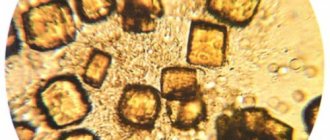
What are kidney salts?
As mentioned earlier, salt crystals cannot be detected by ultrasound, but their presence in the organs of the urinary system is confirmed by a general urine test. One-time changes in the analysis are not a cause for concern. However, the regular appearance of crystals in the urinary sediment indicates a metabolic disorder due to congenital or acquired kidney diseases.
Trace elements and minerals are normally present in the human body and are a building element for cells and tissues, and take part in the synthesis of hormones and maintaining homeostasis. When their intake is excessive or their excretion is impaired, they begin to be deposited in the tubules of the kidneys and filtered along with the urine.
With an excess of oxalic acid salts, calcium oxalates are deposited, calcium phosphates are obtained as a result of increased phosphate content, and a high concentration of uric acid contributes to the accumulation of urates. There are also mixed nephropathies - oxalate-phosphate or oxalate-urate.
Diet and medications for oxalates in the urine of a child
Oxalates in a child’s urine indicate possible diseases of internal organs or poor nutrition.
The cause is oxalic acid, the salts of which can accumulate in the body and be deposited in the form of sand and stones, causing urolithiasis and kidney failure.
Drugs
The following drugs are used in treatment :
- Membrane stabilizers - prevent the accumulation of calcium salts in cells and stimulate their excretion (vitamin A, vitamin E, Dimephosphone).
- Xidifon - regulates the level of calcium in the body and prevents the deposition of oxalates.
- Enterosorbents – promote the removal of oxalates from the intestines (Enterosgel, activated carbon, Smecta).
- Probiotics – have a beneficial effect on the intestinal microflora and normalize metabolism.
Diet
Nutrition is one of the most important elements in the treatment of oxaluria.
To begin with, you should give your child plenty of fluids to speed up the elimination of salts. Then you should exclude the following foods from your diet :
- sorrel;
- spinach;
- rhubarb;
- cocoa and chocolate;
- figs;
- smoked meats;
- spicy food;
- salt and salty foods;
- marinades;
- products containing gelatin;
- fatty soups and broths.
Foods high in vitamin B6 contribute to the elimination of oxalates , so they must be included in the child’s diet:
- seaweed;
- prunes (dried fruit);
- buckwheat;
- millet;
- pearl barley;
- oatmeal.
You should eat the following foods in moderation :
- potato;
- carrot;
- tomatoes;
- beet;
- garlic;
- onion;
- plums;
- currant;
- blueberry.
To obtain protein foods from your body, it is recommended to consume lean meats and fish. It is better to cook food boiled, then you can lightly fry it. It is allowed to stew food, but you still need to boil it first. This is necessary to reduce the formation of purine compounds in products.
In this case, you should eat little by little, but often (6-8 times a day). Small portions of food are digested faster and do not overload the body. Meals should be accompanied by plenty of drinking 30-40 minutes after the meal. To do this, it is best to use the following drinks :
- dried fruit compotes;
- Birch juice;
- herbal decoction (corn silk or dill);
- fresh fruit or vegetable juices;
- filtered and boiled water;
- special dietary water for children in bottles.
Oxalates in a child’s urine are a dangerous phenomenon. This may be a symptom of a serious illness , so it is necessary to carefully examine and treat the disease. If measures are not taken in time, there is a risk of disruption of the functioning of internal organs, and in the most severe cases, death is possible.
Find out from Elena Malysheva what products form urates and oxalates in urine:
Source: https://opochke.com/mochevyvedenie/analiz-mochi/oksalaty-u-rebenka.html
Causes of salt deposition in the kidneys in children
Dysmetabolic nephropathy refers to a group of diseases that are characterized by excessive deposition of salt crystals in the kidneys, followed by their damage and the formation of stones. Depending on the causative factor, secondary and primary nephropathies are distinguished.
The main causes of salts in the kidneys in children on ultrasound:
- multiple or combined bone fractures;
- cystic dysplasia (“spongy kidney”), renal tubulopathy;
- hypervitaminosis D, inadequately long-term use of diuretics;
- long-term hormonal therapy (for systemic diseases, adrenogenital syndrome);
- hyperfunction of the thyroid or parathyroid glands;
- sarcoidosis, amyloidosis;
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the urinary system.
