Indications for Nechiporenko analysis in children
Using a urine test according to Nechiporenko, latent leukocyturia can be detected in a child. It is characteristic of chronic, sluggish forms of glomerulonephritis and pyelonephritis. In this course of the disease, leukocytes and red blood cells are not detected in a routine urine test. Identifying the predominance of erythrocyturia or leukocyturia helps to accurately diagnose the baby.
The Nechiporenko test is prescribed for suspected kidney disease, which includes the following symptoms:
- change in the color or smell of urine;
- frequent or infrequent, painful urination;
- pain in the lumbar region;
- swelling on the face;
- poor appetite;
- prolonged elevated temperature.
The analysis is carried out for children with chronic kidney disease to monitor the effectiveness of treatment. The study is not indicated for healthy children.
Increased red blood cells in urine in pathology
In some diseases, the content of red cells in a child’s urine increases significantly. What are the causes of increased red blood cells in a child’s urine? They are usually divided into two groups.
- Causes of diseases of the kidneys, bladder and ureters.
- Reasons: when a child has a pathology of any organ, then the reaction of the kidneys is such that red blood cells begin to enter the urine.
With pathology of the kidneys or excretory system, the number of red cells almost always increases significantly. What does an increase in red blood cells in a child’s urine mean?
Inflammation of the kidney, ureters, or urinary tract (urethra) causes large numbers of red blood cells to enter the urine, and this is called hematuria.
Depending on their quantity, which is determined by the activity of the inflammatory process, it can be:
- microhematuria. When the number of red blood cells in the field of view during microscopic examination of urine sediment does not exceed 20 elements. It is impossible to visually determine their presence, since its color does not change with such a quantity.
- macrohematuria. It is characterized by a very large number of red cells. The urine turns pink or red, making it difficult to count cells.
Inflammation leads to a change in urine acidity (pH), it becomes more acidic due to an increase in the content of lactic, pyruvic, uric and other acids. The impact of acids and toxins that are released on red blood cells causes their structural changes.
Subjected to prolonged exposure to acids and toxins, they change, some of them lose hemoglobin, become colorless, and acquire a spherical shape. In others, toxins and acids change the structure of the membranes, it becomes rough, the cells change shape, shrink, and decrease in size.
If the color, clarity or odor of urine changes, you should immediately seek advice from a pediatrician or pediatric nephrologist.
Inflammatory kidney diseases
If a child has elevated red blood cells in his urine, this most often indicates a pathology of the kidneys or urinary tract with accompanying inflammation.
Escherichia coli
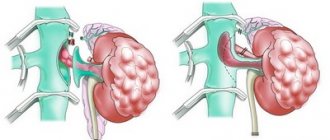
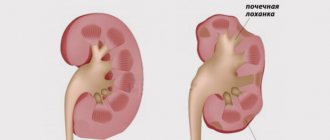
Pyelonephritis. A disease caused by infection, characterized by inflammation of the calyces and pelvis of the kidneys. Most often this pathogen is Escherichia coli, less often (Klebsiella pneumonia, Staphylococcus saprophyticus). Inflammation increases the permeability of cell membranes and pores, so red blood cells enter the urine (diapedesis). The number of red cells is inferior to the number of white blood cells, which can be very high.
- Glomerulonephritis. Autoimmune kidney disease, which is caused by the formation of autoantibodies, i.e. own antibodies (immunoglobulins) against their own kidney proteins. Antibodies bind to kidney proteins, destroying their structure. As a result, the inflammatory process intensifies, the pores of the glomerulus increase, allowing cells to pass through from the blood filtered through the kidneys.
- Cystitis. The introduction of bacteria into the bladder wall causes inflammation, increased permeability and cell release. The child experiences pain during urination.
- Urethritis. Inflammation of the urethral mucosa causes this disease. This may be due to infection of the urethra, followed by inflammation and minor hematuria. During urination, the child experiences pain and pain.
