Sometimes an ultrasound reveals that the fertilized egg has a deformed shape.
This diagnosis does not always indicate an abnormal course of pregnancy and fetal development. Only together with additional factors can this become an indication for abortion. In addition, everything depends directly on the type of deformation.
The main reason for the development of deformation of the ovum is the increased tone of the uterus. A significant reduction in the walls occurs for various reasons: stress, the presence of infections or inflammatory processes, hormonal imbalance, diseases of internal organs, etc.
To eliminate pathology, agents are used that help relax the muscles of the uterus (magnesium, magnesium, etc.). It is also important to completely stop sexual activity, avoid physical activity and stressful situations. The patient is prescribed semi-bed rest and complete rest. Such measures make it possible to maintain pregnancy, provided that the fetal heartbeat is heard.
Pathology of the ovum
One of the first signs of pregnancy is the presence of a fertilized egg in the uterus. It consists of the embryo and its membranes (membrane). The first trimester of pregnancy is the most important stage in the development of the unborn child; it is during this period that diagnosis is based on studies of the ovum.
The size and growth of the fetal egg are analyzed during an ultrasound examination. The main indicator is the SVD (average internal diameter of the ovum), in accordance with the size of which the gestational age is determined.
The fertilized egg should normally have a spherical or oval shape, its size corresponds to the established period of pregnancy and the age of the embryo.
However, in some cases, at the beginning of pregnancy, diagnoses established during an ultrasound examination may become a cause for concern for women: an irregularly shaped gestational sac, a large gestational sac, an elongated gestational sac, etc. How dangerous is this or that pathology of the ovum and whether it poses a threat to the health and life of the mother and unborn child, we will try to figure it out in this article.
Irregularly shaped ovum (deformed ovum)
The diagnosis of “irregularly shaped fertilized egg” should not be perceived by the expectant mother as a death sentence. Despite its frightening name, this condition is not a pathology that inevitably leads to termination of pregnancy or to any disturbances in fetal development. In images obtained during an ultrasound examination, this condition looks like an elongated fertilized egg. Serious concern can only be caused by a combination of certain factors against the background of the abnormal structure of the fetal egg.
The main reason for the appearance of such a pathology as an irregularly shaped fertilized egg is an increase in the tone of the uterus due to a number of factors that
Source
Symptoms
A fertilized egg without an embryo does not have clear symptoms. But despite this, certain features can be identified in the clinical picture that make it possible to suspect obstetric pathology. As a rule, we are talking about the following manifestations:
- The size of the uterus does not correspond to the gestational age.
- Signs of pregnancy gradually disappear.
- Uterine tone is reduced.
- Scanty bleeding from the vagina appears.
During a dynamic gynecological examination, the size of the uterus does not grow, as is normal, but, on the contrary, decreases. Cyanosis of the mucous membrane of the cervix and vagina disappears. Rectal temperature also decreases.
If a non-developing embryo lingers in the uterine cavity for a long time, then complications arise. First of all, we are talking about a blood clotting disorder (coagulopathy or DIC syndrome). In this case, increased bleeding occurs from various parts of the body and internal organs, which is difficult to stop. The second danger is infection of the mummified ovum and the development of endometritis.
large gestational sac beyond gestational age
Fertilized egg size
The union of a male cell with a female cell is considered the first stage of pregnancy development. The resulting embryo and its membrane are called the fertilized egg in medicine. The sperm that lands on the egg fertilizes it, and it begins to multiply by division. As the number of cells in the fertilized egg increases, the size of the embryo itself increases. In addition to division, the embryo moves internally through the fallopian tube. Ultimately, the fertilized egg attaches to the walls of the uterus.
It takes approximately seven days for a fertilized egg to reach the uterus. The nutrients of the egg itself do not allow it to die before implantation in the uterus. The woman's uterus is also preparing to receive the fertilized egg. The mucous membrane of the uterus becomes thicker, and this is what the egg will feed on until the placenta forms. The process of placenta formation begins immediately after the egg attaches to the walls of the uterus. The surface of the fertilized egg is covered with villi, which liquefy the mucous membrane and penetrate into the desired location. At the site of attachment, the walls of the blood vessels burst, and the mucosal area fills with blood.
The appearance of a fertilized egg in the uterus can be seen on an ultrasound 2 weeks after a delay in a woman’s menstrual cycle, and means a normal pregnancy. The appearance of an embryo on ultrasound can be expected by the fifth week. If the embryo is not visible on ultrasound by this time, most likely the fertilized egg is empty. Usually, doctors prescribe a repeat examination after some time to confirm the results of the absence of an embryo.
At about 6-7 weeks after the delay of menstruation, the embryo begins to have a heartbeat. By this time, various complications are possible. In the absence of an embryo, doctors state that there is no
The fertilized egg is smaller than
Source
Development and structure
The growth of the fertilized egg begins from the moment of conception. The fertilized egg begins to move through the fallopian tube, during which cell fragmentation occurs. Making its way to the uterus, the fertilized, crushed egg needs nutrients and oxygen, so after a week a chorion begins to form on top, which subsequently transforms into the placenta.
