The tonsils are considered one of the most important organs in the human body, because they play the role of a so-called barrier against various bacteria and viruses that every second want to penetrate into the middle of your body by airborne droplets.
Basic designations for tonsil sizes:
- 0 – tonsils are located in a recess and do not look out of it;
- 1+ – tonsils protrude from the recess and cover no more than 25% of the throat;
- 2+ – the tonsils protrude strongly from the recess and cover no more than 50% of the throat;
- 3+ – the tonsils protrude strongly from the recess and cover no more than 75% of the throat;
- 4+ – the tonsils protrude strongly from the recess and cover more than 75% of the throat.
The normal size of this component of the throat is 0, and 1+ and 2+ are considered moderately enlarged tonsils. Tonsils 3+ and 4+ are considered very enlarged; doctors call this phenomenon tonsil hypertrophy. With hypertrophy, the tonsils will be constantly enlarged.
Why does a child have constantly enlarged tonsils and why is this dangerous? Enlarged tonsils in a child can be due to various inflammatory diseases of the throat. Constantly enlarged tonsils in children can cause the following consequences:
Breathing problems at night. In this case, the child may stop breathing for a certain period of time, causing the child to constantly wake up during the night. That is, the child will not get enough sleep, as a result of which irritability, inattention, weakness may increase, and a disease such as urinary incontinence may develop. Snoring may also occur. Naturally, such symptoms will interfere with the normal development of the child.
Pain when eating or swallowing saliva. Enlarged tonsils in a child will interfere with him and cause pain when eating food. As a result, children will have a noticeable decrease in appetite. Unreasonable vomiting may also occur, and when drinking water, fluid may leak from the nose.
The child coughs constantly. Quite often in such cases, the cough may not go away until the tonsils are removed. But such a cough occurs quite rarely. A persistent cough does not threaten the child’s life, but doctors are constantly trying to cure it, which means they will prescribe various examinations and medications.
What are the reasons for enlarged tonsils in a child? At the moment, the reasons for enlarged tonsils have not yet been precisely established, but we will name the currently known reasons why a child’s tonsils may be enlarged:
- Frequent colds;
- Unfavorable living conditions;
- Poor nutrition;
- Hypothermia of the body;
- Poor immunity;
- Allergic reactions.
Tonsils - what are they?
There are six tonsils located in our oropharynx. They are formations of lymphoid tissue. Tonsils are paired (palatine and tubal) and unpaired (pharyngeal and lingual).
Palatine tonsils are also called tonsils. They are located in the throat on either side of the roots of the tongue. Healthy tonsils look like small spherical structures. Their size does not exceed a walnut, they do not extend beyond the boundaries of the palatine arches. In normal condition, the tonsils are pink.
In case of inflammation, the tonsils are palpated from the outside. To do this, place your hands on the neck under the chin on both sides and massage. The tonsils will feel like dense balls.
The main function of the palatine tonsils is to protect against viruses and bacteria that enter the body through airborne droplets. The lymphoid tissue of the glands “identifies” the pathogen and transmits information about it to the immune system. After which it produces specific antibodies and prevents the development of inflammation.
The palatine tonsils are involved in the process of hematopoiesis. They produce lymphocytes necessary to fight infections.
Causes of enlarged tonsils
A child’s tonsils become loose due to an inflammatory process in the throat or hypertrophy of lymphoid tissue.
In the first case, the reasons are:
- ARVI. Its first symptoms are redness of the throat and runny nose. In this case, there may be no painful sensations. But if you delay treatment, tonsillitis, bronchitis or pharyngitis will develop against the background of ARVI.
- Angina. A serious illness that affects the throat. The tonsils turn red and increase significantly in size. A white or yellowish coating appears on them. All this is accompanied by increased body temperature.
- Pharyngitis. It causes inflammation of the throat mucosa, which spreads to the lymphoid tissue. Pharyngitis is accompanied by a sore throat, dry cough, and elevated body temperature.
- Tonsillitis. It is considered a special case of sore throat. Most often it is provoked by streptococcal infection. In addition to a sore throat, a severe cough develops. A white coating appears on the tonsils.
