Sepsis of newborns - this term refers to a general infectious process throughout the body; the disease occurs due to the entry of pathogenic and pyogenic bacteria into the bloodstream and is always accompanied by severe complications.
According to statistics, the incidence of sepsis is less than 1% in premature babies and children with perinatal pathologies, and about 14% in those in the intensive care unit.
About 35% of babies suffering from this pathology die, since sepsis weakens the baby’s immune system and defense mechanisms.
This high mortality rate is also due to the fact that correctly diagnosing this disease in the early stages is quite problematic. Modern equipment and fundamental knowledge of doctors and scientists cannot always save the life of a small patient. Treatment of advanced cases often does not produce any results.
Only regular examinations and a measured pace of life will help the expectant mother undergo pregnancy with better results.
Classification of the disease
Despite the fact that this disease was first identified many years ago, there is still no generally accepted classification for it. Experts around the world call it “bacterial sepsis of the newborn.”
Nevertheless, doctors distinguish this disease depending on the time and conditions of infection - it enters the body at the stage of fetal development or after the birth of the child. Treatment of the disease depends entirely on these factors.
The location of the septic focus and the clinical features of the pathology also play a major role in the classification. Based on these factors, specialists will select treatment methods and anti-epidemic measures.
According to the time of development, sepsis is distinguished:
- intrauterine sepsis (appears even before the birth of the child). It is characterized by infection even at the stage of formation of the organism; the purulent focus will be located outside the fetus. Most often, chorionitis or placentitis acts as a septic focus. This form of the disease involves antenatal or intrapartum infection of the fetus;
- neonatal - is divided into early neonatal sepsis: symptoms appear during the first 3 days after the birth of the child, as well as late neonatal sepsis (characteristic signs will begin to appear no earlier than 4 days after the birth of the baby).
Based on the location of the primary septic focus, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- cutaneous;
- umbilical;
- pulmonary;
- urogenic;
- otogenic;
- rhinopharyngeal;
- rhinoconjunctival.
Sepsis is divided according to the signs of multiple organ failure:
- septic shock;
- cerebral edema;
- heart failure;
- pulmonary failure;
- renal failure;
- intestinal failure.
What is neonatal sepsis
Sepsis is one of the most dangerous diseases. About 30-40 percent of newborns die from it. You can save a child by noticing the symptoms of the disease in time. Over a short period of time, the body is affected by inflammation, which is provoked by a bacterial or fungal infection. Among the causative agents of sepsis are streptococcus, staphylococcus, pneumococcus, and salmonella. The disease begins almost immediately after the baby is born or during the first month of his life. The factors that cause it can have an effect during pregnancy, during childbirth, or after it.
Causes
Sepsis can be caused by many different pathogens; doctors now distinguish about 40 types of opportunistic microflora. The most common pathogens in a child’s body are:
- staphylococci and streptococci;
- coli;
- Klebsiella;
- various gram-negative bacteria.
The infection enters the baby’s body in various ways; the entry gates usually serve as:
- lungs;
- skin covering;
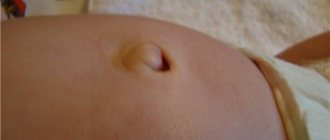
- umbilical wound;
- ears;
- eyes;
- oral cavity.
Navel wound
The causes of this pathology also differ significantly; according to statistics, the primary source most often is:
- the birth of a baby earlier than expected;
- excessively low body weight of the child;
- receiving various birth injuries (damage to the skull is especially dangerous);
- the presence of intrauterine infections in the baby;
- birth of a child in inappropriate conditions (outside a hospital):
- anhydrous period of more than 6 hours;
- prolonged stay of the baby on artificial ventilation;
- surgery immediately after childbirth.
A separate category includes causes of infection associated with violation of sanitary and epidemiological standards in the hospital and the maternity ward itself.
Such an infection of a child can only be provoked by the introduction of an infectious pathogen into the blood; the leading positions among them are occupied by staphylococci and streptococci.
Symptoms
Whatever acts as the primary source of the pathology, its harbinger is usually a very lethargic state, which is completely unusual for children after birth.
