What happens if the membranes rupture before contractions?
In some cases, labor begins with the rupture of water. Moreover, it can be complete or partial. According to statistics, such a deviation can occur in 12% of all women. This process is called premature rupture of amniotic fluid.
Women immediately notice this phenomenon, especially if it happens with a large amount of water.
The amniotic fluid should be light or pink and odorless. If black, brown or green color is mixed with it, this means that there is feces of a newborn in the waters. This indicates that the fetus has experienced oxygen starvation, which requires rapid delivery. An admixture of yellow color may indicate the presence of a Rh conflict, which also requires quick action.
When the water breaks at home, the woman in labor must urgently go to the maternity hospital. In the hospital, the woman must accurately report the time of their departure.
If the body is completely ready for the birth of a child, contractions begin immediately or some time after the water breaks.
A short excursion into physiology
Normally, labor begins with contractions. Contractions help open the cervix and move the fetus through the birth canal. The cervix smooths and opens due to contraction of the uterine muscles. The dilation of the cervix is also facilitated by the amniotic sac. During contractions, the uterus begins to actively contract, as a result of which intrauterine pressure increases, the amniotic sac tightens, and amniotic fluid rushes down. The lower pole of the bladder penetrates the internal uterine os and helps dilate the cervix.
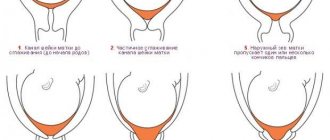
Cervical dilatation occurs differently in primiparous and multiparous women. In first-time mothers, the internal uterine os opens first, the cervix smoothes and thins, and then the external uterine os opens. In multiparous women, the external uterine os is slightly open at the end of pregnancy. During childbirth, the opening of the internal and external pharynx, as well as the smoothing of the cervix, occur simultaneously.
The degree of cervical dilatation is determined in centimeters during vaginal examination. Dilation of the cervix by 11-12 cm, at which its edges cannot be determined, is considered complete.
The first stage of labor is characterized by the occurrence of regular contractions and the advancement of the presenting part of the fetus (the part that first passes through the birth canal, and before birth is facing the cervix) along the birth canal. Most often, the presenting part of the fetus is its head. During normal childbirth, the waters recede on their own. Typically, the membranes rupture when the cervix is fully or almost fully dilated, and the anterior amniotic fluid (they are so called because they are in front of the presenting part of the fetus) is poured out. Rupture of the membranes is a painless process, since there are no nerve endings in the membranes.
In 10% of women, the water breaks before labor begins. When amniotic fluid ruptures, about 200 ml of liquid is released at once, that is, approximately a glass. This cannot be ignored. But it also happens that the fetal bladder does not open directly near the exit from the cervix, but higher up, where it comes into contact with the wall of the uterus. In this case, water leaks from the genital tract drop by drop, and the watery spot on the underwear gradually increases.
When labor begins with the rupture of water, they speak of premature rupture of amniotic fluid. The release of water after the onset of labor, but with incomplete dilatation of the cervix, is called early release of water.
With premature rupture of amniotic fluid, the course of labor depends to a large extent on whether the woman’s body is ready for childbirth, and with early rupture of water - on the regularity and strength of labor and the location of the presenting part of the fetus. If a pregnant woman’s body is ready for childbirth, premature rupture of amniotic fluid will not become an obstacle to its normal course. Typically, labor in such cases develops 5-6 hours after the rupture of the membranes, but the first contractions may appear immediately after the rupture of water. However, often premature or early rupture of amniotic fluid leads to weakness of labor, protracted labor, fetal hypoxia, and inflammatory processes of the membranes.
Therefore, if your water breaks outside the maternity hospital, even in the absence of contractions, you must go to the maternity hospital immediately. In this case, it is necessary to remember the time of rupture of amniotic fluid and inform the doctor about it. Pay attention to the color and smell of amniotic fluid. Usually the waters are clear or slightly pink, odorless. A slightly greenish, dark brown or black color of the amniotic fluid indicates the release of meconium (original feces) from the baby’s intestines, which means that he is experiencing oxygen starvation and needs help. Amniotic fluid is colored differently, depending on the amount of discharge. If contractions do not begin soon after the water breaks, doctors resort to induction of labor.
It is not known exactly what causes early or premature rupture of water. However, in women who were prepared for childbirth, such cases are less common. This is largely due to the woman’s emotional state, her ability to relax and her general attitude towards a successful birth.
Very rarely, the amniotic sac does not rupture at all, and the baby is born covered with membranes. People say about such a baby that he was “born in a shirt.”
