Children often get sick because their immune system is not yet perfect. Often, younger patients develop infectious diseases of the respiratory organs, which are caused by bacteria. They suffer from sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, otitis, sore throat, pneumonia, etc. Parents must help the child overcome the disease, for this they use medications.
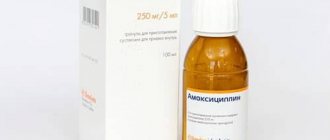
Flemoklav Solutab is an antibacterial agent with a wide spectrum of activity. A drug based on amoxicillin and clavulanic acid quickly exhibits a therapeutic effect and helps overcome various diseases. Then parents wonder how safe the antibiotic Flemoklav Solutab is. If you follow the instructions and recommendations of doctors, the drug is not dangerous for children.
Description of the dosage form
The drug is presented in dispersible tablets, which include the following components:
- potassium clavunalate;
- amoxicillin;
- dispersed and microcrystalline cellulose;
- vanillin;
- crospovidone;
- aromatic additive lemon, tangerine;
- saccharin;
- magnesium stearate.
The dosage of amoxicillin in pills is different: 125, 250, 500, 875 mg. The white-yellow tablets have an oblong shape and single brown inclusions. For children under 12 years of age, syrup, drops and suspension are produced.
The therapeutic effect of Flemoklas Solutab is due to the components that are included in its composition. Amoxicillin is an antibacterial agent with a broad spectrum of activity. This substance penetrates the wall of the pathogenic microorganism, disrupts its synthesis and provokes death. This is how the bactericidal effect of this substance manifests itself.
Amoxicillin is a representative of β-lactam antibiotics. However, some pathogenic bacteria are resistant to its action; as a rule, such microbes contain β-lactamases (enzyme).
To enhance the effectiveness of the drug against pathogens, the composition of the product was supplemented with clavulanic acid. The second component enhances the bactericidal effect of the antibiotic and accelerates the death of bacteria.
Flemoklav Solutab for children is used for infectious diseases caused by bacteria:
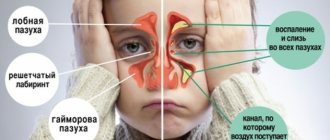
- Inflammation of the paranasal sinuses.
- Inflammatory lesion of the ear.
- Tonsillitis.
- Inflammation of the pharynx.
- Chronic bronchitis.
- COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease).
- Pneumonia.
In addition, Flemoklav Solutab is used if a child has an acute sore throat. The drug is used to treat infections of the skin, soft tissues, kidneys, etc. It is used to treat bacterial infections of joints and bones. The drug is also used to restore the body after surgery. Your doctor will advise you in more detail about taking the medicine.
Instructions for use FLEMOCLAV SOLUTAB®
In patients with hypersensitivity to penicillins, anaphylactic reactions may occur (more often in the presence of a history of hypersensitivity).
Treatment with Flemoclav Solutab® in such cases should be stopped immediately and replaced with other appropriate therapy. Treatment of anaphylactic shock may require urgent administration of adrenaline, corticosteroids and elimination of respiratory failure.
There is a possibility of cross-resistance and hypersensitivity with other penicillins or cephalosporins. As with the use of other broad-spectrum antibiotics, superinfections of fungal (in particular candidiasis) or bacterial origin may occur, especially in patients with chronic diseases and/or impaired immune system function. If superinfection develops, the drug is discontinued and/or corrective treatment is prescribed.
For patients with severe gastrointestinal disorders accompanied by vomiting and/or diarrhea, the administration of Flemoclav Solutab® is not advisable until the above symptoms are eliminated, since absorption of the drug from the gastrointestinal tract may be impaired.
The appearance of severe and persistent diarrhea may be associated with the development of pseudomembranous colitis, in which case the drug is discontinued and the necessary treatment is prescribed. In case of development of hemorrhagic colitis, immediate discontinuation of the drug and corrective therapy are also necessary. The use of drugs that weaken intestinal motility in these cases is contraindicated.
In a single study, prophylactic amoxicillin/clavulanate in women with premature rupture of membranes increased the risk of neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis.
In patients with impaired liver function, the amoxicillin/clavulanic acid combination should be administered with caution and under constant medical supervision.