The surface of the chorion has villi, which help the formation to attach to the uterus. In the future, these villi are contained only at the site of implantation of the formation into the uterine wall. The rest of the structure loses lint and remains smooth. The chorion provides the fetus with all vital functions, one of which is protection against infections.
Twenty days after menstruation, during a hardware examination, you can see the yolk sac, which is designed to provide the fetus with nutrients. The presence of a yolk sac in the fertilized egg does not guarantee a normal pregnancy, but if it is absent, this indicates pathology. Inside the shell, surrounding
The embryo contains the amnion, a hollow sac that produces the optimal environment and amniotic fluid for the development of the child.
Often, during an examination, an ultrasound specialist may detect a second fertilized sac. In this case, the woman can be congratulated, as she will have twins. Such a pregnancy develops when simultaneous fertilization occurs
two eggs or the development of two zygotes from the same egg.
If a woman is expecting twins, the fertilized egg may form one or two placentas at the time of division. If the moment of attachment of the egg to the uterus occurs after 8-13 days from the day of fertilization, then 2 fetuses and one placenta are formed for two. This means that both fetuses will develop in the same amniotic sac. If division occurs earlier than this period, then each embryo will develop in its own fertilized egg.
Fertilized egg 4 mm gestation period
Fertilized egg and changes in its size
If a doctor, during an ultrasound examination, tells a woman that she sees a fertilized egg in the uterine cavity, then you can congratulate this patient, because in nine months she will become a mother. The presence and size of the fertilized egg can be determined by ultrasound as early as the seventh to ninth day of a missed period.
If the fertilized egg is located in the uterus, therefore, the pregnancy is normal. The specialist immediately determines the size of the fetal egg by timing, its shape and location. In addition, he will pay special attention to whether there are detachments or other pathological conditions.
The fertilized egg is a round or oval body, the diameter of which is several millimeters. During the first ultrasound, the size of the fetal egg is measured (4 mm is usually the diameter of the egg on the first ultrasound of most women). Given its size, the doctor can determine the gestational age. However, in some situations the error in detection ranges from one to one and a half weeks. Therefore, when trying to set a deadline, a specialist must also take into account the coccygeal-parietal size indicator.
Already in the third to eighth weeks of pregnancy, the fertilized egg resembles an oval or ball-shaped formation.
In the fifth to sixth weeks, the yolk sac, which provides nutrition to the embryo and performs a hematopoietic function in the earliest stages of embryonic development, resembles a vesicle located inside the fertilized egg. At this stage, the fertilized egg normally measures from one and a half to two and a half centimeters. You can examine the embryo already at this time. It resembles a five-millimeter strip located near the yolk sac. At this time, it is not yet possible to determine which part and structure of the fetus, but a heartbeat is already being recorded. At this time, the heart of the unborn baby beats with a frequency of 150 beats
Source
What does a fertilized egg look like?
Having learned about their pregnancy, many curious expectant mothers begin to ask the doctor questions about how and at what stage the fertilized egg is visible and what it looks like. We will try to answer them.
The fertilized egg, the diameter of which is very small in the first days of pregnancy, can be seen within two to three weeks after a missed period. The formed structure in most cases is located in the upper part of the uterine cavity, has a dark (gray) tint and a round or oval shape. The embryo at this time is still microscopic in size, so it is not detected by ultrasound.
Deformations of the ovum and developmental abnormalities
This diagnosis does not always indicate an abnormal course of pregnancy and fetal development. Only together with additional factors can this become an indication for abortion. In addition, everything depends directly on the type of deformation.
The main reason for the development of deformation of the ovum is the increased tone of the uterus. A significant reduction in the walls occurs for various reasons: stress, the presence of infections or inflammatory processes, hormonal imbalance, diseases of internal organs, etc.
To eliminate pathology, agents are used that help relax the muscles of the uterus (magnesium, magnesium, etc.). It is also important to completely stop sexual activity, avoid physical activity and stressful situations. The patient is prescribed semi-bed rest and complete rest. Such measures make it possible to maintain pregnancy, provided that the fetal heartbeat is heard.
Abnormal development of the fertilized egg
In addition to deformation of the fertilized egg, the development of any anomalies is possible. Many of them can cause miscarriage or fetal death. The most common anomalies are presented below.
1. If there are two embryos in the fertilized egg, then this is not an anomaly, but rather the norm for the development of twins. The sizes of embryos may differ from each other. A difference of several millimeters is most often characteristic of monochorionic twins. However, at an early stage it is impossible to accurately determine whether the children will be twins or twins.
2. Small fertilized egg. This pathology is diagnosed by comparing the gestational age and the size of the ovum. Such studies help determine the correct development of the fetus in the uterus. The gestation period is also determined by the size of the fertilized egg. It is necessary to carefully monitor the development of the fertilized egg; too slow growth may indicate
Source
Causes and mechanisms
The causes of undeveloped pregnancy are diverse and complex. It is difficult to single out one factor that has the greatest impact on a woman’s body before and after conception. Most often we are talking about an association of several reasons. Of these, the following are important:
- Infections (viral-bacterial, chlamydial, fungal).
- Chromosomal abnormalities (trisomy, monosomy, tri- and tetraploidy).
- Endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, adrenogenital syndrome).
- Autoimmune disorders (antiphospholipid syndrome).
