» Surgical treatment methods
Intestinal obstruction is a complex of symptoms. characterized by congestion of the gastrointestinal tract with chyme. All causes of this syndrome are divided into two categories: mechanical and functional.
Mechanical reasons:
- Violation of the structure of the peritoneum, internal organs of the abdominal cavity
- Hernias
- Spikes
- Congenital bands of peritoneum
- Impaired intestinal formation
- Volvulus of one of the intestinal sections
- Reduced intestinal lumen due to neoplasm, endometriosis. vascular diseases
- Neoplasms
- Inflammation
- Entry of foreign elements into the intestines
- Intestinal obstruction
- Hematoma
- Meconium
- Feces, gallstones. bezoars
- Accumulation of worms
Factors contributing to the development of mechanical obstruction:
- mobile cecum
- presence of peritoneal pockets
- abdominal adhesions
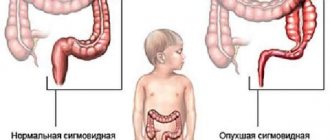
- increase in the length of the sigmoid colon.
Functional reasons:
- Spasms
- Paralytic phenomena
- Pseudo-obstruction of the intestine
- Hirschsprung's disease.
Factors contributing to the development of functional type obstruction:
- A sharp increase in the share of fresh fruits and vegetables in season
- Overeating after a long fast
- Transfer of infants under one year of age to adapted milk formulas.
Adhesive intestinal obstruction
A fairly common form of the disease, observed in a third of cases of obstruction. This form of intestinal obstruction develops if adhesions form in the abdominal cavity, compressing the intestines, and also if the intestinal mesentery is compressed by adhesions.
The presence of adhesions often leads to volvulus. This type of obstruction often returns frequently: as soon as the amount of food consumed exceeds the norm, the patient begins to feel pain. The intestinal walls are stretched, the muscles stop contracting fully, and the chyme does not move forward. Treatment is usually conservative, but sometimes it is necessary to resort to surgery.
Small intestinal obstruction
- Entry of foreign objects into the intestines
- Intestinal torsion, hernia, volvulus
- Malignant neoplasm.
Types and causes of obstruction
Intestinal obstruction can be not only acquired, but also congenital, which is associated with anomalies and pathologies of the development of the gastrointestinal tract in the prenatal period.
Acquired obstruction has various causes, depending on which the disease is divided into two types: mechanical disorder and dynamic.
Mechanical obstruction occurs when tumors or hernias form in the abdominal cavity, blocking the intestines and preventing its normal functioning. The disorder may also appear after certain operations during the formation of adhesions, illnesses, and even taking certain medications as a side effect.
Mechanical obstruction in a child also includes conditions such as volvulus and intussusception, when one of the sections of the intestine penetrates into the underlying area and forms a blockage.
In most cases, mechanical obstruction occurs in the small intestine, but sometimes blockage of the large intestine can occur. The causes may be diseases, for example, colon cancer, volvulus, diverticulitis, narrowing of the lumen caused by scarring or inflammation, severe compaction of stool.
Dynamic obstruction is divided into:
- spastic, caused by prolonged tension of the intestinal walls;
- paralytic or functional, caused by complete relaxation of the intestines.
Functional obstruction may have common symptoms and signs, but does not form a mechanical blockage. The intestines cannot function normally due to nervous or muscular disorders, causing a decrease in the number of natural contractions or their complete cessation, which greatly complicates the movement and removal of contents.
The causes of paralytic obstruction in any intestinal section may be:
- operations performed on the pelvic and abdominal organs;
- some medications;
- intestinal infections;
- Parkinson's disease and other disorders of a nervous or muscular nature.
Classification
The main classification involves dividing pathology by origin:
- Congenital . Congenital intestinal obstruction often occurs due to abnormalities in the development of the digestive system. Late diagnosis of this form can lead to intestinal perforation with further peritonitis.
- Purchased . Acquired intestinal obstruction in children is formed due to insufficient motility of the digestive organs. This form develops suddenly and has a clear clinical picture.
The disease is also divided according to the mechanism of occurrence:
- Dynamic . Dynamic intestinal obstruction is divided into spastic (where the cause is colitis, helminthic infestations) and paralytic (as a complication due to surgery).
- Mechanical . The mechanical type of obstruction is divided into strangulation (due to stenosis of the intestine or disruption of its trophism) and obstructive (caused by blockage by a neoplasm or foreign body).
In addition to the main classifications, the disease is divided into acute and chronic, partial and complete forms.