Uncontrolled or long-term use of salicylates and cytostatics can also lead to the formation of metabolic nephropathy. In addition, the cause of the disease can be an unbalanced diet.
In some cases, dysmetabolic nephropathy is a complication of chronic hemolytic anemia, erythremia, glomerulonephritis, Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis.
Drinking regime and diet
During drug therapy, as well as in the period after treatment, the patient must adhere to a certain diet and drink plenty of fluids. Salt consumption should be limited, or better yet eliminated altogether. During treatment, women and men should completely avoid fruits and vegetables containing oxalic acid.
More on the topic: Why does the bladder feel like it’s not completely emptying?
Preference is given to those products that contain a lot of vitamins B1 and B6, as well as magnesium. The norm for one dose is about 100 grams of fish or lean meat. The norm for water per day is about one and a half liters. This advice is not given in vain; such an amount will effectively remove salts from the body. Experts recommend drinking a glass of clean water at night, before bed, to reduce the concentration of morning urine and not treat excess salts in the future.
Urates in urine
Symptoms and signs
For some time, the pathology may be asymptomatic or be a transient phenomenon against the background of some infectious-inflammatory process (acute intestinal infection, acute tonsillitis, etc.). In most cases, excess salt excretion is detected during a routine urinalysis.
If the release of oxalates, urates or phosphates is a complication of the underlying kidney disease, then the following symptoms may appear:
- Increased blood pressure. The kidneys have a renin-angiotensin system, which also regulates the level of systemic pressure.
- The appearance of edema. Against the background of chronic pathology of the urinary system, in addition to crystals, blood cells and proteins penetrate through the glomeruli. Increased loss of protein fractions contributes to a decrease in oncotic pressure and the appearance of external edema.
- Weakness, increased fatigue, loss of appetite. Violation of the detoxification function of the kidneys leads to the development of intoxication.
In childhood, dysmetabolic nephropathies can manifest as spastic pain in the lateral abdomen, lower back, increased sweating, and urination problems (pain, frequent urge). Nonspecific symptoms include headache, dry skin, and discomfort in the heart area.
If a child has excessive deposition of salt crystals in the kidneys, the urine collected for analysis will have a whitish sediment visible to the eye. Also characterized by a lack of transparency and a standard straw-yellow color.
Methods for diagnosing salt deposits in the kidneys
The diagnostic and treatment plan depends on the complaints and the expected diagnosis. The following tests can be used to detect and confirm crystalluria:
- general urine analysis;
- biochemical blood test (to identify excess trace elements);
- urine analysis according to Zimnitsky, Sulkovich;
- laboratory determination of the anti-crystal-forming ability of urine;
- Ultrasound scanning of the kidneys and bladder.
A single detection of uric acid or phosphate crystals is not a basis for making a diagnosis of dysmetabolic nephropathy. It is important to keep in mind that the excretion of salts in the urine in childhood may be a transient condition, completely unrelated to metabolic disorders.
If crystalluria is detected in several consecutive analyzes of urinary sediment, then a biochemical study of urine is performed. Large laboratories are able to test for calciphylaxis and peroxide formation in urine.
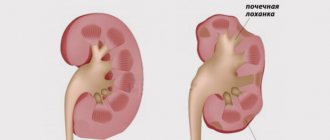
How are salts in the kidneys diagnosed by ultrasound in a child?
Ultrasound examination is considered a dubious method for diagnosing crystals in the kidneys. The eye of a sonologist is able to detect stones whose size exceeds 3-4 mm. Hyperechoic (dense) stones with an acoustic track are visualized with great success.
Nonspecific signs of salts in the kidneys of a child on ultrasound include:
- moderate increase in echogenicity of the renal parenchyma (normally it is equal to or slightly lower than the liver parenchyma);
- determination of hyperechoic linear inclusions in the sinuses of both kidneys (however, in most cases these are the walls of small blood vessels when scanning them transversely);
- disturbance of urodynamics (pathological expansion of the lower or upper segments of the ureters, renal pelvis and/or calyces);
- a symptom of “white pyramids”, which most often serves as a sign of nephrocalcinosis or such hereditary syndromes as “spongy kidney”, tubulopathy, etc.