Flemoklav Solutab® should not be used for longer than 14 days without assessing liver function. With long-term use of the drug, it is necessary to regularly monitor peripheral blood parameters, kidney and liver function.
While taking the drug, an increase in prothrombin time is sometimes observed, so in patients receiving anticoagulants in combination with amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, this indicator must be regularly monitored.
Due to the high concentration of amoxicillin in the urine, it can be deposited on the walls of the urinary catheter, so such patients require periodic catheter changes. Forced diuresis accelerates the elimination of amoxicillin and reduces its plasma concentration.
Non-enzymatic methods for determining urine glucose, as well as the urobilinogen test, may give false positive results.
If seizures occur during therapy, the drug is discontinued.
One dispersible tablet Flemoklav Solutab® 875 mg/125 mg contains 25 mg of potassium.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
Studies of the effect of taking the drug on the ability to drive a car and work with moving mechanisms have not been conducted. However, the possibility of undesirable effects (allergic reactions, dizziness, convulsions) may affect the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery.
Antibiotic use
The method of administration of the drug is oral. The tablets are taken before eating, swallowed and washed down with 220 ml of filtered water. It is better to give the product to infants in the form of a suspension.
Children under 3 months of age should take Flemoclav Solutab at a dose of 20 mg/1 kg of total weight. This is the dosage of the drug per day, which is divided in half and taken in the morning and evening. If the child is from 3 months to 2 years old, then the portion of the medicine is increased to 25 mg/1 kg, it is divided into equal doses and taken twice.
If the patient's age is from 2 to 6 years, and the weight is from 13 to 25 kg, then take tablets with a dosage of 125 mg twice or three times a day. Children from 6 to 12 years old with a body weight of 25 to 37 kg take a pill with a dosage of 250 mg twice or three times. A pediatrician will advise you in more detail about the rules for taking the drug by children.
Patients over 12 years of age with a weight of 40 kg or more take 1 tablet (250 mg) three times. In case of pneumonia or other serious illness, the doctor will increase the dosage of the antibiotic to 1 pill (500 mg) three times in 24 hours. Flemoklav Solutab with a dosage of 875 mg is used by patients over 12 years of age twice. The therapeutic course lasts no longer than 2 weeks. Your doctor will advise you in more detail about the choice of dosage and frequency of use of tablets.
Flemoklav solutab
Pharmakinetics
Amoxicillin Absorption After oral administration, it is quickly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Absorption of amoxicillin after oral administration is 90-94%. Absolute bioavailability reaches 94%. Concomitant food intake does not affect absorption. Cmax in blood plasma is achieved 1-2 hours after administration. After taking a single dose of 500 mg/125 mg (amoxicillin/clavulanic acid), the average concentration of amoxicillin (after 8 hours) is 0.3 mg/l. After a single dose of 875 mg/125 mg (amoxicillin/clavulanic acid), the Cmax of amoxicillin in blood plasma is 12 mcg/ml. Distribution After a single dose of 875 mg/125 mg (amoxicillin/clavulanic acid), the AUC of amoxicillin is 33 mcg? h/l. Serum protein binding is approximately 17-20%. Amoxicillin crosses the placental barrier and is excreted in small quantities into breast milk. Metabolism A small part of amoxicillin is metabolized by hydrolysis of the beta-lactam ring to inactive metabolites (the main ones are penicillic and penamaldic acids). Excretion Approximately 60-80% of amoxicillin is excreted through the kidneys during the first 6 hours after taking the drug. T1/2 is 0.9-1.2 hours. Pharmacokinetics in special clinical cases In case of impaired renal function (creatinine clearance within 10-30 ml/min) T1/2 is 6 hours, and in the case of anuria it ranges between 10 and 15 hours. Excreted during hemodialysis. Clavulanic acid Absorption After oral administration, it is quickly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Absolute bioavailability is approximately 60%. Concomitant food intake does not affect absorption. Cmax in blood plasma is achieved approximately 1-2 hours after administration. After taking a single dose of 500/125 mg (amoxicillin/clavulanic acid), the average concentration of clavulanic acid reaches 0.08 mg/l (after 8 hours). After a single dose of 875 mg/125 mg (amoxicillin/clavulanic acid), the Cmax of clavulanic acid in blood plasma is 3 mcg/ml. Distribution After a single dose of 875 mg/125 mg (amoxicillin/clavulanic acid), the AUC of clavulanic acid is 6 mcg? h/l. Serum protein binding is 22%. Clavulanic acid penetrates the placental barrier. There is no reliable data on excretion in breast milk. Metabolism Clavulanic acid undergoes extensive metabolism through hydrolysis and subsequent decarboxylation. Excretion Approximately 30-50% of clavulanic acid is excreted through the kidneys during the first 6 hours after taking the drug. T1/2 is approximately 1 hour. The total clearance for amoxicillin and clavulanic acid is 25 l/h. Pharmacokinetics in special clinical cases In case of impaired renal function (creatinine clearance from 20 to 70 ml/min) T1/2 is 2.6 hours, and with anuria it ranges between 3-4 hours. It is eliminated by hemodialysis.