Symptoms of intestinal obstruction in newborns
The cause of obstruction in newborns is pathologies of intestinal development, narrowing of the lumen or lengthening of certain areas, as well as individual characteristics of the structure and location of intestinal loops.
Symptoms of the disorder:
- severe bloating without passing gas;
- retention of meconium stool, its complete absence or meager amount;
- vomiting, often mixed with bile;
- severe polyhydramnios in the prenatal period.
Symptoms in children under one year of age
At this age, in children, the disorder has its own specifics. The most common cause of obstruction in infants is intussusception, when part of the intestine, inverted, enters the lower section and leads to the formation of a blockage. Most often, this condition is observed in boys aged 5 to 10 months. This disorder is rare in older children.
The cause is usually immaturity of the intestine and instability in the functioning of its mechanisms, which, as a rule, goes away as the child grows. Other factors can also lead to disruption of the natural functioning of the intestines, for example, the introduction of a new product into the baby’s diet, a change in diet (a sudden forced transition from breastfeeding to artificial feeding), infections.
Signs of intussusception:
- vomit;
- frequent attacks of pain in the abdominal area;
- the presence of bloody discharge with mucus instead of feces;
- bloating;
- compactions in the abdominal cavity, clearly palpable upon palpation;
- attacks of pain with a sudden sharp appearance and the same ending; after a short time they are repeated, causing babies to cry, scream and become very worried.
In the presence of acute low obstruction caused by the presence of an obstruction in the lower part of the small intestine or in the large intestine, the child has no bowel movements at all, the abdomen is greatly distended due to accumulated gases, and vomit appears, smelling of feces.
Diagnostics
If disturbing symptoms appear, the child should visit a pediatrician and then a surgeon. Specialists will collect complaints and medical history, conduct a general examination of the patient, and palpate the abdomen. After clinical diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe additional studies:
- general blood analysis;
- clinical examination of urine;
- X-ray examination of the abdominal cavity with the introduction of a contrast agent;
- ultrasound examination of organs located in the abdominal cavity.
After the doctor examines the results of the studies performed on the child, a final diagnosis is made and appropriate treatment is prescribed.
Symptoms of children after one year
In children older than one year, the disease manifests itself abruptly, so parents can usually name not only the day the problem occurred, but also the almost exact time. The child develops severe pain in the abdomen, vomiting, while there is no stool and gases do not pass away, the accumulation of which causes visible bloating. Babies cannot sit still, are constantly looking for a comfortable position and may periodically scream in pain.
The type of obstruction can be determined by a set of signs, for example, the closer to the stomach the resulting blockage is located, the stronger the vomiting will be and the sooner it will occur. If the problem is in the large intestine, there is usually no vomiting, but children experience a painful urge to defecate, accompanied by severe bloating, causing babies to cry loudly and hysterically.
In the presence of intussusception, bloody discharge may be observed from the rectum, which indicates tissue damage and severe irritation of the intestinal walls.
If you do not provide timely assistance to the baby, necrosis of intestinal tissue may begin, as evidenced by a decrease in pain against the background of a sharp deterioration in the general condition.
An important sign of the disorder in children older than one year is the presence of Wahl's symptom, when there is a persistent, often asymmetrical swelling of the abdomen, visible to the eye and clearly palpable upon palpation, while the resulting tumor does not move.
Diagnostics
The symptoms of the disorder are pronounced, which allows parents to detect the problem in time and consult a doctor, in this case a surgeon, since only he can accurately diagnose and provide assistance to the child. If it is not possible to see a surgeon, you need to show the child to a pediatrician, but in no case should you self-medicate.
Diagnostic measures include:
- Examination of the baby, assessment of his condition, identification of symptoms.
- Anamnesis collection.
- General blood analysis.
- X-ray of the abdominal cavity.
- An ultrasound can also be performed, but such a procedure in case of obstruction is not particularly informative.
Intestinal obstruction
Intestinal obstruction is a condition in which the movement of food through the intestines is seriously impaired or completely stopped. Intestinal obstruction most often occurs in older people, as well as in those who have undergone surgery on the stomach or intestines.
Normally, the movement of food through the intestines is ensured by contractions of the intestinal wall. Disruption of intestinal motility can be associated either with complete relaxation of the muscle layer, or vice versa with prolonged spasm. Both of these forms belong to the so-called dynamic intestinal obstruction. As a rule, dynamic intestinal obstruction develops:
- after abdominal surgery
- complicates the course of appendicitis. acute cholecystitis, acute pancreatitis, etc.
