What to do when an embryo is not visible on an ultrasound at 9 weeks? Repeat it after a week, or preferably after 3. The examination will show what size the fertilized egg is when it is 1 cm or more. Most often, the fetus reaches this size by 6 weeks of gestation. But everything is individual. It happens that an ultrasound can clearly show that a woman is pregnant only at 8-12 weeks.
Many expectant mothers who dream of a son or daughter are concerned with the question: from what week will an ultrasound definitely confirm that she is pregnant? Experts say that from the age of 7 you can take a referral from your gynecologist and undergo diagnostics. If the examination does not show anything, and there are no menstruation, do not be upset, it happens. Sign up again in a month.
- How do specialists see an embryo?
- Embryo examination method
- Is ultrasound safe for the fetus?
- When will the ultrasound clearly show the embryo?
- It is important to know when an embryo is clearly visible on an ultrasound? What will they look at on an ultrasound?
- The doctor did not detect pregnancy on an ultrasound?
What does a fertilized egg look like?
Having learned about their pregnancy, many curious expectant mothers begin to ask the doctor questions about how and at what stage the fertilized egg is visible and what it looks like. We will try to answer them.
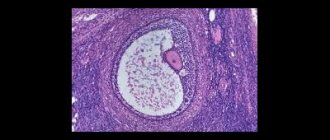
The fertilized egg, the diameter of which is very small in the first days of pregnancy, can be seen within two to three weeks after a missed period. The formed structure in most cases is located in the upper part of the uterine cavity, has a dark (gray) tint and a round or oval shape. The embryo at this time is still microscopic in size, so it is not detected by ultrasound.
At what stage can pregnancy be determined?
Conceiving a child is such an important and responsible matter that the last days of the next menstrual cycle can turn into a real test of mental strength for a woman: everything that can be done has been done, the result can no longer be affected, but what will it be? It’s no wonder that the most important question becomes: at what stage can pregnancy be determined, or its absence, and you want to get the answer as accurate as possible and as early as possible. Delayed menstruation, nausea, drowsiness, unusual emotionality - all these symptoms are characteristic of pregnancy, but can have many other causes
There are much more informative ways to find out the truth, both “at home” and laboratory or outpatient:
Delayed menstruation, nausea, drowsiness, unusual emotionality - all these symptoms are characteristic of pregnancy, but can have many other causes. There are much more informative ways to find out the truth, both “at home” and laboratory or outpatient:
- maintaining a graph of basal body temperature;
- rapid pregnancy test strip;
- gynecological examination;
- blood test for hCG;
- ultrasound diagnostics.
Basal temperature
When planning a pregnancy, gynecologists often advise a woman to monitor her menstrual cycle by measuring her basal temperature. In a fertile woman, in the first phase of the cycle, BBT is low, at the time of ovulation it drops even lower, then it rises sharply and remains at this level until the end of the cycle, and before the onset of menstruation it decreases again.
If your next menstruation is due and your temperature still does not drop, you can suspect pregnancy.
A knowledgeable person can read a lot about women's health from the BT chart, but starting the morning with a thermometer is still not an ideal method for determining pregnancy, so it is better to use it in combination with others.
Express pregnancy test
An express pregnancy test is perhaps the most popular way to find out the truth without leaving home. Test strips react to an increase in the level of the hormone hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) in a woman’s urine, which is directly related to conception and early development of the embryo.
How long can pregnancy be determined in this case? The results can be indicative already on the first day of a missed period, although the second line at such a short period is often very pale. But it should be remembered that even their manufacturers do not recommend 100% trust in such tests - the results obtained should be confirmed in the laboratory.
Gynecological examination
If “at-home” methods have allowed you to diagnose yourself as “pregnancy in question,” it’s time to pay a visit to the doctor to dot the i’s. An experienced gynecologist can determine whether a woman is expecting a child by barely looking at the cervix, starting from the second week of conception.
