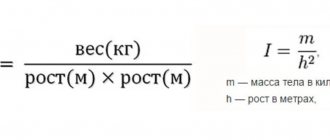The onset of labor is considered to be the appearance of regular contractions, under the influence of which the cervix begins to dilate. This process is also facilitated by the pressure and weight of the amniotic sac. Gradual expansion continues for 8-14 hours and ends with the outpouring of amniotic fluid and complete dilatation. Then the fetus is directly expelled.
Period of contractions
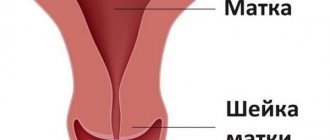
Contractions refer to the first, longest stage of labor, which lasts until the cervix dilates to allow the fetus to pass through.
Many women are interested in the question: how many fingers should be dilated for labor to begin? We can say that before the onset of labor, the cervix is effaced and open by at least two fingers. To answer the question - if a woman in labor has dilation of two fingers, then how long will it take for her to go into labor, then we first need to consider how dilatation occurs during contractions. But first things first. The period of contractions is divided into a slow period, called latent, and a fast period (the so-called active phase of contractions). Contractions last 10-12 hours in primiparous women and 6-8 hours in women who have given birth.
The latent phase begins from the moment when the rhythm of contractions is established, they occur with a frequency of one or two contractions every 10 minutes, this phase lasts about six hours and usually passes without severe pain. In primiparous women, this phase always lasts longer. The use of medications is not yet required, but for women who are too young or, conversely, older, the use of antispasmodics may be required. At this time, a dilation of 3 cm is already observed, but it will not be possible to say exactly how long it will take for labor to begin. At this moment, alternating contraction of the muscles of the uterus and their relaxation are just taking place, as a result of which the length of the cervix is shortened, the fetal head is located at the entrance to the pelvis, the fetal bladder begins to put pressure on the internal pharynx, causing it to open.
If a dilatation of 3-4 cm has occurred, then the doctor can see how long it will take for labor to begin. Complete smoothing of the cervix and dilation of 4 cm indicates that the active phase of contractions has begun. This phase for both first-time mothers and women who have already given birth lasts up to four hours. During this period, subsequent opening occurs very quickly. For every hour, the cervix opens by 2 cm in first-time mothers, and by 2.5 cm in repeat births.
If the dilation is 5 cm, then the doctor knows for sure how long it will take for labor to begin. In order for the fetal head and body to pass through the birth canal, the cervix must dilate to 10, sometimes up to 12 cm. Therefore, in the active phase, an experienced doctor can accurately determine both the time of labor and its course. For example, if the dilation is already 6 cm, it is quite simple to answer the question - how long will it take for labor to begin? You just need to count how many centimeters are left until the cervix is completely dilated. At this time, the baby’s head is already moving along the birth canal and the cervix is opening faster and faster. The most painful contractions become after five centimeters of dilation. This pain is natural, but not every woman can withstand this pain. To maintain the condition of the pregnant woman at this time, various methods of pain relief are used. These may be non-drug methods:
• massage; • taking warm baths; • listening to soothing music; • various exercises.
If these methods are not enough, the obstetrician-gynecologist will prescribe a medicinal pain reliever, based on the characteristics of the woman, the complexity of labor, and the pain threshold.
When dilated to 3 fingers, how long will it take for labor to begin - you can answer quite accurately - in about two hours the contractions should end, after which pushing will begin. By the end of the active period of contractions, the cervix is already completely open, or almost completely. Usually at this time the water breaks, it is believed that this is a timely process. However, if the water does not break on its own when the cervix is fully dilated, the doctor must perform a procedure called amniotomy to open the membranes.
Full dilatation of the cervix will occur with sufficient labor activity. With weak labor or its absence, the cervix does not open. In this case, it comes to stimulate labor.
We've looked at what cervical dilatation looks like during childbirth. Let's try to consider whether it is possible to influence this process with the help of posture.
Possible problems
Why are there no contractions and the cervix is not ready if it’s time to give birth? As the due date approaches, women's anxiety increases. First-time mothers are afraid of possible pain and the unknown; women with a second pregnancy are frightened by previous experience, especially for those who have encountered problems during childbirth. The emotional state affects the functioning of the endocrine system. Due to stress, adrenaline is produced, which leads to the fact that the cervix is closed at the time of birth.
Other reasons for weak labor:
- polyhydramnios – when there is a large amount of amniotic fluid, the walls of the uterus stretch excessively, which reduces their contractility;
- oligohydramnios – if there is a lack of fluid, it is difficult for the child to pass through the birth canal, since the force of pressure on the cervix is provided by the amniotic sac;
- pathologies of the endocrine system in a pregnant woman - the production of necessary hormones is necessary for normal labor.
