Hello, friends! Today I want to talk about what parents should do if their child eats salt. The fact is that my own daughter, Christina, often sins with this. The child eats salt while other kids feast on sweets and candies. The salt shaker can be found anywhere in her room - on the desk, on the windowsill, near the computer. This didn’t cause me much concern, but still I decided to look at the information about what this might be connected with and share what I found with you, dear readers. So, what are the reasons for the phenomenon when a child eats salt? Let's figure it out.
The benefits and harms of salt
Speaking about salt, it is impossible to say unequivocally whether it is beneficial or harmful, since in small quantities it benefits a person. But abuse can cost a person his life.
Why is salt useful?
- Sodium in salt maintains normal fluid reserves in the body. It is needed for normal muscle function, as well as for conducting nerve impulses to the brain. Its deficiency can cause drowsiness and weakness.
- White seasoning also contains a lot of chlorine. It is necessary for good stomach function. With a deficiency of chlorine in the body, the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted.
How salt can harm you:
- Salt retains fluid in the body, which increases the load on the urinary system, swelling can occur in a person, and salts can be deposited under the skin.
- Abuse of “white death” is fraught with an increase in blood pressure, and hence the development of hypertension, the terrible consequence of which can be a stroke.
- Excess salt in the human body disrupts the functioning of important organs such as the kidneys and liver.
- Salt has a stimulating effect on the human nervous system, often causing irritability and nervousness.
- Excess salt promotes the removal of calcium from the body, which has a harmful effect on bone health.
- Due to the abuse of this ingredient, taste buds atrophy and become less sensitive. The tastes of food seem “uninteresting”, bland.
Harm or benefit?
Why does a child eat a lot of salt? There has long been debate about whether salt is healthy at all. And even more so for a child. There is no definitive answer yet. There are many people who have completely given up salt. But this is not true either, because it also brings benefits.
Salt contains sodium chloride, and it also has a positive effect on muscles, including the main one - the heart. It is thanks to the correct and coordinated functioning of the heart that blood circulation in our body is possible; normal functioning of the body is simply impossible without salt balance.
Nature also intended that salt is necessary for all living organisms. You can observe how herbivores lick salt outlets; if salt does not enter their body from the outside, then the body will take it from the internal organs.
The saying “everything should be in moderation” also applies to salt. In case of excessive use, negative consequences may occur. It has been noted that people who consume a lot of salty foods have problems with blood pressure, and the functioning of the urinary and cardiovascular systems is disrupted.
But let's get back to the children. Actually, salt itself is not dangerous for a child. Excessive consumption is dangerous; it can lead to health complications. Of course, you can prohibit your child from eating salt, but it is more important to find the reason for such taste preferences.
At what age can children salt food?
When to introduce salt into a child's diet? Children also need sodium and chlorine to fully develop. But nature took care of them too. The very first particles of these microelements begin to reach babies through mother's milk. Yes, breast milk, as well as formula milk, also contains sodium! What to do with complementary foods: should you salt them?
Until the age of 9 months, not only do babies not need to add salt to their food, but it is even forbidden to do so. Otherwise, the pancreas and kidneys may simply not cope with the load!
After 9 months of life, you can (but not necessarily!) add a little salt to complementary foods. At the same time, you should not trust your taste and focus on it. The dish should not taste salty.
Dr. Komarovsky does not deny the need to add salt to complementary foods after this age, but he clarifies that babies’ need for salt is much less than that of adults. Keep this in mind when trying to make baby food “tastier.”
It is important to remember that once you teach a child to eat salty food, it will later be very difficult to retrain him to eat bland food. Therefore, many experts advise not to add too much salt to children’s food. For a small portion of baby food, just a few crystals of white seasoning are enough. The inability of the enzyme system to absorb salt is one of the reasons why infants should not eat salt.
Can a child eat salty, sweet and fatty foods?
Authors : American Academy of Pediatrics
Coercion, as we know, does not work when it comes to preventing children from eating certain foods. Just as, by and large, bans on certain foods do not work. Moreover, a product prohibited by parents becomes more desirable.
Therefore, both children and adults should remain sensible and tolerant of the wishes of others when consuming certain foods and drinks. Naturally, you should try not to overdo it with any of them. Just remember that even sweets and high-fat foods are acceptable in your diet. Of course, in moderation.
