Doctor Komarovsky about what to do if your nose is stuffy but there is no mucus
When a child has a stuffy nose, parents immediately begin to look for the causes of the runny nose. And they are frankly at a loss when it turns out that the child’s illness does not fit into the general idea of rhinitis - there is congestion, but no mucus.
Evgeniy Komarovsky, a famous pediatrician, TV presenter and author of books on children's health, talks about what this can mean and how to deal with it.
About the problem
Dry nasal congestion is medically called “posterior rhinitis.” This condition is more dangerous than any runny nose accompanied by discharge, since it may indicate serious “problems” in the ENT organs.
Congestion is associated with swelling of the mucous membranes, and the absence of mucus indicates the non-infectious nature of the disease . If a runny nose is caused by viruses, the nose will definitely run, this is how the body removes foreign “guests”. Dry congestion, according to doctors, is most often caused by an allergic reaction, a foreign body that gets stuck in the nasal passages. This condition is also typical for children with congenital or acquired curvature of the nasal septum, in which nasal breathing as a whole is significantly impaired.
Sometimes a runny nose without discharge is a sign that the child’s mucus has dried out in the posterior sections, which is what caused the swelling. In rare cases, a dry runny nose is a symptom of heart and circulation problems.
A dry runny nose can also be caused by medication; it usually affects children whose parents, contrary to all doctor’s orders and common sense, treated them for ordinary rhinitis with vasoconstrictor nasal medications for too long.
If a child accidentally inhales a particle of food, a crumb, or a small part from a toy, then it is most likely that he will only have one nasal passage blocked; the second nostril will breathe without problems.
Why does a child constantly sigh and yawn?
If a child sighs heavily and yawns deeply three to four times a minute in a short period of time, the mother needs to pay close attention to this fact. There are several reasons for the baby's strange behavior.
Neurological pathologies
Nervous children sleep poorly, throw daily tantrums at their parents, have difficulty making contact, and are easily excitable. With the help of deep breaths, the baby tries to relax the tense, tight muscles and calm down.
A child with such symptoms should be shown to a pediatrician. If the disease is detected in time, it is cured faster and more effectively.
After examination, the neurologist may suspect the following disorders:
- Asthenoneurotic syndrome; The child is depressed, weak, and constantly tired. The cause of the pathological condition is stress. Asthenia can be intrauterine in nature or acquired during life.
- Nervous tic; Provokes yawning in moments of emotional stress, with severe fatigue. It goes away with adequate treatment at puberty.
- Hyperventilation syndrome; Ventilation of the lungs increases several times in 1–2 minutes. The person breathes at a rapid pace, but he does not have enough air. The pathology is classified as a psychoneurological type. The attack is provoked by stress, fear, allergic reactions, and malfunctions of internal organs. It is extremely rare in children.
On a note! In rare cases, frequent yawning is accompanied by epilepsy. Simultaneously with gasping for air, you can notice other symptoms of “falling sickness”: convulsions, numbness, attacks of rage, apathy.
Lack of oxygen in the blood
Hypoxia is typical for newborns, children under 4–5 years of age with a stuffy nose, adenoids, and older adults. The lack of oxygen can be explained by the following reasons:
- Increased heart rate. Heart rate increases for natural reasons or due to heart pathologies.
- Slow metabolic processes. A slowdown in metabolism occurs due to viscous blood; it needs to be thinned with medication, and you need to drink more fluids. Lack of microelements, vitamins, and lack of sleep also negatively affect the functioning of internal organs and systems; the body cannot cope with the load and reduces the speed of work.
- Nervous tension. Stress and unpleasant situations shake up the central nervous system. The system needs more oxygen to restart. Feelings of suffocation and dizziness may occur.
- Sudden hypothermia, overheating. At elevated or lower temperatures, the brain turns on the brakes. Oxygen moves through the cells, the blood more slowly. Hypoxia occurs. The man wants to sleep. Once thermoregulation is restored, oxygen levels stabilize.
Overwork
- Emotional or physical burnout syndrome. In simple words, the child is tired. Constantly lacks sleep. Chronic fatigue provokes yawning. Babies often sigh while awake because they have not slept at night due to colic, itching, diaper rash, hunger due to a lack of mother's milk.
- Static pose. If a baby sits in front of the TV, is frozen in one position with toys, or lies in a crib for a long time without his parents, he will yawn. The muscles become numb, oxygen does not circulate through the blood in a normal rhythm. The body needs physical activity.
