There are not many products available to everyone that are rich in various microelements, without which a person cannot maintain his health. These include eggs, since they are an extremely necessary product not only for adults, but also for children. It contains a large number of useful microelements that have a beneficial effect on the baby's development, so every parent should know how and when to give an egg to a child. It is useful for children as for growing organisms.
A huge amount of material is devoted to this product, its properties and methods of preparation, but not much good and reliable information can be found about the age at which eggs can be given to babies.
What do newborn testicles look like and what should they look like?
In general, a baby's scrotum looks about the same as an adult's, the only difference being the size. During the initial examination, the neonatologist may notice some structural features. For example, undescendedness of one or both testicles into the scrotum, or cryptorchidism, may be detected. In addition, their size is also increased compared to the norm.
The doctor can also determine the following developmental disorders of the scrotum and testicles:
- a two-chamber scrotum is a manifestation of its incomplete fusion (this phenomenon may also be accompanied by cryptorchidism);
- fusion of the scrotum with the penis;
- dark staining of the scrotum in combination with a greatly enlarged penis (megalopenis) may indicate adrenogenital syndrome (salt-wasting form);
- small size (hypoplasia);
- atrophy;
- lack of one or both testicles at once (anorchism);
- displacement of one or both testicles (ectopia);
- dropsy of the testicles or spermatic cord.
What is the normal state of a baby's testicles?
Normally, both testicles are already in the scrotum. Their sizes vary from six to eleven mm, and the size of the right one may be slightly larger than the left (this is not a pathology, but a variant of the norm). Also, normally the scrotum may be slightly enlarged. Some enlargement and swelling, including in combination with hyperpigmentation, indicates a hormonal crisis (this is also a completely normal phenomenon, it is the child’s body’s response to the removal of maternal estrogens from it).
Is it normal for newborns to have enlarged testicles?
Exceeding the size of the testicles in a newborn compared to the norm can be either a manifestation of pathology or a completely normal phenomenon. For example, the above-mentioned hormonal, or, as it is also called, genital crisis, is not a disease, but a reaction to a change in the child’s hormonal background. In this case, the scrotum increases in size and becomes hyperpigmented, and some swelling of the testicles is detected. You should monitor the baby’s condition in order to eliminate possible problems.
ATTENTION! If this is truly a hormonal crisis, then it will pass without a trace in three weeks. And if this symptom does not disappear within the specified period, then the child should be shown to a doctor.
Testicles can also enlarge due to diseases: hydrocele, or hydrocele. In this case, there is an accumulation of fluid between the testicular membranes.
Ultrasound of the testicles: features of the procedure, preparation, norms and pathologies, interpretation of tests
Ultrasound of the testicles is a very effective procedure that is often performed to diagnose various diseases of the scrotum. This is a simple technique that allows you to get accurate results almost instantly.
Of course, patients are interested in additional information. What can an ultrasound of the testicles show in men? What are the indications for the procedure? How much will such a diagnosis cost? Is the examination dangerous? The answers to these questions are in our article.
Ultrasound of the testicles: the essence of the technique, its advantages and disadvantages
It is no secret that ultrasound today is widely used to diagnose certain diseases. And men are often referred for a procedure that involves examining the scrotal organs using ultrasound equipment.
A special ultrasonic sensor generates pulses that are reflected from the tissues of the human body. The reflected signals are recorded, which makes it possible to determine the density of a particular structure.
This technique has a huge number of advantages. First, let us note that this is a quick, simple and non-invasive procedure. When performed, there is no contact with the patient’s blood, which makes infection impossible.
The examination is painless and harmless, and results can be obtained almost instantly. Equipment for ultrasound examination is usually available in every clinic.
For patients financially, this is a completely affordable procedure.
The technique allows you to examine not only the testicles, but also the vessels and soft tissues of the scrotum. As for the disadvantages, small tumors, abscesses and other structures are not always visible on ultrasound. In any case, in modern medical practice, ultrasound is an integral part of diagnosing almost any disease of internal organs.
