How does the disease manifest itself?
Hydronephrosis of the kidneys in newborns is dangerous because its symptoms appear only at the third stage.
Therefore, parents should notice the first symptoms. They should be alarmed that the baby has become lethargic, capricious, has begun to eat poorly, and has had trouble sleeping. When there is pain in the abdomen, the child twists his legs and pulls them up. You should pay attention to the condition and quality of urine. If you suddenly start bleeding on your diapers, don’t delay your visit to the doctor.
The main symptom of the disease is an enlarged kidney, which can be easily palpated during bimanual palpation and can also be detected on ultrasound. A strong enlargement of the organ is manifested by a large volume of the abdomen. Often, renal hydronephrosis in newborns is accompanied by an infectious complication with an increase in temperature. In this case, urine contains a large number of leukocytes.
Causes of congenital pathology
The exact cause of hydronephrosis in newborns still cannot be determined. Most experts are confident that the beginnings of the disease can be laid in intrauterine development. Failure of a woman to comply with basic requirements during pregnancy (smoking, drinking alcohol, taking medications) significantly increases the risk of developing pathology in the child.
The development of hydronephrosis in infants is associated with physiological abnormalities of the urinary system:
- underdeveloped lumen of the ureter;
- incorrect structure of the pelvic region;
- narrowing of the bladder wall;
- violation of the innervation of the kidneys from the central nervous system;
- reflux (backflow of urine into the kidneys);
- stones in the ureter (occurs in rare cases in newborns).
The acquired form of hydronephrosis in newborns can develop against the background of other kidney diseases as a complication.
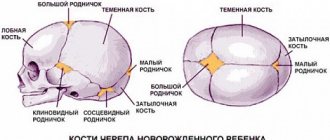
A 4-month-old embryo's kidneys are almost the same as those of a newborn - there is an excretory system, parenchyma, pelvis, and calyces. The fluid is already leaving, the fetus empties its bladder several times a day.
Congenital hydronephrosis in an unborn baby develops due to defects of the genitourinary system that arose at the intrauterine stage. Most often, the lumen of the ureter is blocked in one way or another, so the excretory function is impaired.
Basically, pathology occurs for the following reasons:
- abnormal development of the kidney in the form of a horseshoe;
- multicystic disease (usually the left kidney);
- the presence of an additional vessel in the kidney;
- incorrect origin (location) of the ureter.
If we talk about the specific causes of hydronephrosis, then it occurs as a result of:
- narrowing of the internal lumen of the ureter;
- squeezing it from the outside with a vessel, inflamed tissue or tumor;
- obstruction of urine flow due to reflux, the presence of a stone, or the presence of injury;
- special pathological structure of the ureteral mucosa.
Why exactly certain defects in the fetus develop during pregnancy is not exactly clear. However, experts name factors that can lead to a certain risk, including:
- pollution and other environmental problems;
- ionizing radiation;
- burdened heredity.
Thus, gynecologists refer families planning a new pregnancy to a geneticist who have previously given birth to a baby with a defect, in order to rule out various congenital pathologies of the unborn child.
Description and types of hydronephrosis
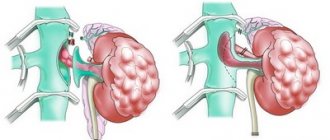
The kidneys are a paired organ of the urinary system, which is responsible for filtering and purifying urine. Under the influence of unfavorable factors, blockage or narrowing of the lumen of the ureter may occur, which leads to difficulty urinating. The retention of urine for a long time leads to an increase in the size of the pyelocaliceal system, and later the renal parenchyma. In medicine, a similar process is called hydronephrotic transformation, or hydronephrosis.
Hydronephrosis in newborns goes through three stages: pyelectasia, hydrocalycosis and terminal stage. With pyeloectasia, there is a slight expansion of the renal collecting system under the pressure of urine. At this stage of the disease development, disturbances in kidney function are not observed.
Hydrocalycosis is the second stage of the development of pathology. It is characterized by a significant increase in the pyelocaliceal system, which puts pressure on the kidney tissue. As a result, there is an increase in the size of the diseased organ by 40%. At this stage, kidney dysfunction occurs.
