Caries in the primary dentition is dangerous due to damage to the rudiments of permanent teeth
In children, damage to enamel and dentin often occurs much faster than in adults. This is especially observed in baby teeth.
During this period, hard tissues have the least protection from negative factors. This is dangerous due to the rapid development of complications and possible problems with a permanent bite.
That is why treatment of caries of primary teeth in children should take place even with the slightest suspicion of the destruction process. It is important for parents to know why this pathology develops and how to prevent its consequences.
Causes of caries in childhood
The biggest misconception of parents is that if you do not eat sweets, then your child’s baby teeth will not be at risk of caries. But in addition to the abuse of candy, chocolate and other sweet foods, caries has a number of other causes:
- Improper oral hygiene in young children. Milk teeth immediately after eruption require proper care. Many parents neglect this fact, which causes the accumulation of plaque on the enamel. Since a baby’s teeth are not quite “mature” and mineralization processes continue for 2-3 years after their appearance, caries develops quickly, affecting almost the entire tooth.
- Infection with pathogenic microorganisms that occurs if a child eats from the same spoon with an adult whose mouth has carious teeth.
- Genetic predisposition and disruption of the formation of tooth enamel during fetal development under the influence of smoking and medications taken by the mother during pregnancy.
- Early childhood caries, which appears before the age of 2, can be caused by a child taking medications that negatively affect enamel, as well as a lack of fluoride and calcium in food.
- Long-term drinking of sweet drinks by a child through a pacifier leads to the formation of bottle caries, affecting all front teeth.
Caries of primary teeth in children
Diagnostics
To diagnose the disease at an early stage, often invisible to the normal eye, the following procedures can be performed:
- examination of the toddler’s oral cavity by a specialist using a mirror and probe;
- X-ray, which allows you to examine the initial stage of caries;
- transillumination - the baby’s teeth are scanned;
- photopolymerization;
- electroodontometry - a pain symptom is determined using a weak discharge current;
- drying is a method for diagnosing the early stage of the disease;
- vital staining - blue is applied to the tooth, the affected areas are painted blue;
- fluorescent stomatoscopy - diagnosis is carried out using ultraviolet radiation. At the same time, healthy areas are painted blue, and affected areas are dark.
Types of caries in children
There are several classifications of the carious process in children, which reflect its location, depth and intensity.
Depending on which teeth are affected, caries occurs:
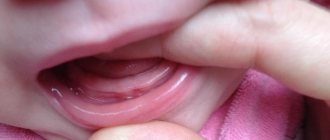
- Milk teeth - can appear even in infants immediately after teething.
- Permanent teeth - occurs in children over 5 years old, after the change of temporary teeth has begun.
Depending on the depth of caries spread:
- The spot - initial caries, represents the first stage of development of the pathological process, which has not yet affected the anatomical structures of the tooth enamel. It can be treated with minimal interventions and can be easily reversed.
- Superficial enamel caries - damage to dental tissues does not extend beyond the enamel.
- Medium caries is the destruction of not only the entire enamel layer, but also part of the dentin tissue.
- Deep caries is the most complex variant of the disease, when the pathological process affects the entire thickness of the tooth and almost reaches the pulp.
According to the primacy of the carious process on teeth, there are the following types:
- Primary caries, which appears on previously unaffected teeth.
- Secondary caries, in which a recurrence of the disease occurs, affecting a tooth that has already been treated. Sometimes the pathological focus is localized under the filling and is not visible to the eye; in this case, caries is called internal caries.
Depending on how quickly the disease develops, caries is classified:
- Compensated - the progression of the disease is extremely slow or stops altogether.
- Subcompensated - the development of caries occurs quite slowly and parents do not notice its presence in the child for a long time.
- Decompensated or acute - destruction of dental tissue occurs very quickly and is accompanied by severe symptoms: pain, inability to chew. This form of caries requires emergency treatment.
Depending on the location of the carious process, caries exists:
- Fissure, which develops in places of natural depressions on the surfaces of the teeth.