When ultrasound is necessary, indications for the procedure
There are a huge number of indications for performing ultrasound of the testicles. In boys and adult men, the procedure helps identify various diseases. The list of indications is worth familiarizing yourself with. Diagnostic manipulation is prescribed in the following situations:
- Male infertility.
- Enlargement of the testicles or their appendages.
- Reduction of the testicles (both on one and both sides).
- Erectile dysfunction and other problems with sexual activity.
- Orchitis, epididymitis and other inflammatory diseases of the scrotal structures (or suspicion of their development).
- Minor hemorrhages and hematomas in the tissues of the scrotum, formed as a result of trauma to the groin area.
- Suspicion of the presence of tumors (both benign and malignant).
- If during the analysis traces of blood were found in the semen samples.
- Enlargement of regional lymph nodes (for example, femoral, inguinal), which may indicate an inflammatory or malignant process in the organs of the scrotum.
- Dilatation of the veins of the spermatic cord.
- Cryptorchidism (a pathological condition in which the testicle, for one reason or another, did not descend into the scrotum, but remained in the abdominal cavity).
- Before performing surgical procedures on the scrotal organs.
- Suspicion of the presence of an indirect inguinal hernia.
- Scrotal swelling.
- To monitor the patient's condition after surgery or therapeutic treatment.
- Boys are prescribed a test if puberty is too late or too early.
Of course, sometimes additional tests are required to make a definitive diagnosis. Therefore, doctors prescribe not only ultrasound. This is normal practice and should not be feared.
Ultrasound of the testicles is a very simple procedure that does not require special preparation. Only standard hygiene procedures immediately before the diagnosis will be sufficient. If we are talking about ultrasound of the testicles in children, then it is worth understanding that the child sometimes needs psychological preparation. It is important to explain to the boy the specifics of the procedure.
Survey methodology
Ultrasound of the testicles is a quick and painless procedure. First, the doctor treats the scrotal tissue with a special conductive gel, after which he moves a high-frequency sensor over the skin. Such manipulations do not cause painful or unpleasant sensations.
The patient lies on his back or side, which depends on which part of the scrotum the specialist needs to examine.
Local anesthesia is required only if palpation of this part of the body is accompanied by sharp pain (this is observed, for example, with testicular torsion, inflammation, severe swelling).
The procedure lasts no longer than 15 – 30 minutes. The results are displayed on the computer monitor. After completing the diagnosis, the specialist draws up a conclusion with which the patient will go to the attending physician.
Interpretation of results, norm and pathology
During the procedure, the doctor pays attention to many physiological characteristics of the male body. What is one of the most important criteria when performing an ultrasound scan in boys? The size of the testicles (testicles) is what the specialist looks at first.
How to decipher the results of the examination? What is the normal size of testicles in boys on ultrasound? In this case, much depends on the age of the patient.
In a child aged 2 to 8 years, the width of the testicles ranges from 0.76 to 0.78 cm, and the length - from 1.48 to 1.53 cm. In boys 8 - 10 years old, this figure is 0.86 - 0.88/1.82 cm.
In children aged 11 - 13 years, the testicular sizes are 1.62/3.09 - 3.12 cm. The testicular sizes among adolescents 14 - 17 years old are 2.05-2.12/3.84-3.96.
After the age of 18, the testicles acquire their final size. The width of the testicles of an adult male is 2.5–3 cm, and the length is 4–6 cm.
What diseases can be identified
What does a testicular ultrasound show? This diagnostic procedure makes it possible to quickly determine the presence of certain problems.
- For example, ultrasound allows you to determine the presence of tumors in the tissues of the scrotum, which on the screen look like small heterogeneous structures. The procedure makes it possible to identify small benign or malignant tumors and begin treatment immediately.
- During the procedure, you can see stones and other concretions and determine their exact location and size.
- The presence of a large amount of free fluid between the membranes of the testicle indicates the development of dropsy. This can also be seen on the screen during the examination.
- The appearance of a homogeneous formation of increased density often indicates the presence of an abscess.
- If there has been an injury, then during an ultrasound the doctor can see the presence of blood and tears in the structures of the scrotum.
- The procedure allows you to diagnose varicocele - a pathology that is accompanied by varicose veins of the spermatic cord.