- Intoxication with chemicals.
- Heavy physical activity.
- Radioactive exposure.
- Taking certain medications.
The sensitivity of the embryo to external unfavorable factors is greatest in the early stages. There are critical periods during pregnancy when the risk of pathology is significantly higher. This is mainly observed 7–12 days after conception, during implantation of the fertilized egg into the uterine mucosa, and from 3 to 8 weeks of gestation, which is associated with active processes of embryogenesis.
Among the mechanisms of development of anembryonia, the main role belongs to disruption of the life support processes of the embryo, which leads to its death. This occurs against the background of cessation of chorionic blood flow, involution of the villous membrane and exudative-fibrous reaction of the endometrium. The latter, instead of decidual transformation, acquires signs of glandular-cystic hyperplasia. If the pregnancy is not rejected, the fertilized egg without an embryo can persist in the uterus for a long time, increasing the risk of complications.
Anembryonia is a type of non-developing pregnancy. And its causes include external and internal factors that have an adverse effect on the fetus in the early stages of gestation.
fertilized egg
If a doctor, during an ultrasound examination, reports that he sees a fertilized egg in the uterine cavity, the woman can be congratulated, because in 9 months she will become a mother. The presence of a fertilized egg can be determined already on the 7-9th day of missed menstruation. If the fertilized egg is in the uterus, then the pregnancy is normal, uterine. The specialist will immediately determine the size of the fertilized egg, its shape and location. In addition, he will pay special attention to whether there is a detachment or other pathological conditions.
What does a fertilized egg look like?
The fertilized egg is an oval or round body with a diameter of several millimeters. The diameter of the ovum is measured during the first ultrasound. Taking into account its size, a specialist can determine the gestational age. But in some cases the error in determination is 1-1.5 weeks. Therefore, when trying to establish a period, the doctor also takes into account indicators of the coccygeal-parietal size.
the fertilized egg looks like a formation in the form of a ball or oval. Already at 5-6 weeks, the yolk sac, which provides nutrition to the embryo and performs a hematopoietic function in the early stages of embryonic development, is similar to a bubble inside the cavity of the fertilized egg. The size of the fertilized egg at this stage of pregnancy is from 1.5 to 2.5 centimeters. It is already possible to examine the embryo at this time. It looks like a five-millimeter strip located next to the yolk sac. And although it is not yet possible to determine which structure and part of the embryo, the heartbeat is already being recorded. At this time, the baby’s heart beats at a frequency of 150-230 beats per minute.
In addition, the neural tube is already forming in the fetus, and the cells distribute “responsibilities” among themselves, who will create which organs.
By the end of the 7th week, the embryo has already acquired its characteristic shape in the form of the letter C. At this time, it has already become detached from the surface of the fetal
Source
Disorders and pathologies
If the fertilized egg develops incorrectly, a specialist will notice deviations from the norm on an ultrasound.
Deviations from parameters
The growth and size of the fertilized egg and embryo must correspond to the duration of pregnancy. If the fetus is less than 2 mm in size at 5 weeks, a developmental disorder can be stated. Fetal size less than 4 mm at seven weeks so
also indicates a violation. With these parameters, you need to make sure that the set deadline is correct.
A large fertilized egg with a small embryo often indicates a frozen pregnancy. But re-examination is necessary to confirm. A frozen pregnancy can also be indicated by a too small fertilized egg. However, again we need to observe the dynamics of development.
Irregular shape
We can also talk about a violation when the structure surrounding the embryo has a non-standard shape. If the angles of the membrane are uneven, then the specialist may suspect increased uterine tone. In many cases, this condition is harmless, however, if there is pain, dark vaginal discharge, or dilatation of the cervix, then there is a possibility of miscarriage.
To correct the situation, doctors remove the tone of the uterus, after which the egg takes the correct shape. What the fertilized egg looks like during a miscarriage depends on the gestation period. At 1-2 weeks, a miscarriage may look like menstrual bleeding. At later stages, the formation looks like a blood clot. If a miscarriage occurs at 7-9 weeks, the woman may find pieces of fetal tissue.
If the structure is oval and at the same time flat, this may also indicate a frozen pregnancy. However, in the absence of pain and other ailments, it makes sense to continue monitoring the pregnancy. A repeated examination will allow the doctor to draw the correct conclusion.
Wrong location
A low gestational sac does not indicate a serious pathology, but requires more careful monitoring throughout pregnancy. If the formation is very close to the cervix, then cervical pregnancy may occur, which can lead to removal of the uterus.
Empty fertilized egg
With an ectopic pregnancy, you can find an empty ovum when the cavity contains only fluid or a blood clot.