If dilatation occurs before the due date, it can lead to miscarriage. They try to stop the increase in lumen from the 28th week of pregnancy. When the lumen increases by 1–2 cm, the inner edges of the cervix are sutured before delivery, which slows down further opening. If the lumen reaches 3–4 cm and the fetal head has dropped, then the woman is prescribed complete rest and the introduction of special medications that accelerate the development of the child.
Preparation before childbirth
Cervical preparation begins if by 39-40 weeks of pregnancy doctors recognize it as immature or not mature enough. In order to make an appropriate conclusion, one finger method will not be enough.
For correct conclusions, the Bishop assessment system is used. It includes several important signs that are taken into account during a vaginal examination. For each sign, 0 to 2 points are awarded. A cervix of 8 points on the Bishop scale is considered mature. At the same time, the neck is soft, ready for faster and easier expansion during childbirth, the length of the neck is less than a centimeter, the external pharynx allows 1-2 fingers to pass through, the neck itself (its contraction ring) is located clearly in the middle, without deviating either to the right or to the left , neither back nor forward.
If the assessment of the degree of cervical maturation is less than 8, preparatory medical measures are taken. In this case, the choice of preparation methods depends on the stage of pregnancy and on the specific number of points.
3-4 points on the Bishop scale - insufficient maturity. If the pregnancy period allows, the woman can be left alone, because the cervix can still ripen on its own. A fairly mature cervix receives 5-8 points and its condition does not need correction if there is still a week before giving birth.
There are two types of inpatient training – medicinal and mechanical. Mechanical methods include kelp sticks and a Foley catheter. Medicines are usually represented by hormonal drugs - tablets, suppositories, gel for application directly to the cervix. The choice of method is the doctor’s task.
At 38-39 weeks or a little earlier, women are often recommended to take No-Shpu, since this antispasmodic drug effectively relaxes smooth and round muscles and speeds up the process of smoothing and maturation.
If the cervix does not open and soften at 40-41 weeks, doctors take other measures to prepare it for labor.
Foley catheter
A medical device used to catheterize the bladder. Some types of catheter (in particular, catheter No. 18) are used to induce labor.
It is a thin latex tube coated with silicone. There is a small balloon at the distal end. The tube is inserted into the cervical canal through the vagina and the balloon is filled with 10 ml of saline solution or water. A small amount of saline is additionally injected into the uterine cavity through a catheter. The balloon, having increased in size, puts pressure on the cervix, due to which its mechanical expansion occurs.
Recently, the method is used infrequently, mainly in cases where other methods are contraindicated for a woman.
Laminaria
Sticks made from dried kelp seaweed are about 6 cm in length, and their thickness varies from 3 to 9 mm. The doctor determines which size to choose, basing his choice on the actual condition of the cervix at the time of preparation.
The sticks are inserted into the cervical canal. Laminaria has the ability to expand and increase in volume upon contact with liquid media. The stick in the canal begins to swell, and the cervix, as a result, expands mechanically. In addition, algae stimulates the production of prostaglandin F2A. This substance at the biochemical level promotes faster shortening and smoothing of the cervix.
Set the sticks for a day. After this time they can be removed. The doctor decides whether it is necessary to install new, wider ones.
Medicines
This method is the most popular and often used in modern obstetrics. In addition to No-Shpa, the antispasmodic effect of which was described above, Buscopan or Papaverine suppositories can be prescribed.
Among the hormonal drugs that are used in a hospital under the supervision of a physician, the predominant drugs are estrogens and prostaglandins.
The exact names of the drugs, as well as the dosage and frequency of use are selected individually for each woman. The method is considered quite effective.
What happens to the cervix after fertilization?
If conception occurs during ovulation, serious changes begin to occur in the woman’s genitals. Experienced specialists determine the presence of pregnancy by a change in the position of the cervix, which can be felt with a finger. A characteristic sign of fertilization is a change in the shape of the external pharynx and the color of the epithelium.
In the first days after conception
After conception has occurred, the production of the hormone progesterone in a woman’s body increases significantly. This promotes the dilation of blood vessels in the genital organs, resulting in softening of the endometrial tissue. In the first days of pregnancy until the missed period, the cervix retains firmness and elasticity for successful implantation of the fertilized egg. Subsequently, the cervix becomes softer.
The development of the embryo in the uterine cavity activates the glands that produce cervical mucus. The secreted secretion becomes very thick and accumulates in the supravaginal area. The resulting clot is called a “plug” in gynecology and performs several functions in the expectant mother’s body:
- protects the reproductive organ from infection from the outside;
- helps create optimal conditions for the formation of the fertilized egg;
- maintains the balance of vaginal microflora.