- During the examination, an inflammatory process can be detected.
Are there any contraindications?
Ultrasound is a procedure that can be performed on patients of any age. There are contraindications to such diagnostics, but they are all temporary.
For example, you should not examine the scrotum using an ultrasound probe if there are open wounds, erosions, ulcers and other damage on the skin tissues of this part of the body. In this case, you must first wait for it to heal.
Temporary contraindications also include the postoperative period. If there are fresh stitches on the skin of the scrotum, then the procedure is prescribed after healing.
Many people are interested in whether such a procedure is dangerous to health. Despite rumors about the dangers of ultrasound radiation, numerous medical studies have shown that this diagnostic technique is absolutely safe, especially when compared with alternative procedures, such as x-rays of the scrotum
Features of the formation and development of testicles in newborns
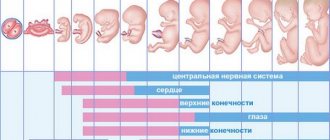
Testicles develop almost at the very beginning of pregnancy due to the fact that the fetal body is formed according to the male type under the influence of male hormones. Initially, the germ cells are the same for both sexes and are associated with the reproductive and urinary ducts. When the gonads begin to form according to the male or female type, either the reproductive (in male embryos) or urinary (in female embryos) ducts develop. From these ducts the organs of the genitourinary system are obtained.
Which eggs to choose for complementary feeding
Many parents do not know whether it is better to give their child quail eggs or chicken eggs? It is difficult to give a definite answer. Pediatricians have not reached a consensus on this matter, but there is no talk of a categorical ban on any of these products.
Chicken eggs provide all the microelements necessary for a baby. Their content in quail eggs is slightly higher, however, the cost of this food product is much higher. Quail eggs are a complementary food approved by a large number of experts due to the lower risks of developing allergies. In addition, children like them because of the size and interesting color of the shell. For those who are interested in how to give quail eggs to children, there is a fairly simple answer: quail eggs for children as complementary foods are introduced according to the same rules as chicken eggs.
Hydrocele of the testicles in newborns: causes and treatment
Hydrocele primarily affects newborns. Hydrocele of the testicle occurs in every sixth baby, and in 85% of them it resolves spontaneously at the age of about one year. Hydrocele that occurs in a newborn is usually physiological, but there are also cases of hydrocele associated with trauma, surgery and some diseases.
The following causes of testicular hydrocele during the newborn period can be identified:
- hormonal imbalances;
- genetic predisposition;
- infectious diseases that the mother suffered from while carrying the baby: rubella, measles, ARVI;
- premature birth of a baby;
- increased pressure inside the abdominal cavity (due to constipation or characteristics of the baby’s nervous system).
Introducing eggs into baby food
Complementary feeding is the addition of foods that are denser than breast milk to your baby's diet. It is recommended to start using any additional products after the baby reaches six months of age. This is explained by the fact that when the baby is six months old, he needs much more nutrients. Mother's milk is no longer able to provide all the substances that are important for his health. Most often, children at this age develop deficiencies of phosphorus, iron and calcium. Since the baby cannot yet take solid food, you need to start introducing some foods into complementary foods.
You need to be careful when it comes to complementary feeding; every parent should know how and when to give their baby this or that product, as well as how its dosage depends on the month of the baby’s life. It is recommended to start feeding eggs at six and a half months. If relatives of an infant are allergic to the product, it is recommended to start egg feeding when the baby is nine months old.
Some experts have a different opinion about when to introduce an egg into a baby's complementary foods. Many of them believe that it is undesirable to give them to children under one year old, since this can provoke allergies.
Unfortunately, not all parents know how to introduce eggs into their baby's complementary foods. You should start with small quantities of the product - approximately the size of a match head. At first, it is better to give children boiled yolks. This allows you to reduce the risk of allergies to almost a minimum. The yolk should be introduced into the baby’s diet by mixing it with breast milk. As a rule, children under one year old are allowed to give yolk no more than three times a week.