Many doctors, however, consider a chair-based examination in the early stages undesirable - but, in any case, the gynecologist will advise and reassure the patient and write her a referral for the necessary tests.
Blood analysis
The surest, but also the most troublesome method to determine successful conception is to donate blood to determine the level of the same hCG.
A clear advantage of this method is the ability to detect pregnancy 7-12 days after the expected meeting of the egg with the sperm, that is, long before the missed period.
Laboratory methods make it possible to find out both about the increase in the level of the “pregnant hormone” as such, and about the specific period for which the resulting figure is typical.
Ultrasound diagnostics
Using the ultrasound diagnostic method, you can, firstly, confirm the very fact of expecting a child already at the end of the first - beginning of the second month of the obstetric period - let us remind you that it is counted from the first day of the cycle in which conception occurred. Even if the doctor does not see the fertilized egg itself, he will note, at a minimum, the rapid growth of the endometrium in the uterine cavity, which is already preparing to receive the unborn baby.
Secondly, an ultrasound performed in the period from 5 to 8 obstetric weeks will help to exclude or promptly identify a serious danger to the health, and sometimes even the life of a woman - ectopic pregnancy.
Experts disagree on the effect of ultrasound on the fetus, but unanimously agree that if the expectant mother is nervous, this is definitely not good for the matter. Therefore, if doubts and fears are very disturbing and provoke serious stress, it is better to conduct this study.
Development and structure
The growth of the fertilized egg begins from the moment of conception. The fertilized egg begins to move through the fallopian tube, during which cell fragmentation occurs. Making its way to the uterus, the fertilized, crushed egg needs nutrients and oxygen, so after a week a chorion begins to form on top, which subsequently transforms into the placenta.
The surface of the chorion has villi, which help the formation to attach to the uterus. In the future, these villi are contained only at the site of implantation of the formation into the uterine wall. The rest of the structure loses lint and remains smooth. The chorion provides the fetus with all vital functions, one of which is protection against infections.
Twenty days after menstruation, during a hardware examination, you can see the yolk sac, which is designed to provide the fetus with nutrients. The presence of a yolk sac in the fertilized egg does not guarantee a normal pregnancy, but if it is absent, this indicates pathology. Inside the shell, surrounding
The embryo contains the amnion, a hollow sac that produces the optimal environment and amniotic fluid for the development of the child.
Often, during an examination, an ultrasound specialist may detect a second fertilized sac. In this case, the woman can be congratulated, as she will have twins. Such a pregnancy develops when two eggs are simultaneously fertilized or two zygotes develop from the same egg.
If a woman is expecting twins, the fertilized egg may form one or two placentas at the time of division.
If the moment of attachment of the egg to the uterus occurs after 8-13 days from the day of fertilization, then 2 fetuses and one placenta are formed for two. This means that both fetuses will develop in the same amniotic sac. If division occurs earlier than this period, then each embryo will develop in its own fertilized egg.
Sizes of fertilized egg by week
A table will help you find out the size of the fertilized egg by week of pregnancy, according to which the obstetrician-gynecologist compares the size of the fetus with the norms for the expected period. The parameters indicated in this table are the most important indicators of the formation of pregnancy, therefore, when the fertilized egg is already visible, the doctor is obliged to determine them.
Ultrasound of the fetal egg at 4 weeks determines the size of only 1 mm. A woman at this time may not even know about the birth of a new life, but a hardware study will already reveal and even show what the fertilized egg looks like at 4 weeks. At this time, the cells of all future organs of the baby are formed.
The size of the fertilized egg increases daily by about 1 mm. When the egg reaches a size of 3 mm, it already has a yolk sac, which provides hematopoietic function and nutrition to the embryo. All elements of the fertilized egg within the fourth week make it possible to confidently establish the presence of pregnancy. It is already possible to examine the embryo during this period. It happens that at a given size the structure of the embryo is not visible. There is no need to panic, since in individual cases the embryo may still be forming at this time.