A sure sign of sepsis is also poor appetite and lack of weight gain, constant regurgitation after eating. Especially if it is accompanied by navel suppuration and conjunctivitis.
Weighing a newborn
When studying the general clinical picture, the doctor often encounters the following symptoms:
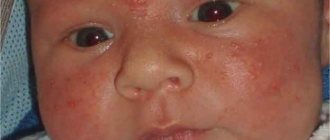
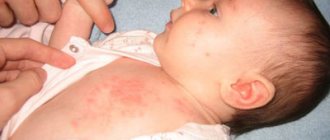
- local inflammation on the skin. To avoid such damage, special attention should be paid to the treatment of the baby’s body in the initial days of life;
- excessive pallor of the skin;
- too fast or, conversely, muffled heartbeat;
- low body temperature;
- the appearance of shortness of breath, in which no changes will be noticeable on an x-ray of the lungs;
- swelling of the skin;
- low blood pressure;
- too weak manifestation of reflexes;
- bleeding of mucous membranes;
- problems with blood clotting (DIC syndrome);
- local tissue necrosis.
In some cases, this disease develops septic shock - a severe condition with rapid progression of all symptoms. The chances of saving the life of a newborn in this case will be minimal.
Routes of entry of infection
- Mucous membranes of the baby.
- Umbilical cord and umbilical wound.
- Middle ear.
- Injection site.
- Intubation site.
- Microtraumas.
- Bruising.
It is worth saying that if the baby is breastfed, resistance to the virus is many times stronger (mother's milk contains special antibodies that actively fight the virus).
Diagnostics
Parents may suspect sepsis if fever persists for more than 3 days or if hypothermia worsens. The doctor should be especially alert to the manifestation of such symptoms.
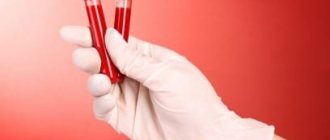
To identify the overall clinical picture, the first step is to do a general detailed analysis of blood and urine, as well as study the nature of the inflammatory process.
Blood test procedure
To choose the appropriate treatment, the first step is to identify what exactly is the causative agent of the infection. If sepsis is suspected, diagnosis usually includes:
- blood test for sterility;
- bacteriological examination of a smear from the conjunctiva;
- urine microflora analysis;
- skin scraping for microflora;
- throat swab analysis;
- stool examination for dysbacteriosis.
The difficulty of diagnosis also lies in the fact that sepsis is often confused with diseases that manifest themselves in a similar way, for example, peritonitis, necrotizing enterocolitis, meningitis.
What happens during sepsis
The pathogenesis of sepsis begins with the appearance of a focus of purulent inflammation in the patient’s body. It serves as a source of infection. It is delivered through the blood and lymph to tissues and organs, affecting them. As a result, their functions are impaired.
Note! With sepsis, not only does blood poisoning occur, but blood vessels are also damaged and become easily permeable. Because of this, the infection spreads faster, spreading throughout the body. Babies have weak immunity, and it is impossible to contain it and stop the action of the purulent focus.
Treatment
Treatment of sepsis is carried out only in a hospital; it is impossible to get rid of this disease at home. Therapeutic therapy is usually divided into 2 categories: etiological and pathogenetic.
Etiological therapy is prescribed immediately after confirmation of the diagnosis or if the baby was prescribed antibiotics after birth.
Until the specific causes of sepsis are identified, the child will be prescribed a systemic antibacterial drug or several medications with a pronounced bactericidal effect.
After passing and studying the tests, therapy will be aimed at combating a specific primary source. When deciding on a treatment method, the physician will need to consider:
- exactly how the infection entered the body;
- baby's age;
- where exactly the infection was contracted (in the hospital or outside the clinic);
- toxicity and activity of the drug;
- how strong is the child’s immune system;
- presence of allergies;
- Are the kidneys functioning properly?
At the initial stage of treatment, specialists, as a rule, prescribe several antimicrobial drugs at once, since until the test results are received, doctors will not be able to determine which strains of infection they are dealing with.