The third - terminal - stage is characterized by atrophy of the kidney tissue as a result of pressure and rapid expansion of the pyelocaliceal system. The organ is growing, which is easily determined during palpation. The functioning of the organ is completely disrupted. Urgent treatment is required.
Causes
This anomaly occurs during intrauterine development, so during an ultrasound examination a specialist can notice it. The following factors may influence the appearance of pathology:
- smoking and alcohol during pregnancy;
- stress;
- taking medications;
- past infections.
Hydronephrosis is usually caused by blockages that reduce the ability of urine to pass from the kidneys to the bladder. The blockage involves obstruction of the pelvic and ureteric fragment - this is a blockage where the kidney and ureter (the tube that allows urine to pass into the bladder) meet.
Acquired hydronephrosis in newborns is much less common than in adults. The reasons for the acquisition may be:
- lumbar injuries;
- inflammation of the ureter of various origins, which provoke scar formation and narrowing in it;
- kidney stones due to impaired metabolism;
- due to surgical interventions.
Hydronephrosis can be congenital or acquired. In newborns, the most common congenital form is characterized by abnormal development of the kidneys and their vascular system during intrauterine development. A child is born with an abnormal ureter, which may be narrowed or misplaced, with an extra arterial vessel. It, in turn, puts great pressure on this organ, resulting in the obstruction of urine flow.
A newborn may have a violation of the outflow of urine either from one kidney or from both at the same time. In this case, a diagnosis is made of unilateral or bilateral hydronephrosis.
It is still not completely clear what causes the abnormal intrauterine formation of the kidneys, leading to the occurrence of this disease. One thing is obvious - the abuse of alcoholic beverages by a pregnant woman can provoke possible abnormalities in the fetus. In addition, smoking and taking certain medications negatively affect the health of the unborn baby.
The acquired form of renal hydronephrosis occurs due to complications that are caused by other kidney diseases.
Causes of disease in newborns
The cause of congenital hydronephrosis is the anatomical features of the baby’s body. The internal cause is considered to be a narrowing of the ureter due to the fact that its lumen is underdeveloped. The external reason lies in an additional vessel that strongly compresses the ureter. Another external cause may be an abnormal pelvic outlet from the ureter.
It is still impossible to say exactly why this pathology occurs, but, of course, women who do not comply with the necessary requirements from the moment of news of pregnancy, continue to smoke and drink alcohol, use medications without a doctor’s permission, risk the health of the child and the occurrence of such pathologies to a greater extent. degrees.
Acquired hydronephrosis occurs as a complication due to other kidney diseases.
Symptoms of the disease
The insidiousness of the disease means that its special symptoms may not be noticed in a newborn.
- Perhaps an enlarged belly, but it does not always indicate this disease, and does not always accompany it.
- As a rule, the disease is detected at the stage when the baby’s body is attacked by some kind of infection. When this happens, the child experiences paroxysmal pain, and the baby’s body temperature rises.
- Another possible symptom is lethargy in the child. Despite its subjectivity, it is often very informative. Lethargy in a baby is an early sign of kidney disease. Fatigue, the baby sleeps a lot, refuses to eat, does not want to play.
- Itching. It can also be a symptom of hydronephrosis. The disease prevents the normal flow of urine, and toxic secretions accumulate in the tissues of the baby’s body. Toxins irritate infant skin a lot, which causes itching. The child is nervous, scratches himself, scratches himself.
A doctor, examining such a baby, can detect a tumor using palpation. It happens that the presence of a diagnosis is indicated by blood streaks in the urine of a two to three week old baby.
Let's find out
At what age can a child be given goat milk?
why it is useful and which milk is better.
We’ll talk about dysbacteriosis here and discuss the symptoms and treatment.
And here we’ll talk about lactose deficiency in young children.
Pathology in newborns can be unilateral (one kidney is affected) and less often – bilateral. With hydronephrosis of 1 kidney, symptoms of the disease may not even appear, since the second kidney performs a compensatory function for the outflow of urine. Bilateral kidney damage can be life-threatening for the baby and cause uremia. Most often, hydronephrosis in newborns is diagnosed at the stage of development of kidney inflammation (for example, pyelonephritis).