Leading children's doctors and scientists have not yet come to a consensus on how many months old children can be given yolk from. However, there are general rules that are suitable in any situation, regardless of the age at which parents decided to start egg feeding:
- the first feeding with yolk should be done after a walk during the daytime feeding;
- it is important to monitor the baby’s reaction to a new product;
- You can reintroduce egg yolk two days after the first complementary feeding.
This table will help parents determine how much yolk is needed for infants at different ages, since eggs should be given to children under one year of age, strictly following the prescribed dosage. It will give them the opportunity to figure out when they can give eggs to their child:
| Baby's age | Amount of yolk (in pieces) |
| 4-6 months | — |
| 7 months | 0,25 |
| 8-12 months | 0,5 |
We give egg whites to young children only after reaching the age of twelve months, when the introduction of the yolk has been successfully completed. You can also give the whole egg after the baby is one year old. From two to three years old, it is possible to feed an omelet several times a week. At one year old, you can give your kids a taste of an omelet or a steamed casserole. These are very favorite dishes among children of all ages.
The first food for babies should consist of a tiny portion of yolk, which increases as the baby gets older. It is not recommended to give the product to four to six month old babies. You can boil whole eggs after reaching twelve months.
Cryptorchidism in children
Cryptorchidism in newborns is characterized by the undescendability of one or two testicles into the scrotum. This developmental pathology is quite common. Most often, the right testicle does not have time to descend in time. For physiological reasons, this phenomenon is usually observed in premature infants.
How and when does testicular descent occur in newborns?
The testicle itself appears in the fourth month of pregnancy from the genital ducts. Then, in the seventh or eighth month, it passes through the inguinal canal, causing the testicles to be said to “descend” into the scrotum (the genital ligaments lag behind the pelvis and corpus in growth, so the testicles appear to “descend”). The physiological meaning of the descent of the testicles into the scrotum from the abdominal cavity is to maintain the temperature required for normal spermatogenesis. In premature babies, the testicles do not have time to descend into the scrotum; this happens after birth. But this can also happen in full-term babies.
False cryptorchidism in children
In this case, the testicle seems to “travel” from the scrotum to the inguinal canal and back, in contrast to the true testicle, when the testicle gets stuck in the inguinal canal. False cryptorchidism is associated with a structural feature of the muscles that raise and lower the testicle. The main difference between false cryptorchidism is its inconsistency: with careful observation, you can notice that the testicle in the scrotum appears and disappears.
Treatment of cryptorchidism in children
Since an undescended testicle is fraught with both impaired spermatogenesis in the future and testicular torsion in the near future, this condition must be treated. Treatment is divided into medication (taking gonadotropin drugs) and surgery (used more often, since the first method has a lot of side effects).
Testicles in newborns
Initially, the laying of the testicles goes into the abdominal cavity, where they develop and form the main structural elements. The development of the testicles occurs in embryos that were equipped with sex chromosomes X and Y. At the same time, the production of hormones responsible for the direction of development of the body along the male path occurs. Of course, this explanation is quite simple and primitive, but the main line is correct and understandable for any reader. Under the influence of dihydrotestosterone, the formation of testicles occurs, as male genital organs and internal secretion organs.
During normal development of the body, the testicles of newborns are already located in the scrotum. Their migration is under the control of male sex hormones, which promote movement along the guide ligament. This process is complex and its correctness is incredibly important. When the system fails, infants' testicles may remain in the abdomen, called cryptorchidism. Subsequently, they may descend into the scrotum, but this is not reliable. Most often, with cryptorchidism, they are underdeveloped and have a huge number of differences with those that normally emerge from the abdominal cavity.
At birth, the child must be examined by a neonatologist and must check for testicular descent in infants. If they are present in the scrotum, you can be calm, but if intrauterine prolapse has not occurred, it is necessary to conduct a series of examinations to find their location, check the condition of the inguinal canal, and predict their future fate. Cryptorchidism may indicate congenital malformations that may be hidden from the naked eye, so instrumental research methods cannot be avoided.
Various problems during migration of the testicles into the scrotum are associated with abnormalities in the development of the child’s body, as well as with diseases of the mother during pregnancy, especially infectious ones, since many viruses and bacteria have a teratogenic effect or are simply tropic to certain types of biological tissues. Normal testicular descent occurs in most cases, but testicular hydrocele in newborns and children of the first three years of life, cryptorchidism, when the testicles remain in the abdominal cavity, testicular trauma, etc. are also common. All these situations require an individual approach and unique solution methods from conservative to operational.