What is amniotomy?
Amniotomy is an operation in which the amniotic sac is opened. In utero, the fetus is protected by a special membrane - the amnion, which is filled with amniotic fluid. It protects the child from shocks and infection from the vagina.
If an opening or rupture occurs naturally, the uterus begins the process of expelling the fetus. As a result, contractions develop and the baby is born.
The operation to puncture the bladder before childbirth without contractions is carried out with a special device in the form of a hook at the moment of its greatest severity, so as not to affect the soft tissues of the baby’s head.
Types of amniotomy
Bladder puncture before childbirth can be divided into several types, depending on the time of the operation:
Do you always follow doctors' orders?
Yes, they know us better.
43.82%
Not always, because more information can be obtained from other women in labor.
20.88%
I comply, but I check reviews and advice from various mothers.
35.29%
Voted: 340
- Prenatal. It is carried out before contractions occur to induce labor.
- Early. It is performed if the opening of the cervix is up to 7 cm.
- Timely. If the cervix is open to 8-10 cm.
- Belated. Can be carried out at the time of expulsion of the fetus. The procedure is used to prevent hypoxia in the fetus or bleeding in the mother.
The process of childbirth does not change at all and corresponds to nature. The condition of the fetus is necessarily recorded using a CHT apparatus.
When is amniotomy necessary?
Labor is stimulated by puncturing the bladder in case situations arise where emergency delivery is required. The procedure can be carried out in the absence of contractions:
- Post-term pregnancy. A normal pregnancy lasts 40 weeks; if it is longer, then the question of the need for obstetric care is raised. In this situation, the placenta ages and cannot perform its functions. As a result, the child suffers, experiencing oxygen starvation.
- Preeclampsia. This disease is characterized by swelling, high blood pressure and the presence of protein in the urine. Preeclampsia negatively affects the health of the mother and fetus, so an amniotomy is needed.
- Rhesus conflict. Such a pregnancy is considered difficult, so this operation helps stimulate labor.
If labor has begun, then surgery is resorted to in the following cases:
- Weakness of labor. If the contractions do not intensify, but weaken, the cervix slows down the labor process, and to prevent them from stopping, the bladder is punctured. The woman in labor is observed for 2 hours; if there is no positive dynamics, then a decision is made to resort to Oxytocin.
- Polyhydramnios. The presence of a large amount of amniotic fluid leads to the fact that the uterus cannot contract naturally.
- High blood pressure. Kidney and heart diseases, gestosis contribute to increased blood pressure, which negatively affects the birth process and the condition of the fetus.
- Flat amniotic sac. In this situation, the anterior waters are almost completely absent, which makes labor difficult, and its cessation may occur.
- Low location of the placenta. This position of the placenta can lead to abruption and bleeding.
In some cases, there are contraindications for this procedure.
Early amniotomy
During childbirth, there may be a need for an early amniotomy - it is performed when the opening of the cervix is still small. Let us list the indications for its use.
- Cases when acceleration of labor is necessary:
- with weakness of labor
(there is a close relationship between the low level of uterine contractility and the slow progress of labor at any stage of the first and second periods), early opening of the membranes leads to increased production and release of prostaglandins - special physiologically active substances. Prostaglandins cause uterine contractions and also contribute to increased uterine activity during labor; - with a functionally defective amniotic sac
(“flat” or “flaccid”). The usual volume of anterior waters located in front of the fetal head is up to 200 ml. If there is little anterior water, which happens with oligohydramnios, the membranes are stretched on the fetal head (“flat amniotic sac”). A decrease in the volume of amniotic fluid in most cases is associated with the presence of malformations of the fetal urinary system; during postmaturity, a decrease in the amount of amniotic fluid to 50-100 ml is also observed. In the case of leakage of water due to a lateral tear of the fetal bladder, the membranes hang “sluggishly”. Such a bladder (“flat” or “flaccid”) does not fulfill its function as a “hydraulic wedge” in dilation of the cervix, which is also the reason for the slow progress of labor; - with polyhydramnios,
due to a large amount of amniotic fluid, the uterus is overstretched, its contractions are weak. More often than half of the cases, the causes of polyhydramnios remain unclear. Polyhydramnios is not only a disease of the amnion (fetal membranes) - it can be associated with maternal disease (diabetes mellitus, inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system), with the development of fetal diseases (hemolytic disease or the presence of various defects and chromosomal abnormalities). The infectious nature of polyhydramnios is possible when the mother is ill with syphilis, influenza, etc. Early amniotomy for polyhydramnios reduces the volume of the uterus, as a result of which uterine contractions become stronger. - The use of amniotomy for therapeutic purposes achieves:
- hemostatic (hemostatic) effect for bleeding
associated with partial presentation or low placenta attachment, that is, in cases where the placenta is attached close to the exit of the uterus. Placental tissue is not capable of stretching; during contractions, the membranes pull the edge of the placenta with them. As a result, a section of the placenta is torn away from the presenting wall of the uterus, which leads to disruption of the integrity of the vessels of the placental area and bleeding. After amniotomy, the wall of the lower segment of the uterus, along with the membranes and placenta, moves upward, the placenta no longer exfoliates, so bleeding stops. The presenting part of the fetus descending into the pelvic inlet presses the bleeding part of the placenta to the walls of the uterus and to the walls of the pelvis and thereby also helps to stop the bleeding; - hypotensive effect
- lowering blood pressure during labor in women in labor with late toxicosis (preeclampsia), as well as with hypertension. In this case, the reduced uterus after amniotomy puts less pressure on large vessels, and blood pressure decreases. - The presence of indications from the fetus, if additional examination methods during labor reveal signs that threaten the life of the fetus:
- detection of green amniotic fluid
(mixed with meconium) during amnioscopy, examination of amniotic fluid through the membranes with an optical device - this indicates that the fetus is experiencing a lack of oxygen; - disturbance of blood flow in the vessels
of the umbilical cord according to Doppler measurements; - pathological type of fetal cardiotocogram curves
that does not require cesarean section.
Are there any contraindications?
Puncture of the bladder before childbirth helps to facilitate the process of giving birth, but in some cases there are some limitations of the procedure. Amniotomy is not performed if:
- a pregnant woman has herpes on the genitals in the acute stage;
- the placenta is low;
- umbilical cord loops interfere with surgery;
- natural childbirth is not recommended;
- finding the fetus in oblique, transverse and breech presentation.
The procedure is prohibited if the mother has heart disease, if there are scars on the cervix and other pathologies.
Who is indicated and contraindicated for amniotomy?
Not all women have their amniotic sac pierced, and only in the following cases:
- Full-term pregnancy from 38 weeks for a single pregnancy and 36 weeks for a multiple pregnancy.
- Head presentation of the fetus.
- Estimated body weight is more than 3 kilograms.
- Fully mature cervix and normal pelvic size.
- There are no contraindications to natural childbirth.
Indications
Like any operation, the bladder is punctured only according to the doctor’s indications and after a thorough examination.
The amnion is most often punctured
during postterm pregnancy, namely after 41.5 weeks. If a woman has not given birth to a child before this period, then continuing the pregnancy can be dangerous both for the fetus and for the woman in labor. The placenta begins to age, oxygen supply to the baby becomes worse, which is why children born late are usually diagnosed with hypoxia.
In addition, amniotomy is indicated in cases where urgent delivery is necessary. These include:
- Intrauterine death or fetal hypoxia.
- Premature placental abruption.
- Preeclampsia and polyhydramnios in a pregnant woman.
For some diseases in a woman, labor must be induced after reaching 38 weeks. For example, in case of Rh conflict between mother and child or severe chronic diseases of the woman
.
A special case for puncture of the bladder is the long preliminary period, when contractions occur over several days, but they never progress into labor. The cervix does not dilate, the woman in labor suffers from endless painful contractions, and the fetus suffers from hypoxia. In this case, amniotomy helps to give birth faster.
Contraindications
Despite all the benefits of such an operation, amniotomy has a number of contraindications, in which this procedure is strictly prohibited and doctors should choose a different method for delivery. Almost all of them are similar to contraindications for natural childbirth.
. Among them:
In the absence of contraindications, amniotomy does not threaten the condition of the mother and child and, contrary to popular belief, it is not painful at all. You should not refuse this procedure
, because if the doctor prescribed this operation, then there are good reasons for it. It’s worth thinking about how many women amniotomy has helped them give birth easily and quickly, and all doubts will immediately be dispelled. By fully following the instructions and advice of your obstetrician-gynecologist, you can be completely calm about the health of your child and be confident that the birth will be successful and without pain.
In an ideal labor process, amniotic fluid drains immediately before delivery itself, when the uterus opens 8 or more fingers. However, if stimulation of labor is necessary, or there are other indications, women in labor are prescribed an amniotomy.
How is a bladder punctured?