In children with reduced immunity, looseness of lymphoid tissue develops against the background of hypothermia. Usually there is no cough, high body temperature, or sore throat.
Causes of tonsil hypertrophy
The proliferation of tonsils is called hypertrophy. Moreover, the tonsils are enlarged even when the child is healthy.
The growth of the palatine tonsils is a compensatory process, in this way the body tries to increase the efficiency of their “work”. It starts against a background of reduced immunity, with often inflamed tonsils. Those at risk, first of all, are frequently ill children and children with chronic diseases of the ENT organs.
But the prerequisites for an increase in lymphoid tissue are laid during the mother’s pregnancy and the intrapartum period (during childbirth).
To a large extent, hypertrophy of the tonsils is provoked by fetal hypoxia. It affects the formation of the fetal immune system: the functioning of the thymus (the main organ of the immune system) decreases. Lymphocytes form and mature in it.
A decrease in the “activity” of the thymus triggers a compensation mechanism - the proliferation of peripheral lymphoid tissues. Lymphocytes are also formed in it, but in smaller quantities.
Hypoxia during childbirth, associated with a long anhydrous period, also provokes hypertrophy of the tonsils. During this process, disturbances in the functioning of the adrenal glands occur. Which, in turn, provokes the proliferation of the palatine tonsils.
Inflamed tonsils in a child
Before moving on to the question of how to treat inflammation of the tonsils, you should understand what kind of disease it is and what it is associated with. And also why children often experience complications with this particular lymphoid tissue. Knowledge of how to avoid the inflammatory process, which leads to serious consequences, will also be important.
Inflammatory process
In medical Latin, tonsils are called tonsillae. This word gave the name to the disease - tonsillitis. Therefore, if you hear that your child has tonsillitis, know that this is inflammation of the tonsils. In common parlance, they are usually called tonsils, and their inflammation is called sore throat.
The disease can occur in acute and chronic form. In both the first and second cases, you can encounter complications, the process of which will be very difficult to stop. Affected tonsils lead to new, unnecessary health problems.
The bacteria that cause the disease are:
- staphylococci;
- streptococci.
Symptoms and consequences
The first symptom to look out for is a high temperature. If a child talks, he will complain of a sore throat and problems with swallowing; babies are simply capricious.
Upon self-examination, parents may see red tonsils with thin blood veins. If the situation is advanced, you can see white pustules or a milky coating on them.
The throat passage becomes very narrow, making it difficult for children to breathe. As a result, the voice becomes hoarse, speech causes pain, so you should try not to talk.
Self-treatment for inflammation of the tonsils is strictly prohibited. Tonsillitis has a lot of serious consequences that will affect your health.
- disorders of the cardiovascular system, complications, including surgical intervention;
- disorders of the urinary system, especially the kidneys;
- problems with the digestive system;
- problems with the circulatory system.
In addition, when the tonsils are inflamed, children often develop a high fever, which also causes irreparable harm to the growing body. Adults should remember that body temperature above 38 °C must be brought down. Remember, the higher the body degrees, the higher the risk. If you don't lower the temperature, you can get:
- convulsions;
- fainting;
- dehydration;
- disruption of the functioning of certain organs;
- irreversible disorders of brain activity processes.
You need to not only take care of your children, but also treat them properly. At the first signs of replenishment in the tonsils, you should immediately consult a doctor, without waiting for fever and its consequences.
Treatment for inflammation of the tonsils
You cannot treat the child yourself, but you need to provide symptomatic treatment before the doctor arrives.
Symptomatic help
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which relieve pain, fever and inflammation at the same time, are well suited for such assistance. For children there is children's "Nurofen", "Ibuklin-junior", "Ibuprofen".
You will need to carefully read the instructions, especially any contraindications for the drugs. The appointment should be one-time before the doctor arrives, but only if the child is suffering from severe pain and high fever.
If there are no such symptoms, taking the medicine is contraindicated.
Usually, mom always has NSAIDs in her medicine cabinet. For infants they are available in suspensions, for older children - in tablets. Abuse of such treatment leads to serious gastroenterological problems.