- Monotone. Yawning, due to the same cycle of mechanical actions, occurs more often in adults. This is how the body signals the need to change the rhythm of work, shake yourself up, and rest.
Congenital and acquired physiological pathologies
The culprits of the obsessive state, frequent yawning and loud sighs are dysfunction of internal organs or temporary disruptions in their functioning.
- Diseases of the thymus gland. These are DiGeorge syndrome, hyperplasia, myasthenia gravis, tumors. Children with a congenital defect get tired quickly, become out of breath if they climb stairs, and suffer from ischemia and arrhythmias.
- Vegetovascular dystonia. The functioning of the autonomic nervous system is disrupted. The person sleeps poorly, feels pain in the heart area, and the body temperature is unstable. Another common symptom is STS (sad sigh syndrome). In patients with VSD, the functioning of the respiratory system is disrupted, and the person experiences short-term suffocation. All symptoms are part of the internal experience, the stress of the body.
- Ventilation failure. A child with this disorder experiences frequent shortness of breath. First during physical activity, then at rest. Newborns are diagnosed with pathology immediately after leaving the womb. The baby cannot breathe the first breath of oxygen on his own; resuscitation comes to the rescue. The cause of the disorders is prematurity and immaturity of the lungs.
- Asthma. It is more often diagnosed in children prone to allergies, with weak immunity, and who have had pneumonia at an early age. With asthma, temporary asphyxia and shortness of breath occur, and the rhythm of the lungs and bronchi is disrupted.
- Adenoids. The tonsils, enlarged three to four times, block the passage of air. The baby is forced to breathe through his mouth. Lack of oxygen provokes periodic deep sighs and coughing.
- Cardiac pathologies. Defects and heart failure in infants manifest themselves externally in the form of difficulty breathing, deep sighs with sounds.
Colds, viral diseases
ARVI, tonsillitis, pharyngitis cause cough, sore throat, and pain. During the acute course of the disease, the tonsils become inflamed and block the passage of air. The baby experiences mild suffocation and lack of oxygen. The child is forced to swallow it in large portions. Inhalation looks like a yawn.
Other reasons
- Allergies. Dust, wool, and products hazardous to children cause difficulty breathing and rhinitis. The most dangerous scenario is Quincke's edema. Severe shortness of breath, blue lips, panic, swelling of the skin of the face and limbs accompany the attack. You need to urgently call for medical help.
- Curvature of the spine, osteochondrosis. The irregular curvature of the spinal column puts pressure on the internal organs (lungs, bronchi). To breathe deeply, the baby sometimes raises his shoulders and straightens his back. Makes deep yawns and breaths. Scoliosis has a bad effect on sleep, the child constantly experiences pain in the back and legs, and gets tired quickly.
- Pain in the stomach, gastritis. The increased volume of the stomach prevents the respiratory organs from functioning fully. The child is breathing intermittently. May cough.
- Helminths. Cause extensive intoxication of the body. Coughing, sighing, and difficulty breathing are symptoms of an advanced stage of the disease.
- Recovery period after pneumonia, sore throat, pharyngitis, laryngitis. Rehabilitation after acute conditions takes 1–2 months. Infrequent sighs during this period are not a dangerous sign.
Note to parents! You should not hold back a yawn or sigh in moments of extreme fatigue. The brain is actively looking for a way to restore strength.
How often during the day does your child take deep breaths?
- More than 5 times a day 84%, 1304 votes
1304 votes 84%1304 votes - 84% of all votes
- 2-3 times a day 7%, 105 votes
105 votes 7%
105 votes - 7% of all votes
- 4-5 times a day 7%, 104 votes
104 votes 7%
104 votes - 7% of all votes
- Once a day 3%, 45 votes
45 votes 3%
45 votes - 3% of all votes
Total votes: 1558
25.10.2018
×
You or from your IP have already voted.
Danger
The main danger of nasal congestion without mucus secretion is the possible atrophy of the mucous membrane of the nasal passages. This can happen if the problem is ignored or the condition is treated incorrectly. It is possible that secondary diseases of the nasopharynx will develop, which will cause irreversible changes in the tissues of the respiratory organs.
Children with a dry runny nose usually have disturbed sleep, develop neurosis due to lack of sleep, and become restless and nervous. If the cause is pathological (and only a doctor can determine this), untreated posterior rhinitis can cause a deterioration in the sense of smell and hearing loss.