If the consistency of the cervix remains hard to the touch for a long period after fertilization of the egg, this indicates hypertonicity of the reproductive organ. This pathological condition is observed with a lack of progesterone.
Immediately after conception, a network of blood vessels rapidly grows in the internal genital organs of the expectant mother. Increased blood flow in the uterus contributes to the appearance of swelling and redness of the vagina. For the same reason, when pregnancy occurs, the cervix hurts and changes its color from pink to lilac-blue.
The process of implantation of the fertilized egg into the endometrium lasts for 2–4 days after fertilization. After implantation, the position of the cervix changes to reduce the risk of spontaneous miscarriage. It gradually lowers and deviates towards the rear wall. The level of the cervix is a characteristic sign in determining the nature of the course of pregnancy. If it is too high, it means that the expectant mother is developing hypertension.
Sometimes the high position of the lower segment of the uterus in the early stages of pregnancy is a physiological feature of the female body. In this case, in order to assess the risk of spontaneous abortion, it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound of the reproductive organs.
Characteristic signs of a pathological location of the cervix in a pregnant woman are the following symptoms:
- copious vaginal discharge of a liquid consistency;
- frequent urination;
- nagging pain in the abdomen and lower back;
- the presence of blood impurities in the cervical mucus.
In early pregnancy
In the early stages of pregnancy, the cervix acquires a softer consistency. A change in tissue density contributes to the gradual swelling of the cervix and a significant increase in the mobility of its isthmus. A large number of formed vessels give the organ a blue tint.
The lumen of the cervix begins to narrow as the embryo grows. If during the period of ovulation the visible part of the cervical canal was slightly open, in the early stages of pregnancy it closes completely and remains in this state until labor begins. This helps protect the fetus from infections that can enter the uterine cavity from the vagina.
During a gynecological examination, pregnancy can be determined with high accuracy starting from the fifth week. The main signs when assessing the development of the gestational age of the fetus are changes in the shade, location and consistency of the cervix.
What to do if the cervix is one finger dilated?
Everything depends on how far along you are in your pregnancy. If the expectant mother is already ready for childbirth and the fetus is full-term, then nothing needs to be done. Most likely, contractions will begin in the near future, which will end in natural childbirth.
If there are still several months left before the expected day of delivery, then it is necessary to sensibly assess the condition of the expectant mother. In some cases, correction with medications and bed rest is required. Other situations do not cause concern, and the woman can easily lead her usual lifestyle.
When the cervical dilatation process begins, particularly careful monitoring is necessary. The expectant mother should be examined in a chair at least at every appointment. In some cases, additional visits to the gynecologist are scheduled for diagnostics. Ultrasound examination may also be recommended to accurately determine the condition of the internal os.
Symptoms of disclosure
When the uterus opens to 1 finger, there is no pain. Among the main signs is heaviness in the lower abdomen, extending to the groin and labia. Unpleasant sensations in the lower back. As it expands, the symptoms increase.
If the opening is at the tip of the finger, the neck is shortened and slightly softened, the condition is called insufficiently mature. After a few hours, the plug comes off, and contractions are regular with an interval of 25 minutes. The neck changes location and becomes closer to the center. Maturity is indicated when the opening is one and a half fingers, the length is less than 3 cm, the organ is soft. This happens by 39 weeks.
If the stomach has dropped and one finger is dilated, in multiparous women at 37–38 weeks this is a clear sign of the onset of labor. Physiologically, the woman is ready for childbirth, but can walk for another 10–14 days. They go to the maternity hospital if, in addition to the plug, the water has come loose or is leaking. As labor approaches, they experience cramping pain in the abdomen and vagina.
The changes that occur at 38 weeks are characterized by aging of the placenta. Hormones are released that are necessary for the normal course of pregnancy, to maintain and contract and dilate the cervix. If the uterus is open to 1 finger, it is in good shape. This factor does not affect the baby's health. The level of estrogen increases, progesterone decreases. The child begins to descend into the pelvic cavity, pressing on the uterus, indicating the imminent start of the process.
Two weeks before birth, the first warning signs appear. It is easier for a woman to breathe, and heartburn goes away. Frequent urination, constipation, false contractions and high excitability of the organ occur. They feel pain in the navel area, pulsating tremors in the lower abdomen, and odorless discharge.