The size of the fertilized egg does not correspond to the gestational age
Hello, I have this problem, I’m 6-7 weeks pregnant, according to ultrasound the size of the fetal egg is 7 mm, it doesn’t correspond to the term, they put it at 4-5 weeks, the size of the embryo is 5.9 mm, there is a heartbeat, it corresponds to 6 weeks. and 3 days They prescribed a dynamic ultrasound, now on Sunday I will go for an ultrasound again, but no one can say what this means. Maybe someone has encountered such a problem, please tell me, I don’t know what to think, they are already threatening to clean it up ((((
I had an irregular cycle - from 35 to 50 days. When I became pregnant, the doctor, upon examination, set a period of 6 weeks (the uterus was curved, difficult to palpate) based on 1 day of the last menstrual period + 2 weeks (obstetric period). In fact, they all think so. And the ultrasound showed 4-5 weeks, that is, ovulation occurred later. Now doctors are trying to determine when I should give birth :-))) Either by obstetric date, or by ultrasound. We haven't agreed yet :-))
So don't worry, send the doctors to the garden with their cleanings. And do not make any decision until you have consulted with 2-3 doctors. In our city there is a perinatal center, there are doctors of the highest category - there is always an opportunity to check whether they are telling you the truth or whether the doctor is an idiot.
But for me it’s the other way around, when I was actually 6 weeks pregnant (I know the date of conception), the ultrasound gave me a gestational age of 8-9 weeks, the doctor said that judging by all the development parameters and the size of the fetus, this is exactly the period. I think this is due to the fact that I will have a large child, since my first daughter was born on 4.100. Maybe in your case the baby is just small?
They say that the size of the fertilized egg is very small, which means there is some kind of pathology, especially since there was bleeding. The discharge was stopped by drinking Dicynon and Utrozhestan, although I still drink Utrozhestan...
I decided so too, but the doctor says that the later the cleansing is done, the more it may be.
Source
Additional diagnostics
Additional methods are of decisive importance in the diagnosis of anembryonia. And the main role in this is played by ultrasound examination of the uterus. Based on its results, the following signs of pathology are determined:
- The absence of an embryo is an “empty” fertilized egg.
- Areas of chorionic detachment.
- Discontinuity of the decidua.
- Enlarged amniotic sac.
- Fuzzy visualization of the embryo.
- Deformation of the fertilized egg, uneven structure.
- No heartbeat.
If the doctor said that the woman does not have an embryo according to ultrasound, but clinically the pregnancy is progressing normally, then the study must be repeated after 7 days. In the absence of pathological changes, the fetus will grow, and it will become not only visible, but also audible (at 8 weeks there should already be a heartbeat). Therefore, you should not rush to conclusions and focus only on the results of a one-time procedure.
According to ultrasound data, there are two types of anembryonia. The first is characterized by the fact that the diameter of the fertilized egg does not exceed 25 mm, the size of the uterus corresponds to 5–7 weeks of pregnancy, but lags behind the actual period. In the second type, the egg grows at a normal speed and reaches 50 mm by 2.5 months, but the villous chorion is not visualized.
In addition to instrumental research, diagnosis includes determination of the hormonal spectrum and biochemical blood parameters. The following indicators may indicate anembryony:
- Low levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), absence of its peak concentration at 10–11 weeks.
- Decrease in prolactin, progesterone, estradiol, cortisol.
- A drop in the level of trophoblastic β1-globulin.
- Decrease in the concentration of placenta-specific α1-microglobulin.
It must be said that increased hCG, as well as other biochemical markers, indicate a normal course of pregnancy. And if even on an ultrasound the embryo is not yet visible - this happens up to 6-7 weeks - then the woman should not worry. Perhaps this is due to her individual characteristics or the imperfection of the apparatus.
To find out why the fertilized egg may be absent, a study of the immune status (immunoglobulins, lupus anticoagulant, cardilipin and antiphospholipid antibodies) is prescribed, and a genetic analysis (karyotyping) is performed. For early detection of complications, analysis of the coagulogram (clotting time, prothrombin index, fibrinogen) is necessary.
Anembryony can be confirmed only by instrumental and laboratory methods. But even their results should be considered in the context of the clinical picture and individual characteristics of the body.
Large fertilized egg in the early stages
Waiting for the stork
Based on the results of the ultrasound, the embryo size was set at 7 weeks and 2 days. My period is approximately 8 weeks. And in terms of the size of the fertilized egg, it is already 12-13 weeks, that is, the fertilized egg is very large. Why might this be? What might this affect? So what should I do now?
Detachment of the ovum in early pregnancy
The daughter-in-law became pregnant seven months after the wedding. There was no limit to joy. In January, the 6th, I had my last period, and at 7-8 weeks I started bleeding and had a brown spot. They looked at the ultrasound - the child’s heart was beating 140 beats. I took duphoston, folic and vitamin E. Bed rest. But on the second day the fertilized egg came out. Cleaned on February 27th. But it still smears a little blood. Today is 12 days after cleansing. The question is: what to do? The daughter-in-law is in despair. What could have happened? I didn’t lift anything heavy, there was no stress.
Pregnancy in the early stages is at great risk, because according to statistics, the majority of miscarriages occur in the first weeks of pregnancy.
Self-abortion begins with detachment of the fertilized egg. It is rejected from the chorion; the vessels connecting it to the inner layer of the uterus are damaged; blood accumulates behind the fetal membrane and forms a so-called retrochorial hematoma. This clotted blood can resolve, emptying itself naturally, or continue to increase in volume, contributing to an increasing detachment of the ovum. In the second case, the embryo faces inevitable death.