- Approximal, when the contacting surfaces of antagonist teeth are exposed to carious destruction.
- Cervical with localization at the point of contact of the tooth crown with the gum.
- Circular, affecting dental tissues along the entire perimeter in the gum area.
Depending on the number of teeth affected, caries can be:
- Single - a single tooth is involved in the pathological process.
- Multiple – the disease affects several baby teeth.
- Generalized - carious lesions are present on most teeth.
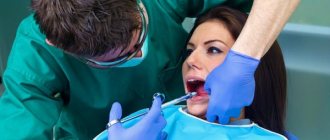
How to diagnose and treat caries
Only a professional dentist can diagnose this disease. The reason is visible changes, you can see them in the photo. In some cases, there is a need for x-rays. future treatment method depends on this
It also depends on the following factors:
- stage of caries development;
- complications of caries (for example, periodontitis, pulpitis and much more);
For example, in the spot stage (first stage), the key principles of treating the disease are:
- strict and careful adherence to oral hygiene;
- the use of specialized medicinal pastes containing large amounts of calcium and fluorine;
- dental procedures (for example, calcium-based compresses placed on the affected area).
But uncomplicated forms of the disease are treated by cleaning the carious cavity from dead tissue and installing a filling. If the caries is deep, then a temporary filling is placed for a period of several weeks, then the doctor must install it on a permanent basis.
If we talk about the treatment of the disease in children, then milk caries is treated in a similar way. First, the doctor must clean the cavity in the tooth from dead tissue, then place a filling. After this, he should prescribe mouth rinses using fluoride-containing solutions or vitamins and minerals for teeth (for example, calcium and vitamins of different groups).
Symptoms in children
Despite the fact that the signs of the disease are very specific, parents do not always know what caries looks like and how to recognize it in children.
Symptoms of the disease depend on the depth of damage to dental tissues.
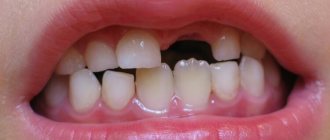
- With initial caries, white spots of various shapes and sizes appear on the enamel surface, which do not cause any unpleasant sensations in the child. Over time, such formations begin to change their color - they become brown, brown or even black. This indicates the progression of the disease.
- With superficial caries, the cavity does not extend beyond the enamel and may be light or dark in color. Already at this stage, children notice the appearance of pain when eating sweets or sour foods.
- With average caries, as the pathological cavity deepens, the early symptoms are joined by pain when the teeth come into contact with cold or hot food. A deep cavity is identified on the tooth surface in which food debris can accumulate. Often there is an unpleasant odor from the child's mouth.
- With a deep process and the addition of pulpitis, the child will complain of intense pain, aggravated by eating. At this stage, the baby’s general condition may suffer with the appearance of weakness, nausea or a rise in temperature. The tooth undergoes significant destruction and cannot perform its chewing functions.
How to recognize caries
In the photo you can see the signs by which this disease can be accurately identified. It includes several stages, each of which has its own distinctive external manifestations:
- the spot stage is the first. It appears as small dark or white spots on the teeth. They appear due to partial demineralization of calcium from tooth enamel. The person does not complain about anything; caries during this period is not easy to identify;
- superficial caries – second stage. Characterized by deeper damage to the enamel. A small cavity forms in the tooth. When eating hot or cold food, as well as salty, sweet and sour foods, unexpressed pain appears, which disappears after the irritating factor is eliminated;
- deep caries - at this stage a deep cavity appears in the tooth. As in the previous case, there are frequent pains when eating salty, sweet, sour, hot or cold. The pain is relieved after brushing or rinsing. And if it does not go away, then this indicates deeper damage to the teeth, for example, pulpitis (inflammation of the nerve).
Stages of caries
Often, caries is accompanied by an unpleasant odor and inflammation of the tissues that surround the tooth - this is called periodontitis.