Rinsing
Before a doctor arrives or goes to a medical facility, you can rinse your tonsils with various anti-inflammatory solutions.
How to make solutions:
- soda solution – 1 tsp. soda per 100 gr. warm water;
- brine. 1 tsp. salt per 100 gr. warm water;
- eucalyptus solution. It will need to be made according to the recipe on the package. For the same purpose they use chamomile, oregano, oak bark, thyme;
- Furacilin solution – 2 tablets per 100 g. water.
Beetroot can be used as a folk treatment; it has antimicrobial and antibactericidal properties. To do this, you need to grate the beets, dilute the juice with 2 tbsp. l. water and let the children rinse their tonsils.
Rinsing should be done slowly, each approach for at least 15 seconds.
For small children, mothers treat the neck with their finger: you need to wrap a bandage around your index finger and dip it in an antiseptic liquid, then remove the plaque from the tonsils.
This is unpleasant and even painful for the baby, so everything must be done very carefully, gently and quickly. If you are afraid, it is better not to do it at all, but to use an aerosol.
Irrigation
For irrigation, you can use aerosols such as “Ingalipt”, “Miramistin”, “Hexidin”. The rest is contraindicated for children. Before irrigating the tonsils, you must carefully read the instructions for using this type of treatment.
special instructions
If a child begins to complain at night simply of pain, you can relieve the symptoms, treat the throat and wait until the morning. If you have a high temperature, you should call an ambulance.
Firstly, as mentioned above, children may have convulsions, and secondly, the tonsils may become very swollen and it will become difficult for him to breathe.
In such cases, treatment will be as first aid: relieving pain and fever with the above drugs.
Place a cool compress on your forehead. Wiping children's bodies yourself is dangerous; convulsions can start from temperature changes. And, then, we still haven’t come to a common opinion: what can and cannot be used to wipe a child. Then treat the throat by treating it. Inflammation of the tonsils is a very dangerous disease; it must be treated responsibly and fully.
After the doctor arrives, you will be prescribed antibacterial treatment. The course must be completed in full within 7 to 10 days, otherwise there will be no desired effect; you can only cause bacteria to become addicted to the active ingredient of the drug.
In this case, rinsing and irrigation are retained as additional effects. It is necessary to rinse 7-10 times a day, irrigate strictly as directed. Older children also use dissolving pills.
As an immunomodulatory and stimulating treatment, you can take drugs such as “Imudon” or “Lizobact”, strictly according to the annotated recommendations and in agreement with the doctor.
Prevention
During the quarantine period, be sure to irrigate your tonsils with any of the above sprays before and after going outside. Wearing a mask, as well as using a quartz procedure after a working day, will not hurt. Since the infection also spreads through the nasal cavity, you can use “Oxolinic ointment” or “Interferon” in drops for no more than 7 days.
At normal times, after going outside, you can rinse your tonsils with herbs, soda or saline solution, irrigate your nose, or do this with a solution of sea salt. And, of course, children should always have clean hands.
Summary
It should be remembered that with untreated inflammation of the tonsils, the child will experience not only the complications described above, but also the “lowering” of the inflammatory process lower into the bronchopulmonary system, which leads to bronchitis and pneumonia. If you stop the above symptoms in the throat at an early stage, there will be no consequences, and accordingly there is no need to treat anyone.
Source: https://GormonOff.com/zabolevanija/vospalennye-glandy-u-rebenka
Symptoms
Inflammation of the tonsils occurs in many diseases. Each of them has its own specific symptoms.
But there are general signs characteristic of damage to the tonsils:
- Bad breath. Small pieces of food are retained on loose lymphoid tissues. They begin to decompose, causing an unpleasant odor. For babies with tonsil hypertrophy, it is important to gargle regularly to flush out any leftover food.
- Pain. The inflammatory process in the throat is often accompanied by painful sensations that intensify when swallowing.
- Changes in the structure and color of the tonsils. Lymphoid tissue turns from pink to red. In a healthy state it is smooth, but when inflamed it becomes loose (bumps appear on its surface). A white coating may also appear.