If a spontaneous abortion begins, immediate measures should be taken to maintain the pregnancy or it will be terminated. Timely treatment and support with hormonal drugs, as a rule, help stop the process of detachment of the fertilized egg, however, many experts see signs of natural selection in such a situation and do not
Source
Source: beroteca.ru
Abnormal development of the fertilized egg
In addition to deformation of the fertilized egg, the development of any anomalies is possible. Many of them can cause miscarriage or fetal death. The most common anomalies are presented below.
1. If there are two embryos in the fertilized egg, then this is not an anomaly, but rather the norm for the development of twins. The sizes of embryos may differ from each other. A difference of several millimeters is most often characteristic of monochorionic twins. However, at an early stage it is impossible to accurately determine whether the children will be twins or twins.
2. Small fertilized egg. This pathology is diagnosed by comparing the gestational age and the size of the ovum. Such studies help determine the correct development of the fetus in the uterus. The gestation period is also determined by the size of the fertilized egg. It is necessary to carefully monitor the development of the fertilized egg; too slow growth may indicate fetal fading. In this case, it is advisable to prescribe the patient a blood test for hormone levels.
3. If the fertilized egg is larger than the embryo, then the pregnancy may be frozen. Pregnancy can also be anembryonic. All signs of pregnancy are characteristic, the membranes of the fetus are formed, but the embryo is missing. Anomalies can only be diagnosed by ultrasound examination of the fetal egg no later than 6-7 weeks after conception. In this case, it is very important to establish the exact duration of pregnancy.
4. Elongated shape of the fertilized egg. Normally, the fertilized egg should be round in shape. Elongated contours may signal the possible loss of a child. The reason most often lies in uterine hypertonicity. It is important to diagnose the deformity in time and take measures to reduce tone with the help of antispasmodics. The fetus can be saved if it continues to develop and a heartbeat can be heard. The patient needs to stop sexual activity, minimize physical activity and avoid emotional turmoil. If this pathology is present, complete bed rest is prescribed. Ultrasounds are performed every few days to monitor changes in the gestational sac.
5. Abnormal location of the fertilized egg. Usually the egg is implanted at the bottom or center of the uterus, but sometimes it occurs in the area of the internal os.
6. Death of the fetus inside the womb. Diagnosed by listening to the heartbeat using ultrasound. The cause may be inflammatory processes in the mother's body, the presence of infections, late toxicosis, placenta previa or abruption, diabetes mellitus, pyelonephritis, pneumonia, influenza, polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios, intoxication with harmful substances.
Such diagnoses are usually made in the very early stages of pregnancy, which makes it possible to control the process. Thus, there are many chances to maintain the pregnancy and give birth to a child.
Fertilized egg without embryo
The anomaly when there is no embryo in the fertilized egg deserves special attention. This pathology occurs quite rarely.
First, pregnancy is confirmed using a test or analysis, but an ultrasound reveals that there is no embryo in the fertilized egg. This phenomenon is called empty egg syndrome. The situation is similar to an anomaly of too large a fertilized egg: the membranes are formed, but there is no embryo.
Pathology is confirmed only by ultrasound examination no earlier than 6-7 weeks. There are cases of erroneous diagnosis, since in the early stages the embryo may not be visualized on the device’s monitor.
When making such a diagnosis, you need to undergo examination by several specialists using different devices. If the absence of an embryo is nevertheless confirmed, curettage is prescribed. The procedure is performed using general anesthesia.
It is impossible to name the exact reasons for the lack of embryo implantation, but it is most likely that this problem is associated with the following factors:
- genetic disorders;
- the presence of any infections;
- hormonal imbalance;
- smoking, drug and alcohol use.
A bacterial or viral infectious process at the beginning of pregnancy can have a negative effect on the embryo, resulting in the development of pathology.
Exposure to toxic substances or radiation can also provoke the occurrence of pathology. To establish the exact cause, both partners need to undergo a full examination. Testing for the presence of STIs, spermograms and karyotype examination are mandatory studies in this situation.
There are cases when such a pregnancy develops in a completely healthy couple. Then the chances of bearing a healthy child in a subsequent pregnancy increase dramatically. However, before planning, it is important to take a break (about six months) and give the body a chance to rest and recover.
Source: www.probirka.org
Formation of the fertilized egg
The first stage of the cycle that a reproductive cell goes through is the release of the egg from the follicle. Usually 3-4 follicles mature, but only one egg passes through a woman's fallopian tubes during ovulation.
The growth and development of a new life begins with the fusion of an egg and a sperm. Immediately after ovulation and fusion, a protective membrane forms around the egg.
This outer protective layer around the embryo will later develop into the amniotic sac containing amniotic fluid.
In the early stages of pregnancy, during an ultrasound, you can see the formation of an ovoid shape of small diameter. This is the fertilized egg. The first stage of its development is the morula, consisting of 12-32 blastomeres formed as a result of division of the zygote, which turn into a compact ball.
As the cells multiply, the embryo continues to move through the fallopian tubes until it attaches to the mucous wall inside the uterus. After this, the outer layer of the membrane begins to produce hCG (chorionic gonadotropin hormone), which is one of the first indicators of a woman’s pregnancy. All this time, the fetus is fed from the internal resource of the egg. In the process of further development, the attachment site is transformed into the placenta. At this time, to prevent infection, a mucous plug is formed, which closes the entrance to the uterus. This whole process takes about two days. If the embryo does not attach to the wall of the uterus, then a miscarriage occurs along with menstruation at the end of the cycle, and often the woman does not even know that she was pregnant. In the next cycle, the egg is released from the follicle again, ovulation occurs, and the whole process is repeated again.