Testicular aplasia in infants and its treatment
This is the absence of one or both testicles in the scrotum due to their immaturity. A unilateral version of this developmental pathology is more common. The occurrence of this phenomenon can be facilitated by exposure to alcohol, drugs, electromagnetic radiation, infections and metabolic diseases in the mother during pregnancy. A gene mutation may also be to blame.
Since the lack of one or both testicles subsequently leads to a lack of testosterone, which affects the development of the body, hormone replacement therapy is carried out starting from adolescence. Also in adulthood, it is possible to have a silicone implant sewn into the scrotum (cosmetic surgery).
Rash on the testicles of a baby
The most common cause of the rash is diaper dermatitis or diaper rash. This is due to wrapping the child too tightly, causing him to sweat excessively and a rash to appear on the skin. The groin area is most susceptible to diaper rash because:
- the baby spends most of the time in a diaper;
- the skin of the groin is constantly in contact with the child’s urine and feces.
To avoid diaper rash, it is necessary to wash the baby more often (at least once every three hours), change the diaper, give the baby the opportunity to ventilate (without a diaper), and use an individually suitable diaper cream.
ATTENTION! If cream has already been applied to the child’s skin, then under no circumstances should powder be applied! This will lead to injury to the baby's delicate skin.
A rash can be a manifestation not only of diaper rash, but also of various infections: fungal (which is often after treatment with antibiotics) or bacterial. In these cases, you need to show the baby to the doctor.
Cooking rules
Any baby food, and especially complementary foods for infants, should be prepared exclusively in accordance with established rules, since the baby’s body is more susceptible to poisoning, diseases and allergic reactions.
To fully understand how to give an egg to a child, you need to know how to properly prepare this product. Not everyone knows how to cook eggs in such a way as to avoid the risk of developing any diseases caused by insufficient heat treatment.
It takes about 10 minutes to boil chicken eggs for babies. You should not overcook them; you must strictly adhere to the recommended cooking time. Almost all people are familiar with boiling chicken eggs. But how long should you cook quail eggs for a child? They are good because they cook faster: the cooking time is only two to three minutes.
For those who didn’t know how to boil quail eggs, the answer is simple - just like chicken eggs, but only for a few minutes.
Inguinal hernia of newborns
This is a dangerous disease characterized by the release of internal organs (intestinal loops, parts of the omentum) through the inguinal canal. This occurs due to weak connective tissue in the abdominal wall (usually due to a genetic predisposition). This phenomenon in infants is congenital. In boys, an inguinal hernia occurs as a result of delayed descent of the testicles into the scrotum during fetal development.
The main danger of this disease is the possibility of strangulation of the contents of the inguinal ring with subsequent necrosis. Treatment is predominantly surgical, but in premature and weakened children it is also possible to use medication (use of promedol, atropine, putting on a bandage).
Testicular torsion in newborn boys
This phenomenon is dangerous due to strangulation of testicular tissues with their subsequent death (necrotization). Hemorrhage is also possible. In infants, fortunately, this pathology is quite rare. However, if such a condition occurs, then prompt surgery is required.
ATTENTION! Under no circumstances should you carry out any independent treatment actions! If torsion is suspected (blueness of the scrotum, enlargement, the child reacts sharply to touch, intoxication is evident: vomiting, diarrhea, pallor), it is necessary to take the child to a specialist within six hours.
How to do an ultrasound of the testicles in men and boys: norm and pathology
Ultrasound diagnostics of the testicles is one of the modern methods that allows you to obtain all the information about the scrotum and its organs, which include the testicles. Ultrasound of the testicles in men makes it possible to make a diagnosis that is 99 percent accurate.
Anatomy of the testicles
The testicle is a male organ that has an oval shape. This glandular organ is fixed using a special spermatic cord. The testicle consists of a head, body and tail. Human anatomy is designed in such a way that the left testicle is located slightly lower than the right one. The scrotum has a very rich blood supply.