Type and symptoms of cervical dilatation
The preparatory process for dilation of the cervix begins at approximately 32 weeks of obstetric pregnancy. During a normal pregnancy, the cervix dilates several days before birth. Doctors judge the condition of the uterus in:
- primiparous woman;
- multiparous
In a woman who is expecting a child for the first time, the cervical canal opens only half a finger at first, and in a multiparous woman, it opens by a whole finger. The closer the time comes to childbirth, the more dilation occurs. It is measured, as a rule, on obstetric fingers. As long as the neck of the T-shirt allows fingers to pass through, it is as open as possible.
The fetus sinks lower and lower, pressing on the organ. Due to this, the uterus becomes loose and soft. The lower the fruit, the more it opens.
Just before labor, the uterus becomes smooth and short - this applies to both first-time mothers and multiparous women. Full dilatation of the uterus occurs up to 10-12 cm - that's 5 fingers.
Symptoms
Based on her feelings, a woman can determine the dilatation of the cervix. Symptoms that make this clear:
- pain in the lower abdomen, similar to pain during menstruation: pulling or aching;
- the presence of bloody discharge on the underwear - the so-called plug, which blocks the cervical canal so that infection does not get into it;
- the presence of cramping pain that appears at regular intervals.
Contraction is the main harbinger of impending birth. The first pain appears after 25 minutes, and the more the cervix opens, the shorter the time between contractions. Also, the discharge of amniotic fluid indicates imminent delivery. But sometimes it happens that the water breaks and there is no contraction, just as there is no dilatation of the cervix.
Important: full dilatation begins only before the onset of labor and after the end of the obstetric pregnancy period.
If the opening occurs before the due date, the birth will be called premature. The longer the pregnancy, the greater the baby's chances of life. There are several reasons for premature cervical dilatation.
- hormonal deficiency;
- placental abruption;
- infections.
The main symptom is aching pain and bleeding. It is important to immediately consult a doctor at the first manifestation. If labor has not begun, the doctor can stitch the cervix until the full term of pregnancy using the necessary medications.
Stages and timing of childbirth
Childbirth begins with the preparation of all organs and systems for this important event; cervical ripening is one of them. This is the beginning of labor, which is rightfully considered the most painful period
Disclosure occurs in three stages. In the first stage, the cervical canal softens and smoothes. The second level represents an increase in the intensity of uterine contractions. The cervix dilates to 4-5 cm before childbirth. The third degree is the absolute expansion of the uterus by 10 fingers.
Cervical dilatation has two phases: latent (1st stage) and active (2-3). The initial level lasts about 6-7 hours for first-time mothers, and for repeat pregnancies - half as much - 3-4 hours. As soon as the canal has opened by 3 cm, labor enters the active stage. We can say that the cervix moves apart by about 1 cm every hour. That is, an opening of 2 cm does not mean that labor has developed into an active period. In the second phase, the baby himself begins to help. – with his weight he presses on the uterus and cervical canal, trying to insert the head into the small pelvis.
To determine the stage of readiness of the cervix for labor, you need to see a doctor. This occurs through an internal examination of the pregnant woman by an obstetrician in the maternity ward. If a section of the reproductive system is not ripe, it is closed, and as an additional protective agent, it is sealed with a mucus plug. At this stage, the neck is 2 cm long, but the organ is considered mature when it opens 1-2 fingers. This is how labor begins. During this period of time, the uterus gradually matures, the mother’s task is not to get confused and get ready for the maternity hospital.
Next comes the stage of contractions. The woman feels periodic petrification of her stomach. These are birth spasms. They should become frequent and regular. The third stage is full disclosure, it is characterized by the beginning of pushing, as a result of which babies are born.
Pathologies of early opening of the cervical canal
It happens that the cervix does not cope with its role of holding and protecting the fetus. As a result, premature birth or the threat of termination of pregnancy begins. This is called isthmic-cervical insufficiency. If the gestation period is too short, there is a danger to the baby's life.
Causes of pathology:
- frequent abortions;
- genital surgery;
- ruptures from previous births;
- multiple pregnancy;
- improper formation of the uterus;
- excess production of male hormones
Constant abortions and curettages traumatize the cervix. It becomes scarred and cannot fully cope with its function. A girl who has not given birth should remember this.
Operations and scars on the cervical canal for the same reason negatively affect the performance of the cervix. As a rule, injury to the genital organ occurs due to health reasons, so there is no prevention for it.
Multiple pregnancies can cause insufficiency. The fact is that the cervix cannot withstand the pressure of two children and opens. Such expectant mothers should visit a gynecologist more often.
Sometimes the reason for early dilation is the abnormal structure of the reproductive system. As a rule, this is a congenital defect or the result of a serious injury. Here you just need to be vigilant and listen to yourself.
Excessive androgen release has a relaxing effect on the cervix. The organ opens ahead of schedule. Before planning a pregnancy, such women should normalize their hormonal levels.
