DTP vaccination is one of the most difficult procedures. Doctors immediately draw attention to the fact that during the post-vaccination period, parents need to closely monitor the baby’s condition.
It has been noted that the second DTP vaccination is more difficult to tolerate than the first immunization. It’s worth figuring out what reaction to expect from her and how to minimize unwanted changes.
Timing of vaccination against diphtheria, tetanus and whooping cough
According to the regulations of the Ministry of Health, the first DPT vaccination is given to children who have reached 3 months of age . Then two subsequent vaccinations are carried out with an interval of 1.5 months.
This approach allows the child’s body to develop a stable reaction to the pathogens of three dangerous infectious diseases. To consolidate the result, revaccination is necessary 12 months after the last vaccination. But in principle, the timing of re-immunization in this case is a formality.
If, due to medical prescriptions or some other circumstances, it was not possible to get vaccinated before the age of 4 years, the child is given an injection without the pertussis component. In this case we are talking about the use of ADS or ADS-M.
According to the official vaccination calendar, the following periods are established for DPT revaccination:
- 5 years (no later than 4 years);
- 6-7 years;
- 14-15 years of age.
Starting from the age of 24, this vaccination is given every 10 years.
If the schedule is fully followed, each person must receive 12 vaccinations during their lifetime.
How many DTP vaccinations should be given?
The vaccine is administered repeatedly.
According to the vaccination calendar, children are subject to immunization during the following periods:
- three months;
- four and a half months;
- six months.
At the age of one and a half years, the first revaccination is carried out. In the future, it is performed at seven and fourteen years of age.
Adults need to be vaccinated every decade, but the whooping cough component is no longer included in the drug. This disease is dangerous for children who have not yet crossed the four-year mark.
Is DPT revaccination necessary and why?
Revaccination with DTP is a mandatory measure necessary to strengthen the immune response. Accordingly, the absence of a timely procedure can weaken the resistance of the developed immunity to the pathogen, which may result in an increased risk of infection.
DPT vaccine
Revaccination, carried out after the age of 4 years, is slightly different from primary vaccinations. The fact is that, having overcome the threshold of 4 years of age, the body is able to provide strong resistance to whooping cough pathogens, so the need for vaccination against this disease disappears by itself. This circumstance most directly affects the composition of the vaccine.
That is, instead of DPT, which includes the pertussis component, during revaccination, ADS or ADS-M, which do not contain this ingredient, is used. That is, a person receives the necessary protection in the form of a vaccination, but with less stress on the immune system due to the absence of an additional component.
What is the difference between Pentaxim and DTP? Composition and properties of drugs
Combination drugs make the task easier and reduce the number of injections needed to instill immunity in children. A vaccine is a set of antigenic materials, the composition of which depends on the nature of the infection. All of them are divided into acellular (consist of fragments) and cellular (contain whole bacterial cells). The former have fewer side effects due to reduced activity. DTP vaccination provides protection against three types of infections:
- whooping cough;
- diphtheria;
- tetanus.
On the territory of the Russian Federation, the use of vaccination preparations is allowed:
- domestic - FSUE NPO "Microgen" Federal Law of the Russian Federation;
- foreign – “Infanrix”.
Both DPT preparations are interchangeable and contain:
- pertussis component in the form of neutralized sticks (there are 20 billion bacteria per milliliter);
- diphtheria and tetanus components in the form of toxoids – 10 and 30 units, respectively;
- "Merthiolate" at a concentration of 0.01%.
Diphtheria and tetanus pose a danger to the body due to the toxins produced by the bacteria that get inside, so toxoids are included in the composition. The last component, “Merthiolate,” the formula of which includes mercury (a pesticide), is used as a preservative due to its pronounced antiseptic properties. This substance is toxic and is excreted from the newborn’s body a month after the procedure; the component composition of the drug contains an amount that is safe for the life of the child.
In addition to DTP, the Pentaxim vaccine is used in pediatrics with a wider spectrum of action and less negative impact due to the removal of membranes from the cells of pertussis infection (whooping cough is split). This ensures less activity of the virus when it enters the body and a reduction in side effects. The imported Pentaxim vaccine prevents the development of the following infections:
- whooping cough;
- diphtheria;
- tetanus;
- polio;
- Haemophilus influenzae (causing meningitis, septicemia, pneumonia, epiglotitis and others).