When is it prescribed?
There can be a huge number of prescriptions for ultrasound:
- if tumors are suspected;
- in inflammatory processes;
- agenesis (a condition where one or both testicles are missing);
- when the size of regional lymph nodes changes;
- infertility;
- when a palpable neoplasm occurs in the testicle;
- if necessary, control over dynamics;
- during a biopsy;
- in case of changes in the size and shape of the testicle;
- atrophy and hypotrophy;
- pain in the scrotum area;
- in case of testicular disorders as a result of torsion of the spermatic cord;
- for scrotal injuries.
For boys
There are several options in which children are prescribed an ultrasound of the testicles:
- untimely psycho-emotional maturation;
- weight problems;
- if you are too short or too tall;
Echodensity of the testicles in childhood is acquired at the onset of puberty. It is worth noting that it occurs in all boys at different times due to various genetic factors, ecology, as well as proper nutrition and possible pathologies .
1. When is an ultrasound of the scrotum performed?
What does the diagnosis show?
- what size are the testicles (normal, enlarged or, on the contrary, reduced);
- what sizes are the appendages and their heads;
- contours (smooth, blurred or not);
- testing tissues for echogenicity;
- assessment of new formations (their size and density);
- presence of free liquid, its volume;
- characteristics of symmetry and vascular pattern.
also used for diagnosis in some cases . The need for it arises:
- with varicose veins (varicocele);
- for various injuries;
- if there is a suspicion of torsion of the spermatic canal;
- for tumors.
Preparation
Before starting an ultrasound, a number of hygienic procedures of the genital organs are first carried out. For ultrasound, you need to prepare a disposable diaper and napkins.
Reference! Since a special gel is used during ultrasound, in order to avoid unpleasant sensations, it is best to shave the area that will be examined before the procedure.
But if a procedure for examining the prostate gland directly through the rectum is planned, the patient must adhere to certain rules.
How do they do it?
Ultrasound of the scrotum and its organs is carried out (like ultrasound of the penis) in several stages:
- The patient exposes part of the torso below.
- Lies down.
- A gel is applied to his skin, which improves the sliding of the sensor over the surface and prevents air from entering, as it can affect the reliability of the research results.
A patient can experience pain during an ultrasound scan only if he has diseases of the testicles and appendages that are inflammatory in nature.
Important! In most cases, with orchiepididymitis, the ultrasound procedure is postponed for a certain period until the inflammation disappears.
If the patient experiences pain during ultrasound, local anesthesia is prescribed.
The ultrasound specialist sequentially examines first one testicle and only then the other. It is mandatory to assess the size and structure.
Standard results
In normal condition, the testicles have smooth and clear contours.
Homogeneous parenchyma is observed.
Gray fluid may be present, but only in small quantities.
It is considered normal if only the head of the epididymis is visible.
Men's sizes
Based on the results of ultrasound, the average sizes of testicles in men have been established:
Average readings:
- 4 or 5 cm long;
- wide from 3 to 3.5 cm;
- thickness from 2 to 2.5 cm.
Sizes for boys depending on age
When performing ultrasound in children, echogenicity is usually reduced, and in men it has an average value .
Pathologies
Thanks to ultrasound examination, it has become possible to diagnose many pathologies of the scrotum and its organs. What does ultrasound show in case of abnormal testicular conditions?
Cryptorchidism
In the presence of this pathology, ultrasound is prescribed for more detailed information about the “disappeared” testicle.
Cryptorchidism is a deviation from the normal location, as a result of which the male sex gland is present, but for some reason did not manage to leave the abdominal cavity in time.
In most cases (90%) the testicle that was “lost” is located in the groin canal.
A testicle that is not located correctly has a smaller size, a heterogeneous structure, and its appendages, as a rule, are not visible.
Varicocele
Varicose veins in the seminal canal in men require immediate treatment, as they can cause infertility.
With varicocele, ultrasound clearly shows veins that are dilated and slightly changed in appearance, and their diameter exceeds 3 mm.
There are several stages of varicose veins:
- First. Veins are visualized only when the pressure is elevated or when the examination is performed in an upright position.