It is very important to become familiar with the signs of pathology during pregnancy so that you can stop the anomaly in time. Premature opening of the uterus can be diagnosed during a routine examination in consultation
Symptoms:
- pain;
- removal of the plug or part thereof;
- leakage of amniotic fluid;
- hypertonicity of the uterus.
Treatment of the anomaly is carried out in two ways: surgical and medicinal. Sometimes even the usual restrictions on physical activity and the prescription of drugs that reduce uterine tone are enough to stop the dilatation process.
If the doctor sees a need, he will prescribe surgical procedures for the pregnant woman that affect the uterus. This is suturing the cervix or installing a pessary (support rings that take on the load, relaxing the cervical canal). This helps keep the mucus plug in place, thereby reducing the chance of fetal infection. Both options are effective and widely used in obstetric practice. They do a good job of protecting the child from premature birth. The choice of method depends on the stage of pregnancy. Cervical suturing is used up to 20 weeks, and a pessary is inserted later.
The dilation of the uterus is an important stage in the process of childbirth. The entire subsequent birth act, as well as its duration and success, depends on how this period of delivery goes. The state of health of the woman in labor at this stage of labor resembles painful menstruation.
It is forbidden to independently use methods to influence the speed of opening of the cervical canal; it is better to consult an obstetrician-gynecologist about this. Stimulant therapy requires medical supervision and is not always appropriate.
If the cervix opens early, you need to try to eliminate the pathology as quickly as possible so as not to harm the baby. This is done by suturing the cervical canal or installing a pessary, a ring to support the fetus
It is important to be aware of a possible anomaly even at the stage of pregnancy in order to respond to alarming symptoms in time
Measuring with your fingers
You can, of course, give a woman a vaginal ultrasound during childbirth to measure how many centimeters the cervix has already dilated. But time can be precious, and therefore obstetricians came up with their own easy and quick “manual” system of measures - they measure dilation in the fingers. Naturally, in our own.
This gives a complete picture of the degree of its development and the rate at which the birth of the child is approaching.
A woman may encounter manual assessment of the condition of the cervix already in the late stages of pregnancy in an antenatal clinic. After the 36th week of pregnancy, the doctor will evaluate the maturation processes of this round muscle and its readiness for the birth process.
At 39-40 weeks, the obstetrician-gynecologist usually reports that the dilatation is 1 finger or 1.5 fingers. This means that the cervix is ready for labor and the birth process can begin at any minute.
By the time you arrive at the maternity hospital with contractions that repeat once every 5 minutes, the dilation is usually about 3 centimeters, and the obstetrician in the emergency room will be able to manually assess the dilation to 2 fingers or a little more.
By the end of active contractions, manual finger measurement will allow you to set the dilation to 3-3.5 fingers, sometimes up to 4 fingers. The opening in centimeters is 6-7 cm.
By pushing, the cervix opens completely. Full expansion is more than 4 fingers. Neither 5 nor 6 in this case are voiced even when dilated to 12 centimeters, since the obstetrician has the opportunity to insert only 4 fingers of one hand. If they enter freely, the head of the baby is felt, ready for birth, then the woman is transferred to the delivery room, where she undergoes the pushing period of labor and the final stage - the birth of the placenta.
A woman can easily calculate the rest herself - such simple mathematical exercises during childbirth will help you to distract yourself, switch a little, relax, and not have to be distracted by doctors with questions about how many centimeters the dilation of 3 fingers will be.
What's happening?
Before talking about fingers and their use in assessing the condition of the cervix, it is necessary to explain what actually happens and when the need arises to assess the condition of the cervix itself.
After about 36 weeks, the cervix begins to actively prepare for childbirth. Until this moment, she was entrusted with the responsibility of preserving the growing baby inside the uterus and preventing him from leaving the womb prematurely. The cervix is a tight round muscle, which is normally, in the absence of pathologies in a woman, tightly closed throughout the entire gestation period. It is she who stands in the way of the baby to the birth canal.
A few weeks before birth, the length of the cervix begins to shorten from the original 3 centimeters, the round muscle gradually softens and shortens. Before birth, the mature cervix is 1-1.5 centimeters in length and opens slightly.
The fetus drops down, pressing its head on the internal pharynx, and this pressure and the weight of the considerably grown baby help the neck to shorten and soften faster.
As labor begins, rhythmic uterine contractions (contractions) gradually increase the dilatation of the cervix. From a tightly closed muscle, it must turn into an open gate so that the baby can pass through it and begin its journey along the birth canal towards its mother.
