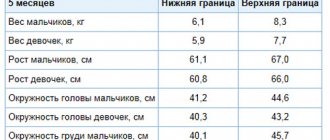
At the age of two months, babies have time to get used to their new life. From this time on, they begin to most actively absorb all possible information, changing daily. At this age, it is important to monitor the child’s nutrition, because in order to actively explore the world around him, he needs a supply of energy. Therefore, it is worth focusing on accepted nutritional standards, which suggest not only how much breast milk a baby should eat at 2 months, but also the baby’s weight gain. Such data exist not only for breastfeeding, but also for artificial and mixed feeding.
All children eat differently
In fact, every child is individual. This applies to everything, including nutrition. Appetite can vary, as can health status and mood. Therefore, how much a child should eat at 2 months is up to him to decide! Producing a strictly defined amount of milk during feeding is, to put it mildly, ridiculous. The exception is premature babies. They only feed by the hour.
District pediatricians closely monitor the child’s development, weight gain and the need for additional feeding. However, the last word will remain only with the mother. By constantly monitoring her baby, she will be able to determine the child’s diet for 2 months and draw conclusions about the advisability of introducing complementary foods.
How much formula does a mixed-fed baby need?
In this case the math will be very complicated. We recommend using one of two methods of introducing supplementary feeding.
With mixed feeding, breast milk is still considered the main one.
Mom introduces the mixture, starting with a minimum amount. For example, 30 ml 1-2 times a day. Once a week, the mother carries out control weighings and, if the gain is less than 125 g/week, increases the amount of supplementary feeding per day by a minimum amount: adds 1-2 more feedings of 30 ml each. If there are 6-7 feedings of 30 ml, then the volume of one-time feeding begins to increase: 6 feedings of 30 ml + 1 feeding of 40 ml until all feedings are 40 ml, etc. Increasing the amount of supplementary feeding should be stopped when the child begins to gain 125g/week or more. You can carry out one more additional control weighing (control - not the one before and after meals, but control - whether you gained 125 g or not) to make sure that this volume is enough. The mother counts the number of times the baby urinates and adds approximately 30 ml of supplementary food for each missing time. For example, a baby peed 8 times in one day. He is 2-4 times short of normal, which means the minimum amount of supplementary feeding can be set to 2 feedings of 30 ml each. After two or three days, the urination count is repeated. As soon as the number of urinations is set slightly above the minimum norm (12–14), the increase in supplementary feeding is stopped
Attention: this method requires confirmation by monitoring weight gain! Those. Once the desired number of urinations has been established, one or two weigh-ins are required, 7 days apart, to ensure that the weight gain is 125 g/week or more.
3 rules for supplementary feeding of children on SV
Following these tips will allow you to supplement your baby's feeding without reducing lactation.
- The mixture is given not from a bottle, but from a spoon. This will avoid a situation where the baby will be lazy to suckle, if there is an easier option - drinking through the nipple.
- Supplementary feeding must be dosed in small portions, that is, the required daily volume should be divided into several times.
- The mixture must be given strictly on an hourly basis. The rest of the time, food needs are satisfied with breastfeeding.
A well-fed toddler is a happy toddler!
If the baby doesn’t eat enough, it’s obvious right away. The baby is nervous, cries, sleeps poorly. A well-fed child, on the contrary, behaves very calmly, plays and smiles. In a word, outwardly he looks strong and healthy.
However, whether a baby has enough milk can be determined using the so-called “wet diaper test.” To do this, you need to avoid using diapers for the whole day. The next morning you need to count the number of wet diapers. If there are more than twelve of them, it means the baby has enough milk.
The baby's nutrition at 2 months also affects his stool. During normal lactation, the baby defecates several times a day. This also needs to be monitored closely.
Introduction of complementary foods
Complementary feeding is recommended for three-month-old babies if they are not gaining weight well, are often ill, or have delayed physical development.