The question of when an embryo appears in the fertilized egg interests many expectant mothers. Normally, around the fifth week of gestation, the embryo is already visualized on the ultrasound monitor and even a heartbeat is recorded. To clarify the progression of pregnancy, hCG levels are additionally monitored.
A value less than 7 mm indicates the middle of the fifth week. This is one of the most important periods when active formation of blood vessels, heart and nervous system occurs. The size of the embryo is usually 2 mm.
When an ultrasound shows a fertilized egg measuring 10 mm, this indicates that the heart and blood vessels are already fully formed and the embryo has a neural tube with a slight thickening at the end (the future brain).
6 obstetric week visualizes a value of 12 mm. At the 6th obstetric week, the fertilized egg is 12 mm in size, has a spherical shape, the embryo looks like a white stripe about 5-6 mm long. At this point, the heart rate is 110-130 per minute. If any abnormality is detected during the sixth week, a repeat examination a week later is recommended.
During the first two days of the 7th week, the value is determined to be 19-20 mm. During this period, the baby’s brain and genitals are forming; on the ultrasound monitor you can see arms, legs, mouth and nostrils.
Structure dimensions of 21-22 mm indicate the middle of the seventh week. At this time, the development of the brain and face continues. From this period, the child cannot be considered an embryo, since it is already a full-fledged fetus measuring about 10-13 mm.
When will the ultrasound clearly show the embryo?
If the egg contains a viable embryo, the doctor confirms that the woman is pregnant and the condition of the fetus is stable. For each woman, even 1st, 2nd and subsequent pregnancies proceed in their own rhythm. In one, the fetus develops faster, in the other slower. Future mothers are wondering, how many weeks does it take for an embryo to become visible on an ultrasound from a dot and then a pea? Scans done through the vagina can diagnose pregnancy earlier than those done through the peritoneum. Average indicators are taken as the norm. It is believed that the fetus should be audible and visualized on the screen already at 6 or 7 obstetric weeks. If the specialist does not notice anything, he will make a diagnosis of anembryonia. Gynecologists advise the woman not to be upset, but to come for an examination in another 7 days. If your cycle before pregnancy was irregular, then perhaps the embryo was behind in development and therefore the specialist did not notice it. See what the baby looks like on day 21 of gestation:
Basic information about the fertilized egg
As you know, fertilization occurs through the penetration of a male sperm into a female egg. After this, the active process of embryo development begins: first, the fertilized egg is divided into 2 parts, then into 4, then into 8, etc. As the number of cells increases, the embryo itself grows. Without stopping to develop, the embryo moves towards its destination, which is normally the cavity of the female uterus. It is the mentioned group of cells that represents the fertilized egg in question.
Once the desired location is reached, the embryo is implanted into the wall of the uterus. On average, this process takes up to 7-10 days after the sperm penetrates the egg. Until reaching its destination, nutrition of the fertilized egg is provided directly by the egg, and after consolidation, by the uterine mucosa.
Over time, the functions of providing nutrition to the embryo are taken over by the placenta, which is formed from the outer layer of the fertilized egg. Directly on the mentioned outer layer there are so-called. villi, which ensure implantation of the embryo in a suitable place.
The formation and successful consolidation of the fertilized egg is the main sign of the normal course of female pregnancy. On average, the embryo becomes visible during ultrasound examination 5 weeks after the missed period, while the fertilized egg can usually be seen after 2 weeks. If during the first ultrasound the doctor sees the so-called. empty ovum, after a couple of weeks the test is repeated.
Normally, the embryo is visualized by the 6-7th week of pregnancy. During the same period, his heartbeat is usually noticeable. If there is no embryo in the ovum during repeated ultrasound examination, a non-developing pregnancy is diagnosed.
In view of this, if menstruation is delayed, a woman should have an ultrasound scan as early as possible in order to promptly detect existing abnormalities and, if such a possibility is present, undergo treatment to eliminate the identified problems.