The child has the following symptoms of renal hydronephrosis:
- enlarged tummy;
- heat;
- lethargy and drowsiness;
- due to paroxysmal pain, the child screams, cries, and is very restless;
- refusal to eat;
- itching - occurs due to the accumulation of toxins in tissues due to impaired urine flow, the baby constantly tries to scratch himself, scratches the skin;
- There are streaks of blood in the urine.
When examined by a doctor, a tumor may be detected in the area of the affected kidney by palpation.
Symptoms of this disease appear depending on the severity of its course.
There are 3 degrees of pathology:
- first degree, in which the kidney is already enlarged, but its function is not yet impaired (the renal pelvis is stretched);
- second - the pelvis and cups are stretched, the fluid puts pressure on the parenchyma, causing it to atrophy;
- third, the kidney tissue atrophies and the kidney dies.
Hydronephrosis of the kidney in a newborn of the first degree does not show any symptoms and can be detected accidentally during examination.
But if the disease develops, the symptoms will also intensify: bloody spots may appear in the urine, the baby’s tummy will swell, the baby’s appetite will noticeably worsen, he will become apathetic and constantly sleeps.
In the third degree, symptoms may include: increased blood pressure, reduced amount or absence of urine, swelling and dryness of the skin, nausea, fever, pronounced weakness and apathy, and the presence of blood in the urine. Individually, these symptoms may also indicate other diseases.
If symptoms of hydronephrosis appear in newborns, the pediatrician or neonatologist will prescribe the following tests:
- blood test for the presence of an inflammatory process;
- Analysis of urine;
- blood from a vein to determine the concentration of urea and for the Rehberg test - to determine kidney function;
- ultrasound examination of the urinary tract;
- urography - injection of contrast into the patient’s vein to make a diagnosis and identify the causes;
- voiding cystourethrography - injection of contrast to see what exactly is obstructing the outflow of urine;
- CT (computed tomography) and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) find the causes of hydronephrosis in children; contrast is used during the procedure, while the infant is under anesthesia;
- nephroscintigraphy is a study using radioisotopes that assesses the degree of kidney damage.
Congenital and acquired hydronephrosis in children
- Quite often, pathology is detected during fetal development. A qualified specialist can identify the disorder starting from the 20th week of pregnancy. If the deviations are insignificant, dynamic observation is indicated, since the anomaly may grow along with the development of the baby. In case of severe defects, the question of treatment is raised, and in some cases, termination of pregnancy, when the identified pathology is incompatible with life.
- Hydronephrosis in the fetus is diagnosed when the diameter of the pelvis increases over 7 mm at 16-20 weeks of pregnancy and more than 9 mm after 20 weeks. The causes may lie in obstruction, underdevelopment or dysfunction of the muscles of the walls of the urinary tract/anterior abdominal wall.
- The only sign of hydronephrosis in newborns is the presence of blood in the urine. Sometimes these babies have more than normal tummy volume.
- They can be moody and restless.
- However, a newborn is diagnosed only after a comprehensive diagnosis, which necessarily includes ultrasound and radiography.
Diagnostics
All diagnostic examinations are recommended to be carried out immediately after birth:
- general urine analysis;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder;
- excretory urography.
A good specialist can suspect hydronephrosis by palpation and detect a characteristic tumor.
Reference! Timely intrauterine diagnosis of a pregnant woman makes it possible to detect hydronephrosis in the fetus even before birth at 16-20 weeks. For every 100 pregnancies, 1 case of hydronephrosis is detected in the fetus.
Hydronephrosis of the kidneys in newborns is diagnosed using ultrasound, computed tomography, excretory urography, laboratory tests, and voiding cystography.
An experienced doctor is able to diagnose this pathology during the first examination. Using palpation, he determines whether the kidney is enlarged or not, and then sends the child for examination. With the help of modern equipment, it is possible not only to confirm the fact of the disease, but also to establish the degree of damage to the organ, as well as to find out the possible causes that led to the occurrence of hydronephrosis.