A true stone is hyperechoic (bright white), round or oval in shape, has a dense structure and a “track” symptom. The last sign depends on the size and chemical composition of the stones, and in some cases it may be absent. Thus, small cholesterol stones may not manifest themselves at all for a long time and may not be detected on ultrasound.
Dysmetabolic nephropathy is a complex disease that is associated with metabolic disorders. One of its manifestations is the constant appearance of a large number of salt crystals in the urine. The treatment plan may include drug treatment of the underlying disease, normalization of the water regime and diet, depending on the type of metabolic disorder and urine pH.
Salt diathesis: features of pathology and treatment methods
Kidney salts are present in the body of every person. But the deviation of their number from normal indicators, both to a lesser and more extent, is considered a pathology.
There are many reasons for the formation of excess or lack of salt, for example, increased acidity of urine. Gradually accumulating in the pelvis, unable to leave the body naturally in time, they form stones.
The disease salt diathesis is diagnosed not only in adult patients, but also in children.
What is this?
The formation of salts in paired organs is essentially urolithiasis. For a number of reasons, salt formations can lead to serious consequences, for example, kidney failure.
In most cases, the dangerous condition is asymptomatic, and it is almost impossible to suspect a disorder in the early stages.
The disease is diagnosed accidentally while undergoing tests for other health problems.
Symptoms become more pronounced at later stages, when the risk of complications is high. A person often turns to a nephrologist too late, when salt crystals have already begun to form kidney stones.
General information
Various chemical elements, including salts, are regularly deposited inside the kidneys. But it happens that their concentration is too high, and there is not enough liquid to dissolve them.
If such a process becomes permanent, this leads to their accumulation and the formation of sand or large stones in the kidney cavity. Salts do not cause discomfort to the patient until they form into stones or sand, causing urolithiasis.
Inflammation appears, which, in turn, leads to the development of kidney failure.
Main reasons
Salt deposits most often form as a result of poor diet or lack of fluid. Some foods, such as sour or salty foods, as well as large amounts of mineral water and vitamin C, can cause problems.
A previous infection is one of the common causes of deviations in the concentration of salts in the kidneys from the norm. After proper treatment, a person can get a relapse of the disease from simple hypothermia. This is why you need to carefully monitor your health.
Other common reasons include:
- hereditary predisposition;
- stagnant processes and slow excretion of urine;
- metabolic disorder;
- pathologies of the functioning of the adrenal glands and pituitary gland;
- hormonal disbalance;
- problems with the thyroid gland.
Patients of both sexes, adults and children, are equally susceptible to pathology. The risk of developing the disease is in sedentary people who do not receive enough vitamin D. Increased levels of uric acid and calcium lead to the formation of salts in the kidneys.
Symptoms of deviation
In the early stages of the disease, a person does not feel any unpleasant symptoms.
However, a constantly increased concentration of salts in the urine leads to the occurrence of urethritis and cystitis, which occur in a chronic form.
Over time, the kidney pelvis becomes inflamed and minerals accumulate, leading to the formation of small and then large kidney stones. At this stage, the symptoms are already more pronounced.
Most often the patient is concerned about:
- pain when emptying the bladder;
- pain syndrome affecting the lumbar spine;
- urine of an unusual reddish color;
- frequent urge to go to the toilet;
- heaviness in the lower abdomen;
- When stones move through the ureter, renal colic may occur.
Pathology in a child
The body of children is more sensitive, and the first manifestations of the disorder can be noticed already in the early stages of the accumulation of salts in the kidneys. The child becomes capricious, eats poorly and sleeps at night, and has frequent urination.
In older children, appetite is disturbed, weight indicators change up or down. A sick baby becomes whiny, concentration is lost, and physical development may be delayed.
This is explained by the child’s low activity and weakness.
Salts during pregnancy
During pregnancy, if a disorder is detected, a woman may feel unwell already in the early stages of the development of the pathology. Body temperature rises, vomiting and nausea, weakness appear.
Salt crystals and sand can harm both the expectant mother and her baby, so treatment should be started immediately.