Dry congestion disrupts cerebral circulation. With prolonged absence of nasal breathing, severe disturbances in the functioning of cerebral vessels may develop.
Doctor Komarovsky about the problem
Evgeny Komarovsky looks at the problem of dry nasal congestion a little more optimistically than most of his colleagues. According to an authoritative doctor, 80% of cases of runny nose without snot are a consequence of excessive parental care. In other words, moms and dads create greenhouse conditions for their children: it’s hot at home, you can’t open the windows, “after all, there’s a small child at home!”, It’s not worth walking in cool and windy weather, because “the baby might get sick.”
Violation of the temperature regime, coupled with excessively dry air in the apartment, leads to drying out of the mucous membrane of the nasal passages. The mucus outflow system is disrupted, swelling forms, and as a result, the nose does not breathe.
Komarovsky urges parents to monitor their child more closely; if there are no other symptoms of ill health other than congestion, there is no need to worry too much.
It is enough to create the “right” conditions for a child to live a normal life: according to the doctor, the air temperature in the apartment should not be higher than 19 degrees, the air humidity should be 50-70%.
The house needs to be wet cleaned more often and the room ventilated. The child should walk often, walks should be as long as possible, as long as the toddler’s age allows.
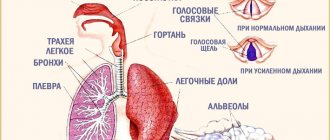
Breathing of a little toddler
We have already found out at what age a child begins to breathe through his mouth. Young parents should be wary of the fact when their very young child begins to breathe this way. Some pediatricians are sure that breathing through the mouth is completely normal for a baby, because his nasal passages are not yet fully formed and are very thin. It can be difficult for a baby to breathe through his nose, so he uses his mouth.
When does a child start breathing through his mouth? If his nose is clogged. To eliminate the situation, you need to drip the necessary medications into the nose and very carefully clean it of foreign bodies. More on this below.
When does a child begin to breathe through his mouth under other circumstances? This happens if the baby sleeps without his pillow and his head is thrown back a little. This way the baby gets oxygen much easier. This situation can be corrected if you place a thin pillow under the baby’s head - the child will receive oxygen, but will not breathe through his mouth.
Another situation is when the baby simply sleeps with his mouth open, but breathes through his nose as usual. Before taking any measures, parents should simply make sure that the baby breathes through the mouth. You just need to listen to how the baby breathes.
Why does a child breathe not through his nose, but through his mouth - at night in his sleep or during the day, what should I do?
Breathing disorders negatively affect the child’s condition. It does not receive enough oxygen, and microbes easily penetrate the respiratory tract, causing the development of diseases. The baby may breathe through the mouth, snore or snore in his sleep, often wake up and cry, which is typical for difficult nasal breathing. Any symptoms and disorders that concern parents should be a reason to visit a pediatrician. What to do if a child breathes through his mouth during the day or at night? Why is this dangerous, and for what reasons does a violation occur?
When and why does a child begin to breathe through his mouth?
Indeed, a child should not breathe through his mouth. This can only happen when his nasal cavities are clogged and he cannot breathe through them. Children may also breathe constantly through their mouths for other reasons. For example, due to a common habit. We can say that this is a very bad habit that will greatly affect the child’s health. This is because when breathing through the mouth, the lungs do not open completely, using only the upper lobes. That is why the body will not receive the required portion of oxygen. This may result in anemia, hypoxia, physical or mental retardation. In addition, the shape of the face may change - it becomes more elongated, the bridge of the nose widens, and the upper lip is constantly turned up.
Breathing through the mouth: reasons
The main reasons why a child breathes through his mouth:
- abnormal structure of the nose;
- congestion and swelling characteristic of a respiratory disease;
- allergic rhinitis;
- disruption of the normal microclimate of the children's room, dry air;
- incorrectly selected pillow.
Abnormal structure of the nose that interferes with normal breathing
Congenital anomalies of the structure of the nose manifest themselves in the form of narrowing of the nasal passages, deformation of the septum, etc. The child may be bothered by snoring and holding his breath during sleep. These symptoms should alert parents and force them to consult a specialist. Usually the listed signs are noticeable immediately and are diagnosed in children from an early age. In difficult cases, surgery is recommended to eliminate the pathology.