When a woman begins to give birth, the dilation of the cervix is gradual, and this is the longest period of labor. It can take up to 14 hours for a first-time woman. With the first contractions, the round muscle expands gradually; as it opens, the intensity of the expansion will be higher.
The initial contractions are not characterized by severe pain, they are quite rare. Usually repeated once every half hour, each contraction lasts no more than 20 seconds. It’s too early to go to the maternity hospital because the latent period is underway. It can last up to 6 hours for multiparous women and up to 10 hours for those giving birth for the first time. Contractions become more frequent, stronger and longer lasting.
Already in the hospital, the woman will enter the active phase of contractions, when the opening will proceed faster. In 3-5 hours of contractions, the cervix will be able to dilate a few more centimeters. Usually, by the end of the period, doctors state that the dilation is up to 7 centimeters. The last contraction period is transitional. It lasts from half an hour to an hour and a half. These contractions are the longest and most painful, each can last a minute and repeat after 1-2 minutes. The cervix makes a “decisive leap” and opens completely - up to 9-10-12 centimeters (it all depends on the size of the pelvis of a particular woman in labor).
This is full disclosure. After it, the woman giving birth begins to experience an irresistible urge to visit the toilet and push. This is how the attempts begin, during which the child will be born.
How does the cervix ripen?
Before labor begins, a pregnant woman may notice so-called “precursors.” They can occur either two hours before birth or two weeks before it. These “harbingers” include:
1. When the presenting part of the fetus (in most cases, this is the head) is pressed against the pelvic arch, the fundus of the uterus descends. After prolapse, it becomes easier for a pregnant woman to breathe, her stomach drops down and this is visually noticeable, and the urge to urinate occurs more often (the fetus puts pressure on the urinary tract).
2. False contractions appear. Typically, these are rare spasms of an irregular nature, causing a pulling sensation.
3. The process of softening is underway; in gynecology they use the term “ripening” of the cervix. The softened structure allows you to skip the tip of your finger. The entire area (length) of the cervix is significantly shortened.
Depending on the woman’s body, the opening of the cervix occurs in its own way:
- · for some, this process proceeds rather slowly until one month and accelerates only in the last days of pregnancy;
- · for others, this process is too rapid and goes through all stages of disclosure in 8–16 hours.
The degree of maturity of the cervix is determined using the Bishop scale.
When the scores obtained are summed up, a maturity level is obtained. The higher they are, the faster the softening occurs.
How does the cervix dilate?
During or before delivery, the cervical canal gradually widens. The plug comes out, freeing the woman's birth canal. After its release, you should be very careful (sex, hygiene) since the passage for pathogenic microflora into the uterus is open. You can read more about how this happens in the article: “How the plug comes out before childbirth.”
The fetal head (with correct presentation) rests on the entrance to the pelvis and forms the amniotic sac from the anterior waters. It acts as an “expander” of the internal pharynx.
The normal period for the start of dilation is from the 36th week of gestation. But sometimes premature disclosure occurs. In medical practice, cervical dilatation is classified into three stages of dilatation.
Stage I: slow or latent
The woman in labor experiences contractions regularly, the uterus actively contracts with a break of +/- ten minutes. The contraction itself lasts approximately 30–40 seconds. At the same time, for a woman in labor, they are painless, but there is some discomfort. Such sensations are typical for the first stage of the labor process, when the cervix is dilated by only one finger.
In primiparous women, the internal os initially expands; this process is always longer than in women who have given birth. Then comes the organization of the external hole. During not the first birth, the cervical canal opens simultaneously along its entire length. Marks the end of the latent phase by almost complete or complete effacement of the cervix.
For more information about contractions during the birth process, read the article: “Contractions during childbirth.” The duration of the first stage of disclosure lasts on average 4–12 hours. After the opening to the finger has occurred, the contractions are accompanied by nagging pain in the pelvis, lower back, and lower abdomen.
Stage II: medium or fast
During this period, contractions actively intensify. Usually the woman is already in the maternity hospital, the gap between spasms is a couple of minutes, and the duration of the contraction lasts up to 5 minutes. When examined on the chair, the obstetrician can record the dilation of the cervix by 4–8 cm. Contractions are already quite painful, during which the woman in labor can perform uncontrolled (unconscious) actions. In order not to harm the child who is about to begin moving through the birth canal, the woman in labor must follow a number of rules of conduct.
1. Don't lie down. This position slows down the dilation of the cervix, which significantly increases the time of the birth process, and, accordingly, the woman’s “suffering”.