Excretory pyelography is performed to assess the excretory function of the kidneys, and with the help of voiding cystography, reflux can be detected, which in some cases provokes hydronephrosis.
If renal hydronephrosis is diagnosed in newborns, reviews from mothers recommend ultrasound diagnostics every three months to monitor changes in dynamics. In this case, complications can be prevented.
How to diagnose the disease?
Hydronephrosis is usually immediately after birth and can be diagnosed. There are several methods for identifying the disease:
- Excretory urography
- CT
- Ultrasound
- General urine analysis, etc.
But a competent doctor, even without these special procedures, can detect a tumor in a child by palpation, which means that in the very first examinations in the baby’s life the disease can be identified.
If hydronephrosis develops in a child for a long time, the disease can cause a serious complication - kidney failure . Therefore, you need to monitor the baby’s condition and follow all doctors’ orders strictly and quickly.
Today, medicine makes it possible to identify the disease even at the stage of intrauterine development of the child - from the 20th week of pregnancy the disease can be “seen” on an ultrasound.
Degrees of renal hydronephrosis in children
It is customary to distinguish 3 degrees of the disease:
Dilated pelvis with intact parenchyma and preservation of the main functions of the kidney
Increased kidney size, parenchyma damage, large expansion of the pelvis, decreased kidney function up to 40%
A noticeable enlargement of the kidneys, atrophied parenchyma, a decrease in renal function up to 40% or even its complete absence.
If the kidney is severely altered, the disease inevitably progresses to the third stage; surgery cannot be avoided. Severe hydronephrosis in children is most often operated on using pyeloplasty.
How does pyelopasticity occur?
- a narrow section of the ureter is excised;
- a new, already wide connection of the renal pelvis and ureter is formed.
The postoperative period of a child can occur in different ways. The baby can be given a catheter with a nephrostomy (drainage tube) - then he will stay in the hospital for 3 weeks. They can also install an internal drainage stent, then the baby will be discharged faster - in five to nine days. After two to three months, the stent will be removed using special equipment.
The surgeon decides which method of urine diversion will be established, based on the characteristics and result of the operation. Pyeloplasty has a very high efficiency, more than 90%. After the operation, the condition of the organ improves, sometimes it becomes able to function like a normal healthy kidney.
So, we can say with confidence that the key to successful treatment of hydronephrosis in children will be timely detection of the disease.
The earlier hydronephrosis is diagnosed, treatment is planned and started, the better quality it is, and the more disciplined the parents are in taking measures to control the disease, the more likely it is that the organ will be restored to a normal state.
In newborns, there are 3 degrees of kidney damage due to hydronephrosis:
- 1st degree (pyelectasia) - the pelvis expands from pressure and accumulation of urine, a slight enlargement of the kidney occurs, the parenchyma is not damaged, the functionality of the organ is not impaired.
- 2nd degree (hydrocalicosis) - the fluid begins to compress the parenchyma and accumulate in the tubules, the calyx expands even more, the organ functions at only 40%.
- Stage 3 (terminal) - the parenchyma irreversibly atrophies, the kidney increases significantly in size, and may gradually lose its function completely.
Congenital hydronephrosis occurs in the following stages:
- 1st stage. It is characterized by an increase in the size of the pelvis, but the kidney parenchyma is not damaged and the functioning of the organ does not interfere.
- Hydronephrosis 2nd degree. It manifests itself as an enlarged kidney, damage to the parenchyma, and pronounced dilation of the pelvis. In this case, there is a violation of the functioning of the organ up to 40%.
- 3rd stage. It is characterized by a pronounced enlargement of the kidney, the development of parenchymal atrophy and a decrease in the functioning of the organ by more than 40%, until complete cessation.
Carrying out surgery
The most gentle method of surgical intervention is laparoscopic plastic surgery. The idea behind it is that a laparoscope, which is a tube with a screen at the end, is inserted through small incisions. With the help of such a device, a narrow section of the ureter is replaced by a new wide connection between this organ and the renal pelvis created by surgeons. This contributes to the normal restoration of urine outflow.
This type of surgery is performed at any stage of the disease. After this, the baby spends one week in the hospital.