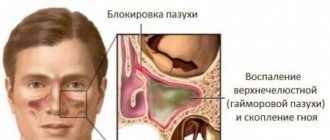
Nasal congestion (ARVI, allergies, adenoids)
Respiratory diseases often lead to swelling of the nasal mucosa and runny nose. This is the main reason for mouth breathing during sleep, because the child cannot breathe fully through the nose.
Allergic rhinitis in its symptoms resembles a common runny nose, but nasal discharge is liquid and clear. Mouth breathing is observed with inflammation of the tonsils or sinusitis. Adenoids are often diagnosed in children of preschool and primary school age.
Dry nasal mucosa due to dry hot air
Dry hot air in the room, especially during the heating season, causes the child’s nasal mucosa to dry out. Crusts form in the nasal passages, making breathing difficult. The same thing happens when there is a large amount of dust, dirt or pollen in the air. The mucous membrane swells, preventing the baby from breathing normally.
Why is my nose stuffy?
To understand why a child breathes through his mouth, you need to analyze his breathing during sleep, during active play, and while feeding. You should also pay attention to the child’s appetite, mood and measure the temperature. Let us conditionally divide the reasons into several groups.
Congenital anomalies
Typically, birth defects are discovered in the first years of life.
Difficulty in nasal breathing may occur due to a deformed septum. Violation of the ventilation function of the nose predisposes to swelling of the mucous membrane and activation of opportunistic microorganisms.
Chronic inflammation leads to wheezing, grunting and even snoring. In this case, treatment may involve surgery. The operation allows you to change the structure of the septum and ensure full nasal breathing.
Among congenital pathologies, it is also worth highlighting infectious and autoimmune diseases that reduce the level of immune defense. Against the background of immunodeficiency, the child becomes more sensitive to the negative influence of environmental factors. Changes in the structure of the nose can be observed as a result of traumatic exposure, which may require the help of an oral and maxillofacial surgeon.
Rhinitis
There are many forms of rhinitis, but we will focus on vasomotor, infectious and catarrhal rhinitis. As for the vasomotor type, it can be manifested by congestion in one nasal passage, as a result of which it is difficult to breathe through the nose, so children open their mouths slightly.
Symptoms usually worsen after hypothermia or prolonged exposure to dry air. When the child lies on his side, congestion is observed in the underlying nasal passage. During sleep, the baby may snore, and during the day, from time to time, breathe through the mouth.
Infectious and catarrhal rhinitis goes through several stages. We are interested in the first stage, when:
- swelling of the nasal mucosa occurs;
- sneezing, itchy nose;
- a deep voice is noted;
- There is no way to breathe through the nose.
At the first stage, small amounts of mucus may be released, which further reduces the lumen of the nasal passages. If children's immunity is strong enough, a runny nose may end in the first stage, but this is extremely rare.
Neoplasms in the nasal passages
Sniffling in children may occur as a result of narrowing of the nasal passages by additional formations, such as polyps, cysts or malignant growths.
The emergence of such neoplasms is promoted by:
- chronic infection in the nasopharyngeal area;
- poor ecology (smoke, smog);
- structural defects of the nose.
This group of causes also includes foreign bodies that have entered the upper respiratory tract. While playing, the child can inhale or insert a button, small construction item, or bead into the nostril. The child’s condition sharply worsens, shortness of breath, lacrimation appear, and hysteria develops.
If the foreign body is located near the nostrils, parents can remove it themselves. When an object moves into the choana zone, its visualization becomes difficult. Sometimes it can be located in the nasopharynx in such a way that the child does not even feel it.
The object can irritate the mucous membrane, causing it to swell and making breathing difficult. Only an otolaryngologist can help in this situation after a thorough examination of the nasopharynx.
Penetration of a foreign element into the larynx is especially dangerous, which can provoke laryngospasm.
Due to irritation of the larynx, a reflex closure of the vocal cords and closing of the gap occurs, which manifests itself as suffocation and threatens the baby’s life. In infants, the lumen of the larynx is smaller than in older adults, so the risk of death is much higher.
The conclusion follows from this - do not leave a small child unattended.
Diseases of the ENT organs
Often a child breathes through his mouth due to adenoids or chronic sinusitis. When contacting an otolaryngologist, the first thing the doctor evaluates is the condition of the nasopharyngeal tonsil. Adenoids in children under 8 years of age are diagnosed quite often, but not every case requires surgical intervention.
Children with:
- lymphatic-hypoplastic diathesis;
- increased susceptibility to allergic reactions;
- living in an area with unfavorable environmental conditions;
- poor nutrition;
- frequent colds.