Vegetable purees made from broccoli, zucchini, cauliflower without salt and sugar, which have a neutral taste and will not provoke allergies, are ideal as complementary foods. Complementary foods should be introduced in small doses, once a day and before feeding with breast milk or formula. You should not give fruit purees or juices as complementary foods. Most of them are allergenic and also have a sweet taste. After them, it is more difficult for the baby to come to terms with tasteless vegetable puree. Since the baby is still quite dependent on the mother emotionally, you should not switch to artificial nutrition at the first difficulties with feeding. The baby may begin to teethe, still have colic, and become more active and often capricious. Breast milk and physical contact with the mother will help him cope with overexcitation and discomfort. In addition, breastfeeding during the first six months of a baby’s life provides the body with all the important and beneficial substances that are so necessary for the active growth and development of the child, as well as the development of his immunity. Therefore, the mother should pay enough attention to her diet.
How much should a baby eat at 2 months, a pediatrician will tell young parents
Children, of course, have different appetites – that’s a fact. However, pediatricians still set an average nutritional intake of 2 months. Doctors focus on weight gain. If at 1 month it is about 600 grams, then at 2 months it is already 800 grams.
Pediatricians focus on special formulas developed by specialists at different times.
For example, according to the Reiche method, the required amount of milk is calculated relative to the baby’s weight and height. The formula is extremely simple. Weight in grams is divided by height in centimeters, after which the result is multiplied by seven.
Shkarin's method says that the baby should consume about 800 milliliters of milk per day. With each subsequent month, this amount should increase by 50 milliliters.
When calculating nutrition using the Gayburn method, the child’s weight is taken into account. There is nothing complicated here either. In the first 2 months, the norm for milk consumption is one fifth of the baby’s weight, in 2-4 months – one sixth.
How often to eat
The established volume of milk or mixture must be divided 6-7 times a day at intervals of 3.5 - 4 hours. If your baby sleeps through one meal, don't worry. This means that he was sufficiently full before going to bed. Many mothers worry about the long gap between feedings at night. This is completely normal. If the baby is healthy and the mother has good lactation, you can completely refuse night feedings.
A break of 6 hours at night is quite acceptable for a two-month-old baby. If you notice that there is less milk, you can return to night feedings to preserve it.
With artificial feeding, the regimen may differ slightly - the mixture remains in the baby’s body a little longer than breast milk. You can safely feed your baby every three hours during the day, and at night take a break for 6 hours. The mixture obtained per day is enough for a restful and long sleep.
Nutrition of a baby while breastfeeding
There is simply no point in talking about the benefits of natural feeding of a baby. Every mother knows about this. The question of how much a baby should eat at 2 months while breastfeeding is absolutely meaningless. Modern pediatricians recommend feeding the baby on demand. In most cases, breast milk will not allow the baby to either undereat or overeat.
However, it is still necessary to weigh the baby before and after feeding. It will simply help the young mother keep records in order to understand exactly when she will have to add complementary foods to her diet.
On average, at 2 months the baby eats seven to eight times, and the amount of milk or infant formula is approximately 120 milliliters. Of course, sometimes a child can eat more, and sometimes less. However, 800 milliliters per day should definitely work out.
What types of mixtures are there?
Modern milk formulas are made from specially processed cow's (less commonly goat's) milk.
In their properties and composition, they are very close to human breast milk and are divided according to the degree of adaptation to it:
- Adapted mixtures are fermented and unleavened, liquid and dry. They contain whey proteins, carbohydrates in the form of lactose, vegetable fats, vitamins and minerals in balanced amounts. Examples of manufacturers of such products: “Agusha”, “Nan”, “Nutrilon-1”, “Tuttelli”, “Frisolak”, “HIPP-1” and many others. etc.
- The second degree of adaptation is mixtures based on casein without the addition of whey proteins. These are “Nestozhen”, “Similak”, “Impress”, “Lactofidus”, “Danone”, etc.;
- Therapeutic mixtures are used for low-weight or premature babies, for babies prone to allergic reactions, suffering from abdominal pain, constipation, regurgitation, and unstable stools. There are strict indications for taking such mixtures and precise schemes for their introduction into the diet. If you start giving them without consulting a doctor, you risk harming your baby.
- Starting from the 7th month, you can use transitional mixtures (the so-called “subsequent formulas”: “Nutrilak 2”, “Gallia 2”, “Nan 6–12”, “Baby 2”, “HIPP 2”, “Enfamil” 2").