- Weakness. It is provoked by intoxication of the body associated with the entry of a virus into it.
- Headache. They are provoked by the onset of swelling of the mucous membrane and difficulty breathing.
It is possible to increase body temperature either slightly (up to 37.5°) or up to 39°.
When the first symptoms appear, consult a pediatrician or ENT specialist. Self-medication can harm your child's health.
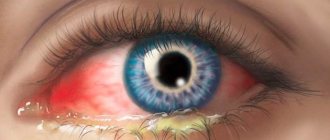
How to treat inflamed tonsils in a child and an adult: photos, symptoms
Inflammation of the tonsils is often called tonsillitis or tonsillitis. This term refers to acute damage to the tonsils of infectious origin. This condition is accompanied by pain of high intensity and requires medical attention.
Inflamed tonsils: physiology
Lymphoid tissues in the nasopharynx and oral cavity form the tonsil glands. They are the main element of the immune system and protect the body from bacteria and viruses that can penetrate the nasopharynx.
When the immune system is weakened, the protective characteristics of the glands are inhibited, and the number of pathogenic microflora increases. As a result, an inflammatory process develops, and inflammation can be either bilateral or separately on the right or left side.
The photo shows signs of inflamed tonsils with sore throat
Possible reasons
The main cause of inflammation is acute tonsillitis, also called tonsillitis. Its causative agents can be microbes that affect the upper respiratory organs - streptococci and staphylococci.
The chronic type of the disease most often appears after tonsillitis, measles, scarlet fever and other anomalies.
The main factors that provoke the appearance of the inflammatory process include the following:
- contacts with infected people or household objects;
- inflammation in the nose and oral cavity, as well as the sinuses - this leads to caries, purulent sinusitis and other anomalies;
- hypothermia;
- harmful domestic and professional conditions.
Provoking factors
There are certain factors that significantly increase the risk of tonsil inflammation:
- insufficient body resistance, weakened immune system, more often this becomes the cause of illness in a child;
- untimely and unbalanced nutrition;
- genetic predisposition;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- traumatic injuries;
- sharp fluctuations in temperature.
Additional symptoms
The development of the inflammatory process is caused by the ingress of pathogenic microorganisms. The first symptoms appear after a few hours or days. These include:
Diagnostics
To identify the pathology and assess its severity, you should consult a doctor. Diagnosis involves examining the oral cavity to determine the appearance of the tonsils. In addition, the doctor performs a survey to find out the clinical picture of the disease.
Inflamed tonsils in various throat diseases
Treatment
To cope with the pathology, you should consult a specialist. The doctor will select medications and recommend traditional recipes that can be performed at home. In some cases, surgical intervention, removal of the tonsils, is required.
First aid
For any form of inflammation, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- isolate the patient - provide him with personal dishes, a towel;
- observe bed rest - this helps speed up recovery and prevent complications;
- give plenty of fluids - teas, decoctions of chamomile, sage, rosehip are good;
- rinse with antiseptic solutions - for this purpose it is worth using lugol, rivanol, furatsilin;
- inhalation – it is recommended to use kameton, ingalipt.
To ensure maximum effect, gargle every hour. An excellent treatment option would be to use a soda solution. To do this, dissolve 1 small spoon in a glass of water. The procedure must be carried out every half hour for several days.
How to treat inflammation of the tonsils, watch our video:
The most popular drugs and methods
Specialists usually prescribe antibiotics from the penicillin category. Similar drugs are required for the development of follicular and lacunar tonsillitis. Sometimes they are used for the catarrhal form of the disease. This category includes drugs such as ampicillin and amoxicillin.
If a person is intolerant to these drugs, the doctor may prescribe doxycycline or cephalexin.
If the disease is severe or complications of the disease develop, antibiotics are prescribed as intramuscular injections. The course of therapy should be 7-10 days.
If you are intolerant to antibiotics or when taking them is not recommended, for example, during pregnancy, your doctor may prescribe antibacterial substances in the form of aerosols. These include ingalipt and hexaspray. You can also use lozenges - for example, faringosept or strepsils.
