HCG stands for human chorionic gonadotropin. HCG is a rather specific hormone, and it is released during the period of gestation by the placenta. In this way, the unborn baby informs the mother’s body about its appearance. This hormone is required for the synthesis of another hormone - progesterone. If pregnancy does not occur, then hCG is not produced.
Hormone levels increase every day until the thirteenth week. If conception occurs artificially, the level of this hormone is constantly monitored. When a week has passed after the fertilization of the egg, it turns into a blastocyte. From this formation the fetus and placenta will subsequently develop. When the blastocyst attaches to the mucosa, biologically active hCG is produced. Thanks to this hormone, the formation of the primary placenta begins.
Peculiarities
HCG affects the body in such a way that the ovaries begin to actively synthesize progesterone. With the advent of progesterone, ovulation stops, since by this time the mother’s body is adjusting to pregnancy. From the sixteenth week, the placenta becomes the main source of progesterone. Therefore, hCG loses its leading role in the further development of pregnancy. If human chorionic gonadotropin is detected in the blood during the study, we can say with confidence that the woman is pregnant.
Does hCG indicate the obstetric period or from conception? As you know, the obstetric period lags behind the period of conception by about two weeks. HCG indicates the period from the moment of conception. This hormone appears in the blood already on the seventh day after fertilization. Familiar strips can detect the presence of pregnancy starting from the fifth week. The level of hCG in the urine, where the strip is always immersed, will be several times lower than in the blood. If a woman has undergone IVF, a pregnancy test is performed on the fourteenth day after the transfer. The development of the embryo is judged by how the level of the hormone increases in the blood.
If several embryos have implanted inside the uterus at once, the hCG level will be very high. A high level of the hormone can also occur if embryonic mutations have occurred or degeneration of the embryonic part of the placenta has begun. If the analysis reveals, on the contrary, a very low level, this will mean that the embryo may die at any time. A low rate can also occur with an ectopic pregnancy. Therefore, in the very early stages of pregnancy, this analysis is very important, as it helps to identify pathology. If necessary, hCG levels are monitored regularly.
Properties of hCG and its role in the body
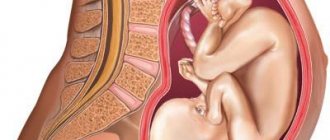
As soon as the fusion of the egg and sperm has occurred, the cells of the embryo begin to multiply intensively and at the end of the first week it can attach to the uterus (inner wall). The embryo at this stage is a small vesicle, but in its outer part (trophoblast) the cells intensively produce a hormone that is responsible for normal growth.
Next, the trophoblast is fixed to the endometrium and transformed into the chorion (villous membrane), which is the main part of the placenta mass. It is with its help that the blood flow of the fetus and the expectant mother is connected, metabolism is carried out, useful substances are delivered and unnecessary substances are removed. Throughout pregnancy, the villous membrane produces human chorionic gonadotropin, which not only helps the fetus develop, but also supports the woman’s body during pregnancy.
As soon as a woman becomes pregnant, progesterone, produced by the corpus luteum of the ovary, becomes an important substance during this period. During pregnancy, hCG is necessary to maintain the function of the corpus luteum and increase the concentration of progesterone. That is why the expectant mother’s corpus luteum does not disappear, which always happens during the physiological menstrual cycle.
HCG consists of 2 substances - alpha and beta. The first is the same as thyroid-stimulating and luteinizing hormones, and the second is unique to human chorionic gonadotropin. Therefore, in laboratory analysis, it is its indicators that matter. The beta unit can be detected approximately 6–8 days after fertilization. After giving birth, within a week there should be no human chorionic gonadotropin in the blood and urine.
So, the functions of hCG are:
- preservation of the corpus luteum and participation in the formation of progesterone;
- promotes proper implantation and chorion formation;
- responsible for feeding the chorionic villi;
- ensures that the pregnant woman adapts to her condition;
- stimulates the functioning of the adrenal glands and gonads in the fetus.
An increase in human chorionic gonadotropin may indicate pregnancy. But can hCG be elevated, but there is no pregnancy? This also happens, but in the presence of abnormalities in the development of the fetus or one or another pathology in the mother. By comparing hormone levels during pregnancy at different stages, one can suspect an ectopic or frozen pregnancy.
Norms
To detect deviations, you can use a special table. The hCG table for weeks of pregnancy may differ from different sources; doctors usually take the average value. The hCG rate during pregnancy gradually changes over the weeks from conception. In the first weeks of gestation, the normal hCG value doubles every other day. In non-pregnant women, the level of the hormone in the blood does not exceed 5 IU/l.
In pregnant women, this result is eight times higher. If the result of the hormone content in a woman’s blood falls between these two values, then the analysis must be repeated after some time. If the daily hCG level is normal, medical intervention during pregnancy is not required.
The highest levels of the hormone are observed from the tenth to the twelfth week. In days from 69 to 90 days. You can verify this by looking at the table. The hormone level rises to 50,000-100,000 IU/l. There is no further increase in values. At the twelfth week, the hormone in the blood begins to decrease. By day 140, these numbers drop to 1000-20000 IU/l. And then the level of the hormone remains unchanged until the birth of the child.
If you study the table values in more detail, then at 2 weeks from conception the hormone level will be 25 – 156 IU/l. When does hCG show pregnancy after conception? HCG at 3 weeks from conception is 2000 honey/ml and this is an accurate sign of pregnancy. If a woman undergoes an ultrasound at this stage, pregnancy can only be detected by indirect signs.
HCG function
The hCG level helps to detect various pathologies of the embryo and the woman in labor.
There are cases of increased or decreased hormone levels. To determine intrauterine infection of a child, fetoplacental insufficiency and some other conditions, measurements of human chorionic gonadotropin are not used. HCG is needed for the corpus luteum to function normally, so that there is sufficient production of progesterogen and the hormone estrogen at the beginning of pregnancy. The hormone also helps a woman’s body change, because after conception, to maintain pregnancy, the body must change in many ways. HCG also serves to protect embryonic cells from the mother's immunity. After all, the body’s defenses can perceive the embryo as something foreign, which can make pregnancy impossible.
Human chorionic gonadotropin is needed for the fetal adrenal glands and gonads to function normally. If the fetus is male, hCG provokes the production of testosterone, due to which the child is formed as a male.
Pathologies
The results of the hCG analysis are especially important when artificially introducing an embryo. If this indicator on the fourteenth day from the moment of the procedure does not exceed 25 IU/l. there is no pregnancy, but the embryo did not implant.