- when taking certain medications
Another type of intestinal obstruction, mechanical intestinal obstruction, occurs when there is an obstruction in one place or another of the intestine. It can be associated with volvulus, nodule formation, pinching of the intestine, for example, with prolonged fasting and large meals, as well as with mechanical blockage of the intestinal lumen with:
- adhesions;
- tumors of the intestine and neighboring organs;
- foreign bodies;
- hernias;
- gallstones
- formation of a bolus of food rich in dietary fiber.
Sources: tiensmed.ru, medeffect.ru, bgmustudents.narod.ru, www.womenhealthnet.ru, gastri.ru, medportal.ru
Treatment
Any type of intestinal obstruction in children requires mandatory hospitalization, since help for children can only be provided in an inpatient setting.
To stabilize the condition:
- A dropper with a solution is installed to restore the water-salt balance in the body.
- If the baby is bloated, a special probe is inserted through the nose, the purpose of which is to remove accumulated gases and liquids.
- A catheter is inserted into the bladder to drain urine and perform tests.
Conservative therapy can be carried out only in cases where the baby has no serious complications due to intestinal obstruction. A set of measures will be aimed at eliminating the existing stagnation in the intestines and eliminating the consequences of poisoning of the body.
Conservative measures include:
- Washing the stomach and esophagus through a special probe. The procedure allows you to stop the vomiting process.
- Carrying out enemas with hypertonic solutions.
- Carrying out siphon enemas using sodium chloride.
- Administration of intravenous water-salt solutions.
- Introducing air into the baby's rectum during intussusception. The purpose of the procedure is to straighten the formed intestinal fold.
- Prescription of medications, antispasmodics, antiemetics, painkillers.
- At the end of all procedures, if the problem is successfully resolved, the baby is injected subcutaneously with proserine, which helps stimulate proper intestinal function.
Paralytic forms of obstruction are treated with drugs that cause contractions of the intestinal muscles, which promotes the rapid movement of contents to the outlet, as well as laxatives.
Surgical treatment (operations)
Surgical intervention is resorted to in cases of direct indications for surgery or when conservative treatment methods have not produced the necessary results. The operation is aimed at eliminating the problem, that is, at removing a section of the affected intestine, eliminating the resulting mechanical blockage and taking measures to prevent recurrence of the disorder.
In particularly complex and severe cases, multiple surgeries may be required to clear the obstruction and prevent the problem from occurring in the future.
Lifestyle and nutrition during treatment
During the period of conservative therapy, as well as surgical treatment, the child requires rest and hunger. It is important to ensure that the baby strictly follows the doctors’ instructions and does not take any food without their permission. The same applies to drinking liquids.
After eliminating the obstruction using conservative methods, the small patient is prescribed a special gentle diet that restores normal intestinal function and its microflora. In case of surgery, intestinal function is stimulated with medications, gradually allowing the baby to take light food in small portions.
In the future, hard-to-digest foods, vegetables and fruits, which have a binding effect and cause constipation, should be excluded from the little patient’s diet. The child’s menu should include fermented milk products, cereals, jelly, light meat broths and soups based on them, boiled and steamed lean meat, fruit jellies, rosehip decoction, green tea.
Author: Vaganova Irina Stanislavovna, doctor
The problem of constipation in children
We recommend reading: What diseases can diarrhea and fever in a child indicate?
Author
Irina Vaganova
Doctor
Share
What causes and what is the danger of intestinal obstruction in a child?
Intestinal obstruction in children implies a violation of the movement of food and liquid through the intestines. This is a very dangerous disease that causes pain and vomiting. The disease requires urgent surgical intervention, since there is a high probability of complications, including the death of the baby.
About the disease
Intestinal obstruction in children is caused by gastroenterological disorders. The degree of development of the disease will depend on the location of the blockage. The higher the education, the more difficult it will be to undergo therapeutic measures. Typically, signs of obstruction appear very quickly and there are noticeable symptoms.
In newborn babies, the pathology appears in approximately 1 case out of 1,500 people. If a child has a stomach ache, bloating, or vomiting, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Undiagnosed or improperly treated intestinal obstruction can lead to damage to the vascular system. Because of this, its blood supply decreases, then tissues begin to die, intestinal walls are damaged, causing infection of the body, which is very dangerous for the baby.
Classification
The specificity of intestinal obstruction is determined by various anatomical, genetic or clinical factors. Treatment will depend on the type of illness. Surgery will be required, or everything can be done with conservative methods.