When assessing the condition of the ovum, the specialist first of all pays attention to its shape and internal diameter. During the first weeks, the shape of the fertilized egg is close to oval. By assessing the internal diameter, the doctor can draw conclusions about the estimated gestational age. Along with this, not every woman’s fertilized egg has the same size, so when determining the gestational age, an error often occurs, averaging one and a half weeks. For more accurate results, fetal CTE and other diagnostic measures are assessed.
Varieties of methods for determining
To perform an ultrasound, a special sensor is used that produces ultrasonic waves.
The waves are not audible to humans, but have the ability to penetrate the body, as a result of which the specialist sees the internal organs of the mother and child and assesses their condition.
During pregnancy, two methods of ultrasound are used:
Transvaginal method
This method is carried out by inserting a special elongated sensor into the vagina. The doctor puts a thin condom on it and puts a small layer of gel or lubricant on top. The method allows you to record changes in the embryo as accurately as possible, since the sensor is located very close to the uterus. This is completely non-traumatic and painless for the mother and fetus.
The transvaginal ultrasound method allows you to determine the viability of the embryo from the fifth week of development, while the embryo is visualized on the screen of the device, and its heartbeat becomes audible.
The transvaginal method is most often used up to 12 weeks. During this period, the uterus is located within the pelvis. At the earliest stages, it allows you to accurately confirm the fact of pregnancy.
In the second and third trimester, transvaginal ultrasound is performed quite rarely, mainly in cases where it is necessary to examine deep-lying structures of the fetus - the head or brain, which cannot be clearly seen when scanning through the abdominal cavity. Also, the transvaginal method helps to assess the condition of the cervix and stop premature opening of the pharynx in time.
After the procedure, sometimes a woman may experience a slight watery or mucous discharge that occurs as a result of an allergic reaction to the condom material, lubricant, or gel. This phenomenon does not pose a threat and does not increase the risk of miscarriage; it goes away within one to two days after the ultrasound. But in case of heavy discharge, especially with an admixture or streaks of blood, you should immediately contact a gynecologist or call an ambulance.
Abdominal method
After 12 weeks, to determine the intrauterine development of the fetus, the abdominal ultrasound method becomes more informative, since the uterus has significantly increased in size and the embryo is clearly visible when examined through the walls of the abdomen.
When performing an abdominal ultrasound, a sensor is used, which is lubricated with gel and moved over the skin of the pregnant woman’s abdomen. During an ultrasound, the fetus is visualized on the screen, which the doctor carefully examines.
Abdominal ultrasound allows:
- establish the exact duration of pregnancy;
- determine the position of the fetus, its weight and size;
- listen to the heartbeat;
- assess the degree of maturity of the placenta and the state of amniotic fluid.
An ultrasound is safe, but after it the pregnant woman may have increased uterine tone and feel slight discomfort in the abdomen. During the study, an increase in fetal activity is sometimes observed.
In these cases, the woman is advised to rest, get distracted and not overexert herself physically and emotionally.
Features of the growth of the fertilized egg
As noted, the size of the fertilized egg, in the absence of various kinds of pathologies, is constantly increasing.
- For example, at a period of up to 5-6 weeks (on average 4), its diameter is about 4 mm.
- At a period of 5 weeks, the internal diameter of the fetal egg is 6 mm, and after 3 days it usually increases to 7 mm.
- At a period of 6 weeks, the dimensions are already more significant - in some cases, up to 18 mm (on average - 11-15 mm).
- The internal diameter of the fetal egg increases to 20-25 mm by 7-8 weeks, by 8-9 – to 28-33 mm, and by 9-10 – to 34-42 mm.
- By the end of the 10th week, the size of the fertilized egg is already approximately 5 cm.
- In general, answering the question about the growth rate of the fertilized egg, we can come to the conclusion that by 15-16 weeks of pregnancy it grows by an average of 1 mm daily, and after that it grows by 2-2.5 mm per day.