But hormone levels can also increase in situations not related to pregnancy. For example, in the presence of cancerous tumors in the body. When pregnancy occurs, future parents are concerned about a very important question, namely, will they have a boy or a girl?
The sex of the unborn child can be determined by the level of the hormone. HCG levels will rise to higher levels if a woman is pregnant with a girl. According to doctors, a pregnancy test when expecting a boy gives a positive result much later. If the expectant mother has a hard time with early pregnancy, which is accompanied by severe toxicosis, then the level of the hormone may also increase.
A high level of the hormone may indicate the onset of a hydatidiform mole, which is a disorder of the development of the placenta. In this case, the hormone level rises to 500,000-1,000,000 IU/l.
In addition, high levels of the hormone occur with the development of diabetes in the expectant mother. Genetic abnormalities in the fetus are also accompanied by an increase in hCG. This is why the hCG test is prescribed by geneticists. Thus, they identify abnormalities in chromosomes.
This test is highly likely to identify infants with Down syndrome. But the final diagnosis is established not only by analyzing the hormone content. Additionally, the expectant mother undergoes an ultrasound, and another blood test is prescribed for hormones. It is immediately worth noting that the test may show possible deviations, but in fact a completely healthy child is born. Therefore, the woman additionally receives amniotic fluid. It is this analysis that makes it possible to accurately identify deviations from the norm in the chromosome set.
Source: 1ivf.info
Types of analysis for hCG
There are several. These include a test for human chorionic gonadotropin or a general analysis and free beta-hCG. The studies have their differences.
General hCG analysis
The analysis is carried out to determine pregnancy at an early stage, when a simple test from a pharmacy is not yet able to show two stripes. It is called perinatal screening or triple test. In the later stages of gestation, the study is carried out over time to monitor genetic abnormalities.
Free beta hCG
Beta hCG is used to determine fetal pathologies: choriocarcinoma, hydatidiform mole, testicular oncology, etc. In the first two trimesters, an hCG test is performed to identify Down and Edwards syndrome. If the result is disappointing, then the expectant mother is referred for further research. Special indicators for prescribing an analysis include age over 35 years, hereditary genetic diseases, and radiation exposure.
HCG norms during IVF pregnancy by week: table
Human chorionic gonadotropin is secreted by the chorion, so a non-pregnant woman should not have it in the blood. If the test is positive, but there is no pregnancy, it is assumed that shortly before this the woman experienced an abortion or early fetal death.
If this was not the case, we can assume the formation of a malignant tumor in the body, which releases cells into the body that are similar in structure to the hCG hormone. In medical practice around the world, there have been cases when men took a pregnancy test for fun, and it turned out to be positive. This is how patients accidentally learn about serious health problems.
After IVF, it is necessary to monitor hCG, which changes during pregnancy. Starting from the first day of fertilization and up to 11-13 weeks, a constant increase is observed, then a gradual decrease in the level of hCG is observed.
In diagnostic centers there are hCG standards, but they are approximate. The level of the hormone in a particular woman may differ from the general indicators. This is due to the fact that each pregnant woman has her own body constitution, her own body characteristics and can tolerate pregnancy differently. That is why the doctor often compares the results of hCG not with “general standards”, but with the patient’s earlier hormone levels. In other words, the dynamics of hCG are monitored relative to individual results, and the presence or absence of an increase is determined based on the past test results of the woman.
Please note: Laboratories that perform hCG tests use different reagents, instruments and equipment, so test results may vary slightly. Sometimes it is advisable to repeat the analysis in several diagnostic centers at once in order to obtain an accurate picture of the course of pregnancy.
In gynecology and obstetrics, it is customary to count the duration of pregnancy in weeks, and the countdown is not from the day of conception or the IVF procedure, but from the day the last menstruation began. This is the so-called obstetric period of pregnancy. However, the level of hCG begins to increase only after conception, therefore, to determine it, it is often not the obstetric period that is taken, but the embryonic period, which is counted from the day of fertilization.
Expectant mothers who do not know such features are confused about the timing and may misinterpret the results of hCG. That is why it is important to consult a doctor in time. If you urgently need to decipher the hCG result and it is not possible to immediately visit the clinic, check with the laboratory where the analysis was carried out about the hCG norms for your gestational age, with a mandatory indication of whether the laboratory takes into account the obstetric or embryonic period.
To illustrate how the level of hCG can differ depending on the same obstetric and embryonic period, we provide a table of hCG norms during pregnancy by week.
| Gestational age (weeks from conception, embryonic period) | Gestational age (weeks from the first day of the last menstruation, obstetric period) | HCG norm, mIU/ml |
| 3-4 | 5-6 | 1 500-5 000 |
| 4-5 | 6-7 | 10 000-30 000 |
| 5-6 | 7-8 | 20 000-100 000 |
| 6-7 | 8-9 | 50 000-200 000 |
| 7-8 | 9-10 | 40 000-200 000 |
| 8-9 | 10-11 | 35 000-145 000 |
| 9-10 | 11-12 | 32 500-130 000 |
| 10-11 | 12-13 | 30 000-120 000 |
| 11-12 | 13-14 | 27 500-110 000 |
| 13-14 | 15-16 | 25 000-100 000 |
| 15-16 | 17-18 | 20 000-80 000 |
| 17-21 | 19-23 | 15 000-60 000 |
Please note that the standards given in the table are the standards of an individual laboratory. HCG levels in other diagnostic centers may vary. The interpretation of the test results is carried out by a doctor.
Below is a table that shows the dynamics of hCG by week during IVF pregnancy.
| Gestational age (weeks from conception, embryonic period) | HCG norm, mIU/l |
| 1-2 | 25-156 |
| 2-3 | 101-4 870 |
| 3-4 | 1 110-31 500 |
| 4-5 | 2 560-82 300 |
| 5-6 | 23 100-141 000 |
| 6-7 | 27 300-233 000 |
| 7-11 | 20 900-291 000 |
| 11-16 | 6 140-103 000 |
| 16-21 | 4 720-80 100 |
| 21-39 | 2 700-78 100 |
Please note that the standards given in the table are the standards of an individual laboratory. HCG levels in other diagnostic centers may vary. The interpretation of the test results is carried out by a doctor.
The following is a table from which you can track the dynamics of hCG levels by day after embryo transfer (D.P.P.).