Why and how do they puncture the bladder before childbirth? Amniotomy is equivalent to surgery, but the presence of an anesthesiologist and surgeon is not necessary. After a vaginal examination, the doctor opens the bladder. The procedure includes several stages:
- Before the operation, the woman takes No-Shpu or another antispasmodic. After exposure to the medicine, the woman lies down on the gynecological chair.
- Then the specialist, wearing gloves, inserts the instrument into the vagina. The amniotic sac is hooked and pulled by the doctor until it ruptures. After this, the amniotic fluid begins to flow out.
- After the end of the manipulation, the woman remains in a horizontal position for 30 minutes. The condition of the fetus is monitored by a CHT device.
The bubble necessarily opens in the absence of contractions, which leads to the convenience and safety of the operation.
How does a woman feel during an amniotomy?
Bladder puncture before childbirth - painful or not? Any woman is afraid of such a procedure because of the possible pain. However, in this case, no unpleasant sensations are observed, because the amniotic sac has no nerve endings.
A woman just needs to relax and take a comfortable position. All she can feel after a correctly performed procedure is only the leakage of amniotic fluid.
When muscles are tense, discomfort and negative consequences may occur in the form of injury to the vaginal walls.
Scratches in a child after puncture of the amniotic sac
If the procedure is carried out according to all the rules, amniotomy cannot harm the child, but there are cases when scratches remain on the baby’s head. This happens when:
- Too little amniotic fluid.
- The baby's head is very close to the exit and when piercing the bubble, the instrument may touch it.
- The water broke earlier, but the doctor did not pay attention.
In general, amniotomy is not a dangerous procedure and is widely used these days to speed up labor, even when there is no particular need for it. However, if there are wounds or scratches on the child’s body, consult a doctor for explanations and advice.
Complications and consequences of amniotomy
If the bladder is punctured correctly before childbirth, the entire process occurs safely. But there are a few exceptions, where after an amniotomy labor may become more difficult. There are the following consequences:
- injuries to the umbilical cord vessel if it is attached to the membrane, which can lead to blood loss;
- the child’s condition worsens;
- umbilical cord loops or fetal limbs (arms, legs) fall out;
- abnormal heartbeat of the child;
- rapid labor activity;
- secondary birth weakness.
There is a risk that puncture of the amniotic sac will not lead to the desired result and labor will not become active. Therefore, doctors resort to using drugs that cause contractions. In some situations, a woman undergoes a caesarean section, because the child’s prolonged stay without water is fraught with negative consequences.
How long does labor last after puncture of the bladder before childbirth? Reviews from women who have gone through this procedure are as follows:
- in women who gave birth for the first time, labor took place within 7-14 hours;
- for multiparous women, this may take 5-12 hours.
Any intervention, which includes puncture of the bladder, sometimes leads to consequences that are not always positive. Amniotomy should be carried out in compliance with all necessary conditions, which will reduce the risk of complications of various types. Therefore, if this procedure is necessary, women should not refuse surgery and other manipulations necessary during childbirth.
The amniotic fluid should be light or pink and odorless. If black, brown or green color is mixed with it, this means that there is feces of a newborn in the waters. This indicates that the fetus has experienced oxygen starvation, which requires rapid delivery. An admixture of yellow color may indicate the presence of a Rh conflict, which also requires quick action.
Consequences and risks
Women worry that manipulation may have consequences. If the obstetrician assesses the situation correctly, then there is no reason to worry.
What happens after puncture of the amniotic sac? The procedure is an element of obstetric care, and therefore should enhance the process. Contractions of the uterus become more intense and lead to further dilatation of the cervix. First-born mothers feel increased pain, but those who give birth again experience relief. If everything is normal, half an hour after the bubble ruptures, the baby is born.
Is it harmful to pierce the bladder during childbirth? In the absence of contraindications, amniotomy does not harm the mother and baby. In a situation where there is little fluid in the membrane and it is in close contact with the body, damage to the head occurs when the amniotic sac is punctured. But these are minor superficial scratches that heal quickly.
If there is no opening after puncture of the bubble, this is due to rapid effusion. This is usually observed with polyhydramnios or loose presentation. Such a situation can provoke undesirable consequences.
Complications:
- umbilical cord prolapse;
- incorrect insertion of the head;
- change in body position;
- premature placental abruption.
A sharp increase in labor for an unprepared baby can worsen his condition. Having lingered in the canal for a long period after the water breaks, the child experiences oxygen starvation. Such situations are rare and can be easily eliminated with professional management of childbirth.