Healthy eating for a healthy heart!
All parents should remember that childhood is the best time to reinforce healthy eating habits in their offspring, but adults should take into account that it is not advisable to limit the amount of fat in the diet of children under 2 years of age. So expand your child’s menu as much as possible from an early age - try different foods with different tastes.
Fat is an integral part of a child's diet
It is fats that provide children with the calories they need as a source of energy for growth and active life, so the amount of different fats in the children's menu does not need to be as strictly limited as in the diet of adults.
The dangers of saturated fat
However, excessive fat intake in children, especially diets high in saturated fat, can cause health problems, including cardiovascular disease, later in life. Saturated fats are those that are solid at room temperature. They are found in fatty meats (beef, pork, veal, lamb) and many dairy products (whole milk, cheese, ice cream).
Healthy, low-fat, low-cholesterol foods for children over 2 years of age:
- Domestic bird;
- fish;
- lean meat (grilled, baked or stewed, but not fried);
- soft margarine (instead of butter);
- low-fat dairy products;
- vegetable oils low in saturated fat;
- eggs (in limited quantities).
General rules for consuming fats
Fat should make up less than 30% of the calories in your child's diet, with no more than one-third of that coming from saturated fat. The rest is unsaturated (polyunsaturated or monounsaturated) fats, that is, those that remain liquid at room temperature and include vegetable oils such as corn, safflower, sunflower, soybean and olive.
Parents often find information about different types of fats confusing and incomprehensible. To put it simply, oils and fats of animal origin are saturated. The easiest way to start eating healthier is to reduce the amount of fatty foods of all types in your family's diet.
Everyone knows that whole milk is recommended for children from 12 to 24 months. However, your doctor may recommend low-fat or low-fat (2%) milk if your child is obese, overweight, or has a family history of high cholesterol or heart disease. Talk to your doctor or dietitian before switching to skim milk.
Offer low-salt foods to children
Table salt, or sodium chloride, actually improves the taste of some foods. However, researchers have found a link between excessive salt intake and high blood pressure in some people. Hypertension affects at least 25% of the adult population and is the leading cause of heart attacks and strokes.
Remove the salt shaker from the table!
Adding salt to food is a bad habit that develops through imitation of adults. Therefore, offer your child low-salt foods, add a minimum amount of salt to dishes during cooking, using more herbs, spices, and lemon juice. Also, remove the salt shaker from the dinner table, and if one of the family members cannot refuse salt, then have him add it by taking it out of the kitchen cabinet.
Check sodium levels in foods
Be sure to read labels to find out the amount of salt in:
- processed cheese;
- instant puddings;
- canned vegetables;
- canned soups;
- sausages and boiled sausages;
- cottage cheese and snacks;
- salad dressings;
- pickles;
- breakfast cereals;
- potato chips and other snacks.
Sugar is a sweetener and preservative
The choice of caloric sweeteners is wide ranging from simple sugars such as fructose and glucose to cane sugar, molasses, honey and corn syrup. Although sugar is primarily used as a sweetener, it can serve other functions. For example, sugar preserves foods, changes the texture of dishes, enhances flavor, and adds color.
Main energy supplier
Sugar in food, whether it is initially contained in them or added later, provides their caloric content - serves as “fuel”, which supplies the energy necessary for daily activities. Therefore, if you give children free rein, they will want to eat sweets for breakfast, lunch and dinner - many scientific studies prove that people have an innate craving for sweets.
Too much sweets - too many calories
Parents should keep in mind that sugar is absorbed very quickly, which means that its excess consumption can lead to excess weight if the child does not expend energy during outdoor games and sports. In addition, the negative role of sugar in the development of caries in children and adults has long been proven by science.
published 04/08/2016 16:17 updated 02/14/2018 — Nutrition, vitamins
How much salt should children have?
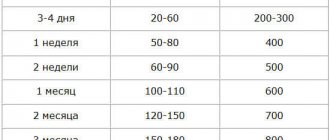
We figured out whether salt is ok for babies. Let's look at the table that shows the daily salt requirements for children:
| Age | Number of grams per day |
| 9 months | 0,2 |
| 10-12 months | 0,35 |
| More than 1 year | 0,5-1 |
| 3 years | 2-3 |
Please note that this is the maximum permissible amount of ALL salt entering the body of a newborn, including complementary feeding products (including cheese, cookies, bread, etc.).