Death of the fetus in the mother's stomach and frozen pregnancy
There are such cases: a woman takes a test that confirms pregnancy, and after some time she notices symptoms that are typical for non-pregnant women. In some cases, the death of the fetus may occur, while it will remain in the mother’s womb. If this happens, the pregnancy no longer develops, the hCG level remains the same as it was at the time of the death of the fetus, and then begins to fall.
In case of a frozen pregnancy or antenatal death of the embryo, ultrasound can show anembryony or the absence of a heartbeat in the fetus. Pregnancy can freeze for the following reasons:
- mother's blood clotting disorder
- defects in the anatomy of the uterus, which does not allow the fetus to develop further
- infectious diseases of a pregnant woman, for example, endometritis, which occurs in a chronic form
- chromosomal abnormalities
If your doctor diagnoses a frozen pregnancy, he may advise you to wait a while for a miscarriage. But very often a woman undergoes uterine curettage or abortion using special drugs. A pregnant woman should be alerted if she has had two or more fetal deaths. You need to be examined to understand why this tendency occurs in this couple.
If a child dies not in the first 3 months of pregnancy, the condition is called “antenatal fetal death.” HCG decreases, as in the cases described above.
HCG for multiple pregnancies after IVF
Often, during IVF, several prepared embryos are implanted into the expectant mother to increase the chances of success of the procedure. There are cases when all fertilized eggs take root. In this case, multiple pregnancy occurs. It is determined by ultrasound at 11-12 weeks, but a high probability of carrying twins can be detected by donating blood for hCG. In women carrying twins, this figure is significantly higher than normal.
Low hCG during IVF pregnancy
Low hCG levels after IVF may indicate a lack of pregnancy, a threat of miscarriage, or fetal death, so values below normal should alert the patient. The analysis is repeated several times, tracking the dynamics of changes in indicators.
A sharp decrease in hCG during pregnancy after IVF
After IVF, you need to monitor your hCG levels during the first trimester, when the likelihood of a missed abortion is high. If there is a sharp decrease in the level of this hormone after IVF, this is a reason to immediately consult your doctor. Sharp jumps in hCG indicate a high risk of interruption. The patient is sent to the hospital for conservation, having previously undergone an ultrasound to check the fetal heartbeat.
When tracking the dynamics of hCG, it is recommended to take tests in one laboratory to eliminate possible errors in the results.
Constant monitoring of hCG levels helps to identify certain problems and risks before they make themselves known in the form of various symptoms. The earlier a problem is identified, the easier it is to fix it.
Source: mirmam.pro
HCG for fetal abnormalities
To understand how the fetus develops, prenatal screening is performed in the first trimester - ultrasound and analysis of hormones, including human chorionic gonadotropin. So, at 10-14 weeks of pregnancy, PAPP-A and hCG are determined. At weeks 16-18, a triple test is performed, which consists of analyzing the level of ACE, human chorionic gonadotropin and estriol-A. To detect chromosomal abnormalities or malformations in a timely manner, if they are suspected, an ultrasound scan is performed. The specialist must take into account whether the woman has previously given birth to children with developmental anomalies, her age, and weight.
Deviation from the norm of this hormone is possible if the fetus has the following anomalies:
- Down syndrome;
- Turner syndrome (while other markers, with the exception of hCG, remain normal);
- Patau and Edwards syndromes;
- Severe defects of the cardiovascular system and heart.
If there is a risk of abnormalities, additional studies are carried out to confirm the diagnosis. Most often these are invasive techniques - chorionic villus biopsy, amniocentesis or cordocentesis.
If your hCG blood test is abnormal, your gynecologist may recommend genetic counseling. Screening becomes more difficult when carrying two or more children. What does a blood test for hCG mean during pregnancy in such cases? In case of multiple pregnancy, it exceeds the norm by 2 times or more during its normal course. Therefore, it is extremely difficult to detect fetal development abnormalities.
At what stage can an ultrasound examination show the fetal heart beating?
When can a fetal heartbeat be heard on an ultrasound? It sounds banal and hackneyed, but pregnancy is the most exciting and at the same time alarming time in the life of every woman. Over the course of 9 months, she has to undergo many procedures, in particular those that evaluate the development of the baby’s cardiovascular system. Starting from what week after fertilization can you hear his heart beating for the first time?
How does a child develop?
» alt=»5 week pregnancy » width=»500″ height=»370″>
According to experts, the time from 3 to 5 weeks (determined by hCG analysis) after conception or embryo transfer during IVF is the most important in its development. In appearance, it resembles the auricle, which allows doctors to get a good look at the back and limbs.
At this stage, the dorsal chord is released, from which the spinal cord and spine will subsequently develop. If the process proceeds without disturbances, the end of the neural tube becomes flattened.
And also the formation of so-called somites begins, cells that are responsible for the formation of absolutely all tissues.
During this early period of development of the baby, the rudiments of the cardiovascular system are laid. Its elements develop so quickly that the largest vessels can already be seen on ultrasound. They are located in the center of the embryo, maintaining a close connection with a clot of tissue that will become the heart in the future. It is worth noting that this tissue takes part in the development of many organs and systems.
Among them:
- respiratory tract (trachea, larynx);
- pancreas;
- liver;
- sex cells.
This is interesting. Despite the appearance of the rudiments of the cardiovascular system, it is impossible to hear the heartbeat even with the help of the most powerful ultrasound machines.
» alt=»Embryo» width=»200″ height=»150″>The rudiments of the heart are located in the cervical region. During their formation, the size of the embryo barely reaches 2 mm, so it is not possible to examine or control what is happening.
The whole process consists of several stages.
- Two separate tubes called endocardial tubes appear.
- The tubes are combined together.
- From the fourth week after conception (obstetric period plus 2 weeks), the heart tube is divided into 2 parts: right and left. Between them a primary septum is formed, which has an oval window. It will not heal until after birth. The hole will close only when the newborn takes his first breath.
- Starting from the fifth week, a septum forms. The endocardium and myocardium participate in this process. It takes about 3 weeks.
- A small hole appears between the ventricles and atria, which, starting at week 7, will be closed by a valve.
- At the onset of the 6th week, the first heart contractions occur. They can be seen and heard during an ultrasound examination.
The heart takes the same shape as in adults by 8 weeks. It is at this time that it becomes four-chambered.
The number of heart contractions depends on two factors:
- child activity;
- gestational age.
For example, at 6-8 weeks the heart rate is 110-130 beats per minute. Before the 11th week it often reaches 190 beats, and after 11 it ranges from 140 to 160 and remains so until later.