In addition, it is recommended to gargle 3-4 times a day. This should be done after meals, using medications - chlorophyllipt, furatsilin. To ensure immune support, vitamin complexes must be used.
Traditional medicine helps speed up recovery. For gargling, you can use medicinal plants - chamomile, sage, clover. It is no less effective to use propolis and elecampane.
In addition, an excellent treatment option would be to use warm tinctures to drink. For inflammation of the tonsils, aloe juice mixed in equal proportions with honey is a great help. It should be consumed 1 small spoon once a day.
You can also make jelly from raspberries, currants or elderberries.
Popular drugs for the treatment of throat diseases
Dangerous consequences
If you do not start therapy, there is a risk of such complications:
Forecast
If you start therapy in time, you can completely cope with tonsillitis. If this is not done, there is a risk of the process becoming chronic. This is fraught with a number of complications in the form of heart and joint diseases, inflammatory kidney damage, and impaired nasal breathing.
Inflammation of the tonsils is considered a rather serious disorder that can lead to negative consequences. To prevent this from happening, it is very important to consult a doctor on time and follow his instructions.
Source: https://gidmed.com/otorinolarintologija/simptomu/vospalennye-mindaliny.html
Treatment of enlarged tonsils
If a child has inflamed tonsils in the throat, how to treat them, an ENT doctor or pediatrician will tell you. To prescribe effective drugs, it is necessary to identify the pathogen, since viral and bacterial lesions are treated differently.
In general, local antiseptics are prescribed: sprays, rinses. If necessary, take a course of antibiotics or antiviral drugs. In case of severe swelling, treatment is supplemented with antihistamines.
After acute inflammation has resolved, therapy is supplemented with physiotherapy. For example, laser therapy or magnetotherapy, heating, inhalations.
Inflamed tonsils in a child: how and with what to treat them?
Hello, dear parents! Does your child have inflamed tonsils? What to do? Do not panic, but rather start treatment immediately. Read the article about how to treat this condition.
Sore throat or tonsillitis: why are the tonsils swollen?
Most often, inflammation of the tonsils is caused by tonsillitis or tonsillitis. How to understand what exactly happened? In fact, these are not different diseases, but one, just sore throat is an acute form, and tonsillitis is chronic. The disease is provoked:
• bacteria – staphylococci, pneumococci, meningococci, etc.;
• viruses - adenoviruses, herpes viruses;
• various fungi.
Without a medical examination, you will not be able to determine the exact cause (causative agent), and this is very important for the correct selection of drug treatment. So what should we do then? How to treat?
At home, you can use only the means and methods described in the article on your own, and let the pediatrician select the medications for treatment. And remember, no conspiracies will save your child from chronic tonsillitis, so don’t be foolish, it’s better to immediately start treating normally.
Gargling: a mandatory medical procedure
A child's inflamed tonsils must be rinsed with antiseptic solutions, and if purulent plugs appear in them, then they will also have to be rinsed. How to rinse at home? I recommend you try:
• decoctions of chamomile, sage, calendula;
• solutions of chlorophyllipt and furatsilin (furacilin for children is diluted in the proportion of 1 tablet per 300 ml of water);
• a solution of soda and salt (a teaspoon of both per 0.5 liters of water, if for children).
Rinsing is a safe procedure that should be taught to a child from childhood. The procedure can be carried out both for the youngest (for example, 2 years old) and for older children.
If the child is very small and cannot gargle on his own, then treat the tonsils with antiseptics as follows:
• wrap a bandage around your finger;
• dip into the solution;
• Wipe your mouth and throat with a gentle circular motion.
Nasal drops and children's throat aerosols
Sore throat itself is not a terrible disease, but its complications can significantly harm vital organs (the heart, for example). Therefore, to prevent complications, you need to use nasal drops and throat sprays.
Be sure to consult your pediatrician before using any medication. Most likely, your child will be prescribed:
• into the nose - special salt solutions, such as Aquamaris or oil drops;
• in the throat - Miramistin (you need to use it 3-4 times a day and always after meals).
Are antibiotics needed?