As can be seen from the table, at the age of 9 months the daily requirement of the child’s body for this ingredient is 0.2 grams. It is noteworthy that exactly this amount of white seasoning is supplied to the baby through mother's milk. Therefore, breastfed children do not need to add salt to their food at 9 months, but it is better to start doing this at 11-12 months.
After 1 year of the baby’s life, the mother can gradually add salt to vegetable purees, soups, cereals and meat.
Types of salt
Such an unremarkable product as salt comes in several types:
- Depending on the degree of purification, it is divided into purified and unrefined. The second type is better known to us as rock salt.
- Depending on the size, salt can be coarse or fine.
Table salt is very familiar to consumers. It is affordable but low in minerals.
Rock salt is mined in mines. Its appearance is unattractive, but it is rich in useful minerals.
Sea salt is of sea origin. It is even more useful than stone. Its unusual subtle taste attracts gourmets. But it is not advisable to use it for children under 5 years of age, because... The child’s body is simply not able to digest all the wealth of minerals contained in sea salt.
Iodized salt is saturated with iodine ions. But not everyone can use it. It is recommended for use by residents of regions with radiation contamination (for example, Belarus). Before giving your baby iodized salt, you should consult an endocrinologist. You need to salt the prepared dish with this salt, because... During heat treatment, iodine evaporates.
A child eats salt: should parents worry?
All children are different: some are noisy and active, others are quiet and thoughtful. Some people like to be the center of attention, always inventing and creating something, others prefer quiet, calm games surrounded by familiar people whom they trust. But, probably, every mother will be able to tell something special about her child, something that distinguishes her baby from millions of others... For example, let’s take this case: a group of kids gathered, fruits, sweets and candies were put on the table. But one baby suddenly disappeared into a separate room, and while other children were enjoying sweets, this child was eating salt from a salt shaker, which he managed to grab from the kitchen. We don’t know whether such phenomena often happen among children, but the fact itself is quite interesting, so let’s figure out what’s what.
Child eats salt: possible reasons
So, if your child eats salt at a time when others prefer sweets, it’s time to wonder if everything is okay with your baby’s health. There is no need to worry too much; an increased desire to eat salt can be caused by several reasons:
1. During pregnancy, my mother preferred everything salty. And mom craves salty foods due to decreased kidney activity, and salt in this case is additional nutrition for the organs of the urinary system.
2. If a large share of a child’s diet is occupied by plant foods rather than meat, then the child may well eat additional salt. This is akin to the instinct of herbivores, who happily lick table salt and burnt ash, replenishing the lack of organic sodium. If there is no additional salt intake into the body, the animal may simply die, since the salt reserves will be completely used up from the tissues.
Consequences of high salt content in children's bodies
However, increased salt content in the body threatens problems with blood pressure and hypertension in the future. A large amount of salt can corrode the oral mucosa and cause a lot of unpleasant sensations in the child, so it is imperative to monitor the child’s general well-being and control the amount of salt he consumes. For cooking, you should not use regular table salt; it is better to replace it with unrefined rock or natural sea salt. Salt should be added to food after the dish is cooked, since during heat treatment some of the beneficial elements of sea salt are lost.
And finally, take a closer look, maybe you yourself are provoking a persistent salty habit in your child? Does he often eat chips, crackers, hamburgers and other equally unhealthy foods? This kind of food is very harmful for a child; it is completely unsuitable for a child’s diet. In addition, such dishes usually contain a high amount of salt, and if a child gets used to such a diet, it will be difficult for him to accept other taste sensations.
Let's sum it up
There is salt in every home. This essential product is not just a food additive, but a source of sodium and chlorine. At what age can a baby try salty foods? Children under one year old receive their first doses of salt from breast milk. Therefore, up to 10 months there is no need to salt baby food. And after 10 months, you can add a little salt to your baby’s food. An allergy to salt in an infant is a very rare but dangerous phenomenon. If a child develops a rash, asthma attacks or other allergic symptoms, it is necessary to stop adding salt to food and consult a doctor.