Starting from the second trimester, you can listen to your heart beat using a stethoscope. One side of it is applied to the woman’s stomach, and the other is pressed by the doctor to her ear.
What does ultrasound show?
Why is ultrasound of the fetal heart prescribed at different stages of pregnancy?
» alt=”Ultrasound” width=”200″ height=”137″>With its help, the doctor can see several indicators:
- Heart rate. As mentioned above, it depends on the age and condition of the baby.
- Where is the heart located? It should be located on the left side of the chest and occupy one third of it.
- How rhythmically the organ contracts.
If at the first ultrasound some indicators do not meet the standards, after about 7 days the specialist will prescribe another one.
All subsequent procedures carried out in the second and third trimester help to monitor the general condition of the child and notice overloads in time. Sometimes, in addition to the planned ones, it is necessary to do several additional studies of cardiac activity.
There are several such cases:
- the expectant mother suffers from diabetes;
- woman's age is over 38 years;
- infectious diseases have occurred;
- there are disturbances in the development of the fetus;
- the woman has a heart defect.
What do deviations from the norm indicate?
» alt=»Doctor and patient » width=»200″ height=»133″>There are only four deviations from the norm:
- the heart beats at a rate of less than 120 beats per minute;
- frequency above 170 beats;
- the heartbeat is difficult to hear;
- There is no heartbeat at all.
What does each one mean?
A heart rate below normal in the early stages is:
- erroneously set deadline;
- normal fetal development;
- risk of miscarriage (cases when heart rate is below 80).
After week 12, this indicates a chronic form of hypoxia or compression of the umbilical cord. During labor, heart rate decreases due to acute hypoxia.
If the number of heartbeats is higher than normal, in the early stages this may be evidence of disturbances in the formation of the placenta. After 12 weeks, the baby may react this way to his movements or suffer from a lack of oxygen. During childbirth, a rapid heartbeat also indicates hypoxia or the fetus's response to contractions.
There are several reasons why heart sounds are difficult to hear in the early stages:
- incorrectly defined period;
- mother's overweight;
- a heart or blood vessel defect in a child.
What if the heartbeat is difficult to hear in a later period?
This may be a consequence of the following conditions:
- obesity in women;
- placental insufficiency;
- placenta previa;
- excess or lack of amniotic fluid;
- uncomfortable position of the baby;
- heart or vascular defect.
If the tones are practically not audible during childbirth, this is either a reaction to strong contractions or hypoxia.
» alt=»Doctor and patient » width=»200″ height=»149″>Complete absence of heartbeat in the early stages threatens spontaneous abortion. This is usually a sign of a frozen pregnancy. Sometimes heartbeats are not visible due to faulty equipment.
If the heartbeat is not heard in the other two trimesters, one can judge the antenatal death of the child. The same applies to childbirth. There are times when it becomes necessary to monitor the fetal heartbeat during labor, from the moment contractions begin until birth.
There are several of them:
- epidural anesthesia was administered to relieve pain;
- the child is developmentally delayed;
- a woman is pregnant with two or more fetuses;
- labor began prematurely;
- the pregnancy is post-term (42 weeks or more);
- the baby suffers from hypoxia;
- labor had to be stimulated;
- a pregnant woman suffers from gestosis;
- have chronic diseases.
How can you control your heart rate?
Usually, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound to assess heart rate. The study helps to evaluate not only this parameter, but also to see the condition of the placenta and the size of the fetus. Particular attention is paid to women whose older children were born with heart and vascular diseases, as well as those who have had infectious diseases.
» alt=”Pregnant woman on ultrasound” width=”200″ height=”133″>
Another diagnostic method is auscultation, which determines the heartbeat using a stethoscope. It can be used by a person without special education. It is enough to attach the device with one side to the stomach and the other to the ear.
It is often very difficult to listen to the heart beat in this way.
And there are several reasons for this:
- overweight;
- location of the placenta on the anterior wall;
- oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios.
Heart rate can also be monitored using CTG or cardiotocography. According to reviews on the forums, this is a fairly informative method. It allows you to determine hypoxia even at an early stage.
The device used to record is a small ultrasonic sensor. It receives a signal from the child and displays it on film. It also records the number of uterine contractions (contractions).
The newest CTG devices allow expectant mothers to monitor the baby’s movements for about an hour. You can watch how to do this correctly in training videos.
The first procedure is carried out at 32 weeks. From this period, a certain connection appears between the number of heartbeats and how the child moves.
The obstetrician-gynecologist compares the general results of CTG with the results of ultrasound and forms a common opinion.
» alt=»Pregnant girl at an appointment with a gynecologist » width=»200″ height=»133″>In which case the results will be good:
- Heart rate ranges from 120 to 160 beats per minute.
- When the baby moves, the heart rate increases.
- The heartbeat does not slow down or speed up (no tachycardia).
Indicators above or below normal are the result of the following conditions:
- acute lack of oxygen;
- pressing the umbilical cord to the body;
- Incorrect mounting of sensors.
Attention! If the CTG results are poor, the doctor may decide to perform an emergency delivery. In this case, the woman undergoes a caesarean section.
And the last method is echocardiography. It is performed at 18 to 20 weeks if there is a suspicion of heart defects.
Other indications for this procedure are:
- the presence of older children with pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- congenital defects in the mother herself;
- infections suffered in the first trimester;
- woman over 38 years old;
- a pregnant woman has diabetes;
- the child has developmental disorders in other organs.
So, you can hear the baby’s heartbeat on an ultrasound starting from six weeks. It is during this period that the heart first begins to contract. By the frequency of contractions, you can determine how correctly the baby is developing.
Source: lechenie.giperton-med.ru
hCG level after childbirth
When a number of pregnancy factors and hCG enter a woman’s bloodstream, we are talking about the biochemical stage of early pregnancy. Typically, women do not feel any changes in their bodies, up to a delay in menstruation. And only a few out of several thousand or tens of thousands of women can feel certain changes in their body associated with the onset of pregnancy. However, it will not be nausea and vomiting, or bloating, breast tenderness - all this will appear later. These will be specific sensations, very individual, which many women cannot characterize - most likely, this is the feeling of the presence of new life in their body. Before a missed period, almost all women have no idea that they are pregnant, although many hope so. Thus, taking into account the entire process of conception and implantation, it is important to understand that at the beginning of your next period you are already at least 4-4.5 weeks pregnant , although You weren’t pregnant for the first two weeks! And there are still at least 8 months of pregnancy ahead. Therefore, do not turn the beginning of pregnancy into a rush, wandering around pharmacies and ultrasound rooms, do not panic whether everything is in order, because the unborn child needs the peace of your body and soul. I am amazed by the fact that some women begin to conduct endless pregnancy tests or run through ultrasounds and almost lose consciousness if the test is negative or they cannot find anything on the ultrasound. Calmness and patience are essential attributes of motherhood, so if you don't have them or don't have them, start working on them today.