More detailed weekly information regarding the normal size of the gestational sac is given in the following table.
Table. Sizes of fertilized egg by week
Determination of gestational age
When a woman ovulates late, the test will show pregnancy only after 2 weeks. If the hCG result is 1000-2000 mU/l, we can talk about successful embryo transfer.
What is the term set by different methods (ultrasound, obstetric, embryonic)
The obstetric method takes 1 day of the last menstruation as the starting point. Embryonic counts the period from the day of conception, which coincides with the day of ovulation. This period is 2 weeks shorter than the obstetric period. When performing an ultrasound, the obstetric method is used as a basis. The accuracy of the study depends on the period - up to 12 weeks the error is 1-2 days, up to 28 weeks a week in both directions. At later dates the error increases even more.
Fetal ultrasound is an inexpensive, fairly informative, accessible and painless way to monitor pregnancy. Thanks to the research, treatment for existing pathologies will be prescribed on time.
What is a fertilized egg
The fertilized egg consists of embryonic membranes and an embryo. This period of pregnancy is its first stage of development. And it all starts with the fusion of two cells – male and female.
Then the fertilized egg actively begins to divide, first into two parts, then into four, and so on. The number of cells, like the size of the fetus, is constantly growing. And the entire group of cells that continue the division process moves along the fallopian tube to the zone of its implantation. This group of cells is the fertilized egg.
Diameter of fertilized egg by week
When the fertilized egg has a diameter of 4 millimeters, this indicates a fairly short period of time - up to six weeks.
- This is often the size of the fertilized egg at 4 weeks. Already at five weeks, the SVD reaches 6 millimeters, and at five weeks and three days the fertilized egg has a diameter of 7 millimeters.
- At the sixth week, the gestational sac usually grows to eleven to eighteen millimeters, and the average internal size of the gestational sac of sixteen millimeters corresponds to a period of six weeks and five days. At the seventh week of pregnancy, the diameter ranges from nineteen to twenty-six millimeters.
- At week 8, the fertilized egg increases to twenty-seven to thirty-four millimeters. At this stage, the fetus can be clearly seen on ultrasound.
- The fertilized egg grows to thirty-five to forty-three millimeters in 9 weeks.
- And at the end of the tenth week, the fertilized egg measures about fifty millimeters in diameter.
As you can see, the fertilized egg at the 4th week is very different in size from the tenth week.
The question of how quickly the fertilized egg grows can be answered with confidence: until the fifteenth to sixteenth week, its size increases by one millimeter every day. Further, the diameter of the fertilized egg increases by two to three millimeters per day.
Next you can see the increase in the ovum by week in the table:
Average size of the fertilized egg in the first trimester of pregnancy
| Date of last menstruation (weeks) | Time at conception (weeks) | Inner diameter (mm) | Area (mm2) | Volume (mm3) |
| 5 | 3 | 18 | 245 | 2187 |
| 6 | 4 | 22 | 363 | 3993 |
| 7 | 5 | 24 | 432 | 6912 |
| 8 | 6 | 30 | 675 | 13490 |
| 9 | 7 | 33 | 972 | 16380 |
| 10 | 8 | 39 | 1210 | 31870 |
| 11 | 9 | 47 | 1728 | 55290 |
| 12 | 10 | 56 | 2350 | 87808 |
| 13 | 11 | 65 | 3072 | 131070 |
Formation and emergence of the fetus
The formation of an embryo is based on active division at the cellular level. The cells of the embryo grow, due to which the size increases. The process continues for 6-7 days, as it moves along the fallopian tube to the uterine cavity, where implantation will occur. Initially, nutrition occurs through independent resources. After attachment, nutrients flow through the uterus, at the same time the placenta begins to form for further protection and breathing of the child.