What does a fertilized egg look like, structure:
- Villous membrane, chorion;
- Amnion (amniotic sac or membrane of water);
- Embryo.
It is difficult to see exactly what the fertilized egg looks like even with the help of an ultrasound. Due to its small diameter, the embryo is difficult to detect inside the uterus if a woman is pregnant for less than a month.
It happens that even at a period of 6-7 weeks the embryo is not visible inside the egg - this may indicate a non-developing pregnancy. An empty ovum is quite rare and is often a symptom of genetic disorders in the woman or her partner.
Examination of the ovum
The diagnostic method used to study the life cycles of the fetal egg is called echography or, in other words, ultrasound diagnostics. It allows you to identify SVD, the average internal diameter of the ovum, and CTR, the coccygeal-parietal size of the fetus.
Typically, the doctor prescribes the first ultrasound for a woman between 10 and 13 weeks of pregnancy. If necessary, diagnosis is carried out at 3-4 weeks. This is due to the fact that the fertilized egg is fully implanted inside the uterus only 10 days after conception. Using ultrasound, you can track the time of ovulation and follicle maturation.
There is no need to worry that ultrasound will harm the fetus. Even in the early stages, radiation does not affect the health of the unborn child.
It is worth considering separately the 4th obstetric week of pregnancy, since it is during this period that nascent life can be seen using ultrasound. In the first days of the fourth week of pregnancy, the fertilized egg has a diameter of only 1 mm, and it is not possible to assess the details of fetal formation. That is why an additional ultrasound is prescribed a few weeks after the first examination. However, after a couple of days, the size of the fertilized egg will increase to 3 mm, and it will be possible to see the yolk sac, with the help of which the embryo is nourished until the umbilical cord appears. Towards the end of the fourth week, the diameter of the fertilized egg increases to 4 mm, during this period vital organs begin to develop: the heart, lungs, liver and pancreas. On the last day of this period, the diameter of the ovum is 5 mm, and during an ultrasound it is already possible to detect an embryo whose size is only 1 mm. Literally in a day the egg grows up to 6 millimeters.
Formula for determining gestational age:
The average internal diameter of the ovum + 35 (if its size is less than 16 mm) or 30 (if the fetus is more than 16 mm). For example, diameter 17+30=47 weeks.
Pathologies of the ovum
When studying the fertilized egg with echography, pathologies can be detected already in the early stages. The absence of an embryo inside the membrane, an “empty egg” or anembryony, may indicate a non-developing pregnancy that will end in miscarriage or purging.
A picture that shows a discrepancy between the sizes of the growing embryo and egg in the absence of a heartbeat may indicate fetal fading, which also leads to miscarriage.
For example, if the embryo is much smaller than the membrane or the size of the bubbles is too small for the given period, then with a high degree of probability a miscarriage will occur at the end of the cycle. The most common cause is chromosomal changes during conception, either congenital or caused by external influences. For example, a woman, not knowing about pregnancy, takes pills, drinks alcohol or is exposed to other harmful influences, which leads to serious pathology in the development of the fetus and miscarriage.
Deformation of the ovum is not always a pathology, and in most cases is caused by increased uterine tone in the first period of pregnancy. Often the tone is accompanied by slight bleeding and pain in the lower third of the abdomen.
This problem can be solved with medication; pills are prescribed to reduce the number and intensity of contractions of the uterine muscles and hormonal pills to keep the fetus inside.
In case of detachment of the ovum in the case of a small affected area, hormonal treatment is carried out. For a woman during this period, bed rest in a hospital setting is required.
An ectopic pregnancy is characterized by the fact that the fertilized egg develops in an unintended place: in the fallopian tubes or ovaries. The main manifestation is heavy bleeding. It is impossible to save such a pregnancy, since the growth and development of the embryo in the fallopian tube leads to its rupture and serious consequences for the woman’s health.
During screening at 12 weeks, the nasal septum is measured. If the bone is less than 2.5 mm in length or is absent, doctors can make a preliminary diagnosis: trisomy 21 or Down's disease. In this case, the woman herself will be able to decide whether to continue the pregnancy.
In rare cases, two embryos are found in the fertilized egg at once - this is not an anomaly, but a factor indicating the presence of twins. A similar situation occurs when two bubbles are found in a woman’s uterus at once. In the latter situation, the chorions of both membranes in the future form placentas, with the help of which each fetus is fed separately. In the first case, the embryos will be nourished from one placenta. Detection of twins in the early period is often not confirmed, and the study gives reliable results only at 6-7 weeks of pregnancy.
When a fertilized egg is visible on an ultrasound: timing and features
For various reasons, a woman may be interested in when a fertilized egg is visible on an ultrasound. Some people want to quickly ensure that there are no pathologies in the early stages of fetal development. Others are interested in whether the pregnancy is multiple. And still others need to find out about the presence of a fertilized egg before going for an abortion.
At what stage will an ultrasound show the fertilized egg?