By origin
The disease happens:
- Congenital – occurs due to disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. For certain defects that develop at the initial stage, the congenital form appears in the womb. Therefore, a newly born baby already has signs of intestinal obstruction. With an increased degree of the disease, the baby has vomiting with the discharge of bile and bloating. If it is low – vomiting, fecal retention.
- Acquired – there are different forms:
- mechanical;
- intussusception;
- adhesive (SKN).
Acquired intestinal obstruction in children often manifests itself in an intussusception, mechanical form. Occurs from 4 months to 1 year, the symptoms are sudden, manifested by pain and vomiting. Blood and mucus are noticeable in the stool. The main cause of the acquired disease is considered to be stagnation of stool caused by intestinal weakness.
When congenital obstruction is detected late, intestinal perforation and peritonitis are possible.
According to the mechanism of formation
There are 2 types of pathology:
- Mechanical disorder – has 2 forms of obstruction:
- obstructive – the intestinal lumen is compressed without neoplasm and feces; there is intense cramping pain;
- strangulation – characterized by circulatory disorders, which can cause peritonitis and necrosis.
- Dynamic - provoked by inhibition of mesenteric regional hemodynamics, changes in the central nervous system that regulate the functioning of digestion. Circulatory disorders lead to inflammation. Dynamic obstruction also has 2 forms:
- paralytic – these are frequent and dangerous complications after surgery;
- spastic - it is characterized by pain in the abdominal cavity, occasionally - single vomiting, body temperature is normal.
The increase in abdominal pressure resulting from paresis disrupts blood circulation in the walls of the large intestine. Their permeability increases, and then re-infection of the gastrointestinal tract can occur.
According to the characteristics of symptoms
The following obstructions are distinguished:
- Complete is the most dangerous form for the life of a small patient. This will require urgent hospitalization and surgery. Often the disease appears after surgery on the stomach for congenital diseases.
- Partial - due to the fact that the intestinal lumen is not completely blocked; a certain amount of feces causes difficulty. This occurs due to the slow functioning of the muscular system. The main symptoms of partial obstruction are watery stools and bloating. The pathology is quite difficult to detect, so therapy is carried out mainly at a late stage.
- Acute - here there is a disorder in the passage of intestinal contents, starting from the stomach itself and to the anus. The formation of acute intestinal obstruction in children is a consequence of various ailments (intestinal neoplasms, hernias in the peritoneum).
- Chronic - classified as cramping pain that occurs almost immediately after eating. The symptom appears in the lower abdomen. The child suffers from constipation and frequent vomiting.
Hence, the symptoms of intestinal obstruction will depend on the form of the pathology and its location.
By type of vascular compression
The following are highlighted:
- Strangulation – twisting of the intestine occurs near the longitudinal axis, and volvulus is possible. The causes of this type are increased abdominal pressure, poor diet, and fasting.
- Obstructive - the passage of the presence of the intestine changes due to complete or partial blockage of the lumen, but constriction of the mesentery is not observed. Obturation occurs due to inflammation, tumors, foreign objects, and bends of the intestine.
- Mixed (adhesive intestinal obstruction in children) - appears due to disorders that cause adhesions in the peritoneum. This type is the most common.
Intestinal obstruction after birth in babies, as well as in slightly older children, occurs in 3 phases: initial (from 3-12 hours), intermediate (from 13-36 hours), terminal (manifested by severe symptoms, damage to internal organs).
Causes
The causes of intestinal obstruction are mainly:
- inflammation in the body;
- helminthic infestations, foreign bodies;
- formation of fecal stones;
- disorders of internal organs;
- hernias, tumor formations;
- a large number of intestinal adhesions or volvulus.
In adults, adhesions occur as a result of operations. In babies who have undergone abdominal surgery, adhesive obstruction is possible. However, it is not fully established what provokes deviation of fibrous tissue in congenital adhesions.
Symptoms
Any type of pathology in infants or older children is characterized by its own symptoms of intestinal obstruction.
But there are common signs that are common to everyone:
- the feeling of pain is of a cramping nature, often coinciding with the pulsation of impaired peristalsis. At the time of the attack, the pain leads to shock; when changing the body, no improvement is observed;
- constipation, increased gas formation - when the patency of the large intestine is disrupted, there may be no stool or gases for several days. In case of disorders of the small intestine, bowel movements occur independently or with the help of enemas. However, if this does not help, then the sign indicates a terminal developmental pathology;
- vomiting is a strong and frequent symptom that does not provide relief;
- weight loss.
Additional symptoms of obstruction in children are as follows: bloating, thirst, increased intestinal motility.