In terms of direction of action, Pentaxim is an improved version of DPT. The composition of the drug per dose, half a milliliter, contains:
- 25 micrograms of pertussis toxoid;
- at least 40 units of tetanus toxoid;
- at least thirty units of diphtheria toxoid;
- 25 micrograms of filamentous hemagglutinin (a surface protein that regulates intercellular interaction);
- inactivated polio viruses of the first, second, third types of 40, 8, 32 units of D-antigen, respectively;
- 300 micrograms of aluminum hydroxide (adsorbent);
- Hanks's medium 199 without phenol red in an amount of 50 microliters (sterilized aqueous solution with inorganic salts, glucose, vitamins, amino acids);
- 0.0125 milligrams of formalin (preservative);
- 2.5 microliters of phenoxyethanol (antibacterial component);
- purified water (to bring the dose to volume);
- the amount of acetic acid or sodium hydroxide required to regulate the pH in the range from 6.8 to 7.3;
- lyophilisate from which the suspension is prepared (includes 10 micrograms of Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide conjugated with tetanus toxoid; 42.5 milligrams of sucrose, 600 micrograms of trometamol).
The lyophilisate (inactivated suspension) is placed in a bottle, the remaining components are placed in a syringe. To prepare the drug, you need to transfer the contents of the syringe into the vial and shake everything thoroughly until the solution is homogenized. Preparation of a suspension with lyophilisate is carried out only during vaccination (if revaccination is done, only the contents of the syringe are injected). The auxiliary components of this vaccine are substances that are widely used in the cosmetic field and have some negative properties. But in the described preparation they are contained in quantities that are safe for children.
From everything written above, there is a significant difference between the French “Pentaxim” and the Russian DPT vaccine. The second vaccine differs from the first:
- smaller spectrum of action;
- whole pertussis viral cells in the composition;
- greater tendency to cause allergies;
- statistics of side effects (every hundredth child vaccinated with DTP experiences severe complications, which very rarely happens when using Pentaxim);
- efficiency (three to four percent higher);
- simple composition (except for the main components, strains of infections, only one substance is used as a preservative - “Merthiolate”);
- The foreign one comes in a syringe, and the domestic one comes in an ampoule.
To the question of how DTP (diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis vaccine) differs from Pentaxim (prevention of diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, polio, hemophilic infections), the short answer will be: composition, side effects and spectrum of infections.
At what age is repeated vaccination carried out?
The first revaccination is carried out from 1.5 to 4 years. This is followed by vaccinations at 6-7 years and 14-16 years. Starting from 24-26 years of age, vaccination is given every 10 years. To strengthen immunity, it is necessary to comply with the timing of vaccination.
Typically, revaccination is carried out within strictly established periods. However, in some cases, the doctor recommends vaccination according to an individual schedule due to the characteristics of the body and the presence of contraindications for the timely implementation of the procedure.
In such situations, vaccination can be carried out earlier than a year later.
Independent determination of the timing of revaccination is not allowed.
Timing of revaccination
The first vaccination is given at three months of age. Afterwards the repetition occurs at 4.5 and 6 months. The last - third DTP revaccination - is given to one and a half year old babies. Subsequent revaccination of children is carried out when they reach the age of 7 and then every ten years, i.e. at 17 years old, then at 27 years old, etc., but already ADS, i.e. a drug that does not contain a pertussis component.
Important: If the regulatory deadlines for revaccination are violated, then subsequent administration of the drug is possible no later than 12-13 months after the previous DTP injection.
Interval between vaccinations
Everything will depend on the age of the person undergoing the immunization process.
For example, at the age of up to 4 years, the first three injections are given at intervals of 1.5 months, and revaccination is carried out after 18 months. Next, re-vaccination, which consolidates the result, is carried out 2-3 years and 7-8 years after the last procedure. Adults over 24 years of age receive booster vaccination every 10 years.
Compliance with the time interval is important, since the break between vaccinations allows the immune system to develop a strong response and maintain the body’s ability to resist the infectious agent for a long period of time.
Violation of intervals is allowed only with the permission of the doctor, who has taken into account the characteristics of the body of the person undergoing vaccination.
Are there differences in the reaction to vaccinations?
According to the instructions for use, the DTP vaccine and the Pentaxim vaccine have side effects that are divided into types - normal and severe. Normal include the presence of:
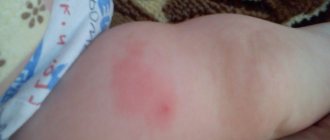
- swelling at the injection site up to 80 millimeters in size;
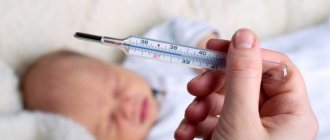
- increased body temperature to 39 degrees;
- vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- weaknesses;
- drowsiness.