The fertilized egg enters the uterine cavity about a week after the fusion of the egg and sperm. And already in the fourth week, with the help of a powerful device, you can see the beginning of embryo development using an ultrasound sensor. Usually the procedure at this stage is carried out through the vagina.
Although the fetus cannot always be visualized at three weeks. Sometimes a specialist can see changes in the condition of the uterus that are characteristic of the onset of pregnancy. In this case, a repeat ultrasound is scheduled after 14 days. At this time, the doctor can already determine whether the fetus has begun to develop correctly.
If the pregnancy has reached 6-7 weeks, then the ultrasound is already performed in the classical way, that is, the sensor is moved along the lower abdomen. If the embryo is not marked at this time, then most likely it has attached outside the uterus, which means it will need to be found and removed before the egg harms the woman.
Based on this, it turns out that the fertilized egg during pregnancy is shown by ultrasound in the 3-5th week from the moment of conception. Although it is not recommended to perform an ultrasound before seven weeks. But after that it’s necessary.
To determine whether the egg has attached correctly (to rule out an ectopic pregnancy), how many embryos there are, and to rule out a frozen pregnancy, which is quite common lately.
When is the fertilized egg not detected?
Sometimes the situation may turn out to be that a woman has a delay, has all the symptoms and the test showed the presence of pregnancy, but the ultrasound did not detect the fetus (at a short term).
This may be for the following reasons: a malfunction of the device, low qualifications of the doctor, structural features of the uterus, or the period is still too short. Therefore, a repeat ultrasound scan is recommended after 10-14 days.
If you have doubts about your qualifications, it is better to contact another specialist.
What does a fertilized egg look like on an ultrasound during pregnancy? The fertilized egg, and subsequently the embryo, changes every week in size and development of organs. The early definition of pregnancy is considered to be the period of the first trimester, starting from the fourth week. What does an embryo look like on an ultrasound week by week? More on this later.
The first and most important week
If the pregnancy is planned, then it is necessary to especially protect the body: you need to give up alcohol, cigarettes, especially medications; it is necessary to take strengthening vitamins; avoid stressful situations; Strong physical activity is canceled. The first week is when the egg is ready for fertilization. An ultrasound will not show the fertilized egg.
Second week
This is the fertilization of an egg by a sperm, the beginning of the development of a fertilized egg. At this time, the body begins to produce hormones for a successful pregnancy. The egg gradually moves into the uterine cavity. The ultrasound still shows nothing.
The third week is also important and dangerous
At this time, the fertilized egg is attached. And this is considered the first week of the embryo’s life. If the endometrium (the place where the embryo attaches) is not developed normally, a miscarriage will occur. At this stage, a woman may mistake this for heavy menstruation. Here it is just a set of cells that carry information about the future baby. At this stage it is very difficult to see the egg.
Fourth week
You can only see an egg measuring up to 7-9 mm in diameter. And changes in the walls of the uterus (they become thicker). The foundation for the development of all organs of the future baby takes place. At this stage (if the egg is examined on the monitor), pregnancy can already be confirmed.
Fifth week
This is the date when the fertilized egg is visible on ultrasound. At this stage, the woman already knows about the beginning of pregnancy, this is manifested by the absence of menstruation. The egg stretches out and can already reach 10-14 mm in size.
The embryo begins to develop a heart and blood vessels, the formation of a nervous system begins, and a face with the rudiments of a nose, ears and eyes is indicated. Here, if there are indications, the first ultrasound can already be prescribed.
The egg will be visible on the screen as a small dot.
Sixth week
The egg already reaches 20-23 mm in size, and you can hear the heartbeat. The embryo itself already reaches a length (from the coccyx to the back of the head) of up to 5-6 mm. The placenta begins to form, which will play an important role until the baby is born. The embryo develops genitals. From this time on, the fertilized egg is clearly visualized on the screen.
Seventh week
The size varies up to 24 mm, the future baby itself is slightly more than one centimeter in size (from the tailbone to the crown of the head). On an ultrasound, even the expectant mother can see a tiny baby doll with arms and legs. Doctors most often prescribe this study at this time, since this is the best period when the fertilized egg is visible on ultrasound. Also from this moment various pathologies may begin to develop.
Eighth week
At this stage, the unborn baby moves from the state of an embryo to a fetus. The rudiments of all organs are already there, their development has begun. The diameter of the egg is up to 3 cm, the fruit has clearer outlines. In girls who are too thin, you can already see a slight rounding of the abdomen.
Ninth week
The diameter of the egg reaches 32 mm, and the embryo develops a torso and head. At this time, the baby begins to completely depend on the placenta. Therefore, the mother must carefully monitor her food intake. The fetus's kidneys are already functioning, and even the first portion of urine is excreted.
Tenth week
The egg is already a little more than 4 cm in diameter, the baby already looks like a person, although the head is still large. Organ development begins.
Eleventh week
The next important stage in development. At this stage, it is possible to determine the pathology in the development of the baby as Down syndrome, but at the twelfth week this will no longer be possible. The fetus is active at this time, moves its arms and legs, and already knows how to swallow. Mom doesn't feel any movement yet.
