile oil on it. Place the compress on your eyes and keep it until it cools completely. Manipulations are carried out 2 times a day. The product relieves swelling and inflammation, soothes irritated tissues.
Potatoes for inflammation
Potato compresses are an effective anti-inflammatory remedy. Peel 1 potato, grate on a fine grater, place on cheesecloth and place over the eyes. Keep the compresses for 10-15 minutes, then wash the child with calendula decoction or warm boiled water.
Rose hip decoction
Grind the dried rose hips to make 2 tsp. raw materials, pour 400 ml of boiling water and simmer for 10 minutes over low heat. Wash the child’s eyes with the broth up to 5 times a day.
Aloe juice drops
Place drops of aloe juice into your eyes 3 times a day. Grind the aloe leaf, squeeze out the juice, mix with warm water or saline in a 1:1 ratio. Apply 1 drop 3 times a day.
Honey drops
Dilute honey in warm water (1 teaspoon of honey per 3 tablespoons of water). Apply 1-2 drops to eyes three times a day. The product is used for children over 3 years of age.
It is possible to quickly and effectively cure a child at home if the therapy is carried out correctly, alternating rinsing with drops and lotions. The basis of treatment is medications, and traditional methods help enhance their therapeutic effect and alleviate the condition of the little patient.
Prevention
Prevention of conjunctivitis begins in the prenatal sanitation of pregnant women with further treatment and use of drops with antibacterial and antiseptic effects for newborns
Even if the inflammatory process is accompanied by a classic clinical picture, injury to the organ of vision should not be ruled out. There is a high risk of infection of internal structures. In this case, it is necessary to proceed to treatment as quickly as possible.
Prevention involves following simple rules:
- compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- hardening;
- proper nutrition, rich in vitamins and beneficial microelements;
- timely diagnosis and treatment of infectious eye diseases.
Eye ointments for inflammation and redness
Lecrolin eye drops with instructions are described in this article.
Levofloxacin: instructions for use https://eyesdocs.ru/medicinaoperacii/lekarstva/osnovnye-pravila-pri-primenenii-levofloksacina.html
Possible complications and consequences
Incorrect or untimely treatment of pus in the eyes leads to a number of complications:
- Myopia - a child has difficulty seeing objects located at a distance from him.
- Farsightedness is a visual impairment that manifests itself in blurred vision when concentrating on near objects.
- Reduced functioning of the eye glands, which leads to dry eyes.
- Increased intraocular pressure.
Important! The most severe consequence of prolonged purulent processes in the eyes is complete or partial loss of vision.
Yellowish discharge
Yellowish discharge indicates the development of conjunctivitis. At this stage, it is important to correctly determine what type of pathogen (bacteria, viruses, allergic reaction) caused the development of inflammation.
In such a situation, parents notice a large discharge of pus, which forms a thin film on the eye. If there is excessive suppuration, the child’s eyelashes stick together and it becomes difficult to open his eyes. Most often, children suffer from bacterial conjunctivitis, which is very easy to catch from dirty hands.