Most often, children's sore throats are provoked by bacteria, or more precisely staphylococci, so pediatricians prescribe antibiotics (specifically penicillin) to almost all patients. Are they really needed?
If the sore throat is bacterial, then you need it, but keep in mind that these are serious and dangerous drugs, so do not self-medicate under any circumstances.
By the way, at the present time, namely after numerous mutations of bacteria, treatment with penicillin antibiotics is effective only in 35% of cases. The bacteria simply got used to the drugs, which is why they stopped responding to them.
But as for children's allergic reactions to penicillin drugs, their number has increased significantly. Therefore, treating children who have any form of antibiotic intolerance with penicillin drugs is strictly prohibited!
Additional therapeutic measures
To speed up recovery and improve the well-being of a little patient, do this:
1. Use the “dry heat” method, but only if the disease occurs without fever. Wrap the throat with inflamed lymph nodes with a warm scarf and let your child not take it off. Small children may resist, so you can tell them that this is a magic scarf that quickly gets rid of illness, so that it is more interesting to wear it.
2. Maintain bed rest - the body needs strength to recover, which means it cannot be physically overloaded.
3. Put the sick person on a special diet - nutrition should be balanced, correct, and safe. You can eat soft foods without spices, for example, porridge, soups, purees. Be sure to give the patient plenty of fluids - compotes, teas, juices.
4. Give antipyretics, but only if the temperature is above 38 degrees. If it is lower, you cannot give pills, since the body must overcome the inflammatory process on its own and develop immunity.
5. Give special throat lozenges or honey to make swallowing easier and relieve pain.
6. Take care of the patient - spend more time with him, read fairy tales, play sedentary games, listen to him carefully. The sick person really needs your care and attention.
Now you know what to do if your child has inflamed tonsils, namely how to treat this condition at home. I hope my advice will help you quickly cure your child.
But keep in mind that a visit to the doctor is mandatory in all cases. You will not be able to notice complications on your own in time and choose the right medications.
Prevention
Healthy tonsils are the key to general health for frequently ill children and children who have started attending kindergarten.
Prevention is especially important for them:
- Multivitamin courses. They are drunk twice a year, for example, in spring and autumn.
- Hardening. It starts in the summer, allowing the child to walk barefoot on the sand and grass. Regular sunbathing, outdoor games, and long walks are also important. You can arrange contrast gargling. They start with water at room temperature and gradually reduce it to cold.
- Courses of antibacterial rinses. For a month, gargle with a decoction of chamomile or sage once or twice a day. Then they take a break for 30-45 days and repeat the course.
- During epidemics of ARVI and influenza, protect your child from visiting large crowds of people. Avoid visiting shopping centers and children's entertainment centers in favor of walks in the fresh air.
You shouldn’t “shake” over your child and turn him into a houseplant. A reasonable approach to hardening will help avoid frequent ARVI and hypertrophy of the tonsils.
When you can't do without surgery
Enlarged tonsils are considered a variant of the normal development of the child’s immune system up to 10 years of age. In recent years, doctors have been trying to prescribe their removal as rarely as possible.
But there are still indications for surgical intervention:
- Difficulty breathing, due to which the child walks with his mouth constantly open. This is what causes the formation of an adenoid type of face with a sagging lower jaw.
- Night attacks of suffocation. The child does not easily snore in his sleep, but also suffers from apnea (loss of breathing for several seconds). This condition not only impairs the quality of night sleep, but is also life-threatening for the child.
- Hearing impairment due to proliferation of lymphoid tissue.
- Constant drowsiness, weakness, decreased cognitive function. Due to enlarged tonsils, the child lacks oxygen, which affects the overall well-being and functioning of the brain.
As a rule, surgery is not prescribed for children under three or four years of age. Since there is a high risk of relapse and the need for repeated surgery.
The optimal age for removal of tonsils or adenoids is 5-6 years.
The operation is performed under short-acting general anesthesia. Long-term hospitalization after it is not necessary. During rehabilitation, a special diet (soft food) is prescribed and a ban on visiting kindergarten for 3-4 weeks is established.