Twelfth week
Conclusion of the most important and dangerous period of fetal formation. It is already possible to make a full assessment of the condition of the unborn baby and whether the important organs that develop during this period were formed correctly. At this stage, you can determine with precision down to the day which week you are pregnant. An experienced specialist can already name the gender of the baby.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d7zBj4Onsa8
When undergoing the procedure, it is advisable to choose a trusted specialist with high-quality equipment. It is important at this stage not to overlook the beginning of the development of possible pathologies.
What abnormalities can a doctor see?
We have already found out when the fertilized egg is visible on an ultrasound. Sometimes a woman needs to undergo research for a short period of time. For example, there was a serious illness in the first days of pregnancy, there is a high risk of embryo failure, in previous pregnancies there were abnormalities in the fetus.
Ultrasound at a short term allows you to determine the following deviations in the development of pregnancy:
- due to a slight placental abruption or increased uterine tone, the egg may be deformed. If treatment is started immediately, there is a high chance of a normal pregnancy outcome;
- improper attachment of the fertilized egg. If it attaches to the very bottom of the uterus, then the threat of miscarriage is great, the woman needs complete rest, sometimes bed rest is possible until the birth;
- absence of an egg in the uterine cavity;
- discrepancy between the size of the egg or embryo;
- frozen pregnancy. This occurs because the egg shell did not allow the embryo to develop normally; in this case, the egg is removed by scraping;
- there is a tumor in the fertilized egg that puts pressure on the embryo and will not allow it to develop;
- in rare cases, there may be no embryo in the fertilized egg, this is noticeable after the seventh week of pregnancy;
- the amount of water is determined, since its excess or deficiency negatively affects the development of the fetus.
If one of the listed anomalies is detected, this is not a mandatory indication for termination of pregnancy. Most often, a repeat ultrasound is prescribed after two weeks. If the diagnosis is confirmed, treatment or abortion is prescribed.
An ultrasound scan at 12 weeks helps to accurately determine the gestational age and expected date of birth, identify serious developmental abnormalities, and also find out how many embryos are in the uterine cavity.
Myths about ultrasound
Women are often afraid to go for an ultrasound scan because of prejudices and horror stories told by friends and grandmothers, without thinking that the procedure makes it possible to identify dangerous abnormalities in time and the ability to bear a healthy baby.
It is believed that ultrasonic waves are harmful to the baby. Unfortunately, there is neither evidence nor refutation of this statement. There can be a danger to the fetus when an ultrasound scan is performed through the vagina at a short term, as this can cause a miscarriage.
And three mandatory procedures (at 12, 24 and 33 weeks) must be completed. They won't do much harm. It is important for the doctor to look at what the fetal egg looks like on an ultrasound to determine whether there are any pathologies, and this is also necessary to set the exact date.
It is believed that waves during examination can change the DNA of the fetus. There is no evidence to support this claim.
There are mothers who are simply not interested when a fertilized egg appears on an ultrasound, since they consider the procedure unnatural. When a mother has such convictions, she has the right to refuse the procedure; if pathologies in the development of the fetus are missed, then all responsibility falls on the mother’s shoulders.
There is a myth that ultrasound is a kind of experiment on people. And this is partly true, since with the help of the procedure it became known how the baby develops - from the stage of a fertilized egg to the embryo. But this has brought a lot of benefits and allows us to detect even the slightest deviations at an early stage and save the life of the child and mother.
The procedure is carried out only with the written consent of the woman, not necessarily. The doctor knows when the fertilized egg can be seen on an ultrasound and prescribes the procedure for an approximate period if there is a likelihood of pathology developing or it is necessary to determine the exact duration of pregnancy.
Conclusion
With the help of ultrasound, you can save the child’s life if placental abruption is noticed in time and bed rest with medications is prescribed. You should not decide on your own when to do an ultrasound.
Now it is possible to pay for the procedure at least every day. But it is recommended to do this only on the recommendation of a doctor, and not every time the expectant mother is sick or does not like the sensations in her stomach.
The doctor can use an initial examination to determine whether there is a threat of miscarriage, or prescribe an ultrasound from a specialist.
Source: https://fb.ru/article/421827/kogda-na-uzi-vidno-plodnoe-yaytso-sroki-i-osobennosti
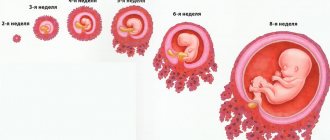
Sizes of fertilized egg by week
The fourth obstetric week was discussed above. However, the development of the fertilized egg continues up to 8 weeks, and according to some sources up to 10, and in further periods of development the embryo is called a fetus. Data on the stages of embryo development in each week can be seen in the table below. This table with a detailed description of each stage of development of the fertilized egg will help a woman understand how the baby develops inside her uterus during this period. Rates of growth:
- Up to 15-16 weeks 1 millimeter per day;
- From 16-17 weeks 2-2.5 millimeters per day.
Sizes of the fertilized egg by week, table:
The sixth week is especially important during this period of intrauterine development, since during this period the birth of the digestive system, spleen and cartilage buds occurs. When the size reaches 16 mm, we can say that the embryo has the rudiments of the stomach and esophagus, as well as 3 intestinal loops. By the end of the week, the embryo has formed fingers and muscle tissue.
Source: uziwiki.ru