Diseases of the genitourinary system without inflammation
Red blood cells can also be elevated in diseases that occur without inflammation of the tissues of the genitourinary system.
Salts or stones in the kidney or excretory system. In young children, it is extremely rare for salts to be deposited or stones to form in the kidney or urinary system. But, if this is observed, then salts and stones can damage the mucous membrane, and red blood cells are released into the urine.- Tumors. The occurrence of a tumor, its growth and germination into tissue with damage to the blood vessels of the kidney, bladder or ureter is the cause of hematuria.
- Injury. After surgery on the kidney or urinary tract, hematuria may occur. Also, the injury received by the child serves as a source of blood.
The appearance of red blood cells in the urine can also occur due to diseases of other organs of the child. In this case, their release is called “reactive hematuria” because it is caused by the kidneys’ reaction to the disease.
Diseases that cause the formation of toxins
In some pathologies, toxins are formed, released by bacteria, viruses, and parasites, which negatively affect all organs and tissues of the child, including kidney tissue.
- Acute respiratory diseases. The introduction of a virus (influenza) or bacteria (pneumonia) leads to an increase in temperature (38-40°C), which causes hematuria.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Infectious diseases, which are characterized by the introduction of bacteria that cause dysentery, salmonellosis, typhoid fever, cholera, occur with elevated temperature, high intoxication with waste products of bacteria, causing hematuria.
- Sepsis. The entry of pathogenic microflora into the bloodstream leads to damage to the body with severe intoxication, contributing to hematuria.
- Purulent foci of inflammation. Abscesses and phlegmons occur as a result of bacterial infection and are accompanied by inflammation and sometimes hematuria.
- Osteomyelitis. A severe infectious disease of the bones, in which purulent foci are formed that secrete toxins. Intoxication is the cause of hematuria.
After recovery, it is necessary to take a morning urine test two weeks later to confirm the result of successful treatment.
Some kidney pathologies, for example, glomerulonephritis, are asymptomatic. A urine test can only show the presence of a slightly increased number of red blood cells.
Therefore, the pediatrician sometimes prescribes additional examination methods, which include ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and less often resort to biopsy (endoscopic analysis of a small piece of kidney tissue) using ultrasound or CT as a control of the procedure.
Preparing children to take a urine test according to Nechiporenko
You need to prepare for a urine test 24 hours in advance. Preparation rules:
- exclude beets, carrots, and protein foods from the diet;
- If possible, stop taking medications;
- limit physical activity.
It is not advisable to take the Nechiporenko test against the background of acute respiratory infections. Teenage girls should not have the test during their periods.
Formula-fed babies are fed as usual. New complementary foods should not be introduced on the eve of the study. If the child is breastfed, the mother should follow the diet. She needs to exclude protein foods, spices, colored vegetables and fruits from her diet.
Rules for collecting urine in children
Urine is collected from the middle portion. The baby releases the first portion into the potty or toilet, then the parent places a sterile container under the stream of urine and collects a little liquid. If the baby does not yet know how to voluntarily hold urination, let him urinate as usual. The parent should place the container a few seconds after the start of urination, draw some liquid and remove the container.
Before collecting urine, the child should be washed with clean water. The girls are washed from front to back. A sample is taken in the morning, immediately after waking up. The container with the collected urine is delivered to laboratory technicians no later than two hours after the sample is taken. Urine should be warm and should not be stored in the refrigerator.
What does urine analysis according to Nechiporenko show in children?
Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko in children shows the number of red blood cells, leukocytes and cylinders in 1 ml of urine. By the predominance of one or another indicator, one can judge the child’s illness.
If, as a result of urine analysis according to Nechiporenko, leukocytes predominate, this indicates a bacterial infection, most often pyelonephritis. The predominance of red blood cells indicates damage to the renal glomeruli - glomerulonephritis.