Obstruction in children under one year of age occurs due to intussusception, that is, an inverted piece of intestine enters the lower section, causing a blockage. The main signs are vomiting, pain, blood, mucus are noticeable in the feces, compaction in the peritoneum (felt upon palpation). The babies are very restless and cry constantly.
Diagnostics
When the first signs appear, you should immediately go to a pediatrician, since in the case of an acute illness, late detection is dangerous with complications or, even worse, death.
The following diagnosis of intestinal obstruction is carried out:
- general examination and interview of the child’s parent;
- palpation of the tummy;
- X-ray examination using barium contrast - it can be used to determine the area of narrowing, adhesions, elongation or decrease in sigma;
- Ultrasound – additional manipulation;
- laparoscopy – used in difficult situations (adhesions, torsions).
Having established an accurate diagnosis, the type of pathology (congenital and acquired form), the doctor prescribes appropriate therapeutic actions.
Treatment
Various intestinal obstruction in a child, regardless of its form, requires hospitalization:
- to establish the water-salt balance, the baby is given a drip with a solution;
- to drain urine and perform tests, a catheter is inserted into the bladder;
- if there is strong rumbling in the stomach and bloating, a probe is inserted into the child through the nasal passage; it helps the fluid and accumulated gases to drain away.
Acute conditions and severe intestinal obstruction require medications to relieve pain, cleansing the digestive tract through an enema, and intensive treatment.
Conservative methods
Conservative treatment is carried out when there are no dangerous complications. All actions are aimed at eliminating stagnation and eliminating the consequences of intoxication of the body.
The following measures are used:
- performing an enema with hypertonic solutions or using sodium chloride;
- gastric lavage;
- in case of intussusception, air is allowed into the intestines, which helps straighten the folds;
- taking medications (painkillers, antispasmodics, antiemetics);
- If the treatment is completed successfully, the child is injected with Proserin under the skin (to normalize intestinal function).
If the baby has a paralytic form of the disease, laxatives and medications will be needed to contract the muscles, this will help the stool move more easily to the exit.
If the obstruction is mild, you can independently alleviate the baby’s condition with the help of laxatives. Therefore, a children's medicine cabinet should have glycerin suppositories. Plum juice softens stool well.
Surgery
Surgical treatment, surgery is performed in difficult situations or in the failure of conservative methods.
The operation is aimed at eliminating the cause of the blockage and preventing relapse. The steps are as follows:
- removal of the pathological area of narrowing (recurrence is often possible);
- elimination of tumor cavities, dead tissue along with a small healthy part of the tissue.
After the operation, the little patient is given saline solutions and anti-inflammatory treatment is performed.
Diet
At the time of conservative or surgical therapy, you will also have to be treated with a certain diet. In the first days you need rest, and after the operation you need to fast for 12 hours. You must strictly follow the specialist’s recommendations and eat only acceptable foods.
Nutrition during treatment in a conservative way requires a gentle diet that improves the microflora and proper functioning of the intestines. But after the operation, intestinal function is restored with medications, gradually introducing light food into the diet. It is recommended to eat food in small proportions, but at least 5 times a day.
Difficult-to-digest foods (raw vegetables, fruits, legumes, milk, soda) should be excluded from the child’s menu. Do not give your baby sweets, flour products, salty or fried foods.
The diet should consist of:
- berry, fruit jelly, jelly;
- low-fat meat broths;
- green tea;
- fermented milk products;
- various cereals;
- vegetable oils;
- lean meat of rabbit, veal;
- rosehip decoction.
It is advisable to eat boiled beets and carrots. During the period of obstruction, dietary nutrition helps relieve the intestines, normalizes well-being, and prevents exacerbations.
Forecast
Intestinal obstruction in a child is considered a dangerous pathology that can lead to death. There are a lot of factors for its formation, both acquired and innate. Therefore, during pregnancy, the expectant mother needs to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat right, and exercise.
Timely detection and a favorable prognosis will occur only with the initial development of the disease. Therefore, it is important in case of various digestive disorders, in case of severe pain, not to hesitate, but to immediately go to the doctor.
The information on our website is provided by qualified doctors and is for informational purposes only. Don't self-medicate! Be sure to consult a specialist!
Rumyantsev V. G. Experience 34 years.
Gastroenterologist, professor, doctor of medical sciences. Prescribes diagnostics and carries out treatment. Expert of the group for the study of inflammatory diseases. Author of more than 300 scientific papers.
We recommend to the doctor: The most effective folk remedies for the treatment of intestinal cancer
Source: https://gastrot.ru/kishechnik/neprohodimost-u-detej