Preparation of the suspension
As mentioned earlier, the suspension is recommended for use in newborns under 3 months. The dosage of the antibiotic depends on the age and weight of the patient. For example, if the child is 2 months old and his weight is not higher than 5 kg, then to prepare the solution you will need a tablet with a dose of the active component of 125 mg. The pill is dissolved in 125 ml of boiled water (room temperature), stirring thoroughly until the suspension becomes homogeneous.
A child aged 2 months should take 20 mg of antibiotic per 1 kg of total weight. If the body weight of a newborn is 5 kg, then 20 × 5 = 100 mg. That is, the baby is given 100 ml of liquid medicine. This dose should be divided in half (50 ml) and given to the child at a certain time. The interval between doses should be equal.
The suspension is poured into a bottle and given to the baby. Just use a pacifier with a large opening. Store the solution on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator for 24 hours.
Contraindications and restrictions
According to the instructions for use for children, Flemoklav is contraindicated for the following diseases and conditions:
- Intolerance to the components of the drug or hypersensitivity to penicillins and cephalosporins.
- Filatov's disease.
- Lymphocytic leukemia.
The medicine with a dosage of 875 mg is prohibited for children under 12 years of age and weighing less than 40 kg.
As a rule, children tolerate Flemoclav Solutab well, but sometimes a negative reaction is observed after taking the tablets:
- nausea;
- eruption of vomit;
- I have a stomachache;
- loose and frequent stools appear;
- inflammation of the colon;
- damage to the intestines by fungi of the genus Candida.
Sometimes an antibiotic negatively affects the nervous system, as a result, children complain that they are dizzy and have a headache, have sleep disorders, anxiety, and aggression. In addition, the child becomes too active and easily excitable.
In some patients, the functionality of the blood and liver systems is impaired. Sometimes after taking the pills, itching and burning in the groin area, interstitial nephritis (inflammation of the interstitial tissue and kidney tubules) appear.
In addition, after taking an antibiotic, there is a possibility of an allergic reaction. Then the little patient develops a skin rash, itching, urticaria, dermatitis, and hemolytic anemia. Severe manifestations of allergies in the form of angioedema or anaphylaxis are possible. If such signs occur, you should stop taking the medication and consult your pediatrician.
If you increase the dose on your own, the likelihood of nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and convulsions increases. To get rid of these symptoms, you should take sorbents (Polysorb, activated carbon). In addition, osmodiuretics are used to relieve unpleasant symptoms. Diuretics direct fluid from the extracellular space into the bloodstream.
The antibacterial agent is not recommended to be combined with anti-inflammatory drugs, for example, Aspirin. In addition, Flemoklav Solutab is prohibited from being taken together with medications containing phenylbutazone, sulfinpyrazone, or indomethacin. This is due to the fact that with simultaneous use, the amount of amoxicillin in the bloodstream and bile increases.
The antitumor drug Methotrexate is also not recommended to be taken with Flemoclav. After taking the drug together, the first drug slowly leaves the body, and this threatens an overdose. In addition, Flemoklav is prohibited from being combined with medications that reduce blood clotting and other antibacterial agents.