In case of severe complications, when medical attention is required, the child has:
- temperature – 40 degrees and above;
- convulsions;
- crying lasting more than three hours;
- swelling at the injection site measuring more than 80 millimeters.
According to statistics, when using Pentaxim, side effects rarely occur; with the domestic vaccine, every hundredth baby suffers a severe form of complications. Regardless of the type of vaccination, you should not leave the medical facility for 30 minutes after the procedure.
How is DPT revaccination tolerated in children: normal reaction and complications
DTP vaccination is usually well tolerated by children. In some cases, parents of a vaccinated baby complain of lethargy of the child, loss of appetite, drowsiness, or slight swelling of the skin at the injection site.
As a rule, the listed symptoms disappear within the first 2-3 days after immunization and do not pose a health hazard.
If a child develops more serious symptoms (convulsions, cough, sudden increase in temperature, vomiting, swelling of the limbs or respiratory tract, and other manifestations), it is necessary to seek help from a doctor.
The first DTP vaccination is considered to be the most difficult for a child’s body. As a rule, it is after this that adverse reactions of varying severity most often occur. Experts explain this state of affairs by the complex nature of the vaccine composition, as well as the lack of developed immunity in the baby.
After all, in fact, DPT is one of the first vaccinations that provides protection against three infections at once, so the load on a child’s body that has not yet become stronger is simply enormous.
Often, parents whose children are immunized are concerned about the last vaccination in the DTP cycle.
But, as practice shows, by the time it is carried out, the body has already managed to form a certain protective reaction, so side effects occur in children extremely rarely and are usually due to the individual characteristics of the body.
Do not forget that complications after infections are more severe and serious than post-vaccination consequences. Therefore, you should not refuse immunization.
How to prepare
The risk that a child will have a strong reaction to a vaccine is quite high. Therefore, you need to prepare for the procedure. There are a number of conditions that must be observed:
- immunization is performed on an empty stomach;
- on the day of vaccination, the baby must be healthy;
- Before leaving, you need to empty your bowels;
- The child should be dressed according to the weather.
Vaccination is carried out against the background of the use of antipyretic medications (Nurofen, Paracetamol, Ibuprofen). The risk of side effects is thus significantly reduced.
In addition, you need to give your baby antihistamines to help prevent the development of allergies.
Preparation for vaccination is carried out according to the following scheme:
- five days before vaccination, antihistamines (Fenistil, Erius) are started;
- three days before visiting crowded places is excluded;
- you need to consult a neurologist in advance;
- blood and urine tests are taken to rule out possible contraindications;
- examination by a pediatrician.
Only by following these rules will it be possible to avoid unwanted reactions..
It is also extremely important to follow medical recommendations in the post-vaccination period:
- do not walk outside for a day;
refuse water procedures for one day;- avoid mechanical impact on the injection site;
- drink enough fluid;
- it is prohibited to introduce new foods into the diet;
- give antihistamines for three days;
- when the temperature rises, give the baby antipyretics;
- avoid crowded places during the post-vaccination period;
- It is forbidden to treat the injection site with antibacterial agents, ointments, solutions;
- avoid overheating and hypothermia;
- Monitor the condition of the baby; any changes are a reason to consult a pediatrician.
By following these recommendations, you will be able to help your baby avoid unwanted side reactions and complications.
What to do if the immunization schedule is disrupted?
It all depends on which DTP vaccine was missed. If we are talking about a vaccine that is administered at 3 months, then vaccination begins at any time until the child is 4 years old.
If the 4-year mark has already been passed, ADS or ADS-M, which do not contain a pertussis component, is used as a vaccination suspension.
ADS vaccine
If the second vaccination was missed, this does not mean that the course must be repeated again. In such a case, the immunization process continues in the same order as if the deadlines had not been violated.
That is, make sure that the interval between injections is at least 30 days. If the third vaccination was missed, it is given as usual, without taking into account the omission.
When vaccination cannot be completed in a timely manner for any reason, you must inform your doctor. The specialist will choose the date that will be most appropriate for vaccinating the child who missed immunization.
What should you not do after vaccination?
To minimize the likelihood of developing adverse reactions from DPT, you need to know what can and cannot be done after immunoprophylaxis. All prohibitions are discussed with the doctor before or after vaccination.