The interpretation of urine analysis according to Nechiporenko in children is carried out by a doctor, taking into account the data of other examinations. If deviations occur, additional examination is prescribed:
- blood chemistry;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
The doctor may prescribe tests for infections and autoimmune diseases.
Interpretation of urine analysis according to Nechiporenko in children
Parents can independently evaluate the result of a urine test by comparing it with the norm. The table shows the norms for urine analysis according to Nechiporenko in children.
| Index | Norm for children per 1 ml of urine |
| Leukocyte | Until 2000 |
| Red blood cells | Up to 1000 |
| Cylinders | Up to 20 |
The decision on diagnosis and subsequent treatment is made only by the doctor. Deviations from the norm are not always pathological. To make a diagnosis, it is necessary to compare the existing symptoms and the data of all examinations.
The norm of leukocytes in the analysis according to Nechiporenko in children
Leukocytes are white blood cells that are responsible for the functioning of the immune system. When inflammation occurs in any part of the body, they accumulate there and destroy microbes. The main part of them is in the blood. The norm of leukocytes per 1 ml of urine in children is up to 2000.
Study of urine using the Nechiporenko method: all the nuances
If the general analysis shows average results of the main parameters of urine and is prescribed for both therapeutic and preventive purposes, then urine testing according to Nechiporenko is performed only if any indicators of structural elements identified during the first study are abnormal. The method makes it possible to detect even hidden latent diseases of the urinary system and provide a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s condition.
Preparation
To get a reliable result and avoid repeated research, you need to properly prepare for it. There are a number of simple norms and rules on how to collect urine according to Nechiporenko from pregnant women, which you need to know about in advance.
Diet
A few days before the due date, it is important to change your diet, completely eliminating hot seasonings, spices, salt, as well as foods high in protein and carbohydrates. At the same time, you need to limit as much as possible the consumption of fried, fatty foods, smoked foods, marinades and meat
You should drink more, and clean water without gas is best for this. Drinking alcohol or light alcohol-containing drinks is strictly prohibited. Hygiene regime. To collect and transport urine, you must purchase a disposable container from the pharmacy in advance. An alternative can be a sterilized glass or plastic container. Before collecting the material, wash the external genitalia with warm water using baby soap. It is prohibited to use products with strong fragrances and chemical additives. After this you need to wipe yourself dry. Rest mode. To prepare high-quality biomaterial, the body must be rested. This means that you need to ensure proper sleep, eliminate physical activity, nervous strain, and avoid stress. Medications. A few days before the procedure, it is necessary to stop taking medications, including diuretics, dietary supplements, vitamin-mineral complexes, of course, having agreed on this measure with the gynecologist.
Doctors warn in advance that the accuracy of the results largely depends on the correct collection of biomaterial. The antenatal clinic will tell you how to collect urine for pregnant women for analysis according to Nechiporenko.
- Immediately after waking up, you need to perform hygiene procedures, and only then begin collecting urine. Since pregnant women often secrete mucous secretions, it is advisable to use a cotton swab to prevent it from getting into the biological fluid.
- Flush the first portion of urine into the toilet, then, without stopping the emptying process, fill the container. There is also no need to collect the remainder. This point is especially important, because the study evaluates not the condition of the urethra, but the function of the kidneys and bladder.
- Close the container with a lid and deliver to the laboratory no later than 1.5-2 hours after collecting urine. After this period, bacteria and pathogenic microorganisms will begin to multiply in it, which will lead to data distortion.
Preparing material for research using the Nechiporenko method is not difficult if you listen to advice and strictly follow the recommendations. The diagnostic value is due to its high reliability, which makes it possible to identify even asymptomatic pathologies, which often worsen during pregnancy.
Decoding
If the interpretation of the results indicates deviations from the norm, then this indicates a hidden pathology that must be urgently identified and therapeutic measures initiated. In some cases, after a urine test according to Nechiporenko, the doctor may encounter atypical readings in pregnant women.