It is believed that a normal pregnancy lasts from 266 days (38 weeks) to 294 days (42 weeks) - an average of 280 days (40 weeks) - from the first day of the last menstrual period. This period takes 9 months of the calendar, but in obstetrics one month is 4 weeks - the lunar or obstetric month. Doctors do not like the word “month”, but prefer the word “week”, so the gestational age is stated in weeks and days (for example, 20 weeks 5 days). Not only women, but also many doctors, especially of the old school, define the period differently, which often introduces more confusion than clarity into the interpretation of many data. Some people calculate the gestational age from the day of conception (conception), but not all women know exactly the day of conception, since the menstrual cycle is not always monitored. So, the duration of pregnancy is determined from the first day of the last menstruation, provided that your menstrual cycles are regular, that is, their duration is 26-30 days, and on average 28 days. If your cycle lasts 35-40 days, then a certain number of days is subtracted, or most often an ultrasound is used at 11-14 weeks to clarify the gestational age and conduct prenatal genetic screening. Traditionally, obstetricians use three methods to diagnose pregnancy: clinical signs of pregnancy, which include the woman's complaints and examination, determination of pregnancy hormones in the woman's serum and urine, and ultrasound examination. A combination of several methods is often used.
The very concept of “diagnosis: pregnancy” is not entirely accurate, because pregnancy is not a disease , but only a temporary condition of a woman. The first sign of pregnancy is a delay in menstruation . Let's start with this. However, 25% of women experience spotting or even bleeding in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy, which could be implantation bleeding, a false menstruation, or a sign of miscarriage. Your period may also be late, a common normal occurrence in the lives of many women. In such cases, you need to wait 7-14 days, and then you can take a pregnancy test. If pregnancy is desired, then you should not rush somewhere in search of something scary and terrible (for example, an ectopic pregnancy). Who seeks will always find! Therefore, look for a normal pregnancy, or rather, accept it into your life patiently and joyfully. Some women experience pain in the breasts, sometimes a tingling sensation, the breasts “fill up” and become sensitive to touch. This usually occurs after 6 weeks of pregnancy. Before menstruation, breasts can also be painful. It is not advisable to use the sign of changes in the mammary glands to diagnose pregnancy. The bladder may send signals that you need to urinate more frequently, especially at night, which some women and doctors perceive as bladder inflammation. The problem is not the growth of the uterus - it is still of normal size or slightly enlarged, but it sends a huge number of signals along the nerve fibers to the lumbar spinal cord. The peculiarity of the nerve plexuses in the pelvic area is that the signals that come from the pelvic organs are “mixed” at the level of these plexuses and then, entering the brain, are not always correctly perceived by a person. Thus, overstrain with nerve impulses due to the entry of the uterus into its completely new quality state leads to the fact that the woman feels discomfort in the bladder, appendages, and lower back. The pain is usually migrating, changing the location of the sensation several times a day: sometimes there is a tingling sensation in the right side, then in the left, then in the front, then in the back. A small number of women complain of general weakness, drowsiness, fatigue, and changes in the sense of smell and taste. It is not worth judging pregnancy only by these signs in the absence of a delay in menstruation or a slight delay, however, you need to be prepared for pregnancy too.
It is very pointless to measure basal temperature and predict the presence of pregnancy or its termination. The normal body temperature for women is 33.2 -38.1°C when measured in the oral cavity, 35.5-37.0°C when measured in the armpit, 36.8-37.1°C when measured in the rectum. More often the temperature rises in the evening, and is often higher in the morning. Body temperature levels fluctuate throughout the day and depend on many factors, but most often do not exceed 1°C. Under the influence of the increase in progesterone in the second phase of the cycle, body temperature usually increases by 0.5-0.8 degrees, which can be recorded on the temperature graph. It is impossible to predict the exact day of ovulation using this method. The temperature may rise the next day and a few days after ovulation, or it will differ little from the picture in the first phase - all these options are normal if the results of ultrasound and hormones are normal. In a third of women, body temperature drops to first-phase levels 3-7 days after ovulation, without reflecting the state of pregnancy. Some doctors recommend that women measure their body temperature in the first weeks of pregnancy in order to predict the outcome of such a pregnancy: allegedly, with a decrease in a woman’s basal body temperature, the threat of miscarriage increases, since there is not enough progesterone. This is an erroneous statement. Try to live without thermometers in the morning. Measuring basal body temperature is not a prognostic sign of the outcome of pregnancy (the threat of its loss or normal progression), and even more so is not a criterion for assessing the saturation of the body with progesterone and prescribing this hormone to a woman.
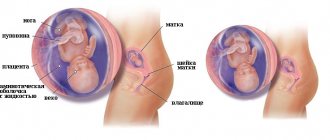
An examination by a doctor can clarify the diagnosis of pregnancy if this examination is not carried out too early, that is, not immediately after conception and not 1-2 days after a missed period. The cervix begins to soften at 4-6 weeks of pregnancy, but not every doctor can determine this. At about 6 weeks, the color of the cervix becomes bluish due to increased blood supply to the uterus. At 6-8 weeks, the doctor may detect softening of the isthmus between the body and the cervix. The uterus is located in the pelvis, the upper boundary of which is the level of the pubis. Until 12 weeks of pregnancy (3 months), the size of the uterus does not extend beyond the pelvis, and only by 12 weeks the upper border of the uterus (fundus) reaches the level of the pubis. The size of the uterus resembles a man's fist by this time. But since there is a lot of space in the pelvis, the circumference of the abdomen/waist does not actually change. In addition, if a woman has nausea, vomiting, or decreased appetite, which often happens, especially during the first pregnancy, then it is possible that even a slight loss of body weight may occur. The tilt of the uterus also changes, that is, its body straightens, and by the 12th week of pregnancy there is no longer any forward or backward bending (bending). By 20 weeks, the fundus of the uterus reaches the level of the navel.