The transition of caries from the first stage to the last can last for years, but it can happen much faster if the listed factors are combined with each other.
Features of caries in childhood
The development of the carious process in children is very similar to that in adults, however, there are a number of serious features that must be taken into account during diagnosis and treatment.
- Low levels of mineralization of tooth enamel, wider dentin tubules and low pulpal activity contribute to more rapid development and progression of the disease.
- Frequent occurrence of caries in a child whose body has reduced resistance due to severe illnesses or infections.
- Multiple lesions. Sometimes the pathological process affects all baby teeth at the same time.
- The presence of special forms of the disease that do not occur in adults: circular caries (ring-shaped damage to all surfaces of the tooth, often leading to the breaking off of the crown) and planar caries (significant damage to the surface of the tooth without spreading into depth).
- For a long time, even significant defects in the dental tissues may not cause any symptoms.
- The possibility of early development of the disease even in a one-year-old child immediately after the eruption of primary teeth.
Treatment
When this disease is detected in a child, immediate and comprehensive treatment is necessary, which is aimed at both eliminating caries and preventing its reappearance. Therapy started in the dentist’s office must be continued at home using both special care products and traditional medicine techniques.
Features of treatment at the dentist
In young children (up to 4 years old), it is possible to use conservative treatment using the silvering method at the stage of enamel stains or caries. In this case, the damaged area, after cleaning from plaque and softened tissues, is treated three times (with an interval of several days) with a 30% solution of silver nitrate. The disadvantage of this method is that it stains the teeth an unpleasant black color.
Deep fluoridation of enamel is similar to the previous conservative method. In this case, the teeth are repeatedly coated with a fluoride composition, which helps restore the destroyed enamel prisms. The inconvenience of the manipulation is the need to repeat it many times, which is difficult to do in a small child.
When a carious cavity is detected on a tooth, it is cleaned and filled with quick-hardening composite materials. This rule is the same for the treatment of both permanent and temporary teeth.
But young patients are often so afraid of the sound of a working instrument that they do not allow the doctor to fully carry out all the necessary manipulations. Modern medicine offers an alternative to traditional methods - the use of chemical preparation. The essence of this method is to introduce special substances into the carious cavity that soften dense pathological masses, after which the dentist cleans the tooth with hand tools and performs a filling. Moreover, all actions are performed without a drill!
Young patients require complete anesthesia during medical procedures. Preference is given to the use of local anesthetics, but in exceptional cases when tooth extraction is required, treatment under intravenous anesthesia is possible.
Treatment at home
In parallel with treatment in the dental office, it is necessary to carry out caries therapy at home. For this purpose, special children's toothpastes and rinses with an anti-caries effect are used.
If your child is under 4 years old, you should purchase toothpaste and mouthwash that do not contain fluoride. Treatment in this case will be carried out due to the presence of active calcium ions and antibacterial components. For older children, oral hygiene products are recommended that contain minimal fluoride concentrations.
Medicinal toothpastes for children:
- ROCS Pro Baby
- LACALUT kids
- Splat junior
- SILCA Putzi
- PresiDENT Baby
The child’s teeth are brushed with such medicinal pastes twice a day.
Children's mouth rinses used in the treatment of caries:
- LACALUT Teens
- Dragon for children
- Active Kids
You should rinse your mouth with such solutions after every meal and before going to bed.
It is important to remember that you can use mouthwashes for a child only when he has learned to rinse his mouth and spit out liquid (not earlier than 1.5 years).
Treatment with folk remedies
For children after two years of age, traditional medicine can be used in the treatment of caries.
- After eating, rinse your mouth with a weak solution of regular or sea salt (half a teaspoon per glass of warm water).
- As a rinse, use an infusion of chamomile, for the preparation of which a tablespoon of dried flowers is infused in a glass of hot boiled water.
- After brushing your teeth, let your child rinse his mouth with a sage decoction, which is made from a tablespoon of dry leaves of the plant and 300 ml of hot water.