The child must be registered with a urologist. For preventive purposes, the baby should take uroseptics for two weeks. In addition, during the first year after surgery, it is recommended to regularly take urine tests.
Treatment with folk remedies
In the presence of a disease such as renal hydronephrosis in newborns, treatment with folk remedies involves eliminating the obvious symptoms of this pathology.
Recommended herbal teas:
- 50 g each of Adonis grass, oat grain, horsetail, bearberry, nettle leaves and 150 g of birch leaves;
- 100 g each of birch buds, sedum grass, horsetail, adonis, oat grain, bedstraw and hop cones;
- 250 g each of bearberry and birch buds, 50 g each of hoofed grass, horsetail and knotweed, 75 g each of bean leaves and corn silks;
- 150 g each of juniper fruits, birch leaves and dandelion roots.
To prepare the tincture, 100 g of any collection is poured into a liter of boiling water, boiled for 10 minutes, then poured into a thermos along with the green mass and left overnight. Strain and drink 100 g of tincture before meals. The course of treatment lasts 4 months, with a break of 2 weeks, after which it is continued.
For children, it is necessary to prepare the tincture in the following daily dose of the herbal mixture:
- up to 1 year – 0.5 tsp;
- up to 3 years – 1 tsp;
- 3-6 years – 1 dec. l.;
- 6-10 years – 1 tbsp. l.;
- over 10 years – 2 tbsp. l.
It should be remembered that some herbs may have contraindications.
General rules and methods of treatment
The choice of treatment regimen for kidney hydronephrosis in children is influenced by several factors:
- degree of pathology;
- duration of the inflammatory process;
- the presence of concomitant pathologies.
There are cases when at the initial stage the disease may go away on its own. A child up to 3 years of age needs to undergo regular kidney ultrasound (every 3-6 months) to monitor the dynamics of the organ. Sometimes it takes time for organs to begin to fully perform their functions. During this period, conservative methods can be used to help stimulate the outflow of urine.
If the dynamics are negative and the condition of the kidney worsens, surgery cannot be avoided. Usually, in case of hydronephrosis in newborns, they resort to laparoscopic plastic surgery, which today is the most gentle method. The operation should not be performed on premature babies with low birth weight.
No incisions are required during the operation. A laparoscope (a tube with a camera at the end) is inserted through small incisions. A narrow section of the ureter is excised. A new connection between the pelvis and the ureter is formed. The child may have an internal drainage stent installed, which will be removed after 2-3 months, or a catheter with a drainage tube. The doctor will determine the method of urine diversion based on the characteristics and results of laparoscopy.
After the operation, the baby must remain in the hospital for about a week. In some cases, his stay there may be longer (up to 3 weeks). During this period, constant monitoring of the condition is important.
After discharge, the newborn is registered at the dispensary. Once every 1-2 months you need to undergo a follow-up examination with a urologist. The doctor may prescribe uroseptic drugs as a maintenance course for 1-2 weeks.
Around 6 months, urine tests may show increased white blood cells, protein, and hematuria. This is considered normal after surgery. Tests must be taken 2 times a month.
To determine the microcirculation of the periphery of the kidneys, a Doppler study is performed. When urinary excretion is restored, the kidney returns to its normal size and tissue regeneration occurs.
Symptoms and signs of hydronephrosis in children
- Very often, at the initial stages of pathology development, it does not manifest itself in any way. As a rule, it is discovered by chance during any inflammatory disease of the urinary system or during palpation (palpation) of the abdomen in older children for other complaints.
- The second and third degrees of hydronephrosis are accompanied by painful, aching sensations in the lumbar region. Moreover, the appearance of pain does not depend on physical activity, body position and time of day. With unilateral hydronephrosis, pain is localized on the right or left, respectively.
- If there is a concomitant infection, the temperature rises. Already in the initial stages of the disease, hematuria may occur - the release of blood in the urine. As a rule, it is discovered accidentally during a urine test (microhematuria). In advanced cases, urine acquires a reddish tint (macrohematuria).
- As the pathology progresses, the specialist will be able to palpate the enlarged organ through the anterior abdominal wall.