Determination of pregnancy hormones is one of the methods of diagnosis . Doctors use this method not to determine the presence of pregnancy, but its progress, and in most cases to diagnose ectopic pregnancy. Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is produced by the cells of the fertilized egg, from which the placenta is then formed. Even in the absence of an embryo in the fertilized egg (empty fertilized egg), a woman’s hCG level may be elevated. In a number of tumors of the ovaries and rarely other organs, hCG can be produced. The peculiarity of hCG is that in its structure it consists of two subunits - alpha and beta: the α-hCG subunit is identical in structure to the same subunit of other hormones of the female body (luteinizing, follicle-stimulating, thyroid-stimulating), but the β-hCG subunit is unique in its structure and is characteristic of hCG pregnancy. Therefore, β-hCG is most often detected in a woman’s blood serum. This pregnancy hormone must reach a certain level before it can be detected in a woman's blood serum. The level of the hormone is measured in special units - miles - international (international) units per 1 ml of blood plasma (mIU/ml, mIU/ml), and it can be detected in the blood on the 7-8th day after conception, that is, on the 21-23rd day menstrual cycle, and in a woman’s urine 8-9 days after conception.
There are four main laboratory methods for determining β-hCG. Each of them is designed for a certain minimum level of this hormone in a woman’s blood or urine. In 5% of women, β-hCG can be detected in the blood on the 8th day after conception and in 98% of women - on the 11th day after conception. The hCG level rises until 10-12 weeks, after which its growth slows down, and then a new rise in hCG growth is observed after 22 weeks. The radio-immunological method allows you to determine β-hCG at 5 weeks of pregnancy. Immuno-radiometric determination of β-hCG levels can be carried out at 4-5 weeks of pregnancy with a minimum hormone level of 150-15000 mU/ml; This is a high-speed diagnostic method, as it requires only 5-30 minutes to carry out. Fluoro-immunological testing is sensitive at a level of 1 mU/ml and can diagnose pregnancy at 3.5 weeks, however, such highly sensitive methods are not used to diagnose normal pregnancy, but most often to diagnose hCG-producing tumors (in both women and men) , after miscarriages and abortions, and for diagnosing ectopic pregnancy. Values below 5 mU/ml are considered negative for pregnancy, all values above 25 mU/ml are considered positive for pregnancy. But again, I repeat that a single measurement of the level of hCG in a woman’s blood serum has no important practical significance, and is used by doctors extremely rarely to diagnose pregnancy. The first four weeks after conception, hCG levels rise rapidly, doubling every 2 days. To be more precise, the process of quantitative doubling of hormone levels is 2.2 ± 0.8 days in the first 4 weeks. After 6-7 weeks of pregnancy, its growth rate slows down slightly, and doubling can take up to 3.5-4 days. In 85% of pregnant women, hCG levels double every 48-72 hours, but it is believed that the increase in levels may be slower, which does not mean that the pregnancy is not progressing and the woman will have an unhealthy baby. Having reached maximum levels at 9-10 weeks, hCG production decreases and after 16 weeks remains at the level of 6-7 weeks of pregnancy. In the second half of pregnancy, the level of this hormone is only 10% of the maximum levels at 10 weeks. Before giving birth, the hormone level increases slightly again. A decrease in hCG levels after 10 weeks characterizes the process of transformation of the child's place (placenta) into an organ of nutrient transport. In other words, the main role of the placenta is not hormonal, but transport: it is a bridge between the mother and the fetus, through which metabolism occurs and the necessary nutrients are supplied to the child.
Women can’t wait to know about their pregnancy, so over the last decade, pregnancy tests, which detect hCG in a woman’s urine, have gained immense popularity. Such tests are primarily commercial, so not all are of high quality, and there is no special control over the production of such tests. Some companies promise a positive pregnancy test almost 2-3 days after conception. If pregnancy is not desired, then the desire of some women to quickly find out about their pregnancy and have an abortion is understandable. I have received more than one letter from women whom doctors “cleaned” even before a missed period or when their period was 1-2 days late, which does not fit into the canons of modern medicine. There are many pregnancy tests using a woman's urine that you can get at the pharmacy, but none of them are superior and each has its disadvantages. According to some manufacturers of these tests, the sensitivity of the tests is 99%, and they can determine the presence of pregnancy several days before menstruation. However, these tests are designed for a certain minimum level of hCG in the urine - from 25 to 2500 mU/ml, which is usually observed in the 5th week of pregnancy. A comparative study of several types of such tests showed that the most reliable results can be obtained with a urine hCG level of 100 mU/ml for 44% of such tests. Many tests give “foggy” results, where the second line is not clearly visible. The test is considered positive when both stripes are clear. Therefore, interpretation of home test results can be difficult and often requires repeat testing. Like all diagnostic laboratory methods, determining the level of hCG in the blood can give a false positive or false negative result. False-positive results are rare (0.01-1%) and are observed in the presence of certain types of antibodies in the blood (in workers on livestock farms, zoos), rheumatoid factor, and LH. Usually, to clarify the diagnosis, hCG is determined in the urine. False-negative tests of β-hCG in the blood are even less common and are associated with technical errors in the determination of this hormone. A false negative result for determining hCG in urine is more common and is associated with low urine concentration or the test being performed too early. A false positive test may occur when using certain medications, such as hCG to induce ovulation. Although the placenta and fetus produce many other substances, their appearance in a woman’s blood is not a reliable sign of pregnancy, since these substances can be produced by the mother’s body, or their level in early pregnancy is so low that it is technically difficult to determine the presence of these substances in the blood mother or her other fluids and tissues.
The third method that doctors use to diagnose pregnancy is ultrasound . Women themselves have created a real stir around ultrasound. If foreign doctors strictly do not recommend performing an ultrasound in the early stages of pregnancy only to determine its presence or duration, with the exception of a number of indications, then doctors in post-Soviet countries not only encourage early ultrasounds, but also conduct them several times in a row in the first weeks of pregnancy. Such speculative use of ultrasound has more commercial benefits than practical value in making a diagnosis. And women themselves have turned ultrasound almost into an object of worship and a panacea. With a vaginal sensor, a fetal sac with a diameter of 2-3 mm can be seen at 4 weeks and 3 days (menstruation is delayed by 3 days with a cycle of 28 days). The yolk sac is the first structural part of the fetal egg, which confirms the presence of an intrauterine pregnancy; it can be seen when the fetal sac is 5-6 mm in size, that is, not earlier than 5 weeks. From 5 to 7 weeks, the fetal sac should grow by 1 mm per day. The embryo can be detected with a vaginal sensor when the embryo is 1-2 mm in size, which corresponds to 5 weeks of pregnancy. Ultrasound doctors use other criteria for diagnosing pregnancy, taking into account the level of hCG in the blood. You can see the fertilized egg when the hCG level is not lower than 1000-2000 mU/ml, and according to the recommendations of most medical associations and societies, it is advisable to perform an ultrasound when the hCG level is more than 2000 mU/ml. In most cases, a clear heartbeat of the embryo can only be detected when it measures 5 mm, which corresponds to 6-7 weeks of pregnancy. At 5.5-6.5 weeks of pregnancy, the fetal heart rate should be 100 beats per minute. Over the next three weeks, the rhythm accelerates and reaches 180 beats per minute. This means that in order not to draw hasty conclusions, to make a diagnosis of pregnancy there must be one or more signs of pregnancy, as well as a positive result when using one of the diagnostic methods.