- Second. Veins that have changed their appearance do not disappear even in a horizontal position.
- Third. Veins are visualized in the area located below the testicle, which has decreased in size.
Hydrocele
If this pathology occurs, fluid accumulates in the area located between the two layers of the testicular membrane.
As a result of ultrasound, it is easy to diagnose the fluid that has accumulated between the membranes.
Cystic neoplasms
Spermatocele or, in other words, seminal cysts can be congenital or acquired. With a congenital cyst, its small size is observed, and the fluid inside it has a transparent appearance.
Reference! Acquired cysts are formed as a result of inflammatory processes or injuries, which result in blockage of the duct.
Based on the results of the ultrasound, you can notice that the cyst has a round shape, a clear and even contour, as well as an anechoic structure.
Orchitis and epididymitis orchitis
These anomalies arise as a result of tissue damage by microbes due to reduced immunity. On ultrasound, the epididymis has an increased size, reduced echogenicity and a heterogeneous structure.
The male gonad greatly increases in volume , and its echogenicity decreases. Very often this anomaly is associated with reactive dropsy.
Chronic orchiepididymitis
The testicle has any size, heterogeneous structure and uneven contours. The appendage is visible, which is slightly enlarged. In the case of such an anomaly, differential diagnosis is prescribed.
Tuberculosis
On an ultrasound, tuberculosis can be determined by the inflamed epididymis, but the specialist still pays attention to other factors during the procedure. With tuberculosis of the testicle and its appendages, a process occurs in both directions and salts accumulate.
Oncological processes
Like any tumors in other organs and parts of the body, oncological formations in the testicles, of course, require urgent study and further treatment. Persistent discomfort and the feeling that there is a tumor are sufficient reasons to visit a doctor. Based on the results of the ultrasound, it will be clear whether a visit to an oncologist is needed.
Seminoma
It is very rare to find testicular cancer, and basically in 95% of cases these are tumors that arise inside the womb. Taking into account the structure of seminoma, homogeneous and non-homogeneous structures are distinguished.
Pathological neoplasms are mainly found in the right testicle. Tumors on both sides at once are very rare (up to 3 cases out of 100).
On ultrasound, the tumor has an irregular shape and in some cases consists of several formations with a heterogeneous structure. The diseased testicle has a size slightly deviated from the norm.
If testicular cancer is suspected, a study of the retroperitoneal zone is performed . A biopsy is also required.
Abscess
The testicle has the appearance of a localized formation with clear contours.
Torsion
This is an abnormal condition in which the testicle has rotated around a vertical or horizontal axis. As a result, blood vessels and/or nerves may be compressed, which often leads to the development of ischemia and suppression of gland function or even necrosis.
Microliths
One of the pathologies during examination of the testicles is small calcifications. They are of the nature of a primary process; the cause of their appearance has not been sufficiently studied. Calcification can be diagnosed in conjunction with cancer, tuberculosis, or problems with metabolic processes.
Contraindications
There are no contraindications that could interfere with an ultrasound scan. The only exception may be a scrotal injury.
Cost and where to do it?
The cost of the study is 900 rubles, and the use of Doppler is 1500 rubles. Patients who have already had ultrasound scans share only positive reviews.
Conclusion
Ultrasound of the testicles is one of the most reliable research methods used in urology; it is highly accurate and low cost.
Source: https://MediGid.com/uzi/organy/malyj-taz/muzhchiny/yaichki.html
Testicular swelling in newborns
A slight swelling after birth is quite physiological: these are manifestations of a hormonal crisis in a baby. But with significant swelling or pronounced asymmetry of the testicles, examination and consultation with a specialist is necessary, since this may be a sign, for example, of the above-mentioned torsion.
The condition of the testicles in newborn boys is an important indicator of health and developmental sufficiency. It is necessary to pay special attention to this area, since the groin area is subject to many influences: the baby spends most of the time in a diaper, and the baby’s urine and feces are almost constantly in contact with the skin in this area. It is very important to maintain the necessary hygiene and optimal temperature conditions: this is the key to the reproductive efficiency of a man’s health in the future.