2. Doesn't sit down. Because in this position the woman “sits” on the baby’s head, which can injure her.
3. Breathe. Read how to do this in the article: “Breathing during childbirth.”
4. Groom yourself. Such actions help opening, and the birth process will proceed faster.
Stage III: full dilatation or active labor
The third stage of disclosure is full disclosure, which is characterized by the entry of the baby’s head into the small pelvis. The duration of this stage is individual for each woman in labor, because the body of each of them is individual. It is better if at this time the pregnant woman is in the maternity hospital under the supervision of specialists (obstetrician, gynecologist).
When the cervix is fully dilated and the waters break, the woman should be taken to the delivery room, where a magnificent little man will be born.
Stages of cervical dilatation in pregnant women
Disclosure occurs in 3 stages:
Latent. It is characterized by mild contractions that occur without any frequency. There are no painful sensations. If a woman is at home at this time, she rarely notices changes in her condition
During this period, it is recommended not to focus on the contractions, try to be distracted or sleep. Breathing exercises and calm music have a beneficial effect on muscles
Medical intervention in the natural process during the latent period is not required. In rare cases, when pathologies develop, it is possible to use stimulants. The period lasts from several hours to several days. Fast. At the same time, the duration of contractions increases and the interval between them decreases. Contractions appear periodically, every 2–5 minutes. They become painful; in case of severe unbearable pain, painkillers are used. During this period, the woman needs to be under the supervision of a doctor so that he can correctly assess labor and provide the necessary assistance. It is not recommended to sit or lie down. A pregnant woman needs to stand with her elbows on a stable surface or walk. This way, the greatest pressure from the baby’s weight is achieved, and the cervix should open faster. If it is more convenient for a woman to wait out contractions while sitting, it is better to use a large ball - a fitball. In the rapid period, dilation occurs by 4–6 cm within 8–10 hours for women with their first pregnancy (primiparas) and 5–7 for pregnant women the second and subsequent times (multiparas). Full disclosure. At this time, the pregnant woman is under the supervision of doctors. The baby's head drops into the pelvis as the cervix is fully dilated, or, as obstetricians say, effaced. The obstetrician seats the woman in labor on a special chair, conducts an examination and asks her to push. The time of the rapid period and full disclosure depends on the individual characteristics of the expectant mother’s body and the readiness of her birth canal.
First stage: slow
At this point, the woman’s contractions are already quite regular. The uterus contracts at intervals of 7-10 minutes. In this case, the duration of one contraction is 30-50 seconds. The woman notes that the sensations are painless, but there is some discomfort.
For early detection in a female doctor, a swab from the mouth of the external mother and the cervical canal, the so-called. If the doctor detects certain changes in the cells in this smear, the next step is to view the lunar crown of the mother's mouth using a kind of microscope, called a colposcopy. This can be observed on the connected screen. The doctor also removes a tissue sample from visible areas. These samples, called biopsies by doctors, are subsequently examined in a laboratory. Sometimes the doctor also immediately administers conization to clear up a noticeable Pap result that shows severe cellular alteration.
Usually, in the first stage of labor, the cervix is dilated by 1 finger. In this case, in first-time mothers, the internal os first expands. Only after this the external hole is transformed. Women who have already given birth undergo simultaneous opening of the cervical canal along its entire length.
The first stage of cervical dilatation can last from 4 to 12 hours. At the end of this period, nagging pain in the lower back occurs. Many representatives of the fairer sex compare these sensations with menstrual pain.
Classification of changes in tissue samples
In a sample of extracted tissue, specialists can see whether there is cervical cancer or a precursor. The precursors are called cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 1. This is a very early stage of cervical cancer: it has not yet crossed the mucous membrane.
Some precursors may re-form over time. How likely it is that regression depends, in part, on: It is significantly more common in women before their thirties than after their thirties. If the changes persist even after anti-inflammatory treatment and further control tests, or if the degree of change even increases, the doctor will suggest abduction. Otherwise, they may develop into cervical cancer. One common way to remove changes is conization.
Acceleration of cervical dilatation. Non-drug method
If a woman has no contraindications, and the due date has already come to an end, then the obstetrician-gynecologist can advise speeding up this process at home.
The most effective way to speed up labor is sex. Due to the content of prostaglandins in sperm, which stimulate the cervix to open. But despite all the effectiveness of this method, there are a number of contraindications:
- the man has an infection;
- the placenta is quite low;
- too active sex and orgasm.
You should not get too carried away with such an interesting method, so that placental abruption does not occur.
A good way to speed up labor is exercise or exercise. In this case, the process of accelerating disclosure will occur much faster. This could be walking at a slightly faster pace, squats, or walking up flights of stairs. Although doing yoga and going to the pool during pregnancy are necessary physical activities, too much of them can lead to early labor.
You can do household chores: clean the house and wash the floors. But again, do not overdo it so as not to harm the child.