Labor induction is used only for indications that pose a threat to the health and life of the mother and baby
In this case, the consent of the pregnant woman is taken into account, and contraindications to amniotomy are also taken into account. The procedure itself is painless and does not require anesthesia - there are no nerve endings on the fetal membrane
Opening the bladder takes a few minutes, significantly speeds up labor and is a good alternative to a caesarean section.
How is the amniotic sac pierced to induce labor?
During contractions, the uterus begins to compress the amniotic sac, causing the fluid to move downward. There part remains and when the muscles contract, it presses on the cervix. This promotes further opening. The bubble penetrates deeper and breaks under increasing pressure. Then the amniotic fluid pours out. In this case, they say that the water has broken. This course of events is considered the norm.
Why do they pierce it specifically?
Why the bladder is pierced before childbirth is determined in each individual case. This can be either planned before the onset of contractions or done urgently during labor.
In order not to be tormented by the question of why the bladder is pierced before childbirth on purpose, it is better to study this topic in advance. There are times when it is necessary to puncture the bladder before childbirth. It is carried out according to the doctor's indications. These include:
- Weak labor.
- Pregnant gestosis in acute form. Late toxicosis, accompanied by swelling of the legs, high blood pressure, deterioration of urine parameters.
- Life-threatening for mother or child.
- Fetal hypoxia, suspicion of it.
- Placental abruption.
- Polyhydramnios.
- Low water.
- The bubble has an irregular shape, flat. The membrane is located on the head of the fetus and prevents it from moving along the cervix.
- Dense membranes of the membranes. The opening is maximum, and the bubble is intact.
- Pregnancy with more than one fetus. After the birth of the first, the bladder of the second and subsequent ones is pierced.
When the bladder is specially pierced during childbirth, they must warn about this in advance. Often, the mother in labor is required to provide written consent for the operation. How long labor lasts after puncture of the bladder depends on further activity.
Does it hurt?
One of the exciting questions is whether it hurts to pierce the bladder before childbirth. Many women in labor claim that they experienced very unpleasant sensations. In a calm environment, you may not feel the bubble bursting before childbirth. Understanding occurs after the pouring out of the waters. You can get similar sensations by pouring a glass of warm water on your feet. It is in this volume that the amniotic fluid initially comes out.
Puncture of the bladder does not cause pain; the membrane has no nerve endings. When contractions begin after the procedure, they note that they are painful and more disturbing than before the puncture. This means everything is going according to plan, stimulation of labor was successful. The main purpose of the puncture is completed.
What do they pierce with?
Many people are interested in what is used to pierce the bladder during childbirth and whether there is a danger to the fetus. With amniotomy, there is a risk of injuring the baby's head. The operation is performed with an instrument similar to a crochet hook. Conditions for puncture of the bladder:
- sterile instrument;
- The external genitals are treated with an antiseptic.
This hook can touch the baby's head. The wounds are not dangerous. A sanitary and hygienic regime is maintained in the maternity room; scratches will be treated and heal quickly.
How is a puncture done?
The question of how to pierce the bladder before childbirth worries many expectant mothers. Fear of the procedure arises due to ignorance of the intricacies of the process.
The hook is inserted into the vagina with your fingers. At the moment of contraction, when the bubble is in its most tense state, the tool clings to the shell.
What happens next is:
- The shells of the bubble are separated through the hole that appears.
- The hook is removed.
- The amniotic fluid is poured out.
Their color is important to assess the baby's condition. Green colored waters are a cause for concern. This condition requires special attention and control.
Without surrounding fluid, the fetus can remain in the bladder for no more than 10-12 hours. Otherwise, negative consequences for the health and development of the baby are possible. The need to puncture the bladder to induce labor is determined by the doctor. If the procedure is performed promptly and correctly, the baby will not experience any undesirable consequences.
Carrying out amniotomy. Progress of the procedure
After treating the external genitalia, the doctor inserts the index and middle finger into the uterine os of the cervix until it comes into contact with the cervix. During childbirth, this is usually done at the height of the contraction with the greatest tension in the fetal bladder during manual reception by pressing on the bladder from bottom to top or using an instrument with a sharp hook at the end, the membranes are opened, after which the obstetrician uses his fingers to spread the membranes apart. The manipulation is painless, because there are no nerve endings in the membranes.