At 4-5 weeks, using ultrasound, you can see a round shape, which reaches about 4 mm in diameter. And only at the beginning of the second month of intrauterine development, the formed baby becomes noticeable on the ultrasound monitor. Due to various anomalies, the absence of an embryo can be diagnosed when the embryo, for various reasons, has not formed. After a certain period of time, a second study is prescribed to confirm the diagnosis by the heartbeat, which occurs in the middle of the second month. The fetometric indicator SVD evaluates the diameter and can vary when determining the gestation period within 10 days. Therefore, to determine the period, it is necessary to take into account additional parameters.
Size of fertilized egg by week of pregnancy: table
The size of the fertilized egg at the 5th week of gestation is about 5-6 mm. As the membrane grows and develops, the cells continue to actively divide. Already from the 12th week of gestation, the embryo is considered a full-fledged fetus, a child. The gestational age according to the size of the membrane is determined in accordance with the diameter, area, volume, and is also measured:
- KTP – coccygeal-parietal measurement;
- Biparietal;
- Diameter of the yolk sac.
It is necessary to understand that the parameters may differ depending on the individual characteristics of the parents. Therefore, if the size does not correspond to the period of conception, then there is some error, which is acceptable and is not a cause for concern.
fertilized egg
Before moving on to the parameters of the baby and amniotic organs, it is worth understanding what a fertilized egg is?
The formation of this new living organism begins from the moment the egg is fertilized by the sperm. This occurs inside a woman's fallopian tube. Next, the fertilized cell passes into the uterine cavity and begins to divide into small cells.
Several cells that have approached the wall of the womb and begun implantation can already be called a fertilized egg. There is nothing in it yet similar to the human body, but very soon this will change.
A week after fertilization, the cells are implanted into the wall of the uterus, after which they begin to exist at the expense of the mother’s body. At this time, the embryo is still very small and cannot be seen on an ultrasound.
After implantation, thanks to substances from the uterine wall that enter through the blood vessels, the new organism begins to grow rapidly. It can be determined by instrumental methods in just a few weeks.
Embryo examination method
If the baby in your womb is not yet 9 weeks old, then experts recommend doing the examination using several methods:
- Using a transabdominal sensor, moving along the anterior wall of the peritoneum;
- Using a transducer. The examination is carried out through the vagina. This is a transvaginal method. The transvaginal method is considered the best way to carry a baby for a short period of time. The wave frequency used is high and on the screen the doctor sees the condition of the woman’s uterus and fetus.
How is it determined?
You can see the size of the baby using a simple transabdominal ultrasound. The study is performed as follows:
- After a woman is registered for pregnancy, the doctor determines the date of the first screening - usually 11-14 weeks.
- The woman lies down on the couch, after which the procedure begins.
- An ultrasound sensor is placed on the expectant mother’s belly and all dimensions of the fetus are carefully assessed.
- This study can be performed earlier, but it will be less informative.
At what size of fertilized egg is the embryo visible? Already at 3–4 weeks of gestation, modern sensors are able to assess the presence of a baby in the uterine cavity, at which time it reaches a size of about 3 mm.
An embryo of 5 mm is already clearly visible on ultrasound, but assessing its internal structure is still quite difficult.
Life-saving ultrasound
More than 92% of pregnant women, according to the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation, today undergo ultrasound diagnostics. And by the end of this year, it is planned to cover at least 98-99% of expectant mothers with ultrasound examination. Needless to say, pregnancy pathologies are becoming more and more common. Poor ecology, stress, lack of vitamins and minerals take their toll. And if it were not for technological progress, the picture would be completely depressing.
If, for example, specialists saw that a woman’s ovaries were not doing well, they would prescribe her hormonal medications. Do you suspect that the baby is not getting enough oxygen? Take some special medicine, expectant mother. Has the placenta aged prematurely? Get medications that improve uteroplacental circulation. In a word, now you can’t go anywhere without an ultrasound! It is recognized throughout the world as the safest and most informative diagnostic method.