The leukocyte level is more than 4000 units. Indicates the development of an inflammatory process. The higher the score, the more severe and serious the disease. It can negatively affect the physical condition and cause an increase in body temperature, pain, and the appearance of signs characteristic of cystitis and pyelonephritis.
The number of red blood cells exceeds 1000 units. This indicates acute glomerulonephritis, the formation of a tumor, stones, damage to the membranes of the bladder or excretory ducts. Characterized by symptoms of infection.
The level of the cylinders is above 20. The most dangerous indicator, since it indicates the development of severe renal pathology - organic damage, which often leads to complete failure of the kidneys.
Even if there are serious deviations in the test results, you should not panic; you must follow the recommendations of your doctor. This will help normalize your well-being and avoid the development of complications.
What do deviations from the norm indicate in urine analysis according to Nechiporenko?
Deviations from the norm in urine tests according to Nechiporenko in children indicate the development of the disease or are associated with violations of sample collection. Only a doctor can correctly determine what the analysis shows, evaluate the norm and give an interpretation of the result.
Leukocytes
An increase in leukocytes in the urine of a child indicates the development of an inflammatory process. Most often it is of bacterial origin. If you receive such a result, you should think about pyelonephritis or a complication of urolithiasis. Purulent inflammation of the kidneys with the formation of abscesses is rare in children.
White blood cells may appear when there is a disease of the bladder or urethra. Common causes of increase are cystitis, urethritis, chlamydial infection.
Red blood cells
A high level of red blood cells in the urine indicates excessive permeability of the blood vessels of the kidneys. This happens with autoimmune inflammation - glomerulonephritis. Red blood cells increase with kidney injuries and urolithiasis.
Cylinders
Elevated cylinders are rare in children. They talk about damage to the renal tubules, when their epithelium is quickly exfoliated. This happens with inflammation, injury, cysts and kidney tumors, and poisoning with drugs or heavy metals.
Red blood cell casts contain red blood cells. They are formed during vein thrombosis or destruction of kidney tissue. Granular casts contain a lot of desquamated epithelium. They appear with severe glomerulonephritis. Waxy casts are dense protein casts. Formed during amyloidosis and renal failure.
Deviations of indicators and possible consequences
As mentioned above, deciphering a urine test according to Nechiporenko reveals the current levels of leukocytes, red blood cells and casts in the biomaterial. An excess of at least one of the parameters, confirmed, if necessary, by repeated tests without identifying external and physiological causes, may indicate a pathological condition in the form of leukocyturia, erythrocyturia or cylindruria with its own possible diseases.
Leukocyturia
In the general classification, it is an overnormalized content of leukocytes in urine. It can have a different character, from neutrophilic and mononuclear to lymphocytic and eosinophilic. Potential pathological causes of the development of leukocyturia are usually associated with infectious or non-infectious lesions of the urethra, bladder, ureters, individual parts of the kidneys, as well as the organ as a whole.
In addition, a high level of leukocytes is typical during severe pregnancy, shock physical and psychological stress, poor nutrition, and also during the active phase of the menstrual cycle. All of the latter circumstances described above can be attributed to physiological reasons that do not require special correction. The most typical pathologies in the context of the presence of leukocyturia are diseases such as pyelonephritis, cystitis, renal infarction and urolithiasis.
Erythrocyturia
In the general clinical understanding, erythrocyturia is a classic hematuria, indicating high concentrations of red blood cells in the urine that do not correspond to basic physiological norms. It is erythrocyturia that most often acts as a secondary symptom of damage to the urinary tract and kidneys.
The main physiological and external reasons for the formation of an increased level of red blood cells in the urine may be prolonged fasting, dehydration, as well as severe physical or psychological stress and injury. The most common pathological conditions are acute forms of thunderonephritis, nephrotic syndrome of various etiologies, and renal infarction.