Also, on the advice of a gynecologist, active massage of the nipples will yield results. This process helps to increase the contraction of the uterus, due to which childbirth will not be long in coming. This activity is recommended only for women who have given birth, so that the “afterbirth” leaves the uterus faster. It also helps contract the uterus after childbirth. This process helps to increase the contraction of the uterus, due to which childbirth will not be long in coming.
Taking a warm bath will help speed up the opening process. The water should not be hot! But this method should not be used if the amniotic fluid has broken or the plug has come off.
At home, you can do a cleansing enema or take a small amount of laxative. The effect of the drug will begin within 30 minutes, after which contractions may begin. Castor oil is a laxative in its properties.
There are also several products whose use will lead to rapid dilatation of the cervix. They are raspberry tea, beets, parsley.
The expectant mother can combine some of these tips together. And then the main event in her life will not take long to arrive. But you need to do this only when the period begins to exceed 40 weeks, not in advance.
Methods and tips for accelerating cervical dilatation vary from person to person. For some women in labor, one thing is suitable and works immediately. Some people try all the methods, but the results take a very long time. Therefore, a woman needs to be under constant medical supervision so as not to harm herself or her child.
Is it possible to stimulate disclosure at home?
Ways to induce labor at home:
- Following a diet and taking special decoctions. A woman's diet should include more fresh vegetables and fruits. A decoction of raspberry leaves and berries helps stimulate the opening of the cervix, as it contains substances that relax muscles and reduce tone.
- Cleansing enema. In this case, the posterior wall of the uterus is affected. In addition, this leads to the removal of the plug, which provokes the onset of labor.
- Sex. During orgasm, the uterus naturally contracts. Sperm contains substances that soften the tissues of the cervix.
- Physical exercise. The exercises should be coordinated with a doctor, since muscle tension is contraindicated in gestosis and other pathological conditions. It is better to select a complex with an experienced instructor. Long walks, slow squats and exercise on a fitball have a beneficial effect (see photo). You can't jump. In addition, exercises with high arms raised should be avoided. During gymnastics, you need to monitor your breathing and relax your muscles in a timely manner.
The beginning of labor will not be scary if a woman knows well the essence of the processes occurring in her body, as well as the secret terminology of doctors and obstetricians who will be with her throughout the entire labor period.
One of these incomprehensible terms is considered to be the opening of the neck to a certain number of fingers. In this article we will tell you why dilatation is usually measured in fingers, whose fingers are considered the standard, what such a measure means and what dilatation indicates that the baby is about to be born.
Other measures and assessments
Unfortunately, during the birth process, there is no other system for assessing dilation other than the “obstetric finger”. But before birth, the maturity of the cervix is determined not only by whether the cervix allows the doctor’s fingers to pass through. The so-called Bishop scale is considered effective and informative. It allows you to give an assessment in points. Therefore, if you hear from a doctor before giving birth that your cervix is 3 points ready, you shouldn’t be surprised. We will tell you in more detail how to understand this.
In the Bishop scoring system, there are several criteria that can characterize the condition of the teres muscle, which closes the outlet of the uterus.
- Density. During vaginal examination, the consistency is determined manually. A dense and hard neck is awarded 0 points. Softened around the edges, but dense inside - 1 point, soft - 2 points. The softer the cervix, the better it will behave during childbirth, dilatation will occur less painfully, more quickly, the likelihood of cervical rupture and injury to the fetal head will be considered insignificant.
- Length. A long neck of more than 2 centimeters is 0 points. An organ whose length is from 1 to 2 centimeters – 1 point. Shortened less than a centimeter – 2 points.
- Bandwidth. If during examination the cervix is tightly closed and does not allow a single finger of the obstetrician to pass through, a score of 0 is given. If the cervical canal located inside the cervix is slightly expanded up to the borders of the internal os, 1 point is given. If the neck misses 1-2 fingers, a well-deserved 2 points are awarded.
- Location. A neck that bends back is considered unready - 0 points on the indicated scale. If the inlet of the neck “looks” forward – 1 point. The best prepared neck is the one that is clearly in the middle – 2 points.
The doctor’s conclusion that cervical maturity is 5-8 points means that labor can begin at any time, the woman’s body is quite ready for it. A calculated score of 3-4 points means insufficient maturity, and less than 3 points according to Bishop means unpreparedness for childbirth, which may require medical intervention.
In this case, preparation will be done in the hospital. The woman will be prescribed antispasmodic drugs to relax the round muscle, hormonal drugs, as well as the introduction of kelp, which, swelling in the cervical canal, will lead to a gradual mechanical expansion of the cervix.