At the time of amniotomy, the doctor evaluates the color of the water: this sign can be used to judge the condition of the fetus. Normally, the waters are clear, but if the waters are green, this indicates that the baby is experiencing a lack of oxygen, which, in turn, leads to relaxation of the intestinal obturator muscles, and the original feces mixes with the amniotic fluid. Yellow amniotic fluid indicates a disease that develops in the fetus when the blood of the mother and fetus is incompatible according to Rhesus or blood group.
Fortunately, serious complications from amniotomy are rare. However, this manipulation may be accompanied by undesirable consequences: pain and discomfort, infection, deterioration of the fetal heartbeat, prolapse of the umbilical cord or small parts of the fetus (arms or legs), as well as bleeding from the fetal vessels in the membranes, from the cervix or from the placenta insertion (partial) .
Opening the amniotic sac is used only when necessary; the manipulation is carried out with the consent of the woman. Since, as already mentioned, the amniotic sac plays a protective role, including protecting the fetus and uterus from infection, no more than a day should pass from the moment the amniotic fluid is released until the baby is born. Currently, time restrictions have become even more stringent, and it is believed that a more reliable protection against infection of the fetus and uterus is a water-free period of no more than 12 hours.
Why is the amniotic sac needed?
The importance of amniotic fluid is great. They prevent the formation of adhesions between the membranes and the fetus; protect the umbilical cord and placenta (baby place) from pressure from large parts of the fetus and uterine contractions during childbirth; make fetal movements possible and easy, which are necessary for its proper development; protect the fetus from shocks and bruises from the outside; influence the position and articulation of the fetus - the relative position of the limbs and torso; make fetal movements less noticeable for the pregnant woman; the integrity of the fetal bladder protects against infection and promotes the opening of the uterine pharynx during childbirth - during each contraction, the fetal bladder wedges into the cervical canal, facilitating the opening of the cervix. Normally, the opening of the membranes occurs when the cervix is more than 6 cm dilated.
Lyudmila Petrova, obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest qualification category, head of the maternity department of maternity hospital No. 16, St. Petersburg Article provided by the magazine “Pregnancy. From conception to childbirth” N 03 2007
When do contractions start?
How long before contractions begin after the bladder is punctured depends on the condition of the expectant mother and her hormones. Almost always, disruption of the integrity of the amniotic membrane is sufficient to induce labor. Contractions start very quickly. Provided that the cervix is in a state of readiness, has contracted, become soft, and dilated. If the bladder is punctured and there are no contractions or labor remains weak, additional stimulants are needed, such as oxytocin. Usually, doctors do not wait long to prevent the child from becoming infected, and prescribe medications 3 hours after the puncture.
When and why is the amniotic sac opened?
Many expectant mothers, even those who have never been to the maternity ward, have heard about such a procedure as amniotomy - the opening of the fetal bladder. Someone may have a logical question: why rush things and “help” the amniotic fluid flow out if this will happen by itself sooner or later? It turns out that this simple manipulation helps to avoid many troubles regarding the health of mother and baby.
How long does it take to give birth?
It is impossible to unequivocally answer the question of how long it takes to give birth after a bladder puncture. Usually after the procedure, childbirth occurs quickly and rapidly.
After amniotomy, a CTG machine is connected to the woman in labor to monitor the condition of the fetus. If everything is in order, then no emergency measures are taken. When the procedure is performed incorrectly, additional measures may be required to speed up the process. For example, if too much water is drained, part of the baby's umbilical cord or limb may fall out.
The result of an incorrectly performed amniotomy
How long does labor last after a puncture?
The procedure directly affects the duration of labor if the body is ready.
- the neck is open at least halfway, that is, 5 fingers;
- it is smooth and short.
Then the puncture will contribute to its rapid opening to the end, and therefore bring the birth closer. A few hours maximum – and the baby will be born. If stimulation with hormonal drugs is required, labor will be longer.
The hook is inserted into the vagina with your fingers. At the moment of contraction, when the bubble is in its most tense state, the tool clings to the shell.
Acceleration of labor - puncture of the amniotic sac
Initially, my husband and I were happy with the birth, but later the child’s health and my well-being showed the doctor’s medical negligence. On the day of birth, at the opening of the 2nd, without any indication, the water was released - they punctured the amniotic sac, this in turn accelerated labor and led to hypoxia - oxygen starvation of the brain, tissues and organs of the child, to internal ruptures and an external incision in me, they stitched 40 minutes. The diagnosis was made by a pediatric neurologist at the age of two months, indicating the reason - accelerated delivery. Regardless of the fact that there was a preliminary agreement, the doctor apparently decided to free herself quickly.