In the first month of life, the baby should be prescribed unleavened formulas, since fermented milk formulas can increase regurgitation. A little later, you can combine both, replacing one, two or three feedings with fermented milk mixture.
Don't worry if your child eats a little less
However, these standards are just recommendations. Don't panic if your baby eats less or less often. The main thing is stable growth and weight gain.
So, how much should a child eat at 2 months is a question to which it is impossible to give an exact answer. All figures are approximate only. If the mother still suspects that the baby is malnourished while breastfeeding, since it is impossible to determine the exact amount of milk consumed, it is necessary to pump for several days in a row at different times. This will allow the mother to more accurately navigate the baby’s nutrition plan.
Normal breast milk for a newborn
How many grams of breast milk should a newborn eat?
Let us immediately note that for the first three days the baby eats colostrum. This liquid is quite fatty and nutritious; it contains a lot of useful substances that are necessary for active and normal growth. To ensure that your baby's nutritional needs are met, very little colostrum is enough.
In the first days, the baby eats quite little, but often . There are some reasons for this fact. Such frequent meals are caused by the fact that the newborn’s stomach is not yet fully developed, its volume is no more than 7-9 milliliters, and also because the baby does not yet have special skills in sucking the breast.
Many children's doctors consider it natural that the child refuses his mother's breast for the first few days. After the period of colostrum ends, the newborn begins to eat breast milk. Of course, parents immediately have a question: “How many grams of breast milk should a newborn eat?”
Let us immediately note that the answer to this question may depend on several factors. First of all, the volume of breast milk depends on how much the baby weighs and how tall he is. The volume of one feeding also depends on the age of the baby, as well as the nutrients contained in the mother's milk. One of the most basic criteria for milk is its fat content. It is known that the more the baby weighs and the greater his height, the more he should eat.
A formula that allows you to calculate the rate of breast milk per feeding:
V=10*W, where V is the volume of milk in milliliters, W is the child’s age in days.
The approximate amount of milk that a child should consume per day, depending on age:
| Amount of milk consumed per day (ml) | Age |
| 600 | 1+ month |
| 700 | 2+ months |
| 900 | 6+ months |
| 1050 | 9+ months |
| 1200 | 12+ months |
Note that different sources report slightly different indicators of breast milk norms for babies. This is due to the fact that the information provided comes from different pediatric schools.
If there is not enough milk
Unfortunately, breastfeeding a baby is not always possible. There is some cyclicality in the appearance of milk in women. For example, at 3-4 weeks the mother already knows perfectly well the child’s diet and regimen. 2 months pass from the moment of birth, and the amount of milk begins to decrease. At this time, it is not at all necessary to supplement the baby’s feeding. However, if the mother sees that there is still not enough milk, and the rate of weight gain is decreasing, complementary feeding may be needed. However, it should not be more than 150 milliliters per day. It's best to do this before bed.
Before and after feeding the baby, you still need to put it to the breast, at least for ten minutes. If the milk supply is restored, you no longer need to feed the baby.
For most young mothers, lactation intensifies at night. Therefore, if the child sleeps peacefully for at least seven hours, it is best to wake up a couple of hours earlier than the baby opens his eyes. By expressing 100 milliliters of milk in the evening, you can feed the baby quite tightly before going to bed.
As soon as a woman notices that lactation is reduced, she urgently needs to take radical measures to restore it. There are many steps to take to establish breastfeeding - the main thing is to correctly determine the cause of the loss of milk.
How to Determine Nutritional Adequacy
Nutrition for a premature baby is carried out taking into account the needs of the body and the capabilities of the digestive system, since the energy needs are very high, and the digestive capabilities are not yet sufficient.
The number of calories per 1 kg of body weight for a premature baby in the first days and weeks of life is presented in the table.
From the second month of life, for children born weighing more than 1500 g, caloric intake is reduced by 5 kcal/kg/day (compared to the first month of life), and for children born weighing 1000-1500 g, the calorie intake is maintained at the same level for up to 3 months. level as in the first month of life. Next, they begin to reduce calorie content by 5-10 kcal/kg/body weight, taking into account the health and well-being of the baby.