It is prohibited during the post-vaccination period:
- wet the puncture area until the wound heals. Otherwise, infection and inflammation may develop;
- swim with hyperthermia of any degree;
- be in crowded places. It is recommended to walk in a green area (garden or forest plantation);
- introduce foods into the diet that can provoke an allergic reaction;
- treat with ointments or creams, seal, rub the puncture area. This can trigger allergies and inflammation;
- overfeed the baby on the day of vaccination;
- limit the child's fluid intake;
- ignore symptoms of complications;
- self-medicate;
- Give your baby vitamin D, which is usually used to prevent or treat rickets. This element regulates calcium metabolism. Calcium is responsible for the severity of the allergic reaction. A severe imbalance of the mineral can cause post-vaccination complications;
- Give the child Suprastin to prevent allergies. The drug dries out the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx. As a result, the baby’s risk of contracting an infectious viral pathology increases.
Komarovsky advises to closely monitor the baby’s condition during the period after vaccination, protect him from negative factors, and if symptoms of complications arise, immediately consult a doctor.
How long can vaccination be delayed if there are contraindications?
If the reason for temporarily refusing vaccination is a cold (even a mild one), then vaccination is postponed for a month.
If vaccination was postponed due to an allergic reaction or individual intolerance to any components of the vaccine, the timing of vaccination will be determined individually by an immunologist or allergist, taking into account the characteristics of the body. If immunization was not completed for some third-party reason (for example, due to departure), the child is given an injection as soon as the opportunity arises.
Contraindications to DTP vaccination in children under one year of age
The whole-cell pertussis component and merthiolate contained in DTP often become the culprits in the development of complications. Side effects occur in sensitive and weakened individuals. The manufacturer Microgen indicates a list of all contraindications to the use of the vaccine in the instructions for the drug.
All restrictions are divided into temporary and permanent. In the first case, immunization is allowed after complete recovery, achievement of a state of remission or cessation of therapy with certain medications.
With constant bans, vaccinations are not performed at all: pediatricians give a medical exemption. Restrictions are also classified into absolute and relative.
In the first case, vaccination is strictly prohibited; in the second, it is allowed, but after special training and under strict medical supervision.
Absolute permanent contraindications are:
- individual intolerance to tetanus, pertussis, diphtheria components or DPT excipients;
- development of a severe reaction to a previous vaccine dose;
- birth head injury;
- state of immunodeficiency (AIDS, HIV infection, psoriasis).
Absolute time restrictions for vaccination:
- cold;
- acute infectious viral pathologies (ARVI, influenza);
- undergoing treatment with immunosuppressants and antibiotics;
- allergies to food, medicines, hygiene products;
- exacerbation of chronic pathology;
- general malaise;
- cancer;
- underweight;
- recent surgery;
- presence of neurological problems;
- hyperthermia of any degree.
List of relative contraindications:
- predisposition to allergies;
- disorders of the blood coagulation system;
- tendency to seizures;
- intolerance to DTP in close blood relatives.
To identify (exclude) contraindications to vaccination, pediatricians examine the child, recommend tests, and undergo a series of examinations. If vaccination against diphtheria, tetanus and whooping cough is contraindicated, then the pediatrician may recommend continuing immunoprophylaxis with an imported drug (for example, Pentaxim).
According to statistics, serious complications from DTP develop in 2-3 people out of 100 thousand vaccinated children.
What happens if you don't vaccinate your child?
Lack of vaccination significantly increases the risk of infection. Vaccination under artificial conditions creates a reaction of the immune system to the infectious agent.
That is, when faced with pathogenic microflora, a vaccinated child will be immune to infection, as a result of which he will either not get sick at all or suffer a very mild form of the disease.
If immunization is not carried out in a timely manner, there will be no protective barrier, so the child can become infected with an infectious disease, even in contact with the patient for a very short time.
By refusing vaccination, parents act at their own peril and risk. It is possible that the child will not get sick at all. However, in the event of infection, the risk of severe consequences must be taken into account.
What is better to choose: Pentaxim or DTP
To answer the question of what is better to choose, you need to consider:
- the baby's tendency to allergic reactions;
- differences in composition;
- effectiveness of the drug.
If a child is prone to allergies, an imported vaccination is more suitable.
Pediatricians' opinion
Some sources provide information about the lower effectiveness of Pentaxim compared to DTP, so pediatricians recommend immunization with a domestic drug.
Is the diphtheria, tetanus and whooping cough vaccine given to adults?
They bet. Only in adults is a vaccine without a pertussis component used - ADS-M . If an adult has completed the full cycle of vaccinations, starting at age 16, he or she is subsequently vaccinated every 10 years.
If a complete list of vaccinations is not available, adults can be vaccinated according to an individual schedule. According to the national calendar, the last ADS-M vaccination for adults is given at 66 years of age.
However, relatively recently this age limit was abolished, according to which older people can now also get vaccinated.