Cylindruria
One of the most important diagnostic parameters of urine analysis according to Nechiporenko is the presence of an increased content of casts in the urine. In the general clinical understanding, casts are the basic residual “casts” of protein or cellular elements that form in the lumens of the renal tubules. In the vast majority of cases, the urine of a healthy person does not contain these components, or their amount is insignificant.
It should also be noted that there are different cylinders, so the presence of certain types of them in biological material may indicate specific pathologies:
- Hyaline elements. Their excess above the norm can be considered a sign of pyelonephritis, hypertension, or systemic uncontrolled use of diuretics;
- Grainy elements. Their excess concentration in a urine test according to Nechiporenko may indicate the presence of a viral infection in the body or severe lead poisoning;
- Waxy elements. They are a secondary product of the metabolism of the granular and hyaline components indicated above. Normally, they are completely absent in the urine, and their presence indicates severe chronic renal failure, complex nephrotic syndrome, or amyloidosis;
- Erythrocyte elements. Appear in the analysis due to the strong permeability of the vascular walls of the renal glomeruli. The presence of such components may indicate acute forms of nephritis, malignant hypertension or thrombosis of the renal arteries;
- Epithelial elements. They are the end product of the death of the internal structures of the epithelium of the renal tubules. Most often it manifests itself in complex tubular necrosis, the systemic influence of acute viral infections, as well as in cases of poisoning with phenol, ethylene glycol or heavy metals.
Possible distortions of the results of urine analysis according to Nechiporenko in children
Inflated test results according to Nechiporenko do not always indicate a disease. Distortions are possible if urine is collected incorrectly according to Nechiporenko, the sample is stored for a long time, or lack of preparation before taking the test. The result is influenced by:
- intense physical activity on the eve of the procedure;
- eating large amounts of protein foods;
- trauma to the urethra;
- menstruation in girls;
- insufficient hygiene procedures before collecting urine;
- long-term storage of the sample container.
In this case, the results are at the upper limit of the norm or slightly exceed it. The doctor will recommend retaking the test, following the rules for preparing and collecting urine.
Red blood cells in the urine of a healthy child
The norm of red blood cells in a child’s urine should be no more than four elements upon microscopic examination of its sediment. Morning urine is centrifuged (10-15 ml) for 10 minutes, obtaining a small sediment. Then the resulting sediment is dissolved in a small amount of urine (0.2-0.5 ml) and examined microscopically, calculating the number of red blood cells that are visible in the field of view.
Before collecting urine for analysis, it is necessary to properly prepare the child so that the result is reliable. During preparation, it is necessary to stop taking certain vitamins (B12), medications (aspirin, heparin, penicillin, cyclophosphamide, phenazopyridine). It is necessary to reduce the consumption of increased amounts of protein in food and protect the child from excessive physical activity and stressful situations.
If the rules for preparing a child for collecting urine for analysis are not followed, there may be an incorrect result, a change in its color, or provocation by drugs of filtering an increased number of red cells into it.
Collection of analysis from infants
It is difficult to collect a urine test from infants, because they do not yet know how to urinate in a potty. For the Nechiporenko study, a medium portion is needed, and this makes urine collection even more difficult.
You can use a urine bag to collect urine from an infant. This is a plastic container that is glued to the crotch. First, the child is washed, then a urinal is placed so that it covers the urethra. When the baby urinates, the container is peeled off and the urine is poured into a container. This method can only collect all the urine without dividing it into portions.
To collect the average portion, you need to undress the baby and put him on the changing table, laying down an oilcloth. Have a container ready. When the child begins to urinate, place the container under the stream of urine. It is easier to collect urine from boys. The Nechiporenko analysis makes it possible to distinguish between hidden glomerulonephritis and pyelonephritis. The method is used to count the number of red blood cells, white blood cells and casts in 1 ml of urine. It is prescribed when there are difficulties in making a diagnosis. The urine collection algorithm should be followed to avoid false results.