Volume of milk in ml for every 100 g of baby’s weight = age in days 10
Child age 4 days, weight 2000 g
- Daily milk volume = (4 10)*20 = 280 ml
- Single serving with 7 feedings per day = 280/7 = 40 ml
The formula is indicative only, as following it exactly can lead to overfeeding. Therefore, it is still preferable to use the calorie calculation method indicated above.
Increasing the amount of food in premature infants should be done gradually and carefully. If the baby’s condition worsens, then the amount of food must be reduced. Feeding in the first 1.5-2 months. are produced 7-10 times/day. They switch to six meals a day when the child reaches a body weight of 3 kg. A 6-7 month old baby will be ready to switch to 5 meals a day.
Read about formulas for premature and low birth weight babies in this article.
Calculation of nutrition for low birth weight and sick children (WHO recommendations)
These recommendations apply to children in the first 10 days of life. Low birth weight babies are defined as babies born weighing less than 2500 grams. This can include both premature babies and children who are simply small for their age.
For such children, the volume of milk per kg of body weight should initially be 60 milliliters. Then, every day, it is necessary to increase the total volume of milk sucked by 20 milliliters per 1 kg of weight, until the child begins to drink 200 milliliters per 1 kg of weight per day.
Sick children are defined as children whose weight is over 2500 grams and who, due to illness, are unable to breastfeed. For such children, the amount of milk should be 150 milliliters per 1 kg of body weight per day.
The best food for a newborn is breast milk. Its composition is unique and constantly changing, so it is best suited for the digestive system. Breastfed children are less likely to suffer from anemia, rickets, dysbacteriosis, respiratory and infectious diseases.
The baby's sucking reflex appears in utero around the 34th week of pregnancy. On an ultrasound scan you can see him sucking his finger. The newborn's stomach is small and initially has a capacity of approximately 20–30 ml. Accordingly, the volume of the first feedings should not exceed these amounts.
| Age, in months | Daily nutritional requirement according to Gayburn |
| 1 – 2 | 1/5 of total body weight (TBW) |
| 2 – 4 | 1/6 from OMT |
| 4 – 5 | 1/7 from OMT |
| 6 – 12 | 1/8 of OMT |
The formula that Reiche derived is based on the individual data of the newborn:
- height measured in centimeters;
weight, measured in grams.
To clearly demonstrate how to work with the formula, let’s take the average statistical information about the height (58 cm) and weight (5600 g) of a 2-month-old baby: 5600/58 x 7 = 675.9 g.
Are there enough feedings? If the amount eaten is slightly more than prescribed, the baby will regurgitate the excess (i.e., slight vomiting will appear). Therefore, there is no need to breastfeed a newborn unnecessarily, a newborn has his own routine, and if he wants to eat, you will immediately understand it.
When feeding your baby, you need to keep it slightly elevated so that air does not get in; it is not convenient for you to eat while lying down, and it is physiologically not pleasant for your baby to drink in a horizontal position. Otherwise, vomiting may occur during feeding, and not after.
In general, the mother understands on her own how to properly feed a newborn with breast milk after several feedings.
If the child is on artificial nutrition, then the required amount of the finished formula can be found on the baby food packaging. Manufacturers of formulas indicate in detail the volume of dry formula and liquid required for preparing ready-made food, as well as the rate of its consumption for children of different ages.
- Pumping before feeding. The accuracy of this method remains in doubt, but it can be used to determine the approximate volume of breast milk consumed. It is recommended to express carefully and thoroughly, immediately before feeding. Even the right approach cannot ensure complete emptying of the mammary glands. During normal breastfeeding, the baby eats 15-20 ml more than the expressed volume. This is important to take into account when making calculations.
- Using household scales. To determine the amount of food eaten, it is necessary to weigh the baby before feeding and immediately after feeding. The difference in weight will be equal to the amount of food eaten. Before weighing, the child must be completely undressed and freed from diapers and nappies, which may cause excess weight.
- The behavior of a baby can tell a lot. If the newborn is calm, cries occasionally, is not capricious, is friendly, and gains weight according to age and normal, then we can say with confidence that he is receiving enough food.