Over the several decades of the technique’s existence, there have been repeated attempts to conduct a global study of the possible negative consequences of ultrasound, but so far no scientific publications on this subject have appeared anywhere in the world. Experts joke that if you do not remove the sensor from a woman’s abdomen throughout pregnancy, then we can still talk about harm. And there is nothing dangerous for the baby in echography. Judge for yourself, because from the point of view of physics, ultrasonic waves are the same sounds as, say, the sounds of musical instruments.
During the examination, the doctor installs a small sensor on the pregnant woman’s stomach - a transducer, somewhat reminiscent of a computer mouse. It produces ultrasonic vibrations, which, penetrating deep into the body, collide with the child’s internal organs. Ultrasound reflects off them at different speeds because they all have different densities. The ultrasonic waves are then sent back to the sensor, which picks them up and sends them to the computer. And an image appears on it. That's all!
Studies have shown that approximately 50% of women experience some kind of fetal reaction to this procedure. The other half's baby sleeps soundly during the study. Apparently, this means that the ultrasound session simply coincides with periods of activity or, on the contrary, sleep of the child.
Typically, the most concerning method is transvaginal ultrasound, in which a probe is inserted into the vagina. In the very early stages of pregnancy, it can actually cause slight uterine tone. But during this period it is very difficult to do research differently. An abdominal (regular) ultrasound may simply show nothing. Transvaginal ultrasound has another advantage - you do not need to go to the examination with a full bladder.
Norm
Most often, women are interested in the size of the embryo even before the time of the first screening. This is necessary to know in order to determine the fact of pregnancy, its duration and detect developmental abnormalities.
During the procedure, the doctor evaluates the shape of all detected formations and the parameters of the internal contents of the fertilized egg.
Size of fertilized egg by week of pregnancy, table:
As can be seen from the table, the size of the fertilized egg increases quite quickly. It is assessed only in the first trimester of pregnancy. Next, the doctor will determine more accurate parameters that reflect the state of the child’s body.
Pathology
When performing an ultrasound examination in the early stages of pregnancy, a fairly large number of different abnormalities can be detected. Among them are the following groups of disorders:
- Change in the shape of the primordium. At the beginning of pregnancy, the embryo is a spherical formation, so on ultrasound it is detected in the form of a circle. After 7 weeks of pregnancy, the fetus takes on an oval shape. Tumors of the uterus, congenital malformations, infectious diseases, pathology of the placenta can cause disruption of the shape of the egg.
- Pathology of location. A properly developing embryo is located in the uterine cavity in the area of the fundus or posterior wall of the organ. Less commonly, the embryo is located in the area of the internal os. Other options for the location of the baby are considered pathological, some of them are generally incompatible with the further physiological course of pregnancy.
- Anembryony. A rather rare developmental defect in which there is no embryo at all in the fertilized egg. Due to genetic disorders and the influence of environmental factors, the amniotic organs develop, but the baby itself does not. In this case, the egg will be of normal size, but there will be no child inside it.
- Dimensional changes are the most common deviation. In the first stage of pregnancy, it is quite difficult to draw a conclusion about the normal size of the embryo, but often already at this time it is possible to guess what is causing the decrease or increase in the fetus.
Is ultrasound safe for the fetus?
Thanks to this method of examination, the doctor can determine at an early stage of development whether the embryo is visible, does it have abnormalities? The doctor will try to carry out the procedure quickly. The examination itself lasts on average 15 minutes.
Now is the early stage of formation of internal organs in the fetus. An experienced doctor will move the sensor faster than usual over the woman's abdomen or uterus. The ultrasound specialist will try not to hold the device for a long time over any internal organ of the baby.
During the entire pregnancy, a woman will be prescribed at least 3 scheduled ultrasounds, and some will have repeat ones. According to statistics, on average, this is 9 times during the period of gestation. The specialist does screenings from the monitor screen. In addition, the woman donates blood for tests.
"Advice. Don’t worry, the doctor will check whether your baby is normal or not? He decides on additional ultrasound examinations.”