Homeopathy for caries in children
The use of homeopathic remedies for caries of primary teeth is not contraindicated. But this should only be done in combination with traditional dental treatment and under the supervision of an experienced homeopathic doctor. You should not count on a significant effect from such drugs, since they are most often used as preventive methods.
Consequences that occur if left untreated
There is an opinion that it is not necessary to treat caries on temporary teeth, because over time they will be replaced by permanent ones. Having heard a negative answer to their question about whether caries passes from baby teeth to molars, parents calm down and leave a carious lesion in the child’s mouth. However, the impact of this disease on permanent teeth in children is very great.
- If left untreated, caries in a child progresses very quickly and causes the development of periodontitis - inflammation of surrounding tissues. This process can cause the death of the molar tooth germ, as a result of which it will not erupt in time.
- Early loss of baby teeth is fraught with disturbances in the normal growth of the maxillofacial system and problems with permanent occlusion.
- If even one baby tooth is missing, a child cannot chew food fully for a long period of time, which can cause digestive problems.
Authoritative specialists in the field of pediatrics (for example, Dr. Komarovsky) also advocate the full treatment of caries in childhood.
Needs treatment
- The problem of many young parents is that they do not take the appearance of changes on their child’s baby teeth seriously. A mother may consider that there is no need to treat her 4-year-old son’s teeth if they are already replaced by permanent teeth. However, she does not know that bacteria that cause caries can harm the baby’s entire body, and the consequences of this disease can be quite serious.
- Mom must understand that caries is an infectious disease. Microorganisms from the oral cavity penetrate into the digestive organs during swallowing, which leads to abnormalities in their functioning. In addition, the affected teeth become quite sensitive to changes in food temperature, so the baby will react sharply to cold or hot food. Due to pain, the child will begin to refuse to eat. It is believed that a toddler suffering from toothache begins to lag behind in development.
- It is important to understand that the lack of treatment will lead to the infection process affecting the rudiments of the molars. In addition, advanced caries leads to premature removal of the baby tooth, which will lead to the development of malocclusion.
- And do not forget that a neglected tooth can begin to decay, inflammation will spread to the roots - the baby will experience unbearable pain.
Prevention
Prevention of caries in primary teeth begins long before the child is born. Since the formation of tooth germs begins quite early, the expectant mother’s diet should contain a sufficient amount of calcium, vitamin D and protein from the earliest stages.
In a 1-year-old infant, the best way to prevent caries is breastfeeding, since breast milk provides the optimal amount of calcium and other minerals necessary for the proper formation of healthy teeth.
After teething, it is necessary to regularly carry out hygienic procedures, which include cleaning the enamel surface from plaque and food debris using special soft toothbrushes and fluoride-free toothpastes. Until the age of 3, you should not introduce sweets into your child’s diet (especially sticky candies and carbonated water), and it is better to completely abandon them. You should visit the pediatric dentist's office at least twice a year.
If a child lives in a region with a low fluoride content in water, then endogenous caries prevention is carried out by taking fluoride preparations. Such measures are carried out strictly under the supervision of a doctor, since excess fluoride can lead to the development of fluorosis of permanent teeth.
As can be seen from our article, caries in childhood is a fairly serious problem. Underestimating it and delaying a visit to the dentist can cause severe complications and problems with a permanent set of teeth.
Possible complications
If caries is not treated promptly, it can lead to serious consequences.
- The child may develop flux.
- The occurrence of periodontitis. Inflammation of nearby tissues occurs and can lead to the complete death of the permanent tooth germ. Such a case will be the answer for parents who have a question “why a tooth falls out but a new one does not grow.”
- If the teeth are not treated, an extensive infection process may begin, which will lead the tooth to such a condition that it will need to be removed. Due to premature removal, there will be a high probability of malocclusion, and even deviations in jaw development.
- If the baby has pain or a tooth is pulled out, this will lead to problems with chewing food, which in turn will cause a disruption in the digestion process.