Prevention
Prevention of the development of sepsis in infants begins from the moment a woman finds out that she is pregnant and should be carried out throughout the neonatal period. Precautions include:
- Timely visit by a pregnant woman to a local gynecologist, passing all the necessary tests to identify hidden diseases.
- The expectant mother must monitor her diet, make it healthy and balanced, and also follow hygiene rules.
- If a pregnant woman develops foci of infection, they need to be stopped as quickly as possible. Women in labor who had an infectious disease the day before, such as tonsillitis or pyoderma, are placed in an isolated delivery room, and the newborn is under special observation.
- Maternity hospital staff are regularly tested for carriage of resistant forms of staphylococci. From time to time, bacteriological examination of air, equipment, and bed linen is carried out.
- At birth, the umbilical cord is cut quickly using sterile instruments and dressings. Make sure that Rogovin's braces are applied correctly. Ultraviolet treatment or fumigation may be used to prevent infection. Subsequently, at home, the umbilical wound is treated using antiseptics.
- To prevent the development of omphalitis, it is recommended that newborns take baths with a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
- Much attention is paid to the disinfection of rooms in which women in labor and mothers with newborns are located. There should not be too many mothers in the room. The premises should also be regularly ventilated.
- Maternity care items and necessary equipment are sterilized.
- A newborn is isolated if he has a staphylococcal infection, even in a mild form.
- Maternity hospitals maintain close ties with clinics, which makes it possible to timely identify cases of infection and prevent their epidemic development.
So, neonatal sepsis is a dangerous and serious disease that is treated exclusively in a hospital setting and can have serious consequences, including death. To avoid such infections, you should take your health seriously, especially when it comes to a pregnant woman, lead a healthy lifestyle and take a responsible approach to treatment if the infection has somehow entered the body.
Antibacterial treatment
Antibacterial agents used to treat newborns can be divided into the following groups:
- First-choice medications are prescribed to treat mild forms of the disease. Such drugs include aminoglycosides and 1st generation cephalosporins, synthetic penicillins;
- Second choice medications - used to combat specific strains. The most effective and common are: aminoglycosides and cephalosporins 3 and 4 generations;
- third-choice medications - they are prescribed only in extreme cases, when the baby is in a very serious condition, and it is already a matter of life or death. Such drugs include carbapenems.
Such drugs are administered only intravenously and are usually prescribed in the maximum allowable doses. Treatment almost always begins with the use of first choice medications. If 2 days after their administration the baby’s condition still does not improve, they are replaced by second-choice drugs. If a child was born premature, it is advisable to start treatment immediately with second-generation drugs.
The duration of the course of antibacterial medications is at least 3 weeks, and doctors will periodically change the drugs to analogues. All this time the child will remain in a separate box and will be under constant supervision.
The child stays in a separate box
Discontinuation of medications is prescribed only if the pustular lesions have completely disappeared and new metastatic inflammation does not appear. In addition, if the treatment is successful, the baby will begin to gain weight well.
Pathogenetic therapy
It is aimed at suppressing the pathological mechanisms of disease development in the child’s body. This type of therapy consists of several stages:
- correction of the child’s immunity - since a weakened baby does not have enough protective forces, doctors prescribe the administration of immunoglobulins or interferon. The best effect can be achieved by introducing recombinant interferons obtained through genetic engineering. A popular drug in this group is Viferon;
- detoxification - to reduce the concentration of pathogenic microbes, the baby is prescribed intravenous administration of glucose-saline solutions or fresh frozen plasma. Such injections help reduce intoxication and reduce symptoms;
- anti-shock therapy - in the event of septic shock, the child requires urgent medical attention, otherwise he will simply die. After correction of immunity, treatment will be aimed at reducing inflammatory cytokines in the circulatory system. If the disease worsens, the baby will be placed in a special chamber with controlled temperature and humidity. Doctors will constantly monitor the concentration of hemoglobin in the child’s blood;
- recovery period - after the child’s condition improves and signs of intoxication pass, the baby will be transferred to a separate room with his mother, where he will be prescribed rehabilitation therapy. To activate metabolic processes, enzyme preparations, amino acids and multivitamins are used. At this stage, it is also extremely important to restore the proper functioning of the internal organs.