Tips for parents
- The artificial formula must be of high quality and the child likes it.
- Powdered milk mixtures are diluted with warm water before feeding. You cannot prepare food for future use and feed your baby ingredients prepared more than an hour ago.
- When feeding a 2-month-old baby with formula, you must carefully monitor his body's reaction. At the slightest sign of an allergy, you should immediately stop feeding this composition and show the child to a pediatrician.
- Try to hold your baby close to you as often as possible, ensuring contact with the skin. This will relieve his anxiety.
- Don't leave your baby alone with a bottle. So he may choke on milk.
A two-month-old baby on IV needs your love and care. To do this, you need to stock up on patience, endurance and faith in success. We hope our recommendations will help you.
The child does not eat well
All parents, without exception, sooner or later face the fact that their child begins to eat poorly.
There are many different causes of poor appetite:
- diseases of various types - high fever, nasal congestion, abdominal pain, headache, thrush. At the same time, the baby may be hungry, but physical inconvenience causes him pain, makes the baby lethargic and does not allow him to get enough satiety. Of course, a full recovery will help restore your appetite;
- change of mixture. Many mothers have to spend a long time searching for a suitable formula for their child that would not cause allergies or problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Changing your diet may lead to a decrease in appetite. Unfortunately, before you find a suitable mixture, you have to study several types of food from different brands using trial and error; For feeding newborns and infants in the first six months of life, the mixtures “Kabrita-1”, “Bebi”, “HiPP Combiotic 1”, “NAN Optipro”, “Humana Expert 1”, “Nutrilak-1”, “Frisolak 1”, “ Nutrilon Premium-1".
- Incorrect position of the baby during feeding. You should carefully ensure that during the feeding process the baby sucks the pacifier correctly, since he can take in air along with the mixture, resulting in a feeling of fullness, but there is no real saturation;
- Bad mood. It is not surprising, but two-month-old children can also have a bad mood caused by excitement, fear, etc. Then the child refuses to eat, and in order to normalize his nutrition, he simply needs to be reassured;
- incorrectly selected nipple with high flow intensity. In such cases, the baby begins to choke, choke on a large volume of formula, and cannot swallow. Then you should replace the nipple and adjust the milk supply;
- mixed feeding. A baby may refuse the mother's breast if he is fed from a bottle in which the nipple has a large hole. Indeed, in such cases, unlike mother’s milk, which must be “extracted” with effort, the mixture enters the mouth easily, without strain;
- family atmosphere. The little one is very susceptible to the microclimate that surrounds him, and if loud quarrels, scandals, and swearing are practiced in the family, then he may refuse to eat. The relationship between the parents should be improved and then the psycho-emotional state of the baby will also return to normal.
Important! Force feeding or feeding large portions discourages the baby from wanting to eat. This attitude towards food can persist into an older age of the child. Each baby is individual, unique and unique.
If he is actively growing and developing, gaining weight well, and feeling great, it means that at this stage of his life, the parents are doing an excellent job of providing adequate nutrition for their child. Isolated cases of refusal to eat should not be alarming, but if the child is capricious, lethargic and does not want to eat, it is better to contact a qualified pediatrician
Each baby is individual, inimitable and unique. If he is actively growing and developing, gaining weight well, and feeling great, it means that at this stage of his life, the parents are doing an excellent job of providing adequate nutrition for their child.
Isolated cases of refusal to eat should not be alarming, but if the child is capricious, lethargic and does not want to eat, it is better to contact a qualified pediatrician.
Complementary foods for a three-month-old baby
Many mothers worry that their baby is only eating breast milk or formula and wonder which formula is best for newborns.
Undoubtedly, some children successfully eat cereals, vegetables and drink juices, but before you start complementary feeding, you should think carefully about whether this is really necessary for your baby. If your baby is eating enough, has no intestinal problems, and is developing normally, then you should not rush into complementary feeding. We should not forget that all children perceive adult food in their own way. It brings benefits to some, and problems with stool and allergies to others.
Sometimes the introduction of complementary foods results in stool disorders, colic, abdominal pain, regurgitation, and food allergies. In these cases, it is necessary to temporarily avoid foods that cause such reactions.