By blocking the normal outflow of urine, salts contribute to the formation of edema and increased blood pressure.
Diagnostics
If symptoms of pathology are detected, you must immediately contact the clinic to make a correct diagnosis. The doctor prescribes a series of laboratory tests that can show the presence of stones, the possibility of developing an inflammatory process, and also specify the location, shape and size of the stones.
Mandatory analyzes are considered:
- General blood analysis. Able to indicate the development of inflammation. Doctors also monitor urea, creatinine and nitrogen levels in the patient’s blood. With salt diathesis, all indicators will be higher than normal.
- General urine analysis. Determines the types of salt accumulations and their quantity. Using additional alkaline reactions, doctors determine whether phosphates or carbonates are present in urine.
In addition to laboratory tests, ultrasound diagnostics are widely used. On the screen, the specialist will see the location of the salts and identify them in the pelvis or tubules. To confirm, an x-ray is sometimes prescribed as an additional study.
Basic treatment methods
There are a number of basic methods for getting rid of pathology, the main task of which is to remove salts from the kidneys or remove accumulated crystals and stones. The choice of treatment method depends on the degree of neglect of the problem and the patient’s condition. All prescriptions are made only by a doctor.
Medications
At the primary stage, doctors prefer to cleanse the kidneys using conservative medicine. To do this, they take special medications that are aimed at removing salts from the body and eliminating unpleasant symptoms.
To alleviate the condition, the patient is prescribed:
- antispasmodics (No-Shpa);
- painkillers;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Norfloxacin);
- a group of drugs that dissolve stones;
- uroseptics (Urolesan, Cyston);
- antibiotics, subject to bacterial environment.
Various diuretics have a positive effect. However, it is not advisable to take them in the presence of large stones. This can cause the stone to move through the urinary tract and completely block or damage it.
Operative therapy
Advanced forms of pathology, when salts form large stones, are treated surgically. In this case, medications are no longer effective. The operation is performed in three different ways:
- cavity;
- laser removal;
- ultrasonic crushing.
For small stones, gentle methods can be used, when the stone is crushed using electromagnetic radiation, and its remains are excreted naturally through urine. In the case of large stones, only open surgery is used.
Folk remedies
The folk recipe can be used at the initial stage of the development of the disease, when the salts have not yet formed large crystals and stones. Infusions and decoctions can be used only after consultation with the attending physician.
- Lemon juice diluted in 100 ml of hot water.
- A mixture of cucumber, carrot and beet juice. The course of therapy lasts 14 days.
- Decoctions of chamomile, thyme, milk thistle, coltsfoot and other herbs.
Recipes are good for removing salts from the body and eliminating unpleasant signs of pathology.
Features of treatment of children and pregnant women
Children and pregnant women who have developed salt diathesis are prescribed sorbents to adsorb toxic substances and prevent their reabsorption into the blood. In addition, it is necessary to adjust the menu and drinking regime.
Eliminate the risk of relapse by adjusting the patient’s nutrition. Based on laboratory tests and types of salts, the doctor makes prescriptions for a therapeutic diet. It is recommended to consume more fluids rich in vitamins and minerals.
Reduce consumption of artificially purified water.
Therapeutic diet
There is no point in treating salt diathesis if a special diet is not followed. First of all, the patient needs to drink at least 2 liters of water per day. However, in hot weather and during physical activity this amount should increase.
If urate salts are detected during analysis, legumes, sweets, meat and offal should be excluded from the daily menu. If oxalates are detected, reduce the consumption of oxalic acid (tomatoes, rhubarb, sorrel).
The patient needs to reduce the amount of salt consumed, establish proper nutrition, eliminate smoked meats, processed foods, various harmful foods, and in some cases reduce the amount of cottage cheese and dried fruits consumed. The result will not be long in coming, the symptoms will quickly go away.
Prevention
Prevention of salt accumulation in the kidneys has a huge impact on the body.
For these purposes, the patient needs to be regularly checked by a doctor, follow a selected diet and drinking regimen, promptly treat infections of the genitourinary system, rest well and not overexert.
Salt diathesis can cause serious complications in the form of urolithiasis. By following preventive measures, dangerous consequences can be avoided.
Source: https://mrfilin.com/soli