How is embryonic gestational age calculated?
In medical practice, pregnancy is measured by obstetric term, also called gestation. This method starts from the first day of a woman's last menstrual period. To calculate the embryonic period of pregnancy, it is necessary to subtract two weeks from the obstetric period. This is assumed to be the actual age of the embryo since its conception.
This calculation is based on an average menstrual cycle lasting 28 days. In the middle of the cycle, ovulation occurs - the maturation of the follicle in the ovary and the release of the egg beyond its boundaries. During this period, the woman’s body is ready for conception. If pregnancy occurs, the embryonic period will be exactly two weeks less than the obstetric period. This can be explained with an example. That is, for a pregnancy of 4 weeks, the embryonic period will be 2 weeks.
How does hCG change by day of pregnancy?
Let's look at the table:
Initially, it takes only two days for the hormone levels to double. At 4 weeks after conception, the amount of the hormone also doubles every two days. Then, from the fifth period, for a twofold increase it takes three days. At seven weeks of pregnancy this figure is four days. After the twentieth week, the concentration of the hormone does not change so dramatically.
Experts explain the uneven growth of gonadotropin by the physiological characteristics of a pregnant woman. The initial increase in hCG is due to the intensive development of the fetus and placenta, as well as hormonal changes in the female body. The chorion produces gonadotropin in large quantities, preparing a place for the fetus and providing optimal conditions for its development.
After the tenth week of pregnancy, a significant change in the placenta occurs: hormonal function fades somewhat, it transforms into a respiratory and nutritional organ for the fetus. A unique mother-fetus system is created. The baby receives the oxygen and nutrients he needs.
Why gestational age is not always reliable
There are cases when the duration of the menstrual cycle differs from the standard 28 days. This situation is not at all uncommon; normally, the length of the cycle can be 21-35 days. The standard calculation formula is not suitable here - in a woman with a cycle of 35 days, conception should occur on the 21st day, and not on the 14th day. With an obstetric gestation period of 5 weeks, the embryonic period will not be 3 weeks, but two. Such an error can lead to errors in the choice of pregnancy management tactics by a gynecologist.
A woman may not remember the start date of the cycle in which pregnancy occurred. It is not uncommon for conception to occur several months after a previous birth, before hormonal levels return to normal and a regular cycle is established. In such cases, it is simply impossible to correctly calculate the obstetric period.
How should hCG increase and decrease?
If there are no deviations from the normal state, then doubling the number, approximately once every two days, is considered normal. The maximum value is observed at 8-10 weeks, that is, in the third month of pregnancy, during this period it is 50,000-10,000 IU/l.
Article on the topic:
Hormone tests in gynecology: which ones and when to take?
After this, in the absence of pathology, the hCG begins to decrease, and by the twentieth week the indicator almost halves. A low reading, as well as a high one, may further demonstrate that pathology is present, which means that the expectant mother needs to undergo a serious, detailed examination.
Preparing for a blood test for hCG
- Venous blood is used.
- Blood should be donated in the morning, on an empty stomach, the recommended time is 8-10 hours.
- The day before the test, you need to give up alcohol, fatty and smoked foods, not take medications and not go to the gym.
- In the morning, you can only drink water, do not drink alcohol or smoke, and avoid stress and conflict situations.
- The analysis will not show an accurate result if before this you undergo physical procedures, visit a massage room, undergo an ultrasound and x-ray.
- The same requirements apply to repeated blood donation.
Why is it important to know the exact date of pregnancy?
Doctors monitor the intrauterine development of the fetus, focusing on its compliance with average indicators. If necessary, treatment is prescribed. A woman goes on maternity leave at 30 obstetric weeks to prepare for the birth of her baby. The expected date of physiologically timely birth (PDB) is also determined. It varies from 37 to 42 complete obstetric weeks.
Fetal genetic screenings aimed at detecting malformations and congenital genetic anomalies must be carried out at a precise time interval. Otherwise, the diagnostic value of the study is lost - the results can be either false positive or false negative.
Causes of high and low hCG levels
The most common reasons for an increase in the amount of hCG in a pregnant woman’s body:
- fetal malformations
- chromosomal diseases of the child
- gestational diabetes mellitus
- multiple pregnancy
- taking hCG as therapy as prescribed by a doctor
- trophoblastic tumors in the mother
The reasons for low hCG include the following:
- some chromosomal abnormalities
- death of the fetus in the mother's womb for one reason or another
- threat of abortion
- frozen pregnancy
- ectopic pregnancy
Calculation methods
There are several methods to calculate the embryonic gestational age. It should be noted that there is no absolutely reliable method; there is always the possibility of a small error. The following methods are used:
- blood test for hCG - in the early stages of pregnancy this type of research is the most reliable;
- ultrasound examination - starting from 9 weeks of gestation, it is recommended to rely on information obtained during an ultrasound scan;
- gynecological examination - the doctor can guess the true gestational age during a manual examination on a chair and by measuring the height of the uterine fundus.
The most reliable data is obtained by comparing the results obtained using different methods. Below we propose to consider in more detail how to determine the embryonic gestational age using these methods.
HCG and ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic or ectopic pregnancy means that the egg has fused with the sperm and attached to areas other than the endometrium. These are mainly the fallopian tubes. But attachment in rare cases can take place in the ovaries, uterus, and extremely rarely in the intestines. It is impossible to carry a child during an ectopic pregnancy. There is a high risk of bleeding.
Doctors have developed a “gold standard” for diagnosing ectopic pregnancy. The earlier this condition is detected, the more favorable the prognosis. They do an ultrasound and take blood for hCG. In an ectopic pregnancy, the hormone level will be reduced. Ultrasound with a vaginal sensor shows exactly where the fertilized egg has attached. If it is impossible to find a fertilized egg, they resort to laparoscopy.
Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy:
- pain during intercourse
- pain during vaginal examination by a gynecologist
- abdominal pain after delay of menstruation
- in cases of bleeding from the genitals
- fainting when menstruation is late
If you notice 1 or more of these signs, immediately go to the gynecologist for an appointment. Delay can threaten your health and life! The doctor takes the material for hCG analysis and also does an ultrasound.
Determination of embryonic period by hCG analysis
The hormone hCG, or human chorionic gonadotropin, is also called the pregnancy hormone. In the blood of men and non-pregnant women, this hormone is absent or contained in small quantities (less than 5 IU/l). But as soon as conception occurs, the cells of the chorion of the embryo, which are subsequently transformed into the fetal placenta, begin to actively produce hCG.
The hormone is intended to regulate metabolic processes through which a woman’s body begins to actively prepare for pregnancy. A blood test can determine the increase in hCG as early as 7 days after conception. Pharmacy rapid tests for the content of hCG in urine are used for the same purpose.
But if a pharmacy test strip determines the very fact of pregnancy, a clinical blood test reveals the quantitative content of the hormone. Based on the level of hCG in the blood, you can calculate the embryonic period of pregnancy by week, since until the 9th week it grows in proportion to the growth of the embryo.
False positive result
In some cases, human chorionic gonadotropin can be detected in the blood and urine of non-pregnant women, and sometimes in men. This manifestation is very alarming. It happens when:
- chorionic carcinoma and hydatidiform mole;
- neoplasms of the uterus, kidneys and other organs of the genitourinary system;
- teratoma and seminoma in men - testicular tumors, which are most often malignant;
- tumors of the digestive organs;
- the use of medications that contain human chorionic gonadotropin (for example, in preparation for an IVF procedure);
- the first week after an abortion.
Therefore, hCG analysis is carried out not only during pregnancy, but also for the diagnosis of various oncological pathologies.
Gestational age according to ultrasound
Ultrasound examinations should be performed at least three times during pregnancy. The timing is determined by the gynecologist. But if necessary, this method can be used to determine the exact embryonic period. There are norms for the development of the embryo and the growth of the ovum, with the help of which the gestational age is quite accurately determined.
The main parameter is the coccygeal-parietal size (CTR). This is the distance from the coccyx to the crown of the embryo, which has diagnostic value at 6-13 weeks. Before 6 weeks, the embryo is too small, it is impossible to accurately measure CTE. After the 13th week, more important parameters of fetal development appear.
Determining the due date for a gynecological examination
An experienced doctor can predict pregnancy already at the 4-5th week of gestation. On manual examination, a woman’s uterus is enlarged and takes on a rounded shape. The nature of the discharge from the cervical canal, the color of the mucous membranes of the vagina and external genitalia change.
At later stages, starting from the 18-19th week, the height of the uterine fundus is determined quite accurately. So, at the 20th week, the fundus of the uterus is approximately 2 cm below the navel, and at the 28th week - 2 cm above.
In addition to the height of the uterine fundus, the circumference of the woman’s abdomen at the level of the navel is measured. But this is a secondary indicator, which is subject to error due to the initial build of the pregnant woman. Fuller women will have a larger abdominal circumference. Therefore, gynecologists pay more attention not to specific numbers, but to the rate of circumference growth - normally, from the second trimester of pregnancy it is about 1 cm per week.
Advice from gynecologists on determining the embryonic period
Nevertheless, there are several tips from gynecologists, based on which you can try to determine the embryonic period. When determining hCG, it is recommended to take a dynamic test several times with an interval of 3-4 days. The dynamics of hormone growth will help not only to accurately determine the embryonic period, but also to assess the pace of development of the baby.
The embryonic period is most reliably determined by ultrasound in the period from the 9th to the 13th week of gestation. It is extremely important to undergo ultrasound screening at 11-13 weeks of gestation. Before this period, the embryo is too small, and after this, signs of developmental defects may not be visible. That is why it is important, when establishing the fact of pregnancy, to register with the antenatal clinic before the 12th week.
There is a “first knock” method - determining the embryonic stage of pregnancy by the first movement of the baby in the stomach. It is believed that women who are pregnant for the first time feel it at 20 weeks. During the second pregnancy, the first kick is felt earlier, at 18 weeks. The diagnostic value of this method is questionable, since due to physiological characteristics, the period when a woman first feels fetal movements can vary greatly. In addition, this method is not at all suitable for early pregnancy.
It should be remembered that the data of any medical study must be interpreted by a doctor. You should not make hasty conclusions if the results obtained are somehow confusing or upsetting. Only a gynecologist will correctly compare all the nuances identified during the examination, make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment. A woman’s attentive attitude to her health, keeping a calendar of menstrual cycles and early contact with the antenatal clinic during pregnancy will help give birth to a healthy baby.
Source: FB.ru
Library of fetal birth control: why it is performed, interpretation of results Questions and answers Ultrasound. Gender of the baby 16 weeks (with photo) Live broadcast Now I found an ultrasound of my daughter at 13 weeks and 4 days and she is 1.3 mm. Ultrasound of my son at this stage (first scan... Questions and answers Ultrasound Questions and answers Screening Live broadcast Girls, if I go for the second screening at 19.5, will it be normal or wait 20 weeks?))) Library CTE of the fetus: the results obtained and their interpretation Library On what week does the embryo's heart begin to beat?
Source: www.baby.ru
If the results are above normal
In a normal pregnancy, an elevated level of human chorionic gonadotropin is not such a dangerous sign. Often, with severe toxicosis, chorionic adenoma (hydatidiform mole) or multiple pregnancy, the hormone is higher than normal. With a significant increase in indicators, diabetes mellitus or gestosis can be suspected. In women taking hormonal medications, hCG levels may also increase. In combination with a reduced level of ACE and estriol, this situation may signal a risk of developing Down syndrome in the fetus.
During pregnancy, two screenings are performed. The first of them is carried out from 11 to 14 weeks from the moment of conception. With elevated hCG levels, chromosomal mutations are likely. The attending physician calculates the likelihood of having a child with chromosomal diseases. In children with trisomy (Down syndrome), hCG is often elevated. An ultrasound is performed and re-screening is performed at 16 or 17 weeks. There are elevated hCG levels even with a completely healthy baby and a successful pregnancy.
In any case, there is no need to panic; you should be even more attentive to your health and strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations.