Emergency conditions
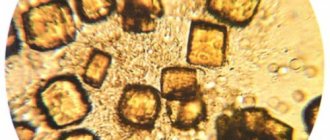
The human body consists of 80% liquid; it consists of water with substances dissolved in it, including salts. Under certain conditions, these components turn into crystals. Amorphous crystals often appear in the urine - this is a structureless salt that is removed from the body in urine. The term “amorphous” means that these formations do not have an exact structure; when there is a large accumulation of salts, they are held together and this is how crystals are obtained. As a rule, these formations do not lead to urolithiasis, but such cases sometimes occur. It is important to consider the causes and treatments for this disease.
Causes
The condition when phosphates are present in a child's urine is called phosphaturia.
The condition when phosphates are present in a child's urine is called phosphaturia. A small amount of phosphate salts in the urine (1-2 pluses opposite this indicator) is a physiological condition and is considered normal, and therefore does not cause any concern to doctors. But if this indicator is 3-4 pluses, then this is a reason for a more detailed examination of the child.
Important: the most common cause of phosphaturia in children is an improper, unbalanced diet and inappropriate drinking regimen. Salts will be found in the urine if you eat foods that contain excess phosphates. There are many of them in sausages and sweet soda.
This condition can occur if the baby eats too many salty and fatty foods, too much milk and fermented milk products, and often drinks sweet carbonated drinks (especially Coca-Cola, since it contains phosphoric acid). Phosphaturia can also occur in children who do not drink enough fluids.
Phosphates in the urine of a child under 7 years of age are more often found in the form of amorphous crystals, that is, compounds that do not form stones, but precipitate. Because of this, the urine becomes cloudy. In most children, such phosphate salts are present in the urine due to poor metabolic processes. As a rule, phosphate crystals appear in urine after eating large amounts of milk and fermented milk products.
However, if phosphaturia is constantly present in the baby, that is, crystals are found in the urine regularly, and the child has signs of rickets, then the pediatrician will diagnose phosphate diabetes. To cure this disease, the baby is prescribed a special diet, phosphorus-containing drugs, as well as vitamins D. At the same time, to monitor the baby’s condition and assess the effectiveness of treatment, a urine test is done every week.
If phosphates are found in large quantities in infants, the reason lies in the following:
Causes of urate formation in urine in children and pregnant women
- malnutrition of the baby;
- improper nutrition of a nursing mother;
- pathological processes in the child’s kidneys;
- metabolic disorders associated with calcium and phosphorus.
Phosphates in urine are the result of excessive alkalization of urine. The following products are responsible for the formation of an alkaline environment in the body:
- seafood;
- fish;
- caviar;
- milk;
- cereals (buckwheat, pearl barley, oatmeal);
- dairy products;
- alkaline mineral waters;
- eggs.
Phosphates in large quantities
If they are found in children in a volume exceeding the norm - more than 2 units, this phenomenon is called phosphaturia or an excess of amorphous phosphates in the body. When their content in urine increases, it becomes cloudy, and a sediment is observed , in which shapeless salt crystals can be seen.
It is possible to confirm that it is phosphates that cause such a reaction only through testing. When they are found in the urine in large quantities, this is not always a sign of a specific disease. Usually this is just a signal that you need to pay attention to the baby’s menu. To obtain more accurate results and eliminate errors, it is better to take a urine sample again.
Diagnostics
To detect phosphates, it is enough to conduct a routine urine test.
To detect phosphates, it is enough to conduct a routine urine test. However, sometimes test results can be inaccurate or false positive. To avoid this, you need to properly prepare for the analysis:
- A couple of days before the analysis, there is no need to make any sudden changes in the child’s diet or introduce new foods. The baby should eat the food to which he is accustomed.
- Morning urine is collected for analysis. To collect urine, it is better to purchase a sterile pharmacy container. For analysis, take an average portion of urine, that is, the first and last part of the stream should not fall into the test container.
- Before collecting urine, the child should be thoroughly washed without using detergents, gels or soap.
- The collected urine must be taken to the laboratory within two hours from the moment of collection.
Decoding
A doctor may suspect phosphaturia not only from a urine test, but also when an atypical sediment is detected in the urine.
In a urine test, several pluses are usually given in front of the salt indicator. They talk about salt concentration. Two “+” are considered normal. A greater number of pluses indicates either a pathological process or poor nutrition. To eliminate the possibility of error and obtain reliable data, it is recommended to take a urine test again.
So, if in the baby’s urine analysis there are more than two pluses opposite salts, then this indicates the following:
- Unbalanced nutrition of the child and a shift in urine acidity to the alkaline side. This means that foods with a high alkaline level predominate in the child’s diet. They contribute to the alkalization of the entire body and urine. In addition, the cause of this condition may be overeating or eating too high-calorie foods.
- This indicator in urine tests may indicate the presence of a number of concomitant diseases - cystitis, Fanconi syndrome, inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract, increased activity of the parathyroid glands. In addition, this is observed during a feverish state, after gastric lavage, and vomiting.
A doctor may suspect phosphaturia not only from a urine test, but also when an atypical sediment is detected in the urine. If, during the study, the acidity of the urine is no more than 7 units, then the specialist can accurately say that the concentration of phosphates is exceeded.
To obtain more accurate data, the baby will be prescribed a detailed urine test for the concentration of phosphate salts. To obtain a reliable result, several days before collecting urine, you need to try to ensure that the baby does not receive unnecessary physical activity. Also, the child does not need to be fed salty, spicy and smoked foods.
Amorphous phosphate crystals
Phosphorus is one of the vital elements in the body. In an alkaline environment, it combines with calcium ions, after which phosphates are formed. It is in this form that the substance takes part in the life of the body. Phosphates can be found in bone, muscle cells, and brain matter. With the participation of phosphorus, contraction of all muscles, including heart muscles, and protein synthesis occur.
The normal ratio of calcium to phosphorus is 2:1. When the content of the second substance increases, calcium is washed out of the bone tissue. To balance the ratio, the body removes some of the phosphorus through the urinary system.
The elements organize until they create amorphous phosphates. This definition applies only to shapeless compounds that do not have a clear structure.
The presence of phosphates in urine analysis is clinically called phosphaturia.
Treatment
Treatment is usually complex, that is, in addition to drug therapy, a diet and proper drinking regimen are prescribed.
If the reason for the appearance of phosphate salts in the urine lies in some disease, then the main treatment is aimed at combating this disease. Moreover, treatment is usually carried out comprehensively, that is, in addition to drug therapy, a diet and proper drinking regimen are prescribed. To monitor the effectiveness of treatment and the baby’s condition, urine tests are constantly performed.
Enlargement of the renal pelvis in a child: symptoms and diagnosis
If the cause of phosphaturia is vomiting, then this indicator in urine tests will normalize by itself after the baby’s body recovers from vomiting. If vomiting occurs for minor reasons, then no treatment is needed, everything will go away on its own. If vomiting is caused by any disease, then it must be treated.
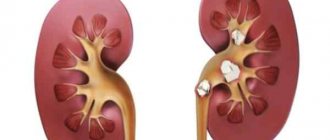
Attention: if phosphaturia is not treated and diet is not adjusted, then over time this condition can lead to the deposition of kidney stones.
What are the reasons for deviations from the norm?
Most often, phosphaturia occurs after a disturbance in the water balance in the body. Fluid loss can be natural - as a result of increased sweat production in the hot season, or it can be associated with pathological conditions - diarrhea, vomiting.
In addition to the above physiological reasons, there are also factors related to diseases. This applies to renal failure and fever due to infectious diseases.
Lack of vitamin D is dangerous at an early age , which can cause rickets. To determine what actually affects the test results, just contact your pediatrician and consult with him about the baby’s health condition.
Diet food
Since children, due to their taste preferences, often eat incorrectly, it is important to adjust the baby’s diet.
Since children, due to their taste preferences, often eat incorrectly, it is important to adjust the baby’s diet. For this condition, dietary table No. 14 is recommended. It is used specifically for phosphaturia.
It is recommended to give the child food in small portions five to six times a day. There should be a minimum amount of fat. It is also important to adjust your drinking regime. The baby should drink at least 1 liter of clean, still water a day. In this case, you need to stop using alkaline mineral waters. It is better to drink sour citrus juices, berry fruit drinks, tea with lemon.
The child is allowed to feed the following foods:
- Lean fish, meat and poultry. It is better to boil, steam or bake meat.
- The soup is prepared in low-fat broth; only permitted vegetables and fruits can be added to it.
- Cereal porridge.
- Vegetables allowed are legumes and potatoes. You can eat pumpkin, zucchini and cucumbers.
- Of the fruits and berries, you can only eat those that contain a significant amount of fruit acids - strawberries, raspberries, plums, apples, grapes, citrus fruits, kiwi, cranberries, currants, strawberries, blueberries and lingonberries.
- You can drink weak tea with a slice of lemon, sour mineral water, citrus juices and other juices from sour fruits, as well as berry fruit drinks and compotes.
The following foods should be completely excluded from the diet:
- Any kind of weakness.
- Fresh baked goods and confectionery products.
- All marinated, salted, pickled and smoked products.
- Canned fish.
- Vegetable and animal fats.
- Milk and dairy products.
- Cocoa and other drinks based on it.
- Any fried foods, as well as anything deep-fried.
- Products with a high content of dyes, preservatives, stabilizers and other chemicals.
There is no need to follow the diet for too long, so as not to excessively increase the acidity of the urine. As a rule, dietary table No. 14 is followed until the acidity of urine returns to normal. This can be understood from urine tests. In the future, the doctor will help you correctly adjust the baby’s usual diet so that there are no problems with phosphates in the future.
Prevention
To prevent phosphaturia in your baby, you should not feed him spicy, salty and smoked foods. Every day a child should drink at least 1.5 liters of water, and in the summer when it’s hot, this norm can even be increased. If phosphates appear in the urine again, you can drink diuretic herbal teas. Urine tests need to be repeated periodically to make sure everything is normal. The baby should be protected from hypothermia and if there is any pain in the lumbar region, immediately consult a doctor so as not to miss the onset of urolithiasis.
Possible consequences
If measures are not taken to eliminate even moderate phosphaturia, serious kidney complications can occur. This primarily concerns urolithiasis. Children and the elderly are thought to be most susceptible to stone formation. In a child, this is due to the immaturity of the urinary system and the inability to completely filter urine.
Kidney stones lead to the development of chronic pyelonephritis and loss of function of these organs. The end result of advanced disease can be kidney failure.